1.线程池简介
线程池,顾名思义,就是一个“池子”里面放有多个线程。为什么要使用线程池呢?当我们编写的代码需要并发异步处理很多任务时候,一般的处理办法是一个任务开启一个线程去处理,处理结束后释放线程。可是这样频繁的申请释放线程,系统的开销很大,为了解决这个问题,线程池就产生了。线程池实现原理是事先申请一定数量的线程存放在程序中,当外部有任务需要线程处理时,把这个任务放到这个“池子”里面,“池子”里面空闲的线程就去取这个任务进行处理,这样既能实现多线程并发处理任务,又能减少系统频繁创建删除线程的开销,这种技术叫做池化技术,相应的池化技术还有内存池、连接池等。
为了更形象理解线程池,举一个例子:线程池就像鸡圈里面鸡,每一个鸡比作一个线程,你手里有一把玉米,每一个颗玉米比作一个任务,鸡吃玉米比作处理任务。当你把一把玉米撒入鸡圈,一群鸡就围过来抢玉米,但是一次一只鸡只能吃一颗玉米,吃完一颗继续吃下一颗,直到鸡圈里面的玉米吃完才停止。线程池处理任务也是一样的,当任务链表上有任务时,通过条件变量通知线程池里面的线程,一群线程就围过来了,但是一个线程一次只能取一个任务进行处理,处理完又去取下一个任务,池子里面每一个线程都是这样处理,直到链表上面的任务全部处理完了,池子中的线程又空闲起来了。
2.线程池-设计实现
实现思路:通过向系统申请多个线程,创建一个任务链表,链表上面存放待处理的任务,当有新的任务加入时候,通过条件变量通知池子里面的线程从链表上面取任务,然后处理任务,一直这样循环下去。

首先定义结构体,定义如下:
/**
* 定义的回调函数
*/
typedef void (*task_func_t)(void *args);
/**
* 定义的任务节点结构体
*/
typedef struct task_t
{
void *args; //任务参数
task_func_t func; //任务函数指针
struct list_head node; //链表节点
}task_t;
/**
* 线程池信息
*/
typedef struct threadpool_t
{
struct list_head hlist; //任务链表
int thread_num; //线程池数量
int max_ts_num; //最大任务数量
volatile int curr_ts_num; //当前线程池存在的任务数
volatile int is_exit; //是否退出线程池标志
pthread_mutex_t mutex; //互斥锁
pthread_cond_t cond; //条件变量
pthread_t *ths; //线程id数组
}threadpool_t;这是线程池实现的程序:
/**
* @brief:线程处理任务函数
* @args: 传入的参数
* @return: NULL
*/
static void* _process_task_thread(void *args)
{
threadpool_t* tp = (threadpool_t*)args;
struct list_head *pos = NULL;
task_t *task=NULL;
if(!args) return NULL;
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&tp->mutex);
while(list_empty(&tp->hlist) && !tp->is_exit){
pthread_cond_wait(&tp->cond, &tp->mutex);
}
if(tp->is_exit){ //判断释放退出线程池
pthread_mutex_unlock(&tp->mutex);
break;
}
pos = tp->hlist.next; //从任务链表取出头节点
list_del(pos); //从链表中删除节点
--tp->curr_ts_num; //更新任务数
pthread_mutex_unlock(&tp->mutex);
task = list_entry(pos, task_t, node); //从链表节点推出任务节点
task->func(task->args); //执行任务
free(task); //释放任务内存
}
return NULL;
}
/**
* @brief:创建一个线程池
* @thread_nums: 线程数量
* @max_ts_num:线程池中最大的任务数量
* @return: 线程池句柄
*/
threadpool_t* create_threadpool(int thread_nums, int max_ts_num)
{
if(thread_nums <= 0) return NULL;
threadpool_t* tp = (threadpool_t*)malloc(sizeof(threadpool_t));
memset(tp, 0, sizeof(threadpool_t));
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&tp->hlist);
tp->is_exit = 0;
tp->curr_ts_num = 0;
tp->thread_num = thread_nums;
tp->max_ts_num = max_ts_num;
tp->ths = (pthread_t*)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t)*thread_nums);
pthread_mutex_init(&tp->mutex, NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&tp->cond, NULL);
for(int i=0; i<tp->thread_num; ++i){
pthread_create(&(tp->ths[i]), NULL, _process_task_thread, tp);
}
return tp;
}
/**
* @brief:往线程池中添加任务
* @tp: 线程池句柄
* @func:任务处理函数指针
* @args:传入任务参数
* @priority: 优先级 1:优先处理 其他:添加到尾部
* @return: 返回状态 0:ok
*/
int add_task_threadpool(threadpool_t* tp, task_func_t func, void *args, int priority)
{
if(!tp) return -1;
if(!func) return -2;
if(tp->curr_ts_num > tp->max_ts_num) return -3;
task_t *task = (task_t*)malloc(sizeof(task_t)); //申请任务节点内存
task->func = func; //给函数指针赋值
task->args = args; //保持参数指针
pthread_mutex_lock(&tp->mutex);
if(priority==1) //高优先级,添加到头部
list_add(&task->node, &tp->hlist);
else //添加到尾部
list_add_tail(&task->node, &tp->hlist);
++tp->curr_ts_num; //更新任务数
pthread_mutex_unlock(&tp->mutex);
pthread_cond_signal(&tp->cond); //通知线程取任务
return 0;
}
/**
* @brief:获取线程池中当前存在的任务数量
* @tp: 线程池句柄
* @return: 当前任务数量
*/
int get_ts_num_threadpool(threadpool_t* tp)
{
return tp ? tp->curr_ts_num : -1;
}
/**
* @brief:释放线程池资源
* @tp:线程池句柄
* @return: 0:ok
*/
int destory_threadpool(threadpool_t* tp)
{
if(!tp) return -1;
while(!list_empty(&tp->hlist)){ //等待线程池执行完链表中的任务
continue;
}
tp->is_exit = 1; //更新标志,退出线程池
pthread_cond_broadcast(&tp->cond);//通知所有线程函数
for(int i=0; i<tp->thread_num; ++i){//等待所有线程函数结束
pthread_join(tp->ths[i], NULL);
}
pthread_mutex_destroy(&tp->mutex); //释放资源
pthread_cond_destroy(&tp->cond);
free(tp->ths);
free(tp);
tp = NULL;
return 0;
}相关视频推荐
手把手实现线程池(120行),实现异步操作,解决项目性能问题
手撕高性能线程池,准备好linux开发环境
线程池在3个开源框架的应用(redis、skynet、workflow)
免费学习地址:c/c++ linux服务器开发/后台架构师
需要C/C++ Linux服务器架构师学习资料加qun812855908获取(资料包括C/C++,Linux,golang技术,Nginx,ZeroMQ,MySQL,Redis,fastdfs,MongoDB,ZK,流媒体,CDN,P2P,K8S,Docker,TCP/IP,协程,DPDK,ffmpeg等),免费分享

3.线程池组-设计实现
有了线程池处理并发任务,为什么还要线程池组呢?原因在于线程池中,所有的线程都使用一个互斥锁阻塞,当你创建的线程池中线程的个数比较多的情况下,存在很多线程对同一个线程抢占,这样会影响线程池取任务处理的效率。因此由"小颗粒"(即每一个线程池中线程个数少)的线程池组成一个"线程池组"这样就能减轻多个线程对同一个锁抢占造成效率低的问题。
设计实现:将多个线程池封装组合到一起,当外部有任务需要处理时,找到线程池组中线程池任务最少的池子,把任务给放进去。

定义一个线程池组管理结构体:
typedef struct manange_thpool_t
{
int thpool_nums; //线程池个数
threadpool_t *thpools[MAX_THREADPOOL_NUMS]; //线程池结构体
}manange_thpool_t;代码实现:
/**
* @brief:创建线程池组管理句柄
* @tp_nums:线程池组中线程池个数
* @thread_num:单个线程池中线程个数
* @max_ts_n:单个线程池中最大的任务数量
*/
manange_thpool_t* create_group_threadpool(int tp_nums, int thread_num, int max_ts_n)
{
manange_thpool_t* mtp = (manange_thpool_t*)malloc(sizeof(manange_thpool_t));
if(!mtp) return NULL;
memset(mtp, 0, sizeof(manange_thpool_t));
mtp->thpool_nums = tp_nums;
for(int i=0; i<tp_nums; ++i){
mtp->thpools[i] = create_threadpool(thread_num, max_ts_n);
}
return mtp;
}
/**
* @brief:往线程池组中添加任务
* @mtp:线程池组句柄
* @func:任务函数
* @args:任务函数的参数
* @priority: 优先级 1:优先处理 其他:依次处理
* @return: 0:ok 其他:err
*/
int add_task_group_threadpool(manange_thpool_t* mtp, task_func_t func, void *args, int priority)\
{
int ts_num= INT_MAX;
threadpool_t *tp=NULL;
int index=0;
for(register int i=0; i<mtp->thpool_nums; ++i){
if(mtp->thpools[i]->curr_ts_num < ts_num){
ts_num = mtp->thpools[i]->curr_ts_num;
tp = mtp->thpools[i];
index=i;
}
}
if(!tp){
tp = mtp->thpools[0];
}
return add_task_threadpool(tp, func, args, priority);
}
/**
* @brief:释放线程池组函数
* @tp: 线程池组句柄
* @return:none
*/
void destory_group_threadpool(manange_thpool_t* tp)
{
if(!tp) return;
for(int i=0; i<tp->thpool_nums; ++i){
if(tp->thpools[i]) destory_threadpool(tp->thpools[i]);
}
}4.测试
测试程序如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "list.h"
#include "threadpool.h"
#include "manange_threadpool.h"
//任务传递的参数
typedef struct info_t
{
int times;
char buffer[32];
}info_t;
void task1(void *args)
{
info_t *info = (info_t*)args;
printf("handle task1 pid=%lld times=%d buffer=%s\n", pthread_self(), info->times, info->buffer);
free(args);
}
void task2(void *args)
{
info_t *info = (info_t*)args;
printf("handle task2 pid=%lld times=%d buffer=%s\n", pthread_self(), info->times, info->buffer);
free(args);
}
void task3(void *args)
{
info_t *info = (info_t*)args;
printf("handle task3 pid=%lld times=%d buffer=%s\n", pthread_self(), info->times, info->buffer);
free(args);
}
//------------split-----------------
void test_threadpool(void)
{
threadpool_t* tp = create_threadpool(4, 128);
info_t *info;
for(int t=0; t<10; ++t){
for(int i=0; i<32; ++i){
info = (info_t *)malloc(sizeof(info_t));
info->times=i;
sprintf(info->buffer, "Test ThreadPool task1 info...");
add_task_threadpool(tp, task1, info, 1); //往线程池组添加任务
info = (info_t *)malloc(sizeof(info_t));
info->times=i;
sprintf(info->buffer, "Test ThreadPool task2 info...");
add_task_threadpool(tp, task2, info, 0);
info = (info_t *)malloc(sizeof(info_t));
info->times=i;
sprintf(info->buffer, "Test ThreadPool task3 info...");
add_task_threadpool(tp, task3, info, 0);
}
sleep(1);
}
destory_threadpool(tp);
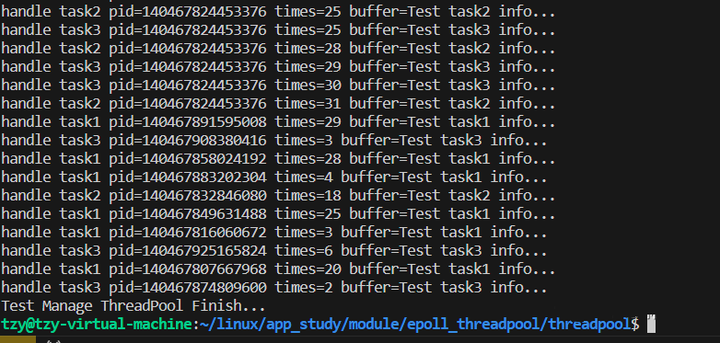
printf("Test ThreadPool Finish...\n");
}
void test_manange_threadpool(void)
{
//创建线程池组句柄,有4个线程池,每个线程池使用4线程,每个线程池最大的任务数是32
manange_thpool_t* mtp = create_group_threadpool(4, 4, 128);
info_t *info;
for(int t=0; t<10; ++t){
for(int i=0; i<32; ++i){
info = (info_t *)malloc(sizeof(info_t));
info->times=i;
sprintf(info->buffer, "Test task1 info...");
add_task_group_threadpool(mtp, task1, info, 1); //往线程池组添加任务
info = (info_t *)malloc(sizeof(info_t));
info->times=i;
sprintf(info->buffer, "Test task2 info...");
add_task_group_threadpool(mtp, task2, info, 0);
info = (info_t *)malloc(sizeof(info_t));
info->times=i;
sprintf(info->buffer, "Test task3 info...");
add_task_group_threadpool(mtp, task3, info, 0);
}
sleep(1);
}
//释放线程池组资源
destory_group_threadpool(mtp);
printf("Test Manage ThreadPool Finish...\n");
}
int main(void)
{
#if 1 //测试单个的线程池功能
test_threadpool();
#else //测试线程池组功能
test_manange_threadpool();
#endif
return 0;
}通过修改宏定义,决定使用线程池还是线程池组
-
测试线程池结果

2.测试线程池组结果
5.总结
使用线程池情况:一般程序中有并发处理任务,但是处理的任务并发量不高时候采用线程池。
使用线程池组情况:程序中任务并发量很大情况下使用。