四、访问数据库
- SpringBoot框架为SQL数据库提供了广泛的支持,既有用JdbcTemplate直接访问JDBC同时支持“object relational mapping”技术(如MyBtais、Hibernate)。SpringData独立的项目提供对多种关系型和非关系型数据库的访问支持,比如MySql、Oracle…
- SpringBoot也支持嵌入式数据库,比如H2、HSQL…这些数据库只需要提供jar包就能在内存中维护数据。
4.1DataSource
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-E9qHwYXq-1692020426865)(C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230812113414453.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a3ba55990b6f4399b908efc590d1c3f7.png)
- DataSource在application配置文件中以spring.datasource.*作为配置项。
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb
spring.datasource.username=dbuser
spring.datasource.password=dbpass
- DataSourceProperties.java是数据源的配置类,更多配置参考这个类的属性。
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
public class DataSourceProperties implements BeanClassLoaderAware,
InitializingBean {
}
- SpringBoot能够从spring.datasource.url推断所使用的数据驱动类,可以不写driver驱动类,如果需要特殊指定要设置
spring.datasource.driver-class-name为驱动类的全限定名称。 - SpringBoot支持多种数据库连接池,优先使用HikariCP,其次是Tomcat pooling,再次是Commons DBCP2,如果以上都没有,最后会使用Oracle UCP连接池。当项目中starter依赖了spring-boot-starter-jdbc或者spring-boot-starter-data-jpa默认添加HikariCP连接池依赖,也就是默认使用了HikariCP连接池。
4.2轻量的JdbcTemplate
- 使用JdbcTemplate我们提供自定义SQL,Spring执行这些SQL得到记录结果集。JdbcTemplate和NameParameterJdbcTemplate类是自动配置的,可以使用@Autowired注入到自己的Bean中。
- JdbcTemplate执行完整的SQL语句,我们将SQL语句拼接好,交给JdbcTemplate,JdbcTemplate底层就是使用JDBC执行SQL语句,是JDBC的封装类而已。
- NamedParameterJdbcTemplate可以在SQL语句部分使用“:命名参数”作为占位符,对参数命名,可读性更好。NamedParameterJdbcTemplate包装类JdbcTemplate对象,“:命名参数”解析后,交给JdbcTemplate执行SQL语句。
- JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration自动配置了JdbcTemplate对象,交给JdbcTemplateConfiguration创建了JdbcTemplate对象,并对JdbcTemplate做了简单的初始设置。
4.2.1准备环境
- 访问数据库先准备数据库的script。SpringBoot能够自动执行DDL、DML脚本。两个脚本文件名称默认是schema.sql和data.sql。脚本文件在类路径中自动加载。
- 自动执行脚本还涉及spring.sql.init.mode配置项:
- always:总是执行数据库初始化脚本
- never:禁用数据库初始化
4.2.1.1准备数据库和表脚本
- 数据库名称springboot,表目前使用一个 article(文章表),初始两条数据。
schema.sql
CREATE TABLE `article`
(
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键',
`user_id` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '作者 ID',
`title` varchar(100) NOT NULL COMMENT '文章标题',
`summary` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '文章概要',
`read_count` int(11) unsigned zerofill NOT NULL COMMENT '阅读读数',
`create_time` datetime NOT NULL COMMENT '创建时间',
`update_time` datetime NOT NULL COMMENT '最后修改时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE = InnoDB
AUTO_INCREMENT = 1
DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8mb4;
data.sql
INSERT INTO `article` VALUES ('1','2101','SpringBoot 核心注解',
'核心注解的主要作用','00000008976','2023-01-16 12:11:12','2023-01-16 12:11:19');
INSERT INTO `article` VALUES ('2','356752','JVM 调优',
'HotSpot 虚拟机详解','00000000026','2023-01-16 12:15:27','2023-01-16 12:15:30');
4.2.1.2添加依赖
<dependencies>
<!--JdbcTemplate : 连接池: HikariCP -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--MySQL驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!--Lombok依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
4.2.2JdbcTemplate访问MySQL
- 项目中依赖了spring-jdbc 6.0.4,JdbcTemplate对象会自动创建好。将JdbcTemplate对象注入给你的Bean,再调用JdbcTemplate的方法执行查询、更新、删除的SQL。
- JdbcTemplate主要有以下几种类型的方法:
- execute方法:可以用于执行任何SQL语句,常用类执行DDL语句。
- update、batchUpdate方法:用于执行新增、修改、删除等语句。
- query和queryForXXX方法:用于执行查询相关的语句。
- call方法:用于执行数据库存储过程和函数相关的语句。
1.将 schema.sql , data.sql 拷贝到 resources 目录
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-K8lXzphL-1692020426866)(C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230812163334993.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9bd1cf3abf114e259cfe9e2ee691663b.png)
2.修改application.properties
#配置数据源
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&autoReconnect=true&useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=030522
#设置执行数据库的脚本
spring.sql.init.mode=never
3.创建实体类
@Data//set、get方法
@AllArgsConstructor//全参构造
@NoArgsConstructor//无参构造
public class ArticlePO {
private Integer id;
private Integer userId;
private String title;
private String summary;
private Integer readCount;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
}
- lombok注解给类的属性生成set、get方法、无参、全参构造方法
4.单元测试,注入JdbcTemplate对象,测试聚合函数
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot09JdbcTemplateApplicationTests {
//注入JdbcTemplate
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Test
void test01() {
String sql="select count(*) as ct from article";
Long count = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Long.class);
System.out.println("记录行数 = " + count);
}
}
测试“?”占位符
@Test
void test02() {
//?作为占位符
String sql="select * from article where id=?";
//BeanPropertyRowMapper 将查询结果集、列名与属性名称匹配,名称完全匹配或驼峰
ArticlePO articlePO = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(ArticlePO.class), 1);
System.out.println("articlePO = " + articlePO);
}
测试自定义RowMapper
- 也可以使用"?"占位符
@Test
void testRowMapper() {
//只能查询出一个记录,查询不出记录抛出异常
String sql = "select * from article where id=1";
ArticlePO articlePO = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, (rs, rownum) -> {
var id = rs.getInt("id");
var userId = rs.getInt("user_id");
var title = rs.getString("title");
var summary = rs.getString("summary");
var readCount = rs.getInt("read_count");
var createTime = new Timestamp(rs.getTimestamp("create_time").getTime()).toLocalDateTime();
var updateTime = new Timestamp(rs.getTimestamp("update_time").getTime()).toLocalDateTime();
return new ArticlePO(id, userId, title, summary, readCount, createTime, updateTime);
});
System.out.println("查询的文章=" + articlePO);
}
测试List集合
@Test
void testList() {
String sql="select * from article order by id";
List<Map<String,Object>> listMap =jdbcTemplate.queryForList(sql);
listMap.forEach(el->{
el.forEach((field,value)->{
System.out.println("字段名称:"+field+",列值:"+value);
});
System.out.println("-------------------------------------");
});
}
测试更新记录
@Test
void testUpdate() {
String sql = "update article set title=? where id=?";
int update=jdbcTemplate.update(sql,"Java编程思想",2);
System.out.println("update = " + update);
}
4.2.3NamedParameterJdbcTemplate
- NamedParameterJdbcTemplate能够接受命名的参数,通过具体的参数提供代码的可读性,JdbcTemplate使用的是参数索引的方式。
- 在使用模板的位置注入NamedParameterJdbcTemplate对象,编写SQL语句,在SQL中WHERE部分“:命名参数”。调用NamedParameterJdbcTemplate的诸如query,queryForObject,execute,update等时,将参数封装到Map中。
示例
@Autowired
private NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate;
@Test
void testNameQuery() {
// :参数名
String sql = "select count(*) from article where user_id=:uid and read_count>:num";
//key是命名参数
Map<String, Object> param = new HashMap<>();
param.put("uid", 2101);
param.put("num", 1);
Long count = namedParameterJdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, param, Long.class);
System.out.println("count = " + count);
}
4.2.4多表查询
- 多表查询关注是查询结果如何映射为Java Object。
- 常用两种方案:
- 将查询结果转为Map,列名是key,列值是value,这种方式比较通用,适合查询任何表。
- 根据查询结果中包含的列,创建相对的实体类。属性和查询结果的列对应,将查询结果自定义RowMapper、ResultSetExtractor映射为实体类对象。
- 现在创建新的表article_detail,存储文章内容,与article表是一对一关系。
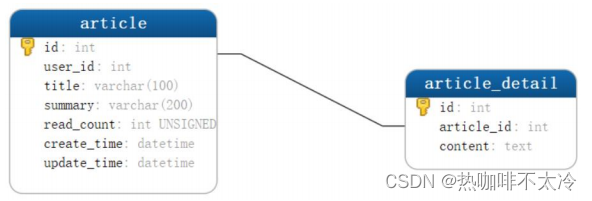
article_detail 表
CREATE TABLE `article_detail`
(
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '注解',
`article_id` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '文章 ID',
`content` text NOT NULL COMMENT '文章内容',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
- 需求:查询某个文章的全部属性,包括文章内容。
1.创建实体类ArticleDetailPO
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ArticleDetailPO {
private Integer id;
private Integer articleId;
private String content;
}
2.创建新的实体类ArticleMainPO,将ArticlePO作为成员变量
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class ArticleMainPO {
private Integer id;
private Integer userId;
private String title;
private String summary;
private Integer readCount;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
//一对一
private ArticleDetailPO detail;
}
3.查询
@Autowired
private NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate;
@Test
void testQueryContent() {
String sql = """
select m.*,d.id as detail_id,d.article_id,d.content
from article m left join article_detail d
on m.id=d.article_id
where m.id=:id
""";
Map<String, Object> param = new HashMap<>();
param.put("id", 1);
List<ArticleMainPO> mainList = namedParameterJdbcTemplate.query(sql, param, (rs, num) -> {
var id = rs.getInt("id");
var userId = rs.getInt("user_id");
var title = rs.getString("title");
var summary = rs.getString("summary");
var readCount = rs.getInt("read_count");
var createTime = new Timestamp(rs.getTimestamp("create_time").getTime()).toLocalDateTime();
var updatetime = new Timestamp(rs.getTimestamp("update_time").getTime()).toLocalDateTime();
//文章内容
var detailId = rs.getInt("detail_id");
var articleId = rs.getInt("article_id");
var content = rs.getString("content");
ArticleDetailPO articleDetailPO = new ArticleDetailPO(detailId, articleId, content);
return new ArticleMainPO(id, userId, title, summary, readCount, createTime, updatetime, articleDetailPO);
});
mainList.forEach(m -> {
System.out.println("m.getSummary() = " + m.getSummary());
System.out.println("m.toString() = " + m.toString());
System.out.println("m.getDetail() = " + m.getDetail());
});
}
- 总结:
- JdbcTemplate的优点简单、灵活、上手快,访问多种数据库。对数据的处理控制能力比较强。RowMapper、ResultSetExtractor能够提供按需要灵活定制记录集与实体类的关系。
- 缺点:对SQL要求高,适合对SQL比较了解,自定义查询结果比较多,调优需求的。
- JdbcTemplate对象的调整参数比较少,可设置spring.jdbc.template.开头的配置项目,比如设置超时为10秒,spring.jdbc.template.query-timeout=10。
4.3MyBatis
-
数据库访问MyBatis、Mybatis-Plus在国内很常用,掌握了MyBatis、Mybatis-Plus就会大部分了。MyBatis-Plus附加的功能需要单独学习。我们以MyBatis来介绍SpringBoot集成ORM框架。
-
MyBatis使用最多的是mapper.xml文件编写SQL语句。本章使用MyBatis的注解,JDK新特性文本块,以及Record完成java对象和表数据的处理。
4.3.1单表CRUD
1.Maven依赖
<dependencies>
<!--MyBatis启动器-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2.创建实体类
@Data//set、get方法
@AllArgsConstructor//全参构造
@NoArgsConstructor//无参构造
public class ArticlePO {
private Integer id;
private Integer userId;
private String title;
private String summary;
private Integer readCount;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
}
3.创建Mapper接口,实现CRUD操作
public interface ArticleMapper {
//查询结果ResultSet和PO对象的属性映射(关闭驼峰命名)
@Results(id = "BaseArticleMap", value = {
@Result(id = true, column = "id", property = "id"),
@Result(column = "user_id", property = "userId"),
@Result(column = "title", property = "title"),
@Result(column = "summary", property = "summary"),
@Result(column = "read_count", property = "readCount"),
@Result(column = "create_time", property = "createTime"),
@Result(column = "update_time", property = "updateTime")
})
//按主键查询
@Select("""
select id,user_id, title, summary, read_count, create_time, update_time
from article where id = #{articleId}
""")
ArticlePO selectById(@Param("articleId") Integer id);
//insert
@Insert("""
insert into article(user_id,title,summary,read_count,create_time,update_time)
values(#{userId},#{title},#{summary},#{readCount},#{createTime},#{updateTime})
""")
int insertArticle(ArticlePO po);
//update 使用参数名可以作为占位符 #{形参名}
@Update("""
update article set read_count=#{readCount} where id=#{id}
""")
int updateReadCount(Integer id, Integer readCount);
//delete
@Delete("""
delete from article where id = #{id}
""")
int deleteById(Integer id);
}
- @Results部分为结果映射(XML中的),或者用MyBatis的驼峰命名也能实现默认的映射关系。
application.properties
#驼峰,下划线命名
mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true
4.启动类加入扫描注解
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.hhb.mybatis.mapper")
@SpringBootApplication
public class Springboot10MyBatisApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springboot10MyBatisApplication.class, args);
}
}
- @MapperScan是扫描注解,参数是Mapper接口所在的包名。参数是数组,可以指定多个包位置。
5.配置数据源application.properties
#配置数据源
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&autoReconnect=true&useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=030522
#配置MyBatis,支持驼峰命名
mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true
#日志
mybatis.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
6.单元测试
@SpringBootTest
class MyBatisCRUDTest {
@Autowired
private ArticleMapper articleMapper;
@Test
void testSelect() {
ArticlePO articlePO = articleMapper.selectById(1);
System.out.println("articlePO.toString() = " + articlePO.toString());
}
@Test
void testInsert() {
ArticlePO articlePO = new ArticlePO();
articlePO.setTitle("TomcatWeb开发");
articlePO.setSummary("使用Tomcat服务器,定制web应用");
articlePO.setReadCount(19);
articlePO.setUserId(new Random().nextInt(500));
articlePO.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
articlePO.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
int rows = articleMapper.insertArticle(articlePO);
System.out.println("rows = " + rows);
}
@Test
void testUpdate() {
int update = articleMapper.updateReadCount(3, 28);
System.out.println("update = " + update);
}
@Test
void testDelete() {
int update = articleMapper.deleteById(3);
System.out.println("update = " + update);
}
}
4.3.2ResultMap
- 查询操作得到包含多个列的集合,将列值转为对象属性使用结果映射的功能,注解@Results,@ResultMap能够帮助我们完成此功能。
- @Results用于定义结果映射,每个列和Java对象属性的一一对应。
- @ResultMap指定使用哪个结果映射。两种方式可以使用@Results,另一种XML文件。
1.创建新的Mapper对象
public interface ArticleDao {
//查询某个用户的所有文章
@Select("""
select id,user_id,title,summary,read_count,create_time,update_time
from article where user_id=#{userId}
""")
@Results(id = "BaseArticleMap", value = {
@Result(id = true, column = "id", property = "id"),
@Result(column = "user_id", property = "userId"),
@Result(column = "read_count", property = "readCount"),
@Result(column = "create_time", property = "createTime"),
@Result(column = "update_time", property = "updateTime")
})
List<ArticlePO> selectList(Integer userId);
//根据id查询某个文章
@Select("""
select id,user_id,title,summary,read_count,create_time,update_time
from article where id=#{id}
""")
//引用定义好的结果映射,value的值是@Results中的id
@ResultMap("BaseArticleMap")
ArticlePO selectById(Integer id);
}
- @Results的id定义当前结果映射的唯一名称,后面内容是列和属性的一一映射说明。
- @ResultMap引用@Results的id。
2.单元测试
@SpringBootTest
public class ResultMapTest {
@Resource
private ArticleDao articleDao;
@Test
void test01() {
List<ArticlePO> articlePOS = articleDao.selectList(480);
articlePOS.forEach(list ->
System.out.println(list));
}
@Test
void test02() {
ArticlePO articlePO = articleDao.selectById(4);
System.out.println("articlePO = " + articlePO);
}
}
- 另一种方法在xml文件中定义标签,在@ResultMap注解引用。
- 这种方式首先创建xml。在resources目录下创建自定义的mapper目录,新建ArticleDao.xml。
1.ArticleDao.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.hhb.mybatis.mapper.ArticleDao">
<!--定义resultMap-->
<resultMap id="ArticleBaseMapper" type="com.hhb.mybatis.po.ArticlePO">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="user_id" property="userId"/>
<result column="read_count" property="readCount"/>
<result column="create_time" property="createTime"/>
<result column="update_time" property="updateTime"/>
</resultMap>
</mapper>
2.修改application.properties配置mapper文件的路径
- mybatis.mapper-locations:自定义mapper.xml文件保存路径。
#指定自定义mapper文件的位置
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:/mapper/**/*.xml
3.修改ArticleDao的查询方法上面的@ResultMap
//根据id查询某个文章
@Select("""
select id,user_id,title,summary,read_count,create_time,update_time
from article where id=#{id}
""")
//引用定义好的结果映射,value的值是@Results中的id
//@ResultMap("BaseArticleMap")
//使用xml中的<resulstMap>的id
@ResultMap("ArticleBaseMapper")
ArticlePO selectById(Integer id);
4.3.3SQL提供者
- 我们能在方法上面直接编写SQL语句,使用TextBloc编写长的语句,方法上编写SQL显的不够简洁。MyBatis提供了SQL提供者的功能,将SQL以方法的形式定义在单独的类中,Mapper接口通过引用SQL提供者的方法名称,表示要执行的SQL。
- SQL提供者有四类@SelectProvider,@InsertProvider,@UpdateProvider,@DeleteProvider。
- SQL提供者首先创建提供者类,自定义的。类中声明静态方法,方法体是SQL语句并返回SQL。例如:
public static String selectById() {
return "SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = #{id}";
}
- 其次Mapper接口的方法上面,应用@SelectProvider(type=提供者类.class,method=“方法名称”)
1.创建SQL提供者
public class SqlProvider {
//定义静态方法
public static String selectArticle() {
return "select * from article where id=#{id}";
}
public static String updateSql() {
return "update article set update_time=#{newTime} where id=#{id}";
}
public static String insertSql() {
return """
insert into article(user_id,title,summary,read_count,create_time,update_time)
values(#{userId},#{title},#{summary},#{readCount},#{createTime},#{updateTime})
""";
}
public static String deleteSql() {
return "delete from article where id=#{articleId}";
}
}
2.创建mapper接口
public interface ArticleRepository {
@Results(id = "NewBaseArticleMap", value = {
@Result(id = true, column = "id", property = "id"),
@Result(column = "user_id", property = "userId"),
@Result(column = "title", property = "title"),
@Result(column = "summary", property = "summary"),
@Result(column = "read_count", property = "readCount"),
@Result(column = "create_time", property = "createTime"),
@Result(column = "update_time", property = "updateTime")
})
//使用提供者
@SelectProvider(type = SqlProvider.class, method = "selectArticle")
ArticlePO selectByPrimary(Integer id);
@UpdateProvider(type = SqlProvider.class, method = "updateSql")
int updateTime(Integer id, LocalDateTime newTime);
@InsertProvider(type = SqlProvider.class, method = "insertSql")
int insertArticle(ArticlePO po);
@DeleteProvider(type = SqlProvider.class, method = "deleteSql")
int deleteArticle(Integer articleId);
}
3.单元测试
@SpringBootTest
public class RepositoryTest {
@Resource
private ArticleRepository articleRepository;
@Test
void testSelect() {
ArticlePO articlePO = articleRepository.selectByPrimary(4);
System.out.println("articleRepository = " + articleRepository);
}
@Test
void testUpdate() {
int update = articleRepository.updateTime(4, LocalDateTime.now());
System.out.println("update = " + update);
}
@Test
void testInsert() {
ArticlePO articlePO = new ArticlePO();
articlePO.setUserId(2345);
articlePO.setTitle("Spring6");
articlePO.setSummary("Spring6全新");
articlePO.setReadCount(6666);
articlePO.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
articlePO.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
int update = articleRepository.insertArticle(articlePO);
System.out.println("update = " + update);
}
@Test
void testDelete() {
int update = articleRepository.deleteArticle(5);
System.out.println("update = " + update);
}
}
- 我们可以分别创建Insert的提供者、Update提供者…每个查询者只提供一种操作,Select提供者的方法只提供Select语句。
4.3.4@One一对一查询
- MyBatis支持一对一,一对多,多对多查询。XML文件和注解都能实现关系的操作。
使用格式:@Result(column=" “,property=”“,one=@One(select=”"))
1.创建两个表的实体
- Article声明了ArticleDetail对象,表示文章内容。
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Article {
private Integer id;
private Integer userId;
private String title;
private String summary;
private Integer readCount;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
//一对一关系
private ArticleDetail articleDetail;
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class ArticleDetail {
private Integer id;
private Integer articleId;
private String content;
}
2.创建Mapper查询接口
public interface ArticleOneToOneMapper {
//一对一查询
//查询文章详情
@Select("""
select id,article_id,content from article_detail
where article_id = #{articleId}
""")
@Results({
@Result(id = true, column = "id", property = "id"),
@Result(column = "article_id", property = "articleId"),
@Result(column = "content", property = "content")
})
ArticleDetail selectDetail(Integer articleId);
//查询文章属性包含详情(内容)
@Select("""
select id,user_id,title,summary,read_count,create_time,update_time
from article where id = #{id}
""")
@Results({
@Result(id = true, column = "id", property = "id"),
@Result(column = "user_id", property = "userId"),
@Result(column = "title", property = "title"),
@Result(column = "summary", property = "summary"),
@Result(column = "read_count", property = "readCount"),
@Result(column = "create_time", property = "createTime"),
@Result(column = "update_time", property = "updateTime"),
@Result(column = "id", property = "articleDetail",
one = @One(select = "com.hhb.mybatis.mapper.ArticleOneToOneMapper.selectDetail",
fetchType = FetchType.LAZY)
)
})
Article selectAllArticle(Integer id);
}
3.单元测试
@Resource
private ArticleOneToOneMapper articleOneToOneMapper;
@Test
void testOneToOne() {
Article article = articleOneToOneMapper.selectAllArticle(1);
System.out.println("article = " + article);
}
4.3.5@Many一对多查询
- 一对多查询使用@Many注解,步骤与一对一基本相同。
- article与comment存在一对多关系,一篇文章多个评论。
使用格式:@Result(property=“”, column=“”, many=@Many(select=“”))
1.创建COmmentPO实体
@Data
public class CommentPO {
private Integer id;
private Integer articleId;
private String content;
}
2.创建新的文章聚合实体
@Data
public class ArticleEntity {
private Integer id;
private Integer userId;
private String title;
private String summary;
private Integer readCount;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
//多个评论
private List<CommentPO> comments;
}
3.新建Mapper接口
public interface ArticleCommentMapper {
//查询评论
@Select("""
select id,article_id,content from comment
where article_id=#{articleId} order by id;
""")
@Results(id = "CommentMapper", value = {
@Result(id = true, column = "id", property = "id"),
@Result(column = "article_id", property = "articleId"),
@Result(column = "content", property = "content")
})
List<CommentPO> selectComments(Integer articleId);
@Select("""
select id,user_id,title,summary,read_count,create_time,update_time
from article where id = #{articleId}
""")
@Results({
@Result(id = true, column = "id", property = "id"),
@Result(column = "user_id", property = "userId"),
@Result(column = "title", property = "title"),
@Result(column = "summary", property = "summary"),
@Result(column = "read_count", property = "readCount"),
@Result(column = "create_time", property = "createTime"),
@Result(column = "update_time", property = "updateTime"),
@Result(column = "id", property = "comments",
many = @Many(select = "com.hhb.mybatis.mapper.ArticleCommentMapper.selectComments",
fetchType = FetchType.LAZY))
})
ArticleEntity selectArticleComment(Integer id);
}
4.单元测试
@Resource
private ArticleCommentMapper articleCommentMapper;
@Test
void testOneToMany() {
ArticleEntity articleEntity = articleCommentMapper.selectArticleComment(1);
System.out.println("articleEntity = " + articleEntity);
}
4.3.6常用配置参数
- Mybatis的项设置,在application文件中“mybatis”开头进行设置。
常用设置
#驼峰命名
mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true
#mapper xml 文件位置
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:/mappers/**/*.xml
#启用缓存
mybatis.configuration.cache-enabled=true
#延迟加载
mybatis.configuration.lazy-loading-enabled=true
#mybatis 主配置文件,按需使用
mybatis.config-location=classpath:/mybatis-config.xml
- 上述设置内容比较多时,可以将设置放在Mybatis主配置文件mybatis.config-location加载主配置文件。
mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<settings>
<!--开启缓存-->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
<!--开启驼峰命名法-->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
<!--开启日志-->
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/>
</settings>
<!--采用别名机制-->
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.hhb.po"/>
</typeAliases>
</configuration>
4.4适合的连接池
- prepStmtCacheSize:这将设置MySQL驱动程序将缓存每个连接的预准备语句数。默认值为保守的25.我们建议将其设置为250-500之间。
- prepStmtCacheSqlLimit:这是驱动程序将缓存的准备好的SQL语句的最大长度。MySQL默认值为256,根据我们的经验,特别时对于像Hibernate这样的ORM框架,这个默认值远低于生成的语句长度的阈值,我们推荐的设置为2048.
- cachePrepStmts:如果缓存实际上被禁用,则上述参数都没有任何影响,因为默认值情况下是禁用的,必须将此参数设置为true使用缓存。
- useServerPrepStmts:较新版本的MySQL支持服务器端准备语句,这可以提供实质性的性能提升,将此属性设置为true。
application.yml
spring:
datasource:
type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/blog?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: 123456
hikari:
auto-commit: true
# # connections = ((cpu 核心数 * 2) + 磁盘数量) 近似值。 默认 10
maximum-pool-size: 10
#最小连接数,默认 10,不建议设置。默认与 maximum-pool-size 一样大小。推荐使用
固定大小的连接池
minimum-idle: 10
#获取连接时,检测语句
connection-test-query: select 1
###
# 连接超时,默认 30 秒。
# 控制客户端在获取池中 Connection 的等待时间,
# 如果没有连接可用的情况下超过该时间,则抛出 SQLException 异常,
###
connection-timeout: 20000
#其他属性
data-source-properties:
cachePrepStmts: true
dataSource.cachePrepStmtst: true
dataSource.prepStmtCacheSize: 250
dataSource.prepStmtCacheSqlLimit: 2048
dataSource.useServerPrepStmts: true
4.5声明式事务
- Spring框架提供了声明式事务和编程式事务管理,推荐声明式事务管理。
- 事务控制的属性:
- Propagation:传播行为。代码可以继续在现有事务中运行,也可以暂停现有事务并创建新事务。
- Isolation:隔离级别。此事务与其它事务的工作隔离的程度。
- Timeout:超时时间。该事务在超时和被底层事务基础结构自动回滚之前运行的时间。
- Read-only:只读状态。当代码读取但不修改数据时,可以使用只读事务。在某些情况下,例如使用Hibernate时,只读事务可能是一种有用的优化。
- AOP:Spring Framework的声明式事务管理是通过Spring面向切面编程(AOP)实现的。事务方面的代码以样板的方式使用,即使不了解AOP概念,仍然可以有效地使用这些代码。事务使用AOP的环绕通知。
- 声明式事务的方式:
- XML配置文件,全局配置。
- @Transactionl注解驱动:和代码一起提供,比较直观,和代码的耦合度比较高。Spring团队建议您只使用@Transaction注释具体类(以及具体类的方法),而不是注释接口。
- 方法的可见性:
- 公共(public)方法应用@Transactional 主机。如果使用@Transactional 注释了受保护的、私有的或包可见的方法,则不会引发错误,但注释的方法不会显示配置的事务设置,事务不生效。
4.5.1准备事务演示环境
- 需求:某个作者发布了新的文章,article、article_detail两个表同时添加记录。需要控制两个表的insert操作。
1.创建实体类
@Data//set、get方法
@AllArgsConstructor//全参构造
@NoArgsConstructor//无参构造
public class ArticlePO {
private Integer id;
private Integer userId;
private String title;
private String summary;
private Integer readCount;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class ArticleDetailPO {
private Integer id;
private Integer articleId;
private String content;
}
2.创建Mapper接口,创建两个方法,添加文章属性,文章内容
public interface ArticleMapper {
//添加新的文章
@Insert("""
insert into article(user_id,title,summary,read_count,create_time,update_time)
values(#{userId},#{title},#{summary},#{readCount},#{createTime},#{updateTime})
""")
//可选的配置,得到自动增长主键值
@Options(useGeneratedKeys = true, keyColumn = "id", keyProperty = "id")
int insertArticle(ArticlePO article);
//添加的文章内容
@Insert("""
insert into article_detail (article_id, content)
values (#{articleId},#{content});
""")
int insertDetail(ArticleDetailPO detail);
}
3.创建Service接口,声明发布文章的方法
@Service
public class ArticleServiceImpl implements ArticleService {
@Resource
private ArticleMapper articleMapper;
@Override
public boolean postNewArticle(ArticlePO article, String content) {
//添加新的文章
int rows = articleMapper.insertArticle(article);
//添加文章内容
ArticleDetailPO detail = new ArticleDetailPO();
detail.setArticleId(article.getId());
detail.setContent(content);
int detailRows = articleMapper.insertDetail(detail);
return (rows + detailRows) == 2 ? true : false;
}
}
4.启动类
@MapperScan("com.hhb.trans.mapper")
@SpringBootApplication
public class Springboot11TransApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springboot11TransApplication.class, args);
}
}
5.编写配置文件
#配置数据源
#默认连接池,可以修改为其它的
spring.datasource.type=com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&autoReconnect=true&useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=030522
#设置自动提交
spring.datasource.hikari.auto-commit=true
#获取最大连接数,默认10
spring.datasource.hikari.maximum-pool-size=10
#获取连接时,检测语句
spring.datasource.hikari.connection-test-query=select 1
#配置mybatis
#支持驼峰命名
mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true
#支持日志
mybatis.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
6.单元测试
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot11TransApplicationTests {
@Resource
private ArticleService articleService;
@Test
void testAddArticle() {
ArticlePO article = new ArticlePO();
article.setTitle("Spring 事务管理");
article.setSummary("Spring 事务属性,事务实现");
article.setUserId(2001);
article.setReadCount(0);
article.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
article.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
String content = "Spring 统一事务管理。事务管理器管理本地事务";
articleService.postNewArticle(article, content);
}
}
- 现在业务方法正常执行,添加数据到两个表,但是事务没有Spring参与,postNewArticle()方法没有事务管理。
4.5.2添加事务注解
1.修改postNewArticle()方法添加@Transactional
@Service
//@Transactional
public class ArticleServiceImpl implements ArticleService {
@Resource
private ArticleMapper articleMapper;
/**
* @Transactional:事务控制注解 位置:1.方法的上面 2.类的上面
* 事务回滚:
* 1.默认对运行时异常,执行回滚rollback
* 2.rollbackFor:需要回滚的异常类列表
*/
@Transactional(rollbackFor = IOException.class)
@Override
public boolean postNewArticle(ArticlePO article, String content) {
//添加新的文章
int rows = articleMapper.insertArticle(article);
//抛出异常
if (article.getReadCount() < 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("文章的阅读数量最小是1");
}
//添加文章内容
ArticleDetailPO detail = new ArticleDetailPO();
detail.setArticleId(article.getId());
detail.setContent(content);
int detailRows = articleMapper.insertDetail(detail);
return (rows + detailRows) == 2 ? true : false;
}
}
2.启动类
//启用事务管理(可选)
@EnableTransactionManagement
@MapperScan("com.hhb.trans.mapper")
@SpringBootApplication
public class Springboot11TransApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springboot11TransApplication.class, args);
}
}
3.单元测试
@Test
void testAddArticleTrans() {
ArticlePO article = new ArticlePO();
article.setTitle("Spring666 事务管理");
article.setSummary("Spring666 事务属性,事务实现");
article.setUserId(new Random().nextInt(1000));
article.setReadCount(0);
article.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
article.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
String content = "Spring666 统一事务管理。事务管理器管理本地事务";
articleService.postNewArticle(article, content);
}
- 添加数据失败,在事务中抛出运行时异常。Spring默认回滚事务。
4.5.3无效事务1
- Spring事务处理是AOP的环绕通知,只有通过代理对象调用具有事务的方法。类中有A方法,调用带有事务的B方法会导致B方法中的事务失效。protected、private方法默认是没有事务功能的。
1.接口中增加方法managerArticle
@Override
public boolean managerArticle(ArticlePO po, String content) {
//调用具有事务的方法
return postNewArticle(po, content);
}
2.单元测试,readCount为0
@Test
void testManagerArticleTrans() {
ArticlePO articlePO = new ArticlePO();
articlePO.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
articlePO.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
articlePO.setTitle("===SpringMVC开发web应");
articlePO.setSummary("===基于MVC架构的");
articlePO.setUserId(new Random().nextInt(500));
articlePO.setReadCount(0);
String content="====Web开发使用SpringMVC";
boolean add = articleService.managerArticle(articlePO,content);
System.out.println("发布新的文章 = " + add);
}
- 测试发现,事务不起作用。
4.5.4无效事务2
- 方法在线程中运行的,在同一线程中方法具有事务功能,新的线程中的代码事务无效。
1.修改接口方法的实现
@Override
@Transactional
public boolean postNewArticleThread(ArticlePO article, String content) {
System.out.println("Start 父线程:" + Thread.currentThread().threadId());
Thread thread = new Thread(()->{
System.out.println("子线程:"+Thread.currentThread().threadId());
//添加新的文章
int rows = articleMapper.insertArticle(article);
//抛出异常
if (article.getReadCount() < 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("文章的阅读数量最小是1");
}
//添加文章内容
ArticleDetailPO detail = new ArticleDetailPO();
detail.setArticleId(article.getId());
detail.setContent(content);
int detailRows = articleMapper.insertDetail(detail);
});
//线程启动
thread.start();
try {
//等他thread执行完成,在继续后面的代码
thread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("End 父线程:" + Thread.currentThread().threadId());
return true;
}
2.单元测试
@Test
void testManagerArticleTransThread() {
ArticlePO articlePO = new ArticlePO();
articlePO.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
articlePO.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
articlePO.setTitle("Python开发web应");
articlePO.setSummary("基于Python MVC架构的");
articlePO.setUserId(new Random().nextInt(500));
articlePO.setReadCount(0);
String content = "Python开发使用Python";
boolean add = articleService.postNewArticleThread(articlePO, content);
System.out.println("发布新的文章 = " + add);
}
4.5.5事务回滚
- 抛出RuntimeException异常时,其实例或子类会回滚事务
- 抛出Error会导致回滚
- 抛出“已检查异常”不会回滚,默认提交事务
@Transactional注解的属性控制回滚
- rollbackFor
- noRollbackFor
- rollbackForClassName
- noRollbackClassName