仿写之前,我们要搞清楚都要用到哪些技术
- 自定义注解,比如Tomcat使用的是@Servlet,我们可以定义一个自己的@MyServlet
- 构造请求体和返回体,比如tomcat使用HttpRequest,我们可以自己定义myHttpRequest
- java去遍历一个指定目录,然后获取到.java文件,再获取到带有@MyServlet注解的类
- 然后将这个注解里的path和这个类本身映射成map
- 通过反射去调用该类的方法(doGet、doPost)
- 还需要用到socket来监听消息,并且对监听到的消息进行处理
第一步:自定义注解
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyServlet {
String path() default "";
}第二步:定义HttpRequest以及HttpResponse、
public class MyHttpRequest {
//定义一个map,用来存放请求体中的参数,key是参数名称,value是参数值
public Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
public String getParameter(String key){
return map.get(key);
}
}public class MyHttpResponse {
public OutputStream outputStream;
public static final String responsebody = "HTTP/1.1 200+\r\n" + "Content-Type:text/html+\r\n"
+ "\r\n";
public MyHttpResponse(OutputStream outputStream) {
this.outputStream = outputStream;
}
}第三步:遍历整个目录,把Java文件放入list中
private static void func(File file){
File[] files = file.listFiles();
String s;
for (File file1 : files) {
if (file1.isDirectory()){
func(file1);
}
if (file1.isFile()){
//取src之后的名字
s = file1.toString().split("src")[1];
//去掉src后边的第一个\,得到全类名
s = s.substring(1);
//判断是不是以.java结尾的文件
if (s.length() >=5 && s.substring(s.length() - 5).equals(".java")){
//把全类名中的\替换成.
s = s.replace('\\','.');
//去掉后缀名.java
s = s.substring(0,s.length()-5);
//把类名加入到list中
javaclasses.add(s);
}
}
}
}第四步:找出带有Servlet注解的Java文件,并把注解中的path,类对象放入到map中
public static void getServlet() throws ClassNotFoundException {
for (int i = 0; i < javaclasses.size(); i++) {
String path = javaclasses.get(i);
Class<?> cl = Class.forName(path);
if (cl.isAnnotationPresent(MyServlet.class)){
servletMap.put(cl.getAnnotation(MyServlet.class).path(),cl);
}
}
}第五步:创建socket连接
InetAddress localHost = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
System.out.println("localhost" + localHost);
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080, 10, localHost);
System.out.println("等待建立连接");
Socket server = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("连接已建立");第六步:定义线程接收报文
HttpAcceptThread httpAcceptThread = new HttpAcceptThread(server);
Thread accept = new Thread(httpAcceptThread);
accept.start();
accept.join();HttpAcceptThread类内容如下:
class HttpAcceptThread implements Runnable{
private Socket socket;
ArrayList<String> strings = new ArrayList<>();
public HttpAcceptThread(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("开始接收http");
try {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
String s;
while ((s = reader.readLine()).length() != 0){
try {
strings.add(s);
System.out.println(s);
} catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("接收Http进程结束");
break;
}
}
System.out.println("接收http进程结束");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}第七步:处理httprequest,也就是通过反射去调用doGet和doPost方法
这一步有些复杂,尤其是对url切割时,但我给每一步都加了注释,方便理解
GET /address1?a=111&b=222
private static void requestHttp(Socket socket,String http) throws IOException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
//GET /address1?a=111&b=222(拿获取到的这个url举例)
//先通过空格判断是GET还是POST
String requestStyle = http.split(" ")[0];
if (requestStyle.equals("GET")){
//如果是GET,取空格后面部分,即/address1?a=111&b=222
String httpPathAndParameter = http.split(" ")[1];
//定义httpPath
String httpPath;
//创建httpRequest对象
MyHttpRequest myHttpRequest = new MyHttpRequest();
//通过索引位置判断url里边有没有带?
if (httpPathAndParameter.indexOf("?") != -1){
//如果有,由于有个/,因此我们要先拿到address1?a=111&b=222这部分
httpPath = httpPathAndParameter.substring(1);
//获取问号前面部分,即address1,\\作为转义字符使用
httpPath = httpPath.split("\\?")[0];
System.out.println(httpPath);
//获取问号后面部分的所有参数
String parameterString = httpPathAndParameter.split("\\?")[1];
//使用&分开
String[] parameters = parameterString.split("&");
for (int i = 0; i < parameters.length; i++) {
//把参数及其值仿佛request的map中
myHttpRequest.map.put(parameters[i].split("=")[0],parameters[i].split("=")[1]);
}
} else {
//如果不存在?,也就说明不存在参数,我们只需要获取httpPath
httpPath = httpPathAndParameter.substring(1);
System.out.println(httpPath);
}
//创建HttpResponse对象
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
MyHttpResponse myHttpResponse = new MyHttpResponse(outputStream);
//反射调用doGet
Class servletClass = servletMap.get(httpPath);
Method doGet = servletClass.getMethod("doGet", MyHttpRequest.class, MyHttpResponse.class);
doGet.invoke(servletClass.newInstance(),myHttpRequest,myHttpResponse);
} else {
//如果不是Get请求,也按照同样的步骤,先取出/address1
String httpPath = http.split(" ")[1];
//去掉/,只留下address1
httpPath = httpPath.substring(1);
System.out.println(httpPath);
MyHttpRequest myHttpRequest = new MyHttpRequest();
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
MyHttpResponse myHttpResponse = new MyHttpResponse(outputStream);
//根据httpPath取出类信息
Class servletClass = servletMap.get(httpPath);
//获取doPost方法
Method doPost = servletClass.getMethod("doPost", MyHttpRequest.class, MyHttpResponse.class);
//调用doPost方法
doPost.invoke(servletClass.newInstance(),myHttpRequest,myHttpResponse);
}
}最后一步:把上面这些方法整合起来,在主方法中调用,同时定义好全局变量
public class MyTomcat {
//用于存放Java类的全类名
public static ArrayList<String> javaclasses = new ArrayList<>();
//用于存放Servlet的类对象,其中key是Servlet的url,value是servlet的类对象
public static HashMap<String,Class> servletMap = new HashMap<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, IOException, InterruptedException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
String inputPath = "D:\\JavaProject\\practice\\src\\tomcat";
File file = new File(inputPath);
//获取.java后缀文件,并获取全类名
func(file);
System.out.println(javaclasses);
//获取带有servlet注解的类对象,并放到map中。
getServlet();
System.out.println(servletMap);
InetAddress localHost = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
System.out.println("localhost" + localHost);
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080, 10, localHost);
System.out.println("等待建立连接");
Socket server = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("连接已建立");
//定义线程接收http报文
HttpAcceptThread httpAcceptThread = new HttpAcceptThread(server);
Thread accept = new Thread(httpAcceptThread);
accept.start();
accept.join();
//处理请求
requestHttp(server,httpAcceptThread.strings.get(0));
}然后就可以进行测试了,在测试类上方加上我们已经定义好的@MyServlet注解
@MyServlet(path = "address1")
public class Servlet1 {
public void doGet(MyHttpRequest request, MyHttpResponse response) throws IOException {
System.out.println("address1 GET响应:");
System.out.println("a=" + request.getParameter("a"));
System.out.println("\n响应的http如下:");
String resp = MyHttpResponse.responsebody + "<!DOCTYPE html>\n" +
"<html>\n" +
"<head>\n" +
" <meta charset=\"utf-8\" />\n" +
"</head>\n" +
"<body>\n" +
" \n" +
" <form name=\"my_form\" method=\"POST\">\n" +
" <input type=\"button\" value=\"按下\" onclick=\"alert('你按下了按钮')\">\n" +
" </form>\n" +
" \n" +
"</body>\n" +
"</html>";
System.out.println(resp);
response.outputStream.write(resp.getBytes());
response.outputStream.flush();
response.outputStream.close();
}
public void doPost(MyHttpRequest request, MyHttpResponse response) throws IOException {
System.out.println("\n响应的http如下:");
String resp = MyHttpResponse.responsebody +
"{\"sorry\":\"we only respond to method GET now\"},\r\n" +
"";
System.out.println(resp);
response.outputStream.write(resp.getBytes());
response.outputStream.flush();
response.outputStream.close();
}
}然后启动项目

可以看到本机ip地址,然后通过浏览器地址栏访问
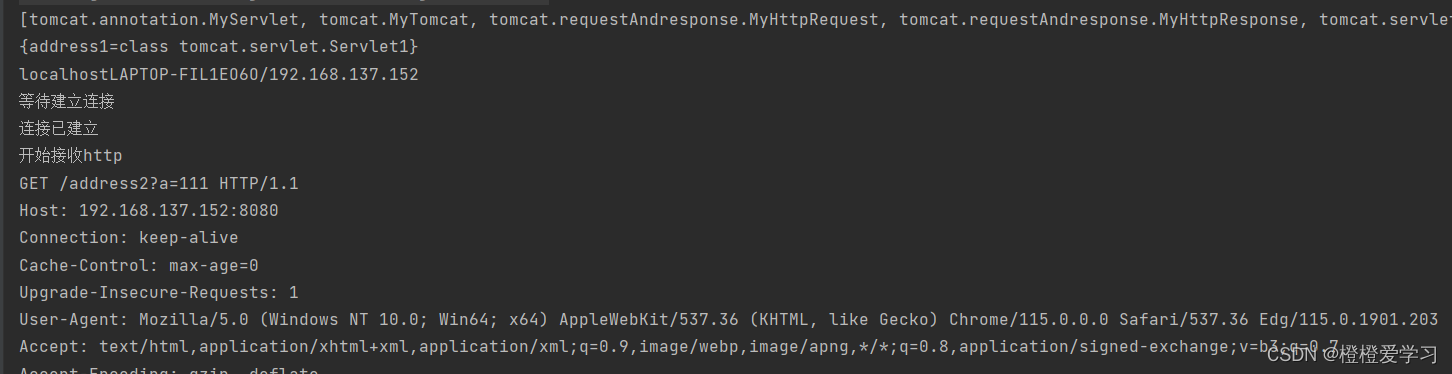
这样就实现了一个简单的tomcat

![详解C#-static void Main(string[] args)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2b1090e9a2fb4fcd8a712eb2f22fe7c4.png)

![BUUCTF [安洵杯 2019]easy_serialize_php 1 详细讲解](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/710ffc9a0a2e43f1850658a4b5888149.png)