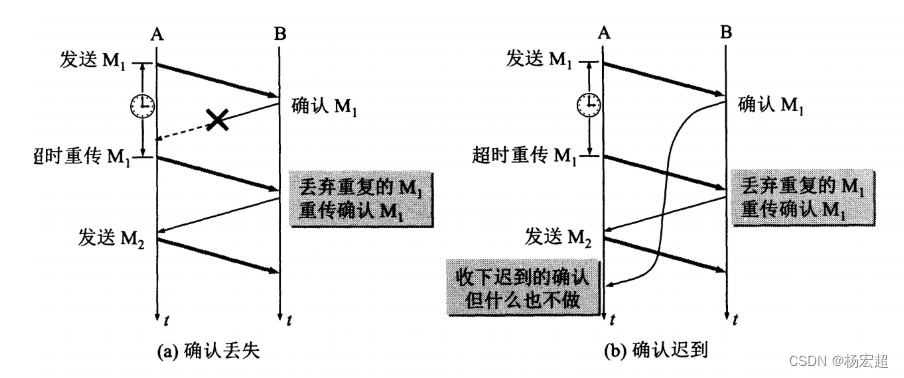
不同平台上的假新闻正在广泛传播,这是一个令人严重关切的问题,因为它导致社会稳定和人们之间建立的纽带的永久破裂。很多研究已经开始关注假新闻的分类。
在这里,我们将尝试在Python中的机器学习的帮助下解决这个问题。
主要步骤
- 导入库和数据集
- 数据预处理
- 新闻栏目的预处理与分析
- 将文本转换为矢量
- 模型训练、评估和预测
1. 导入库和数据集
- Pandas:用于导入数据集。
- Seaborn/Matplotlib:用于数据可视化。
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
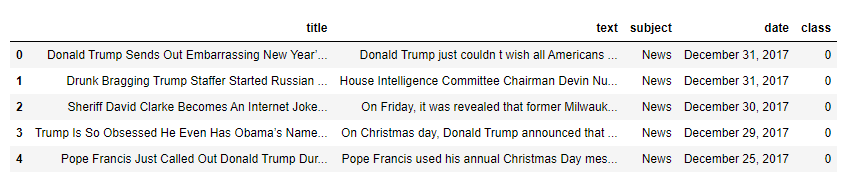
data = pd.read_csv('News.csv',index_col=0)
data.head()
2. 数据预处理
data.shape
输出:
(44919, 5)
由于标题、主题和日期栏对新闻的识别没有帮助。所以,我们可以删除这些列。
data = data.drop(["title", "subject","date"], axis = 1)
现在,我们必须检查是否有任何空值(我们将删除那些行)
data.isnull().sum()
输出:
text 0
class 0
现在我们必须对数据集进行打乱,以防止模型出现偏差。之后我们将重置索引,然后删除它。因为索引列对我们没有用。
# Shuffling
data = data.sample(frac=1)
data.reset_index(inplace=True)
data.drop(["index"], axis=1, inplace=True)
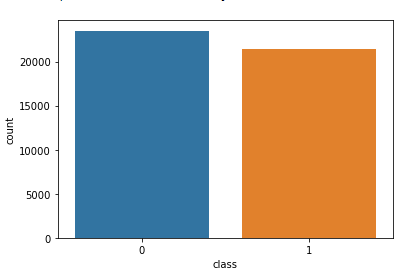
让我们使用下面的代码来探索每个类别中的唯一值。
sns.countplot(data=data,
x='class',
order=data['class'].value_counts().index)
3. 新闻栏目的预处理与分析
首先,我们将从文本中删除所有的停用词,标点符号和任何不相关的空格。NLTK库是必需的,它的一些模块需要下载。因此,运行下面的代码。
from tqdm import tqdm
import re
import nltk
nltk.download('punkt')
nltk.download('stopwords')
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
from nltk.stem.porter import PorterStemmer
from wordcloud import WordCloud
一旦我们有了所有需要的模块,我们就可以创建一个函数名预处理文本。此函数将预处理作为输入的所有数据。
def preprocess_text(text_data):
preprocessed_text = []
for sentence in tqdm(text_data):
sentence = re.sub(r'[^\w\s]', '', sentence)
preprocessed_text.append(' '.join(token.lower()
for token in str(sentence).split()
if token not in stopwords.words('english')))
return preprocessed_text
要在文本列中的所有新闻中实现该函数,请运行以下命令。
preprocessed_review = preprocess_text(data['text'].values)
data['text'] = preprocessed_review
让我们分别为假新闻和真实的新闻可视化WordCloud。
# Real
consolidated = ' '.join(
word for word in data['text'][data['class'] == 1].astype(str))
wordCloud = WordCloud(width=1600,
height=800,
random_state=21,
max_font_size=110,
collocations=False)
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10))
plt.imshow(wordCloud.generate(consolidated), interpolation='bilinear')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
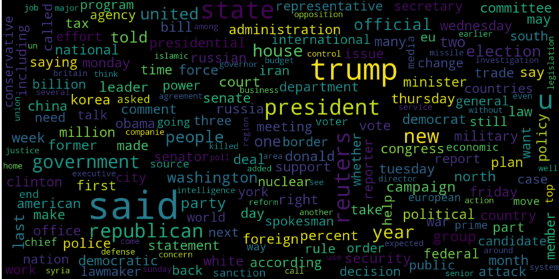
# Fake
consolidated = ' '.join(
word for word in data['text'][data['class'] == 0].astype(str))
wordCloud = WordCloud(width=1600,
height=800,
random_state=21,
max_font_size=110,
collocations=False)
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10))
plt.imshow(wordCloud.generate(consolidated), interpolation='bilinear')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
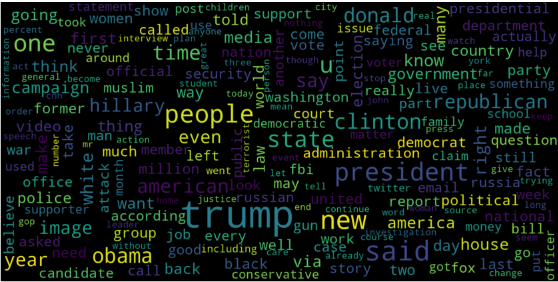
现在,让我们绘制前20个最常见单词的条形图。
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
def get_top_n_words(corpus, n=None):
vec = CountVectorizer().fit(corpus)
bag_of_words = vec.transform(corpus)
sum_words = bag_of_words.sum(axis=0)
words_freq = [(word, sum_words[0, idx])
for word, idx in vec.vocabulary_.items()]
words_freq = sorted(words_freq, key=lambda x: x[1],
reverse=True)
return words_freq[:n]
common_words = get_top_n_words(data['text'], 20)
df1 = pd.DataFrame(common_words, columns=['Review', 'count'])
df1.groupby('Review').sum()['count'].sort_values(ascending=False).plot(
kind='bar',
figsize=(10, 6),
xlabel="Top Words",
ylabel="Count",
title="Bar Chart of Top Words Frequency"
)
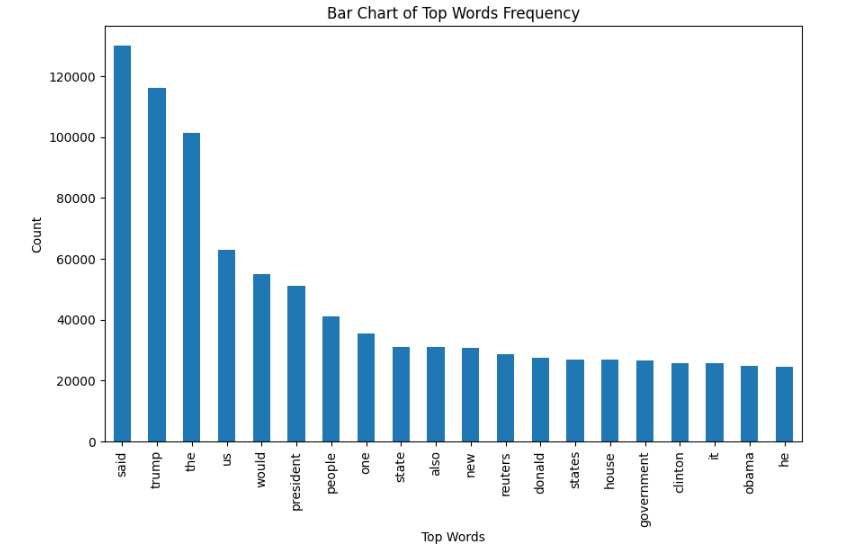
4. 将文本转换为矢量
在将数据转换为矢量之前,将其分为训练和测试。
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data['text'],
data['class'],
test_size=0.25)
现在我们可以使用TfidfVectorizer将训练数据转换为向量。
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
vectorization = TfidfVectorizer()
x_train = vectorization.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = vectorization.transform(x_test)
5. 模型训练、评估和预测
现在,数据集已经准备好可以训练模型。
对于训练,我们将使用Logistic回归并使用accuracy_score评估预测准确性。
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
model = LogisticRegression()
model.fit(x_train, y_train)
# testing the model
print(accuracy_score(y_train, model.predict(x_train)))
print(accuracy_score(y_test, model.predict(x_test)))
输出:
0.993766511324171
0.9893143365983972
让我们使用决策树分类器进行训练。
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
model = DecisionTreeClassifier()
model.fit(x_train, y_train)
# testing the model
print(accuracy_score(y_train, model.predict(x_train)))
print(accuracy_score(y_test, model.predict(x_test)))
输出:
0.9999703167205913
0.9951914514692787
决策树分类器的混淆矩阵可以用下面的代码实现。
# Confusion matrix of Results from Decision Tree classification
from sklearn import metrics
cm = metrics.confusion_matrix(y_test, model.predict(x_test))
cm_display = metrics.ConfusionMatrixDisplay(confusion_matrix=cm,
display_labels=[False, True])
cm_display.plot()
plt.show()
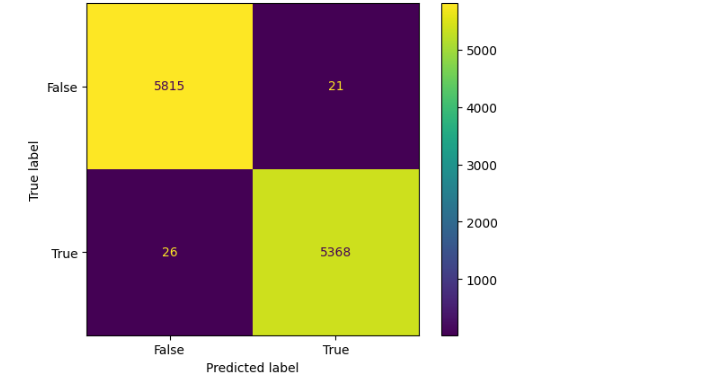
总结
决策树分类器和Logistic回归表现良好。