目录
一、依赖
二、自定义注解
三、切面
一、依赖
以SpringBoot工程为例,导入aop的依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>二、自定义注解
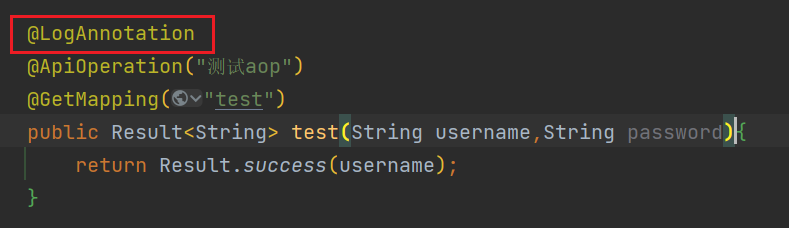
我们自定义一个注解。这里叫LogAnnotation,属性也可以自定义。
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface LogAnnotation {
String module() default "";
String operation() default "";
}
注解有了,我们就可以将这个注解作用到任何方法上面了。
但是仅仅有这个注解还不行,它不能发挥任何功能,起不了什么作用,也仅仅是标记了一个方法。
因此,我们就要为这个注解建立切面。
三、切面
解释如下代码含义:
只要标记了@LogAnnotation注解的方法都会执行环绕通知。
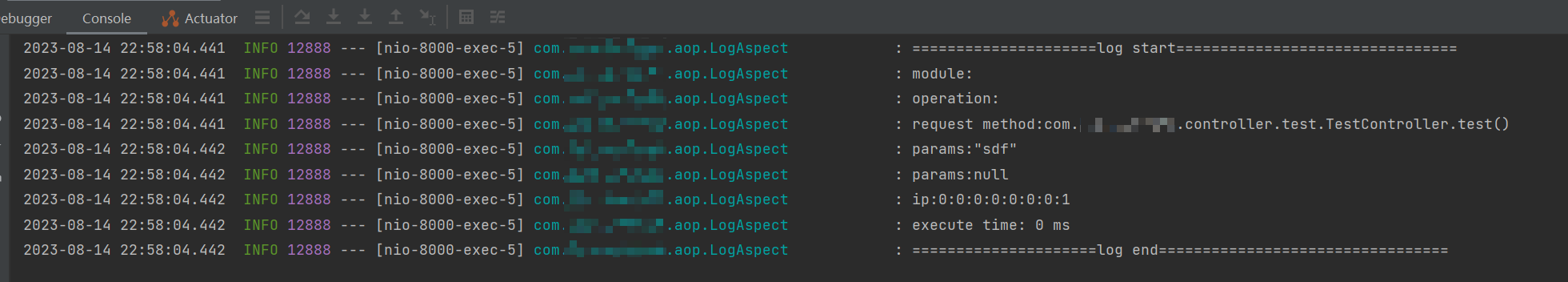
通知中做如下处理:方法调用前记录时间、执行方法、方法执行后记录时间,最后保存日志。
日志显示@LogAnnotation的属性(不写就是空值默认值)、请求参数、方法名、请求者的ip地址、方法执行耗时等信息。
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class LogAspect {
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.pps.aop.LogAnnotation)")
public void logPointCut() {
}
@Around("logPointCut()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable {
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//执行方法
Object result = point.proceed();
//执行时长(毫秒)
long time = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginTime;
//保存日志
recordLog(point, time);
return result;
}
private void recordLog(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, long time) {
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
LogAnnotation logAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(LogAnnotation.class);
log.info("=====================log start================================");
log.info("module:{}",logAnnotation.module());
log.info("operation:{}",logAnnotation.operation());
//请求的方法名
String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName();
String methodName = signature.getName();
log.info("request method:{}",className + "." + methodName + "()");
//请求的参数
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
if (args.length > 0 ){
// 调用的该方法必须有形参才会进入,按顺序记录实参。
for (Object param : args) {
log.info("params:{}",JSON.toJSONString(param));
}
}
//获取request 设置IP地址
HttpServletRequest request = HttpServletUtils.getHttpServletRequest();
log.info("ip:{}", IpUtils.getIpAddr(request));
log.info("execute time: {} ms",time);
log.info("=====================log end=================================");
}
}IP工具类
/**
* 从http请求中获取ip地址<br>
* @author hssy
* @version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j
public class IpUtils {
/**
* 获取IP地址<br/>
* 使用Nginx等反向代理软件, 则不能通过request.getRemoteAddr()获取IP地址<br/>
* 如果使用了多级反向代理的话,X-Forwarded-For的值并不止一个,<br/>
* 而是一串IP地址,X-Forwarded-For中第一个非unknown的有效IP字符串,则为真实IP地址<br/>
*/
public static String getIpAddr(HttpServletRequest request) {
String ip = null;
try {
ip = request.getHeader("x-forwarded-for");
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(ip) || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) {
ip = request.getHeader("Proxy-Client-IP");
}
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(ip) || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) {
ip = request.getHeader("WL-Proxy-Client-IP");
}
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(ip) || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) {
ip = request.getHeader("HTTP_CLIENT_IP");
}
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(ip) || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) {
ip = request.getHeader("HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR");
}
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(ip) || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) {
ip = request.getRemoteAddr();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("IPUtils ERROR ", e);
}
// 使用代理,则获取第一个IP地址
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(ip) && ip.length() > 15) {
if (ip.indexOf(",") > 0) {
ip = ip.substring(0, ip.indexOf(","));
}
}
return ip;
}
}
获取HttpServletRequest工具类
public class HttpServletUtils {
public static HttpServletRequest getHttpServletRequest(){
return ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest();
}
}
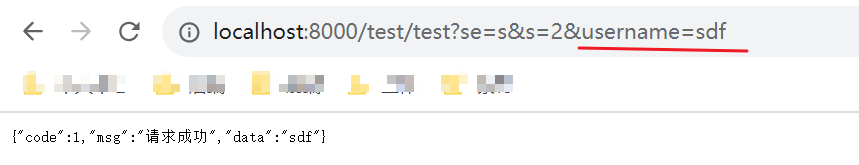
演示效果