1.设计目的与要求
1.1设计目的
本设计的目的是使学生了解动态分区分配方式中使用的数据结构和分配算法,并进一步加深对动态分区存储管理方式及其实现过程的理解。
1.2设计要求
用C++语言分别实现采用首次适应算法和最佳适应算法的动态分区分配过程malloc()和回收过程free()。其中,空闲分区通过空闲分区链来管理;首次适应算法在进行内存分配时,系统优先使用空闲区低端的空间。回收时应注意相邻空闲分区的合并。
2.设计思想及系统平台
2.1设计思想
1)数据结构:采用链式存储结构存储空闲分区链。空闲区的结构体包含分区号、首地址、分区大小、分配标志;链表结点的结构体包含空闲区结构体、front和next指针。
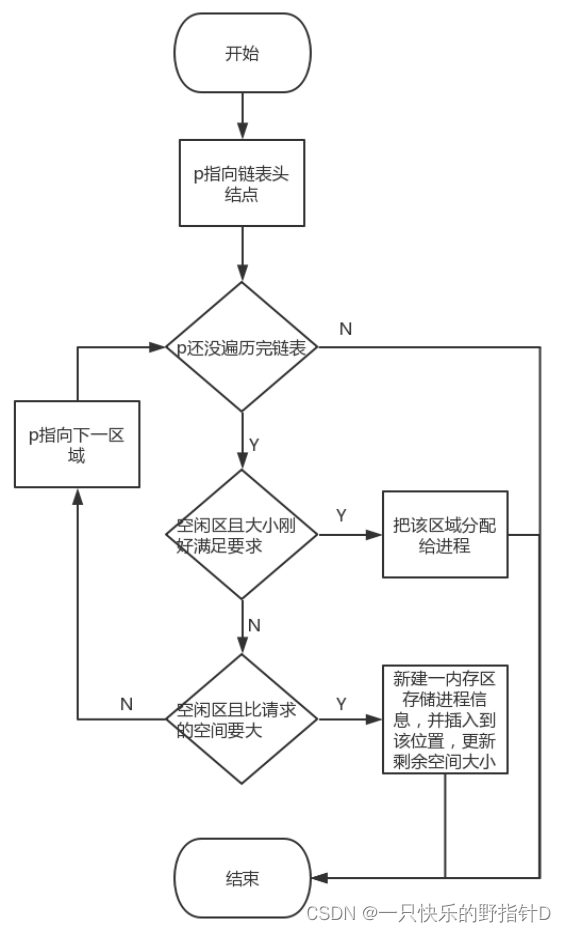
2)首次适应算法:用p指针遍历整个链表,找到第一个空间大于等于请求空间的空闲区,将此空间分配给进程。若空闲区大于请求空间,则将低端空间分给进程后更新空闲区的大小。
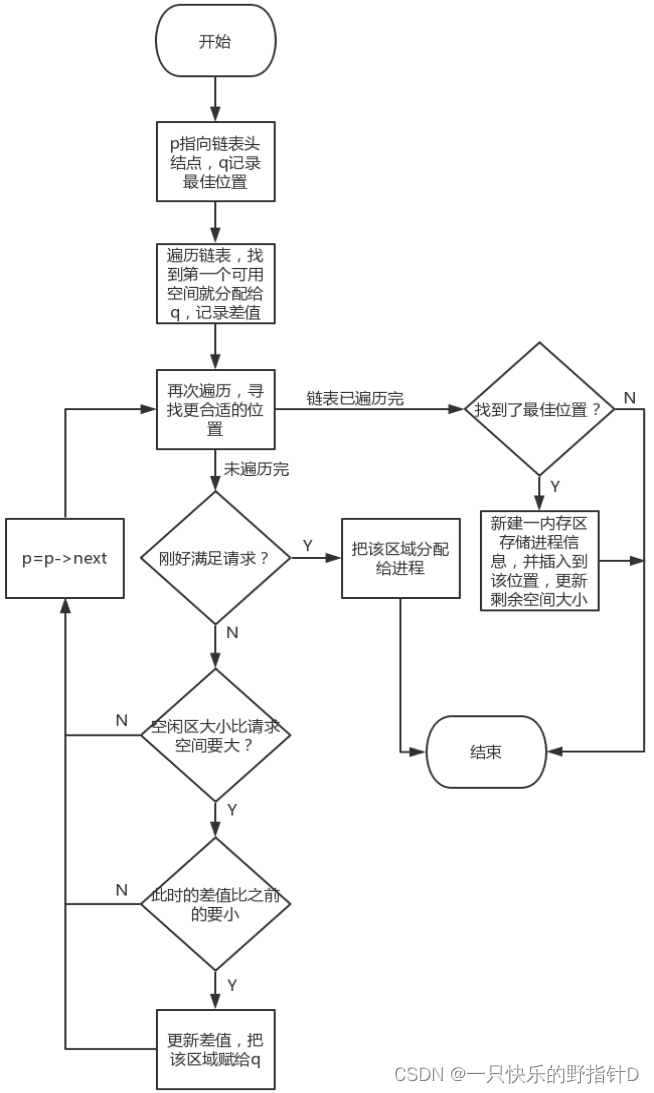
3)最佳适应算法:用p指针遍历整个链表,当找到第一个满足请求的空闲区时,记录此位置为最佳位置q,并将空闲区实际大小与请求大小的差值记为surplus,退出循环。然后再次遍历链表,每当有满足请求的空闲区时,若刚好满足请求,则将此位置分配给进程,算法结束;若大于,则比较二者的差值,如果此差值比原来的surplus要小,则更新surplus,同时修改q。遍历完链表后,如果存在最佳位置,则将该区域分配给进程,更新相关数据,算法结束。
4)内存回收算法:判断回收分区与前后区的关系。如果前区为空闲状态,则合并,起始地址更改为前区的首地址,大小为二者之和;如果后区为空闲,合并后起始地址不变,大小为二者之和;如果前后区都是空闲的,三区合并,起始地址为前区的首地址,大小为三者之和。
2.2系统平台及使用语言
CodeBlocks,C++
3.详细算法描述
1)首次适应算法
2)最佳适应算法
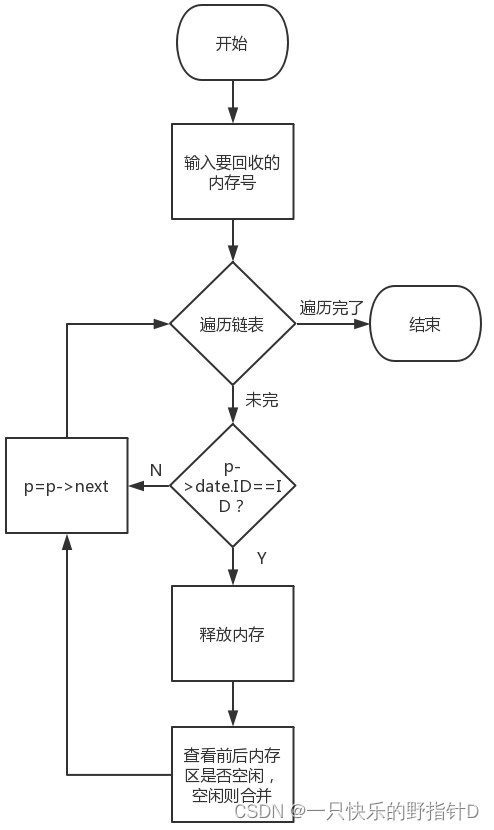
3)内存回收算法
4.源程序清单
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define FREE 0
#define BUSY 1
#define MAX_length 512
using namespace std;
//空闲区分表结构
struct freeArea
{
int flag;//分配标志
int size;
int ID;
int address;//首地址
};
struct node
{
struct freeArea date;
struct node *front;
struct node *next;
};
struct node* head;//链表头指针
struct node* rear;//尾指针
void init()
{
head=new struct node;
rear = new struct node;
head->front=NULL;
head->next=rear;
rear->front=head;
rear->next=NULL;
rear->date.address=0;
rear->date.flag=FREE;
rear->date.ID=FREE;
rear->date.size=MAX_length;
}
//首次适应算法
int first_fit(int ID,int size)
{
struct node* temp=(struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *p=head->next;
temp->date.ID=ID;
temp->date.size=size;
temp->date.flag=BUSY;
//遍历空闲区链表
while(p)
{
//空闲区且请求大小刚好满足
if (p->date.flag==FREE && p->date.size==size)
{
p->date.flag=BUSY;
p->date.ID=ID;
return 1;
}
if (p->date.flag==FREE && p->date.size>size)
{
//将temp插入到链表此位置上
temp->next=p;
temp->front=p->front;
temp->date.address=p->date.address;
p->front->next=temp;
p->front=temp;
p->date.address=temp->date.address+temp->date.size;
p->date.size-=size;
return 1;
}
p=p->next;
}
return 0;
}
//最佳适应算法
int best_fit(int ID,int size)
{
int surplus;//记录可用内存与需求内存的差值
struct node* temp=(struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *p=head->next;
temp->date.ID=ID;
temp->date.size=size;
temp->date.flag=BUSY;
struct node *q=NULL;//记录最佳位置
//找到第一个可用空间就分配给q
while(p)
{
if (p->date.flag==FREE&&p->date.size>=size)
{
q=p;
surplus=p->date.size-size;
break;
}
p=p->next;
}
//继续遍历,找到更加合适的位置
while(p)
{
//刚好满足要求
if (p->date.flag==FREE&&p->date.size==size)
{
p->date.flag=BUSY;
p->date.ID=ID;
return 1;
}
if (p->date.flag==FREE&&p->date.size>size)
{
if (surplus>p->date.size-size)
{
surplus=p->date.size-size;
q=p;
}
}
p=p->next;
}
//找到了最佳位置
if (q!=NULL)
{
temp->next=q;
temp->front=q->front;
temp->date.address=q->date.address;
q->front->next=temp;
q->front=temp;
q->date.size=surplus;
q->date.address+=size;
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
//实现内存分配
int alloc(int choose)
{
char ch;
do{
int ID,size;
cout<<"作业号:";
cin>>ID;
cout<<"所需内存大小:";
cin>>size;
while (ID<=0 || size<=0)
{
cout<<"ERROR,请输入正确的ID和请求大小"<<endl;
cout<<"作业号:";
cin>>ID;
cout<<"所需内存大小:";
cin>>size;
}
switch(choose)
{
case 1:
if(first_fit(ID,size))
{
cout<<"分配成功!"<<endl;
}
else
cout<<"分配失败!"<<endl;
break;
case 2:
if (best_fit(ID,size))
{
cout<<"分配成功!"<<endl;
}
else
cout<<"分配失败!"<<endl;
break;
}
cout<<"还要继续申请内存吗?Y/N"<<endl;
cin>>ch;
}while(ch!='N');
return 1;
}
//内存回收
int free()
{
int ID;
cout<<"请输入需要回收的ID号:"<<endl;
cin>>ID;
struct node *p=head->next;
while(p)
{
//找到要回收的ID区域
if (p->date.ID==ID)
{
//释放p指向的内存
p->date.flag=FREE;
p->date.ID=FREE;
//前空,合并
if (p->front->date.flag==FREE&&p->next->date.flag!=FREE)
{
p->front->date.size+=p->date.size;
p->front->next=p->next;
p->next->front=p->front;
}
//后空
if (p->front->date.flag!=FREE&&p->next->date.flag==FREE)
{
p->date.size+=p->next->date.size;
if(p->next->next)
{
p->next->next->front=p;
p->next = p->next->next;
}
else
p->next=p->next->next;
}
//前后都空
if(p->front->date.flag==FREE&&p->next->date.flag==FREE)
{
p->front->date.size+=p->date.size+p->next->date.size;
if(p->next->next)
{
p->next->next->front=p->front;
p->front->next=p->next->next;
}
else
p->front->next=p->next->next;
}
break;
}
p=p->next;
}
cout<<"回收成功!"<<endl;
return 1;
}
void display()
{
cout<<"--------内存分配情况-------"<<endl;
struct node *p=head->next;
while(p)
{
cout<<"分区号:";
if (p->date.ID==FREE)
cout<<"FREE"<<endl;
else
cout<<p->date.ID<<endl;
cout<<"起始地址:"<<p->date.address<<endl;
cout<<"内存大小:"<<p->date.size<<endl;
cout<<"分区状态:";
if (p->date.flag==FREE)
cout<<"空闲"<<endl;
else
cout<<"已分配"<<endl;
cout<<"---------------------------"<<endl<<endl;
p=p->next;
}
}
void menu()
{
cout<<"------请输入要进行的操作------"<<endl;
cout<<" 1、首次适应算法 "<<endl;
cout<<" 2、最佳适应算法 "<<endl;
cout<<" 3、内存回收 "<<endl;
cout<<" 4、显示内存状况 "<<endl;
cout<<" 0、退出 "<<endl;
cout<<"------------------------------"<<endl;
}
int main()
{
int choose;
init();
do
{
menu();
cin>>choose;
switch(choose)
{
case 1:
alloc(choose);
break;
case 2:
alloc(choose);
break;
case 3:
free();
break;
case 4:
display();
break;
case 0:
break;
default:
cout<<"输入错误,请重新输入!"<<endl;
break;
}
}while(choose!=0);
return 0;
}实验报告:https://download.csdn.net/download/sjhdxpz/88212615

![[HDLBits] Exams/m2014 q3](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/5c948c4752b54ef4984baf968681d1fd.png)
![[HDLBits] Exams/2012 q1g](https://hdlbits.01xz.net/mw/thumb.php?f=Exams_2012q1g.png&width=195)