目录
一、list 容器的基本介绍
二、list 容器的成员函数
2.1 - 迭代器
2.2 - 修改操作
三、list 的模拟实现
3.1 - list.h
3.2 - 详解 list 容器的迭代器
3.2 - test.cpp
一、list 容器的基本介绍
list 容器以类模板 list<T>(T 为存储元素的类型)的形式定义在 <list> 头文件中,并位于 std 命名空间中。
template < class T, class Alloc = allocator<T> > class list; list 是序列容器,允许在序列内的任意位置高效地插入和删除元素(时间复杂度是 O(1) 常数阶),其迭代器类型为双向迭代器(bidirectional iterator)。
list 容器的底层是以双向链表的形式实现的。
list 容器与 forward_list 容器非常相似,最主要的区别在于 forward_list 容器的底层是以单链表的形式实现的,其迭代器类型为前向迭代器(forward iterator)。
与其他标准序列容器(array、vector 和 deque)相比,list 容器在序列内已经获得迭代器的任意位置进行插入、删除元素时通常表现得更好。
与其他序列容器相比,list 容器和 forward_list 容器的最大缺点是不支持任意位置的随机访问,例如:要访问 list 中的第 6 个元素,必须从已知位置(比如头部或尾部)迭代到该位置,这需要线性阶的时间复杂度的开销。
二、list 容器的成员函数
2.1 - 迭代器
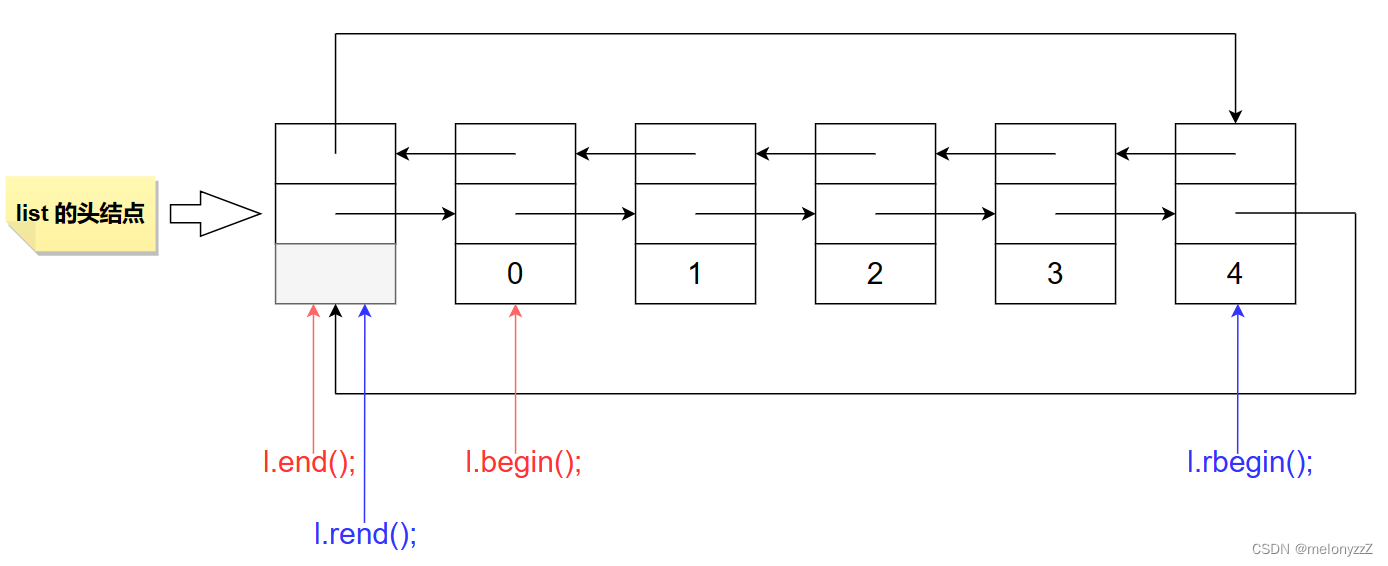
begin:
iterator begin();
const_iterator begin() const;end:
iterator end();
const_iterator end() const;rbegin:
reverse_iterator rbegin();
const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const;rend:
reverse_iterator rend();
const_reverse_iterator rend() const;示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> l;
l.push_back(0);
l.push_back(1);
l.push_back(2);
l.push_back(3);
l.push_back(4);
for (list<int>::iterator it = l.begin(); it != l.end(); ++it)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
// 0 1 2 3 4
cout << endl;
for (list<int>::reverse_iterator rit = l.rbegin(); rit != l.rend(); ++rit)
{
cout << *rit << " ";
}
// 4 3 2 1 0
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
2.2 - 修改操作
push_front:
void push_front(const value_type& val);注意:value_type 等价于 T。
pop_front:
void pop_front();push_back:
void push_back(const value_type& val);pop_back:
void pop_back();insert:
// C++ 98
single element (1) iterator insert(iterator position, const value_type& val);
fill (2) void insert(iterator position, size_type n, const value_type& val);
range (3) template <class InputIterator>
void insert(iterator position, InputIterator first, InputIterator last);相较于 vector,执行 list 的 insert 操作不会产生迭代器失效的问题。
示例一:
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> l;
l.push_back(0);
l.push_back(1);
l.push_back(2);
l.push_back(3);
l.push_back(4);
// 要求:在第三个元素前面插入元素 100
// l.insert(l.begin() + 2, 100); // error
// 因为 list 对应的迭代器类型为双向迭代器,所以不支持加法操作,即没有重载该运算符
// 解决方案:
list<int>::iterator it = l.begin();
for (size_t i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
{
++it;
}
l.insert(it, 100);
for (auto e : l)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
// 0 1 100 2 3 4
cout << endl;
return 0;
}erase:
iterator erase(iterator position);
iterator erase(iterator first, iterator last);因为节点被删除后,空间释放了,所以执行完 list 的 erase 操作,迭代器就失效了,而解决方案依然是通过返回值对迭代器进行重新赋值。
示例二:
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> l;
l.push_back(0);
l.push_back(1);
l.push_back(2);
l.push_back(3);
l.push_back(4);
// 删除 list 中所有值为偶数的元素
list<int>::iterator it = l.begin();
while (it != l.end())
{
if (*it % 2 == 0)
it = l.erase(it); // 直接写 l.erase(it); 会报错
else
++it;
}
for (auto e : l)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
// 1 3
cout << endl;
return 0;
}三、list 的模拟实现
3.1 - list.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <assert.h>
namespace yzz
{
template<class T>
struct __list_node
{
__list_node<T>* _prev;
__list_node<T>* _next;
T _data;
__list_node(const T& val = T())
: _prev(0), _next(0), _data(val)
{ }
};
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __list_iterator
{
typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;
typedef __list_node<T> list_node;
list_node* _pnode; // 节点指针
__list_iterator(list_node* p = 0)
: _pnode(p)
{ }
self& operator++()
{
_pnode = _pnode->_next;
return *this;
}
self operator++(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_pnode = _pnode->_next;
return tmp;
}
self& operator--()
{
_pnode = _pnode->_prev;
return *this;
}
self operator--(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_pnode = _pnode->_prev;
return tmp;
}
Ref operator*() const
{
return _pnode->_data;
}
Ptr operator->() const
{
return &_pnode->_data;
}
bool operator!=(const self& it) const
{
return _pnode != it._pnode;
}
bool operator==(const self& it) const
{
return _pnode == it._pnode;
}
};
template<class T>
class list
{
private:
typedef __list_node<T> list_node;
void empty_initialize()
{
_phead = new list_node;
_phead->_prev = _phead;
_phead->_next = _phead;
}
public:
/*-------- 构造函数和析构函数 --------*/
list()
{
empty_initialize();
}
list(const list<T>& l) // 实现深拷贝
{
empty_initialize();
for (auto& e : l)
{
push_back(e);
}
}
~list()
{
clear();
delete _phead;
_phead = 0;
}
/*-------- 赋值运算符重载 --------*/
// 利用上面写好的拷贝构造函数实现深拷贝
void swap(list<T>& l)
{
std::swap(_phead, l._phead);
}
list<T>& operator=(list<T> tmp)
{
swap(tmp);
return *this;
}
/*-------- 迭代器 --------*/
typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _phead->_next;
// 等价于:return iterator(_phead);
// 返回的过程中发生了隐式类型转换
}
iterator end()
{
return _phead;
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _phead->_next;
// 等价于:return const_iterator(_phead->_next);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _phead;
}
/*-------- 容量操作 --------*/
size_t size() const
{
size_t sz = 0;
list_node* cur = _phead->_next;
while (cur != _phead)
{
++sz;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return sz;
}
bool empty() const
{
return _phead->_next == _phead;
}
/*-------- 修改操作 --------*/
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val)
{
list_node* newnode = new list_node(val);
newnode->_prev = pos._pnode->_prev;
newnode->_next = pos._pnode;
pos._pnode->_prev->_next = newnode;
pos._pnode->_prev = newnode;
return newnode;
}
void push_back(const T& val)
{
// 方法一:
/*list_node* newnode = new list_node(val);
newnode->_prev = _phead->_prev;
newnode->_next = _phead;
_phead->_prev->_next = newnode;
_phead->_prev = newnode;*/
// 方法二(直接复用):
insert(end(), val);
}
void push_front(const T& val)
{
// 方法一:
/*list_node* newnode = new list_node(val);
newnode->_prev = _phead;
newnode->_next = _phead->_next;
_phead->_next->_prev = newnode;
_phead->_next = newnode;*/
// 方法二(直接复用):
insert(begin(), val);
}
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != end()); // 前提是 list 非空
list_node* prev_pnode = pos._pnode->_prev;
list_node* next_pnode = pos._pnode->_next;
prev_pnode->_next = next_pnode;
next_pnode->_prev = prev_pnode;
delete pos._pnode;
return iterator(next_pnode);
}
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
void clear()
{
list_node* cur = _phead->_next;
while (cur != _phead)
{
list_node* tmp = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
delete tmp;
}
_phead->_prev = _phead->_next = _phead;
}
private:
list_node* _phead; // 头指针
};
}3.2 - 详解 list 容器的迭代器
我们可以通过循序渐进的方式来了解 list 容器的迭代器:
-
首先,不能使用原生态指针直接作为 list 容器的正向迭代器,即:
typedef list_node* iterator;否则当正向迭代器进行
++/--操作时,无法让它指向下一个或上一个节点,并且进行解引用*操作时,无法直接获得节点的值,所以需要对原生态指针进行封装,然后对这些操作符进行重载,即:typedef __list_iterator<T> iterator; -
其次,不能按以下方式直接定义 list 容器的常量正向迭代器,即:
typedef const __list_iterator<T> const_iterator;否则常量正向迭代器就无法进行
++/--操作,因为 const 类对象只能去调用 const 成员函数,并且 operator* 的返回值类型为 T&,即仍然可以在外部修改 list 容器。可以重新定义一个常量正向迭代器
__list_const_iterator,但需要修改的地方仅仅是 operatr* 的返回值,即将其修改为 const T&,显然这样的解决方案会造成代码的冗余,所以在__list_iterator类模板中增加一个类型参数 Ref,将 operator* 的返回值修改为 Ref,即:typedef __list_iterator<T, T&> iterator; typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&> const_iterator; -
最后,在重载
->操作符时,对于正向迭代器,返回值类型应该是 T*,对于常量正向迭代器,返回值类型应该是 const T*,所以再增加一个类型参数 Ptr,将 operator-> 的返回值类型修改为 Ptr,即:typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator; typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
3.2 - test.cpp
#include "list.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void Print1(const yzz::list<int>& l)
{
yzz::list<int>::const_iterator cit = l.begin();
while (cit != l.end())
{
cout << *cit << " ";
++cit;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_list1()
{
yzz::list<int> l1;
l1.push_back(1);
l1.push_back(2);
l1.push_back(3);
l1.push_back(4);
cout << l1.size() << endl; // 4
yzz::list<int> l2(l1);
for (yzz::list<int>::iterator it = l2.begin(); it != l2.end(); ++it)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
// 1 2 3 4
cout << endl;
l1.push_front(10);
l1.push_front(20);
l1.push_front(30);
l1.push_front(40);
cout << l1.size() << endl; // 8
yzz::list<int> l3;
l3 = l1;
for (auto& e : l3)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
// 40 30 20 10 1 2 3 4
cout << endl;
l1.pop_back();
l1.pop_back();
l1.pop_front();
l1.pop_front();
cout << l1.size() << endl; // 4
Print1(l1);
// 20 10 1 2
l1.clear();
cout << l1.size() << endl; // 0
cout << l1.empty() << endl; // 1
}
struct Point
{
int _x;
int _y;
Point(int x = 0, int y = 0)
: _x(x), _y(y)
{ }
};
void Print2(const yzz::list<Point>& l)
{
yzz::list<Point>::const_iterator cit = l.begin();
while (cit != l.end())
{
// 方法一:
// cout << "(" << (*cit)._x << ", " << (*cit)._y << ")" << " ";
// 方法二:
cout << "(" << cit->_x << ", " << cit->_y << ")" << " ";
// 注意:operator-> 是单参数,所以本应该是 cit->->_i 和 cit->->_j,
// 但为了可读性,编译器做了优化,即省去一个 ->
++cit;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_list2()
{
yzz::list<Point> l;
l.push_back(Point(1, 1));
l.push_back(Point(2, 2));
l.push_back(Point(3, 3));
l.push_back(Point(4, 4));
Print2(l);
// (1, 1) (2, 2) (3, 3) (4, 4)
}
int main()
{
// test_list1();
test_list2();
return 0;
}