【数据结构1-3】集合 - 题单 - 洛谷
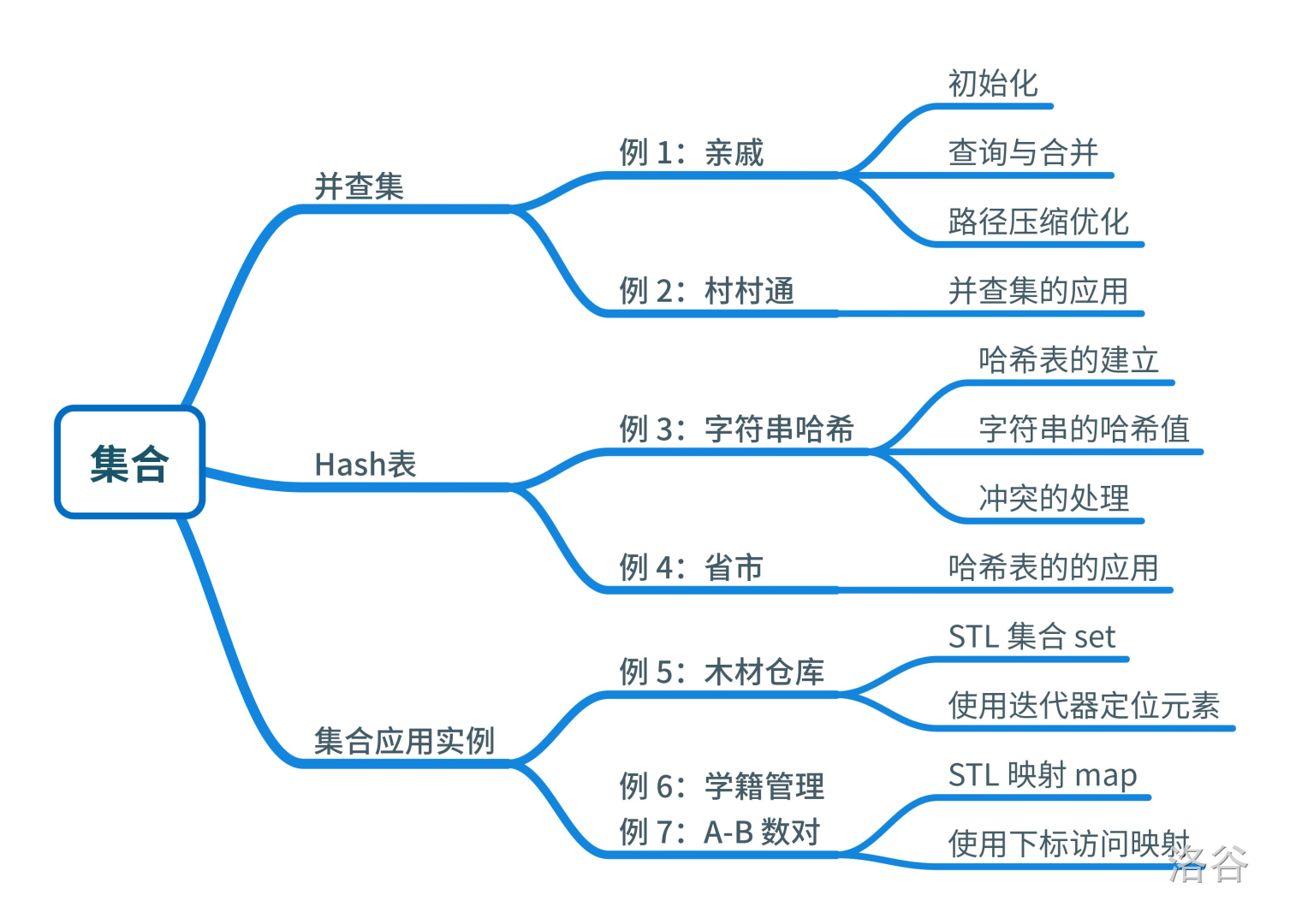
例题
P1551 亲戚
亲戚 - 洛谷
并查集
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,m,q,f[10010],x,y,a,b;
int find(int x)//找出x家的大佬 也就是二叉树的祖先节点
{
if(f[x]==x)//x是x的爸爸,简单的来说就是x没爸爸了
return x;
//他是家里最大的大佬,所以返回的x就是我们所求的祖先节点
return f[x]=find(f[x]);//x不是他自己的爸爸,所以他上面还
//有爸爸,我们的目标是祖先节点,所以我们此时要做的是问他
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&q);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
f[i]=i;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
f[find(y)]=find(x);//合并x子集和y子集,直接把x子集的祖先节
}
for(int i=1;i<=q;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
if(find(a)==find(b))//如果a所在子集的大佬[前面已经解释过了]和b所在子集的大佬一样,即可知a和b在同一个集合
printf("Yes\n");
else
printf("No\n");
}
return 0;
}P1536 村村通
P5250 【深基17.例5】木材仓库
【深基17.例5】木材仓库 - 洛谷
传送门
这道题无论是map的解法还是set的解法都非常值得学习
map:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<int,int> m;
int j,n,x,y;
cin >> n;
while(n--) {
cin >> x >> y;
if (x == 1) {
if (m.count(y)) cout << "Already Exist" << endl;
else m[y] = 1;
}
else {
if(m.empty()) cout << "Empty" << endl;
else if (m.count(y)) {
m.erase(y);
cout << y << endl;
}
else {
m[y] = 1; // 假装存一下该木头
auto it = m.find(y); // 指针定位
auto it2 = it;//auto=map<int,int>::iterator
it++;
// 几种特判
if (it2 == m.begin()) { // 没有比它短的
cout << it->first << endl;
m.erase(it);
}
else if (it == m.end()) { // 没有比它长的
cout << (--it2)->first << endl;
m.erase(it2);
}
// 长度比较
else if (y-(--it2)->first > it->first-y) {
cout << it->first << endl;
m.erase(it);
}
else {
cout << it2->first << endl;
m.erase(it2);
}
m.erase(y); // 删掉假装存的木头
}
}
}
return 0;
}set:
set 里面的 insert(x) 函数其实是有返回值的,会返回一个这样的奇怪的东西:pair<set<int>::iterator,bool>。
返回的这个 pair 到底是什么意思呢?
这个 pair 的第二项是一个 bool 类型的东西,代表插入是否成功。(意思就是只有集合里没有 x 的时候才能插入成功),第一项是一个迭代器,如果插入成功的话,它会返回 x 在集合里的位置,我们可以这样:
set<int> s;
set<int>::iterator p = s.insert(x).first;
以后用 *p 就可以得到 x 啦!
检测是否有相同长度的木材:
if (!s.insert(t).second) cout << "Already Exist\n";
一行直接解决问题!STL大法好
这是啥意思呢?如果有相同长度的木材,插入就会失败,pair 的第二项就会返回 false,如果没有,!s.insert(t).second 这个语句就直接实现了插入的目的,这就是我说 set 更方便的原因。
set.empty() 可以直接返回集合是否为空。
虽然 set 也有 lower_bound() 和 upper_bound(),但是,
set.lower_bound(x) 是返回第一个大于等于 x 的位置,
而 set.upper_bound(x) 是返回第一个大于 x 的位置,
set.find(x) 会返回第一个 x 的位置。如果没有 x,则会返回 set.end()。
set.erase(iterator),删除定位器 iterator 指向的值
set.erase(first,second),删除定位器 first 和 second 之间的值
set.erase(key_value),删除键值 key_value 的值
结合刚刚讲的这些函数,我们可以写出代码的第二部分——出货。(s 已经被定义为 set<int>)
if (s.find(t) != s.end()) cout << t, s.erase(s.find(t)); // 找得到
else { // 找不到
lwb = l2 = l3 = s.lower_bound(t);
if (lwb == s.begin()) cout << *lwb, s.erase(lwb); // 特殊情况1,如果在最开始
else if (lwb == s.end()) cout << *(-- l3), s.erase(l3); // 特殊情况2,如果在末尾
else if (*lwb - t < t - *(-- l2)) cout << *(l3), s.erase(l3); // 选比较长的
else cout << *(-- l3), s.erase(l3); // 选比较短的
}
cout << endl;
那么多方便的函数,果然还是 STL 大法好啊!还不快去用起来?
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
int n, op, t;
set<int>::iterator lwb, l2, l3;
set<int> s;
int main(){
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i ++){
cin >> op >> t;
if (op == 1){
if (!s.insert(t).second) cout << "Already Exist\n";
}
else {
if (s.empty()){
cout << "Empty\n";
continue;
}
if (s.find(t) != s.end()) cout << t, s.erase(s.find(t));
else {
lwb = l2 = l3 = s.lower_bound(t);
if (lwb == s.begin()) cout << *lwb, s.erase(lwb);
else if (lwb == s.end()) cout << *(-- l3), s.erase(l3);
else if (*lwb - t < t - *(-- l2)) cout << *(l3), s.erase(l3);
else cout << *(-- l3), s.erase(l3);
}
cout << endl;
}
}
}C++中set用法详解_byn12345的博客-CSDN博客
P5266 【深基17.例6】学籍管理
值得一说的是map的一些用法
STL中的map
STL中的map以一种效率较高的形式(红黑树)实现了映射。(C++11又提供了一种更为先进的unordered_map,基于哈希表,拥有�(1)O(1)的时间复杂度。因此这里使用map讲解,但代码中使用的是unordered_map,两种容器操作相同)
map的创建
map<A,B> mp;
即可创建一个键类型为A,值类型为B的map。
map的插入与修改
mp.insert(make_pair(a,b));
即可插入一个对象(要求a的类型为A,b的类型为B)。
此外,map还提供一种简易的插入与修改方法
mp[a]=b;
此时,如果mp中a已存在,则会将键为a的项的值设为b;否则,则会插入一个键为a,值为b的新项。
map的查询
mp[a];
查询键为a的项的值。
map的删除
mp.erase(mp.find(a));
将键为a的项删去。
查看map的大小
mp.size()
与其它STL容器相同,map也可通过size查看大小。
查看map中特定项的个数
mp.count(a)
清空map
mp.clear()查看mp中键为a的项的个数(因为只能有一个或没有,这个函数的返回值只能为1或0)。
其实很多字符串题中map都能派上用场。说句题外话:当数据范围非常大时,map也可以当桶排序中的“桶”来用,效果也是棒呆了
当然,map也是有缺点的,单次操作它的时间复杂度是O(lg n),有时候会TLE