目录
putIfAbsent
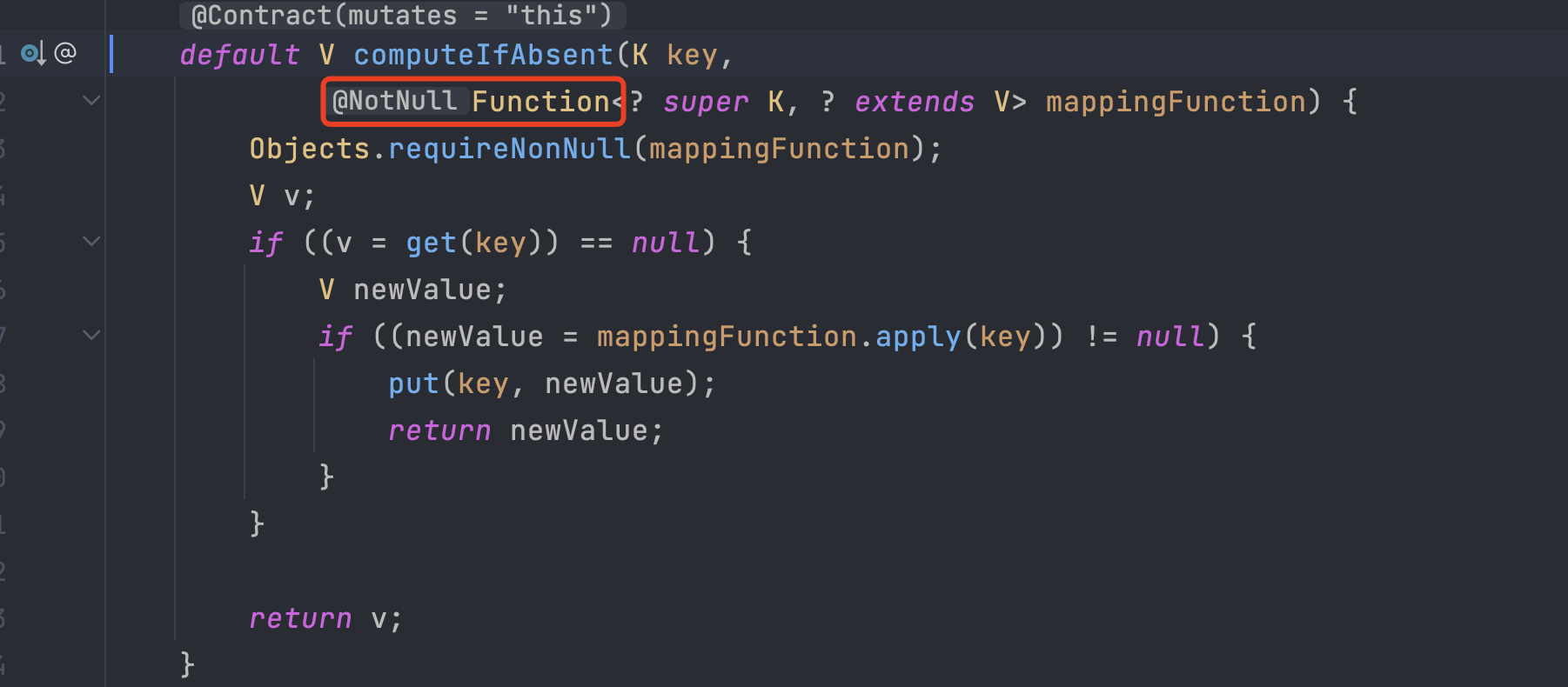
computeIfAbsent
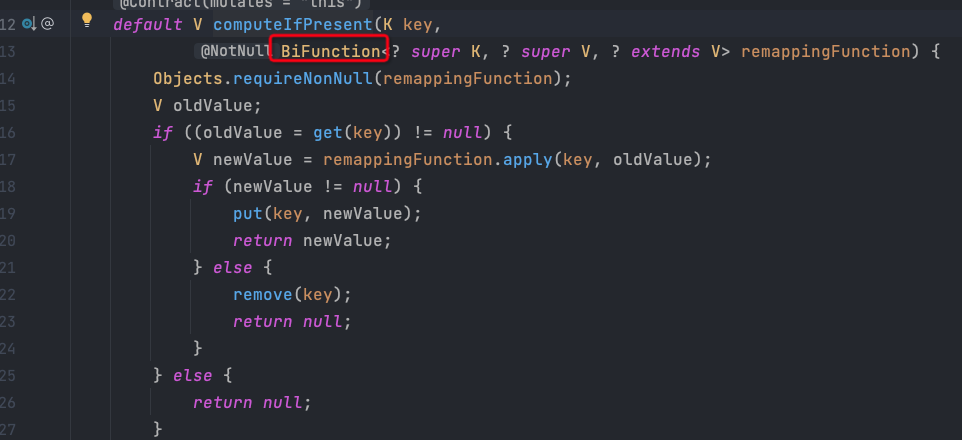
computeIfPresent
compute
merge
putIfAbsent
解释:【不存在则添加】,如果map中没有该key,则直接添加;如果map中已经存在该key,则value保持不变
default V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {
// 根据key获取value
V v = get(key);
// 如果value == null 则将新的value赋值给key 然后返回新的value
// 否则返回历史value
if (v == null) {
v = put(key, value);
}
return v;
} Map<String,Integer> map1 = new HashMap<>();
map1.put("a",1);
map1.putIfAbsent("a",2);
map1.forEach((k,v)->{
System.out.println(k+"->"+v);
});
输出结果为1
Map<String,Integer> map1 = new HashMap<>();
//map1.put("a",1);
map1.putIfAbsent("a",2);
map1.forEach((k,v)->{
System.out.println(k+"->"+v);
});
输出结果为2computeIfAbsent
解释:【不存在则计算】,如果map中没有该key,则会计算出一个符合value类型的值赋给value;如果map中已经存在该key,则value保持不变;由于它是Funcation函数接口,因此只能处理一个参数
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("a",1);
map.computeIfAbsent("c",(k)->2);
map.forEach((k,v)->{
System.out.println(k+"-->"+v);
});
}
输出结果为:
a-->1
c-->2computeIfPresent
解释:【存在则计算】,如果map中没有该key,则该键值对不会添加到map中;如果map中已经存在该key,则会把计算出的值覆盖原来的value;由于它是BiFuncation函数接口,因此能处理两个参数
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("a", 1);
map.computeIfPresent("a", (oldK, oldV) -> {
return oldV+1;
});
map.forEach((k, v) -> {
System.out.println(k + "-->" + v);
});
}
输出结果为:
a-->2
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("a", 1);
map.computeIfPresent("b", (oldK, oldV) -> {
return oldV+1;
});
map.forEach((k, v) -> {
System.out.println(k + "-->" + v);
});
}
输出结果为:
a-->1compute
解释:【计算】,如果map中没有该key,则会计算出一个符合value类型的值赋给value;如果map中已经存在该key,则会把计算出的值覆盖原来的value.可以当成是computeIfAbsent与computeIfPresent的结合体;由于它是BiFuncation函数接口,因此能处理两个参数
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 存在一个需求 如果map中存在key则将原来key的值进行+10
// 如果map中不存在key 则将此值赋值为1
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("a", 1);
if (map.containsKey("b")) {
map.put("b", map.get("b") + 10);
} else {
map.put("b", 1);
}
map.forEach((k, v) -> {
System.out.println(k + "-->" + v);
});
}
输出结果:
a-->1
b-->1
// 使用computeIfPresent + computeIfAbsent
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("a", 1);
map.computeIfPresent("b",(k,v)->v+10);
map.computeIfAbsent("b",(k)->1);
// if (map.containsKey("b")) {
// map.put("b", map.get("b") + 10);
// } else {
// map.put("b", 1);
// }
map.forEach((k, v) -> {
System.out.println(k + "-->" + v);
});
}
输出结果:
a-->1
b-->1
// 使用compute优化
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("a", 1);
// if (map.containsKey("b")) {
// map.put("b", map.get("b") + 10);
// } else {
// map.put("b", 1);
// }
map.compute("b", (oldK, oldV) -> oldV == null ? 1 : oldV + 10);
map.forEach((k, v) -> {
System.out.println(k + "-->" + v);
});
}
输出结果:
a-->1
b-->1merge
merge(key, value, remappingFunction)
解释:【合并】如果 key 对应的 value 不存在,则返回该 value 值,如果存在,则返回通过 remappingFunction 重新计算后的值
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("a", 1);
// if (map.containsKey("b")) {
// map.put("b", map.get("b") + 10);
// } else {
// map.put("b", 1);
// }
map.merge("b",1, Integer::sum);
map.forEach((k, v) -> {
System.out.println(k + "-->" + v);
});
}
输出结果:
a-->1
b-->1