Typhoon 计算几何,点到线段距离
String Magic (Easy Version) Manacher可持久化线段树
Touhou Red Red Blue DP 模拟
Expectation (Easy Version) 签到,组合数学
Tree 树形DP
Cactus Circuit 仙人掌图,tarjan找简单环
Counting Stars 暴力,组合数学

直接套计算几何模板,求点到线段最短距离即可
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long int ll;
# define mod 1000000007
double feng[10000+10][2],wo[10000+10][2];
class Point
{
public:
double x,y;
Point(double x=0,double y=0):x(x),y(y) {}
//向量加法
Point operator+(Point p)
{
return Point(x+p.x,y+p.y);
}
//向量减法
Point operator-(Point p)
{
return Point(x-p.x,y+p.y);
}
//向量伸缩
Point operator*(double a)
{
return Point(x*a,y*a);
}
Point operator/(double a)
{
return Point(x/a,y/a);
}
//向量大小
double abs()
{
return sqrt(norm());
}
//向量范数
double norm()
{
return x*x+y*y;
}
bool operator<(const Point &p) const
{
return x!=p.x?x<p.x:y<p.y;
}
bool operator==(const Point &p)const
{
return x-p.x<1e-10&&y-p.y<1e-10;
}
};
typedef Point Vector;
//向量内积
double dot(Vector a,Vector b)
{
return a.x*b.x+a.y*b.y;
}
//向量外积
double cross(Vector a,Vector b)
{
return abs(a.x*b.y-a.y*b.x);
}
//正交
bool isOrthogonal(Vector a,Vector b)
{
return a.x*b.x+a.y*b.y==0;
}
//平行
bool isParallel(Vector a,Vector b)
{
return a.x*b.y-a.y*b.x==0;
}
//投影
Point project(Point a,Point b,Point c)
{
Vector ab(b.x-a.x,b.y-a.y);
Vector ac(c.x-a.x,c.y-a.y);
double r=dot(ab,ac)/ab.norm();//比例
Vector h(ab*r);
return Point(a.x+h.x,a.y+h.y);
}
//映象
Point reflect(Point a,Point b,Point c)
{
//c到ab的投影点
Point r=project(a,b,c);
Vector cr(r.x-c.x,r.y-c.y);
//cr扩大二倍
Vector cr_2=cr*2;//上面重载过*
//向量加法
return Point(c.x+cr_2.x,c.y+cr_2.y);
}
//两点间距离
double getDistancePP(Point a,Point b)
{
Point c(b.x-a.x,b.y-a.y);
return c.abs();
}
//点到直线距离(利用外积平行四边形)
double getDistancePL(Point a,Point b,Point c)
{
Vector ab(b.x-a.x,b.y-a.y);
Vector ac(c.x-a.x,c.y-a.y);
return cross(ab,ac)/ab.abs();
}
//点到线段距离
double getDistancePS(Point a,Point b,Point c)
{
//定义4个向量
Vector ab(b.x-a.x,b.y-a.y);
Vector ba(a.x-b.x,a.y-b.y);
Vector ac(c.x-a.x,c.y-a.y);
Vector bc(c.x-b.x,c.y-b.y);
if(dot(ab,ac)<0.0) return getDistancePP(a,c);
if(dot(ba,bc)<0.0) return getDistancePP(b,c);
return getDistancePL(a,b,c);
}
//线段到线段的距离
double getDistanceSS(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d)
{
//从4个点到2线段距离中取最小
return min(min(getDistancePS(c,d,a),getDistancePS(c,d,b)),min(getDistancePS(a,b,c),getDistancePS(a,b,d)));
}
int main()
{
int n,m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
scanf("%lf%lf",&feng[i][0],&feng[i][1]);
}
for(int i=1; i<=m; i++)
{
scanf("%lf%lf",&wo[i][0],&wo[i][1]);
}
for(int i=1; i<=m; i++)
{
double minn=1e18;
for(int j=2; j<=n; j++)
{
struct Point A,B,C;
A.x=wo[i][0];
A.y=wo[i][1];
B.x=feng[j-1][0];
B.y=feng[j-1][1];
C.x=feng[j][0];
C.y=feng[j][1];
double temp=getDistancePS(B,C,A);
// cout<<temp<<" ";
minn=min(minn,temp);
}
// cout<<endl;
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(4)<<minn<<'\n';
}
return 0;
} 
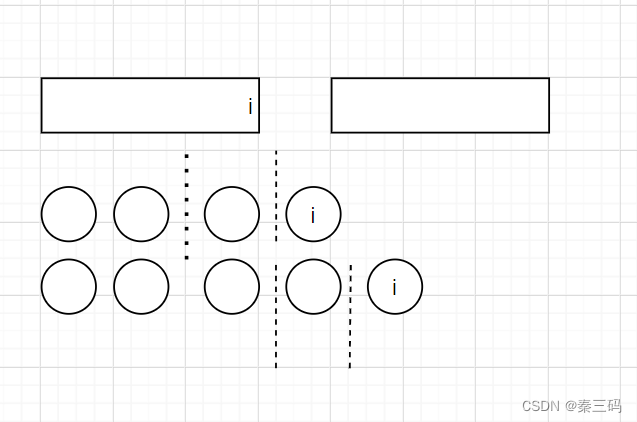
按照给出的约束,可以推出,这是一个偶数长度的字符串,左半部分是回文,右半部分也是回文,并且整体也是回文。也就是说,我们需要找出全部的偶数回文串,它的左半部分也是回文串。按照回文的奇偶性来判断。以左半部分是偶数回文为例,假设i位置到i+1位置的最大回文半径为图中长方形。如果回文半径为偶数,则左半部分的回文中心应该在中间位置,到i-1位置之间。只有这样,对称出来的字符串才能覆盖i,且保证左半部分的内部回文左右相等。比如偏向更左侧,会导致左右不均,超出左半部分的左边界。
而对于奇数回文,也是同理,不再赘述。
维护采用可持久化线段树,每次将回文中心所在线段树的右端点加1,查询时,取合法回文半径区间,求出其大于等于i位置的和即可。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std ;
typedef long long int ll;
int P[200000+10];
string s;
int d[200000+10][2];
int lson[200000*30+10],rson[200000*30+10],sum[200000*30+10];
int tot;
int clone(int root)
{
tot++;
lson[tot]=lson[root];
rson[tot]=rson[root];
sum[tot]=sum[root];
return tot;
}
int build(int root,int l,int r)
{
root=clone(root);
if(l==r)
{
sum[root]=0;
return root;
}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
lson[root]=build(lson[root],l,mid);
rson[root]=build(rson[root],mid+1,r);
sum[root]=0;
return root;
}
int change(int root,int l,int r,int pos)
{
root=clone(root);
if(l==r)
{
sum[root]++;
return root;
}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(pos<=mid)
lson[root]=change(lson[root],l,mid,pos);
else
rson[root]=change(rson[root],mid+1,r,pos);
sum[root]=sum[lson[root]]+sum[rson[root]];
return root;
}
int getsum(int root1,int root2,int l,int r,int pos)
{
if(pos<=l)
return sum[root2]-sum[root1];
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
int ans=0;
if(pos<=mid)
{
ans+=getsum(lson[root1],lson[root2],l,mid,pos);
ans+=getsum(rson[root1],rson[root2],mid+1,r,pos);
return ans;
}
else
{
ans+=getsum(rson[root1],rson[root2],mid+1,r,pos);
}
return ans;
}
int root[200000+10][2];
signed main()
{
cin.tie(0);
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
cin>>s;
string temp="";
temp=" ";
int mid=0,r=0;
for(int i=0; i<s.length(); i++)
{
temp+='#';
temp+=s[i];
}
temp+='#';
temp+='@';
for(int i=1; i<temp.length(); i++)
{
if(r<i)
P[i]=1;
else
P[i]=min(P[2*mid-i],r-i);
while(temp[i-P[i]]==temp[i+P[i]])
P[i]++;
if(mid+P[i]>r)
{
r=mid+P[i];
mid=i;
}
}
for(int i=1; i<temp.length(); i++)
{
if(i%2==0)
{
d[i/2][1]=P[i]/2;
}
else if(i>=3)
{
d[i/2][0]=P[i]/2;
}
}
int n=s.length();
tot=0;
root[0][0]=build(0,1,n);
root[0][1]=build(0,1,n);
ll ans=0;
for(int i=1; i<n; i++)
{
root[i][1]=change(root[i-1][1],1,n,i+d[i][1]-1);
if(d[i][0])
{
int pre=0;
if(d[i][0]%2==0)
pre=i-d[i][0]/2;
if(d[i][0]%2==1)
pre=i-d[i][0]/2-1;
ans+=getsum(root[pre][1],root[i][1],1,n,i);
}
if(i!=n)
root[i][0]=change(root[i-1][0],1,n,i+d[i][0]);
if(d[i][0]>1)
{
int pre=0;
if(d[i][0]%2==0)
pre=i-d[i][0]/2-1;
if(d[i][0]%2==1)
pre=i-d[i][0]/2-1;
ans+=getsum(root[pre][0],root[i-1][0],1,n,i);
}
}
cout<<ans<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}
设dp[i][j]为第一个是i第二个是j的状态时的最大收益。其中i,j=0时代表空,值得注意的是,不能直接用dp数组推dp数组,需要暂时存储一下之前状态,再进行转移。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e5 + 7;
int dp[5][5], cp[5][5];
bool ext[5][5], cext[5][5];
int q[N];
char s[N];
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--)
{
memset(dp, 0, sizeof dp);
memset(ext, 0, sizeof ext);
scanf("%s", s);
int n = strlen(s);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (s[i - 1] == 'R')
{
q[i] = 1;
}
else if (s[i - 1] == 'G')
{
q[i] = 2;
}
else
{
q[i] = 3;
}
}
for(int i=0; i<=3; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<=3; j++)
{
dp[i][j]=-1e9;
}
}
dp[0][0]=0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
memcpy(cp, dp, sizeof cp);
dp[1][0] = max(dp[1][0], cp[q[i]][q[i]] + 1);
dp[2][0] = max(dp[2][0], cp[q[i]][q[i]] + 1);
dp[3][0] = max(dp[3][0], cp[q[i]][q[i]] + 1);
// ext[1][0] = ext[2][0] = ext[3][0] = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j++)
{
dp[j][q[i]] = max(dp[j][q[i]], cp[j][0]);
}
for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j++)
{
for (int k = 1; k <= 3; k++)
{
if (k != j && k != q[i] && j != q[i])
{
for (int u = 1; u <= 3; u++)
{
for (int v = 1; v <= 3; v++)
{
dp[u][v] = max(dp[u][v], cp[j][k]);
ext[u][v] = 1;
}
}
}
}
}
dp[q[i]][0]=max(dp[q[i]][0],cp[0][0]);
for (int u = 1; u <= 3; u++)
{
for (int v = 1; v <= 3; v++)
{
dp[v][q[i]] = max(dp[v][q[i]], cp[u][v]);
}
}
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j <= 3; j++)
{
res = max(res, dp[i][j]);
}
}
printf("%d\n", res);
}
}
签到题, 快速幂解决。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long int ll;
# define mod 998244353
ll fac[1000000+10],inv[1000000+10];
ll qp(ll base, ll pow)
{
ll ans=1;
base%=mod;
while(pow)
{
if(pow&1)
ans=ans*base%mod;
base=base*base%mod;
pow>>=1;
}
return ans;
}
ll sum[1000000+10];
void init()
{
fac[0]=1;
for(int i=1; i<=1000000; i++)
{
fac[i]=fac[i-1]*(ll)i%mod;
}
inv[1000000]=qp(fac[1000000],mod-2);
for(int i=1000000-1;i>=0;i--)
{
inv[i]=inv[i+1]*(ll)(i+1)%mod;
}
}
ll getc(int x,int y)
{
if(x<y)
return 0;
return fac[x]*inv[y]%mod*inv[x-y]%mod;
}
ll sheng[1000000+10],bai[1000000+10];
int main()
{
int t;
init();
// cout<<fac[100]*inv[100]%mod;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
ll n,m,a,b;
scanf("%lld%lld%lld%lld",&n,&m,&a,&b);
ll aa=a*qp(b,mod-2)%mod;
ll bb=((1-aa)%mod+mod)%mod;
sheng[1]=aa;
bai[1]=bb;
sum[1]=qp(1ll,m);
sheng[0]=1;
bai[0]=1;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
sum[i]=qp(i,m);
sum[i]=(sum[i-1]+sum[i])%mod;
sheng[i]=sheng[i-1]*aa%mod;
bai[i]=bai[i-1]*bb%mod;
}
ll ans=0;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
ll now=getc(n,i)*sheng[i]%mod*bai[n-i]%mod;
now*=sum[i];
now%=mod;
ans+=now;
ans%=mod;
}
cout<<ans<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}

很抽象的题意,说的一点不清楚。大致是每一个根节点要么是重儿子,要么不是。是的话,会形成一条重儿子链,这条重儿子链的顶端的父节点,将这条重儿子链形成的线段树叠在自己头顶,父节点其余的轻儿子,坠在父节点下面。问给定树形成的新树高度。
如果是重儿子,每次返回两个值,一个是当前其接龙的重链长度,一个是该节点下面坠的树高。
如果不是重儿子,则返回两个值,一个是将其重链接在头顶和其下端坠着的树高之和,一个是在接龙的重链长度,此时为0.
记录一个up,只对轻儿子有效, 表示接在其头部的长度,初始必须是1,因为单纯一个数字也是一层。
记录一个down,代表当下面连接的高度,对全部儿子节点取max即可。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e6 + 7;
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
int v[N];
void add(int a, int b)
{
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx++;
}
ll res;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
int maxx(int &a, int &b)
{
if (a > b)
{
return a;
}
return b;
}
inline pii dfs(int x)
{
int up = 1;
int down = 0;
int len = v[x];
int flag=0;
for (register int i = h[x]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int to = e[i];
if (v[to])
{
pii tp = dfs(to);
up = ceil(log2((tp.second + 1) * 2));
down = maxx(down, tp.first);
len += tp.second;
flag=tp.second+1;
}
else
{
pii tp = dfs(to);
down = maxx(down, tp.first);
}
}
if(v[x]==0)
len=0;
pii tpp0 = {up + down, len}, tpp1 = {down, len};
return (v[x] == 0) ? tpp0 : tpp1;
}
inline int read()
{
int x = 0, f = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while (!isdigit(ch))
{
if (ch == '-')
f = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(ch))
{
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return x * f;
}
inline void write(ll x)
{
if (x < 0)
putchar('-'), x = -x;
if (x > 9)
write(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
int main()
{
int size(512 << 20);
// 512M
__asm__("movq %0, %%rsp\n" ::"r"((char *)malloc(size) + size)); // YOUR CODE
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
idx = 0;
int n;
cin >> n;
for (register int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
v[i] = 0;
h[i] = -1;
}
for (register int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
register int x;
cin >> x;
add(x, i);
}
for (register int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
register int x;
cin >> x;
if (x)
{
v[x] = 1;
}
}
cout << dfs(1).first << '\n';
}
exit(0);
}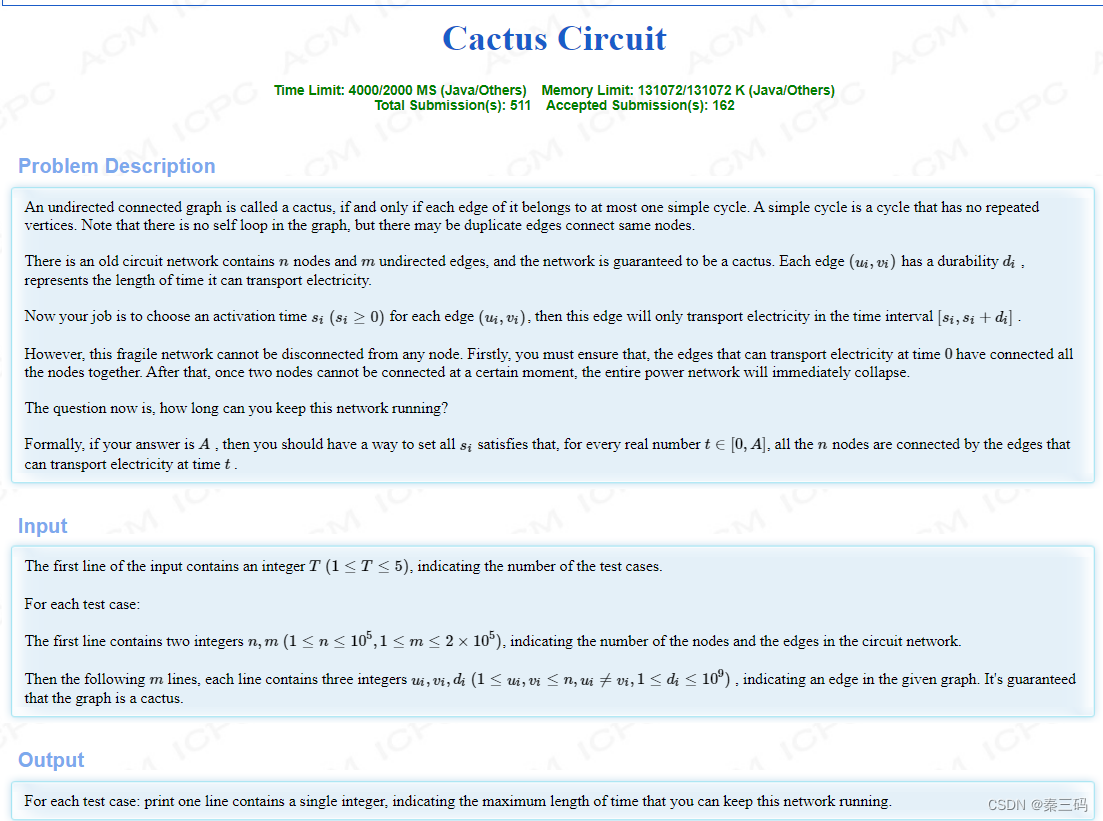
每条边都有一个开始工作的时间,同时也有一个工作持续的时间,不工作的时候,这条边不联通。问图整体联通的最长时间(可以任意安排每个边的起始工作时间)
图是仙人掌,也就是若干简单环的连接。对于环外的桥,必须从0时刻就开始工作,而一旦这样,就决定了要对所有桥边取min,作为答案的初始值。
对于每一个简单环内部,只需要让其len-1条边工作即可。也就是说,两条边的环,工作时间为w1+w2,三条边的w1<=w2<=w3时,为min(w1+w2,w3)意思就是,先让w1和其他除了w2之外的,工作,再让w2和其他除了w1的工作,如果w3>w1+w2,则完全可以,否则就为w3.于是题目转化为求出仙人掌图的每一个简单环的每一条边。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define N 100005
using namespace std;
struct edge
{
int u,v,w,id;
} o[N<<1];
vector<pair<int,int> > e[N];
int dfn[N],low[N],tot;
stack<edge> st;
int ans=2e9;
void tarjan(int x,int f)
{
dfn[x]=low[x]=++tot;
for (auto [p,id]:e[x]) if (!dfn[p])
{
st.push(o[id]);
tarjan(p,id);
low[x]=min(low[x],low[p]);
if (low[p]==dfn[x])
{
edge nw;
vector<int> g;
do
{
nw=st.top();
st.pop();
g.push_back(nw.w);
}
while (nw.id!=id);
sort(g.begin(),g.end());
if (g.size()==1) ans=min(ans,g[0]);
else if (g.size()==2) ans=min(ans,g[0]+g[1]);
else ans=min(ans,min(g[0]+g[1],g[2]));
}
}
else
{
if (dfn[x]>dfn[p] && id!=f) st.push(o[id]);
low[x]=min(low[x],dfn[p]);
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int T;
cin>>T;
while (T--)
{
int n,m,i;
cin>>n>>m;
tot=0;
ans=2e9;
for (i=1; i<=n; i++) e[i].clear(),dfn[i]=low[i]=0;
for (i=1; i<=m; i++)
{
cin>>o[i].u>>o[i].v>>o[i].w;
o[i].id=i;
e[o[i].u].push_back({o[i].v,i});
e[o[i].v].push_back({o[i].u,i});
}
tarjan(1,0);
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
}
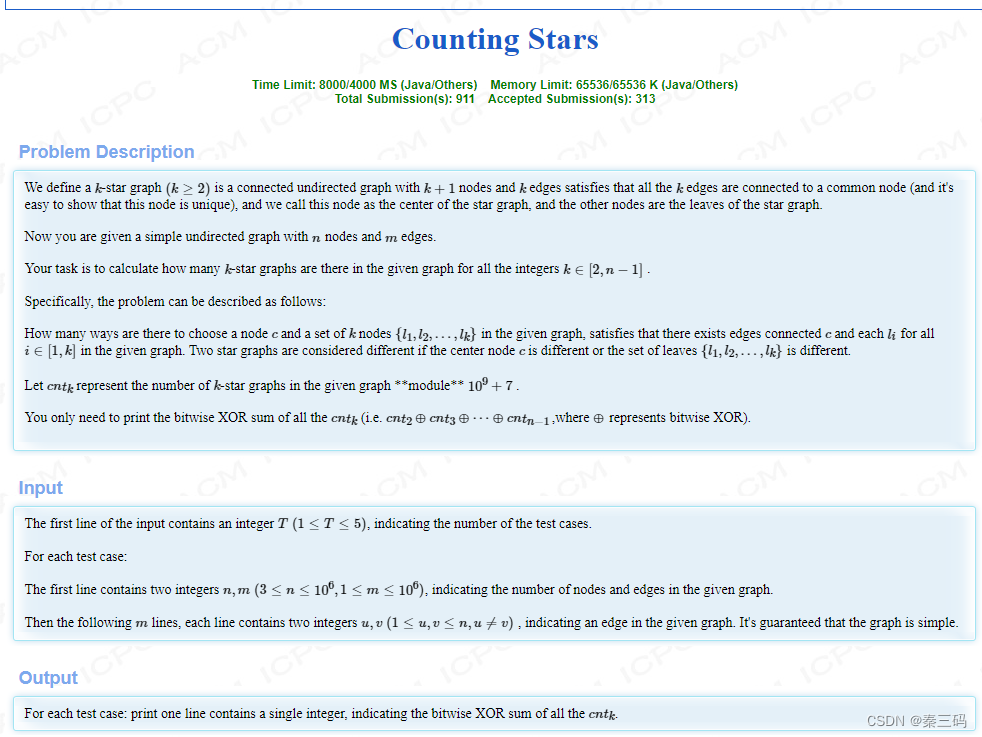
直接模拟,因为度数之和是1e6级别,故直接模拟,但卡常
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long int ll;
# define mod 1000000007
ll fac[1000000+10],inv[1000000+10];
ll qp(ll base, ll pow)
{
ll ans=1;
base%=mod;
while(pow)
{
if(pow&1)
ans=ans*base%mod;
base=base*base%mod;
pow>>=1;
}
return ans;
}
ll sum[1000000+10];
void init()
{
fac[0]=1;
for(int i=1; i<=1000000; i++)
{
fac[i]=fac[i-1]*(ll)i%mod;
}
inv[1000000]=qp(fac[1000000],mod-2);
for(int i=1000000-1; i>=0; i--)
{
inv[i]=inv[i+1]*(ll)(i+1)%mod;
}
}
ll getc(int x,int y)
{
if(x<y)
return 0;
return fac[x]*inv[y]%mod*inv[x-y]%mod;
}
int du[1000000+10];
ll ans[1000000+10];
unordered_map<int,int>mp;
inline int read()
{
int x = 0, f = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while (!isdigit(ch))
{
if (ch == '-')
f = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(ch))
{
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return x * f;
}
inline void write(ll x)
{
if (x < 0)
putchar('-'), x = -x;
if (x > 9)
write(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
init();
while(t--)
{
int n,m;
n=read();
m=read();
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
du[i]=0;
ans[i]=0;
}
mp.clear();
for(int i=1; i<=m; i++)
{
int x,y;
x=read();
y=read();
du[x]++;
du[y]++;
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
mp[du[i]]++;
}
for(auto it:mp)
{
for(int j=2; j<=it.first; j++)
{
ll temp=(ll)getc(it.first,j)*(ll)it.second%mod;
ans[j]+=temp;
ans[j]%=mod;
}
}
ll fuck=0;
for(int i=2; i<n; i++)
{
fuck^=ans[i];
}
cout<<fuck<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}