目录
引言:
主程序代码:
结果呈现:
小结:
引言:
通过一个最简单的测试程序直观Android系统的native层Surface的渲染显示过程。
主程序代码:
#include <cutils/memory.h>
#include <utils/Log.h>
#include <binder/IPCThreadState.h>
#include <binder/ProcessState.h>
#include <binder/IServiceManager.h>
#include <gui/Surface.h>
#include <gui/SurfaceComposerClient.h>
#include <android/native_window.h>
using namespace android;
//int main(int argc, char** argv)
int main()
{
// 设置线程池
sp<ProcessState> proc(ProcessState::self());
ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
// 创建与Surfaceflinger通信的客户端
sp<SurfaceComposerClient> client = new SurfaceComposerClient();
// 创建SurfaceControl并设置名称“resize”、宽高、像素格式,红色分量使用 5 位,绿色分量使用 6 位,蓝色分量使用 5 位。
sp<SurfaceControl> surfaceControl = client->createSurface(String8("resize"),
400, 600, PIXEL_FORMAT_RGB_565, 0);
//通过SurfaceControl获取一个Surface
sp<Surface> surface = surfaceControl->getSurface();
SurfaceComposerClient::Transaction t;
//设置Layer层级,数值越大层级越高
t.setLayer(surfaceControl, 100000)
.apply();
ANativeWindow_Buffer outBuffer;
//从BufferQueue中获取获取一个Buffer
surface->lock(&outBuffer, NULL);
//计算每个像素点的字节大小
ssize_t bpr = outBuffer.stride * bytesPerPixel(outBuffer.format);
//使用memset16对buffer赋值(颜色值)
android_memset16((uint16_t*)outBuffer.bits, 0xF800, bpr*outBuffer.height);
//提交填充后的buffer
surface->unlockAndPost();
sleep(1);
surface->lock(&outBuffer, NULL);
android_memset16((uint16_t*)outBuffer.bits, 0x07E0, bpr*outBuffer.height);
surface->unlockAndPost();
sleep(1);
surface->lock(&outBuffer, NULL);
android_memset16((uint16_t*)outBuffer.bits, 0x001F, bpr*outBuffer.height);
surface->unlockAndPost();
sleep(1);
//对outbuffer进行100次连续的获取与释放
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
surface->lock(&outBuffer, NULL);
printf("%03d buff addr = 0x%x\n", i, (unsigned int)(uintptr_t)outBuffer.bits);
surface->unlockAndPost();
}
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
return 0;
}结果呈现:
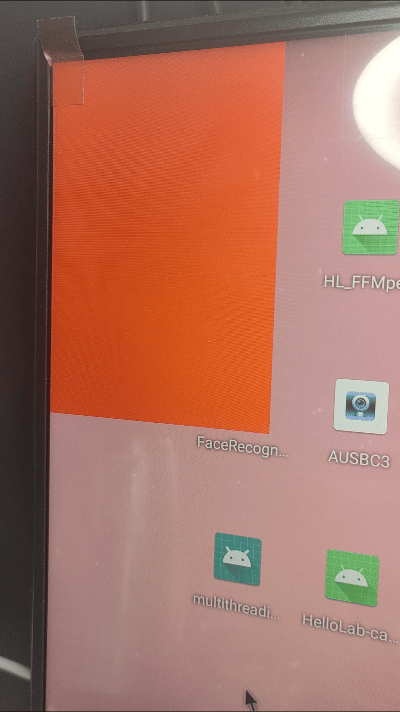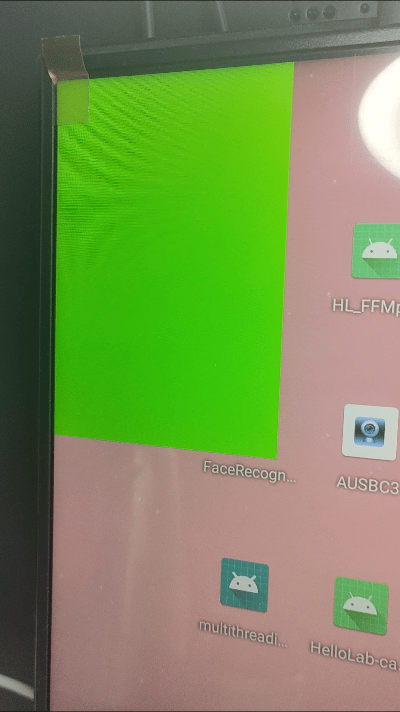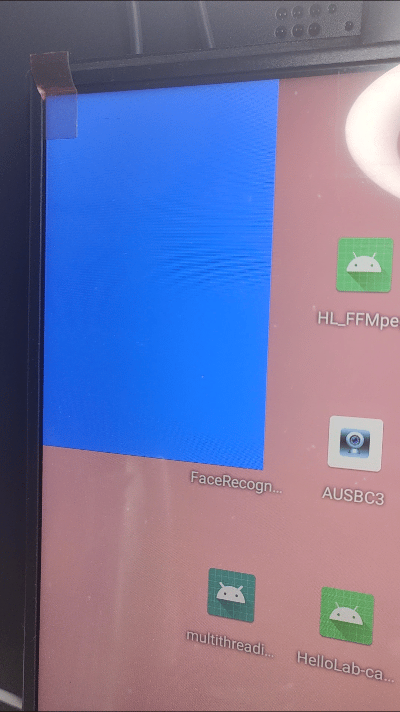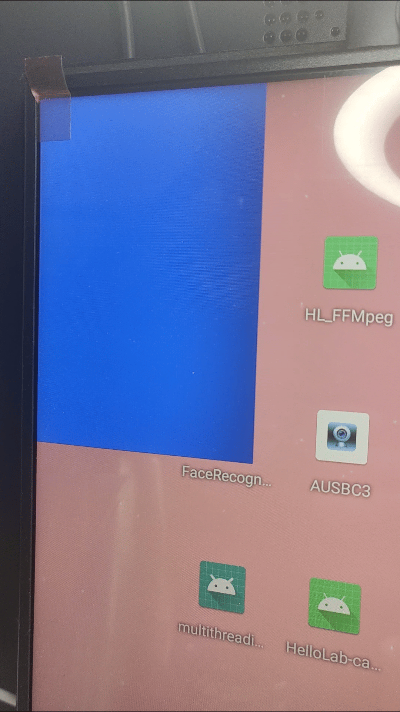
小结:
1、基于线程池的方式,创建一个客户端,并与服务端SurfaceFlinger进行connect,这就有了通信和交互的基础渠道
2、创建Surface,同时通过SurfaceControl来直接管理Surface(demo中只体现了Surface的lock和unlockAndPost来获取buffer)
3、底层是通过BufferQueue的来实现生产者和消费者模型的流水线方式,进行读写图形缓冲区,进行绘制渲染。