项目中经常需要使用到占位符来满足多环境不同配置信息的需求,比如:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="myPropertyPlaceholderBean" class="com.example.demo1.PropertyPlaceholderBean">
<property name="myPropertyName" value="${my.property.key}" />
</bean>
</beans>
其中属性myPropertyName是带有’ ${}’ 符号,也就是占位符的变量,最终需要替换成具体的值,Spring会最终替换,那么它怎么做到的? 下面就通过打断点跟源码方式分析来分析说明。
还是以SpringBoot项目为例,在resources下定义结构如下:
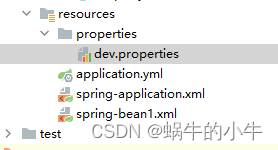
以上结构是为了方便验证,随便定义的,大家可能有区别。
其中dev.properties定义两个key
test.env_var=123
my.property.key=justdoit
spring-bean1.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="myPropertyPlaceholderBean" class="com.example.demo1.PropertyPlaceholderBean">
<property name="myPropertyName" value="${my.property.key}" />
</bean>
</beans>
spring-application.xml如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:properties/dev.properties" ignore-unresolvable="true" />
<import resource="spring-bean1.xml"/>
</beans>
Spring boot启动类定义
@SpringBootApplication
@ImportResource({"classpath:spring-application.xml"})
public class ClientServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ClientServerApplication.class, args);
}
}
好了,下面开始分析整个过程…
首先从PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer开始说,因为占位符默认就是由它来实现的。 进入其源码看到它是一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor 大家都知道,spring bean生命周期过程会执行所有BeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory方法,所以,肯定会进入到这个方法:
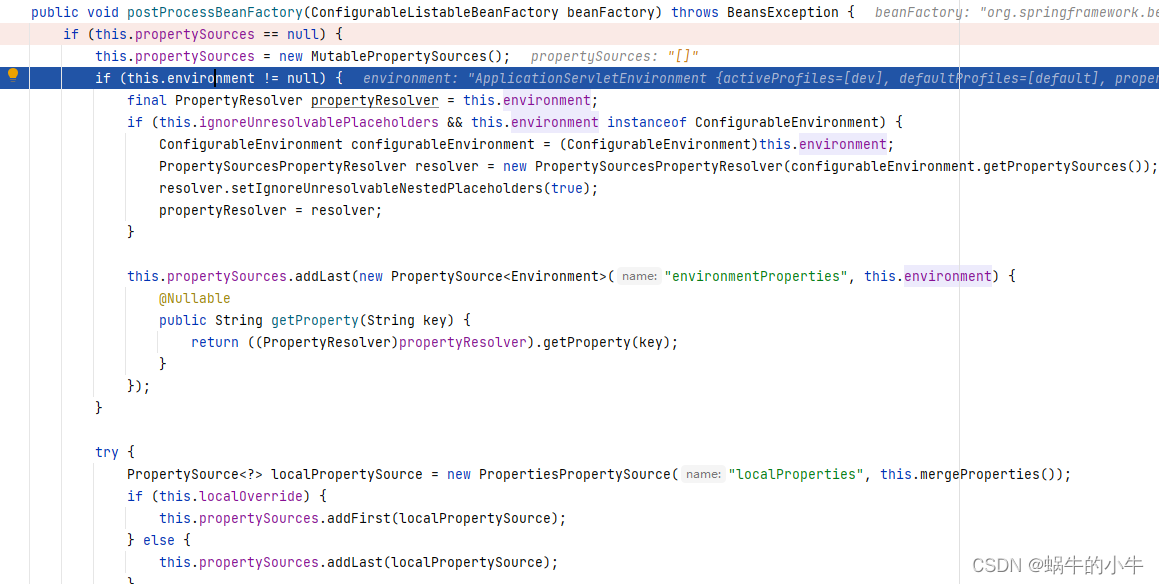
这里看到它尝试从两个地方去读取属性配置,一个是
以Environment为属性源的environmentProperties,另外一个就是通过loadProperties(Properties props)加载本地资源文件作为属性源的localProperties,我这个例子是第二种情况。
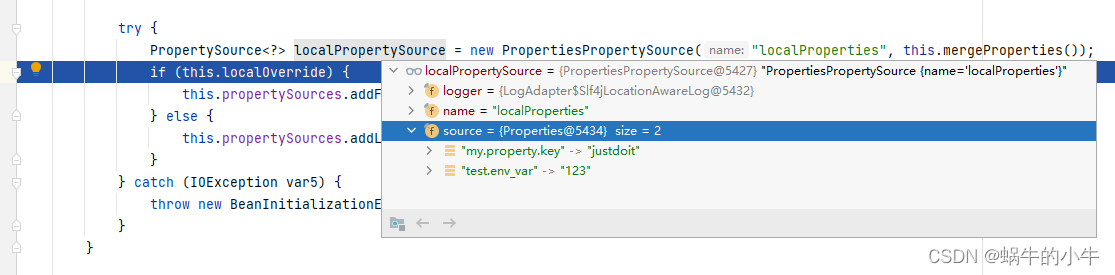
可以看到,已经加载到我上面配置的两个key-value
接着进入到下一步:
this.processProperties(beanFactory, (ConfigurablePropertyResolver)(new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(this.propertySources)));
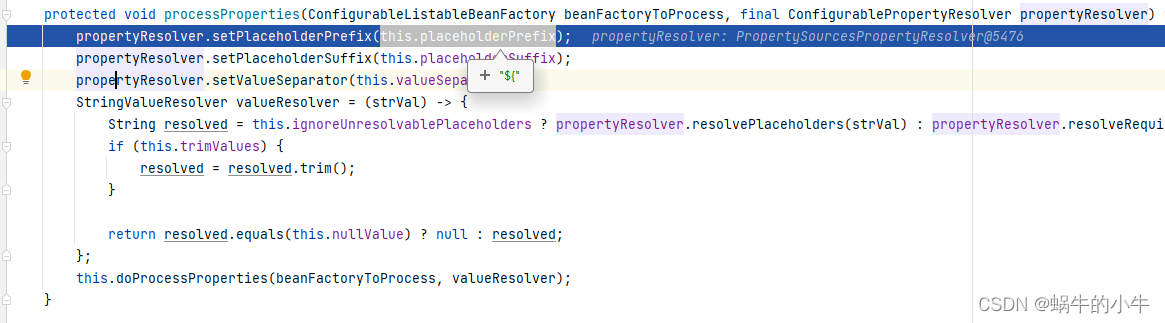
看到propertyResolver.setPlaceholderPrefix(this.placeholderPrefix)这些是设置缺省时,占位符的默认配置,即’${}’
其中注意一点,StringValueResolver valueResolver定义的是labmda表达式,后面会使用到。
接着下一步
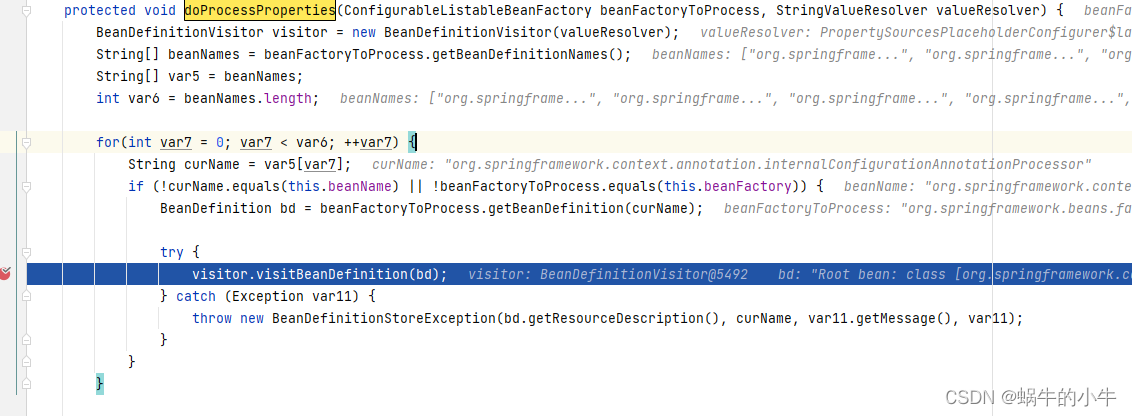
上面这里是开始遍历所有的bean,替换其中包含占位符的bean的属性对象。
接着进入方法:
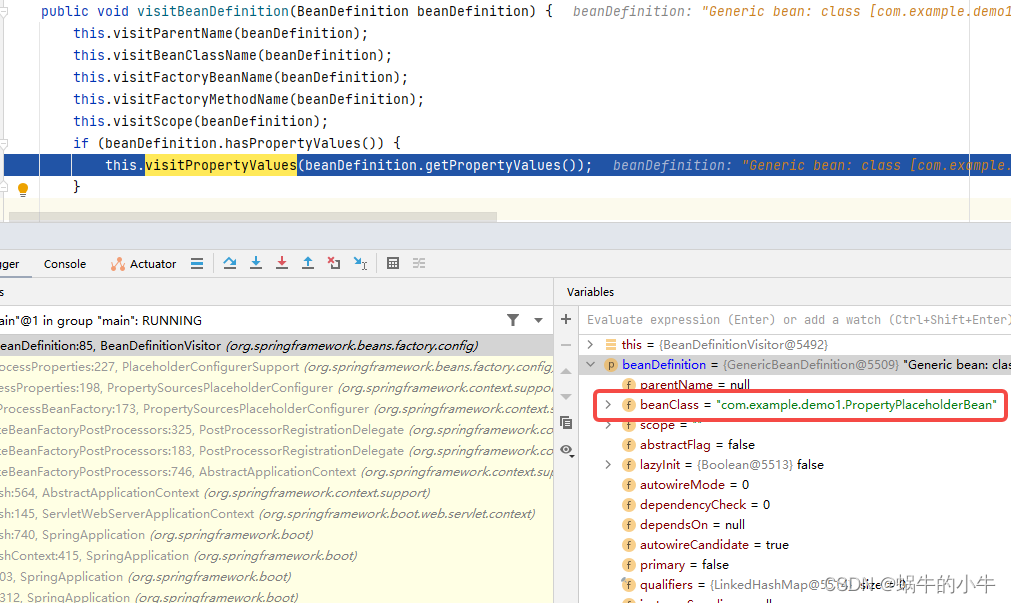 遍历到我们自定义的bean,其中beanDefinition.getPropertyValues()是拿它的所有属性信息,如下图
遍历到我们自定义的bean,其中beanDefinition.getPropertyValues()是拿它的所有属性信息,如下图
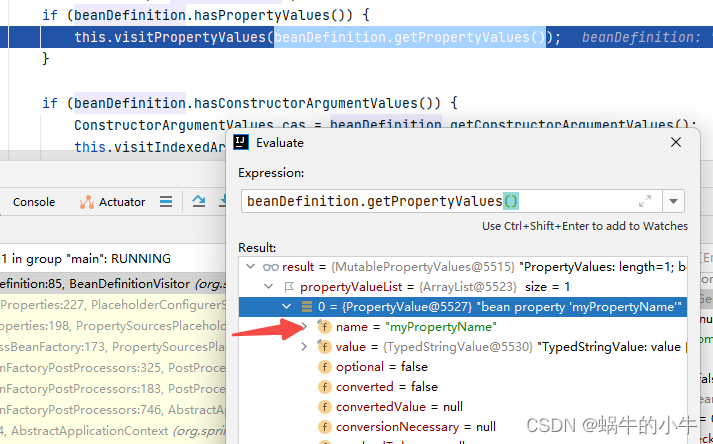
遍历所有的属性,解析值,并且替换占位符
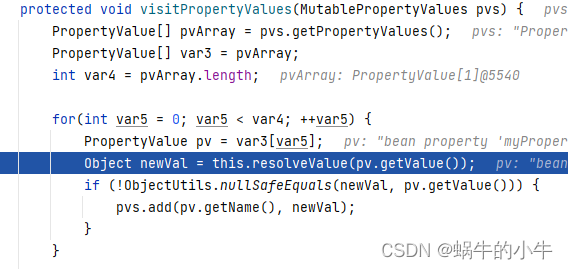
进入resolveValue方法,直接去到以下位置,因为属性类型是string嘛,所以直接跳到这里
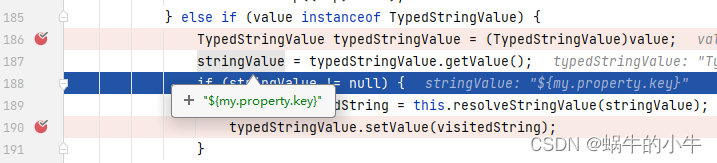
可以看到我们bean中定义的占位符,接下来就是要替换它。接着看
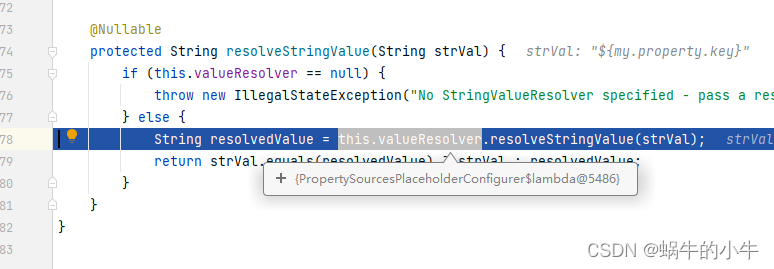
发现此次是一个labmda表达式,就是上面提到的,所以执行回到上面的位置,
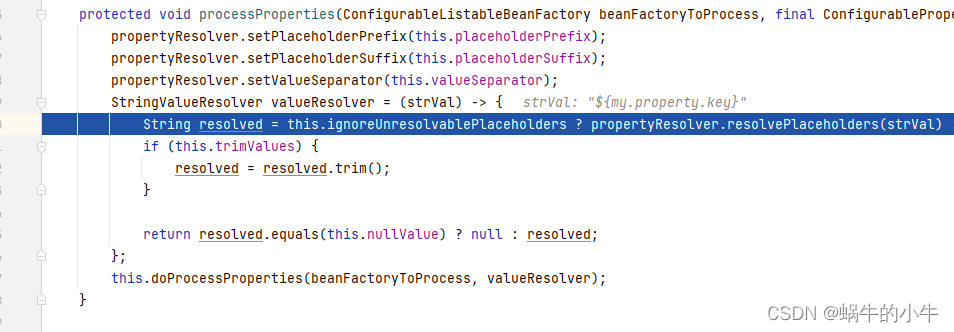
接着跟代码会进入到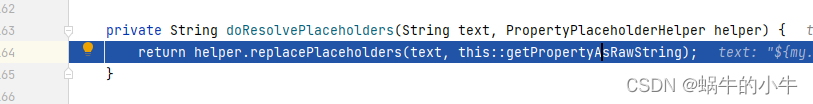
继续进入
parseStringValue
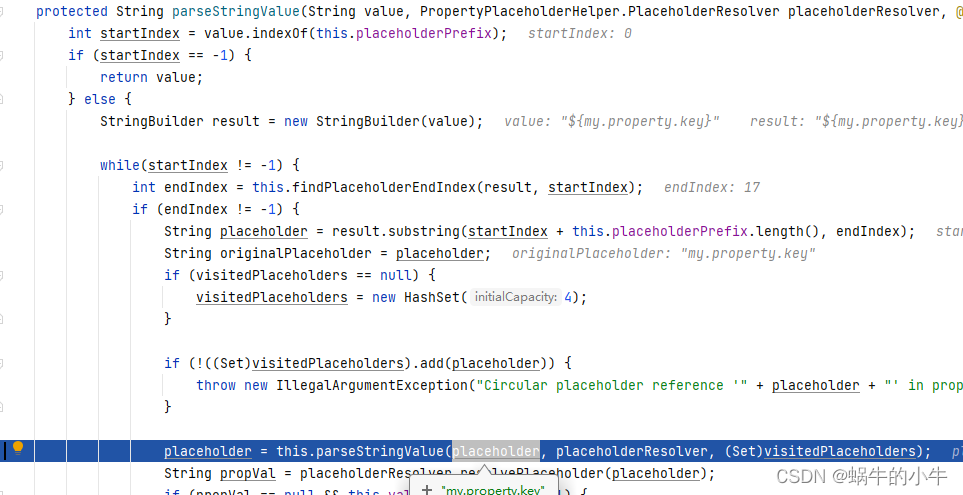
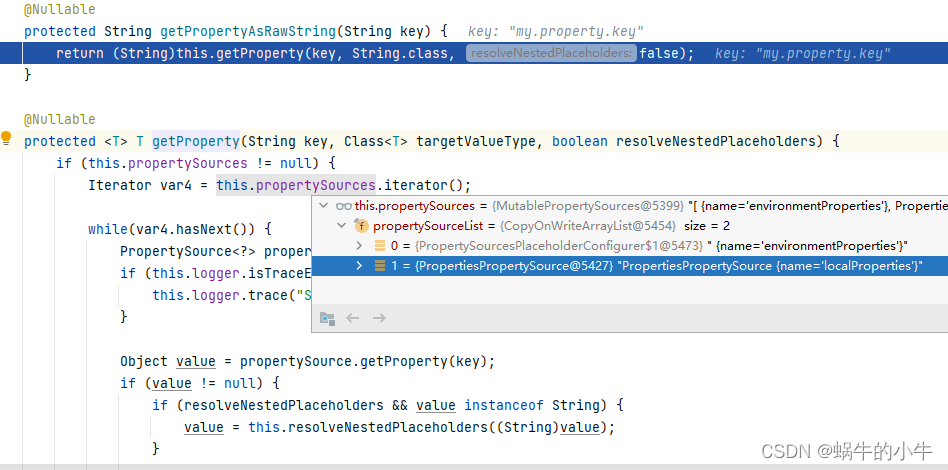
从propertySources里面去解析配置,疑问来了??这个对象什么时候放进去的,其实就是最开始提到的两个读取配置的地方,
一个是
以Environment为属性源的environmentProperties,另外一个就是通过loadProperties(Properties props)加载本地资源文件作为属性源的localProperties。
看以下代码就明白了,
if (this.localOverride) {
this.propertySources.addFirst(localPropertySource);
} else {
this.propertySources.addLast(localPropertySource);
}
解析完占位符得到值以后,出来回到resolveValue方法处,也就是很多if else的方法处,字符串位置
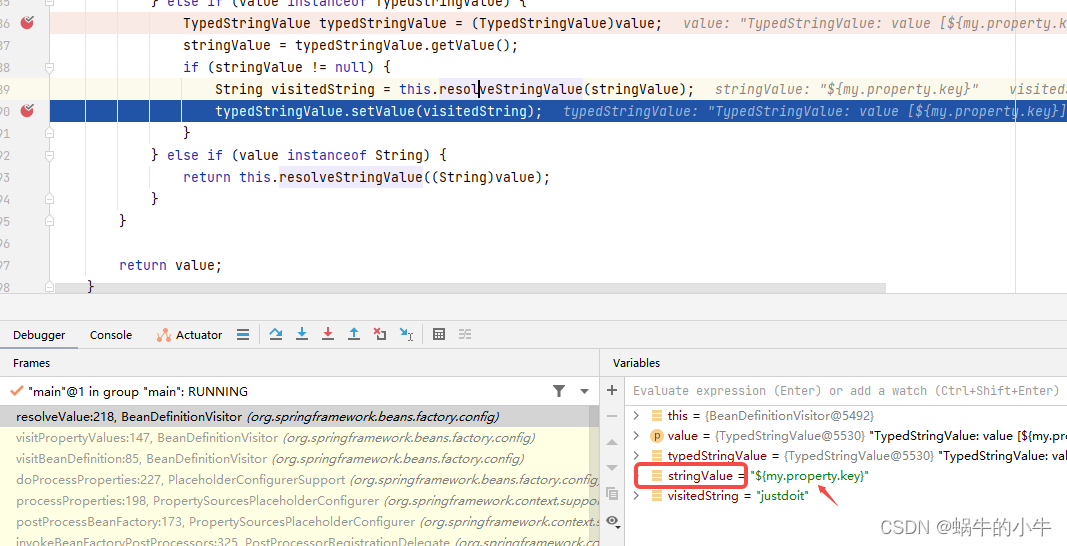
将属性值原本是${my.property.key}替换成justdoit
到此,对象PropertyPlaceholderBean定义的属性myPropertyName就被替换成具体的某个值了,这里也就是被替换成了 justdoit
总结:
基于Spring bean的生命周期,BeanFactoryPostProcessor执行方法postProcessBeanFactory,解析获取到属性源即environmentProperties以及localProperties两种,跟着解析占位符,然后得到具体的值,最后set进去替换占位符为具体的属性值。

![[HDLBits] Exams/m2014 q4a](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/9ae35d2de0c7d4e4e49ccb3affdf36cc.png)