目录
39. 组合总和
40. 组合总和 II
131. 分割回文串
39. 组合总和
难度:medium
类型:回溯
思路:
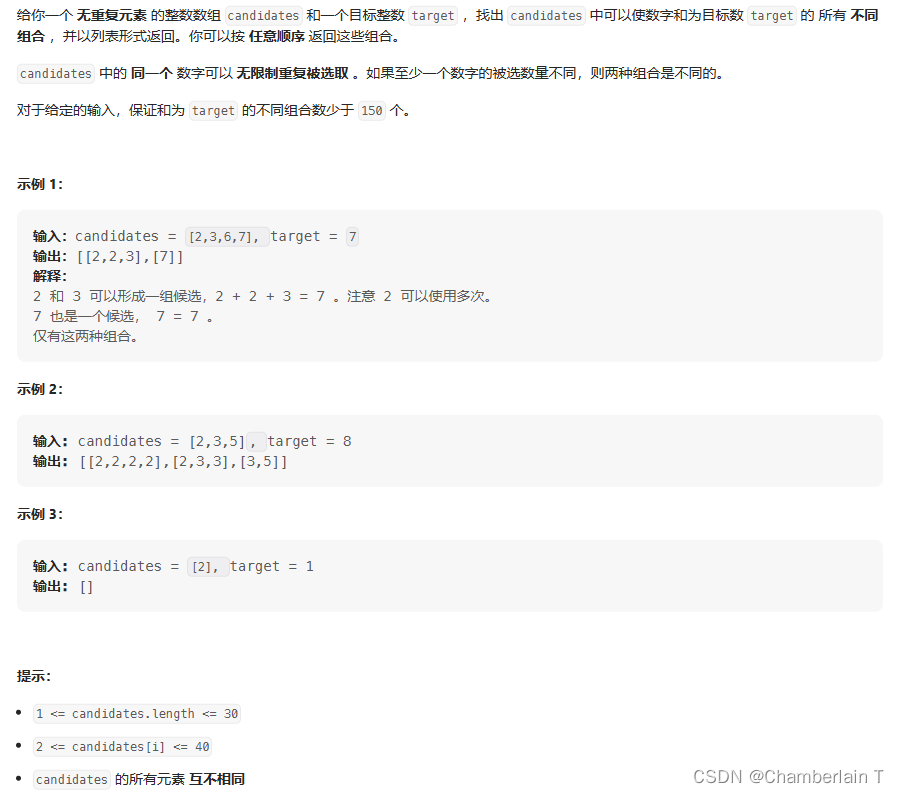
这道题的特点是,组合没有元素个数要求,数组无重复元素,每个元素可以无限选取。
组合没有元素个数要求:不需要通过path长度判断来跳出递归,通过sum来跳出;
数组无重复元素:不需要进行去重操作
每个元素可以无限选取:每次进行下层递归时,startIndex为i,不是i+1
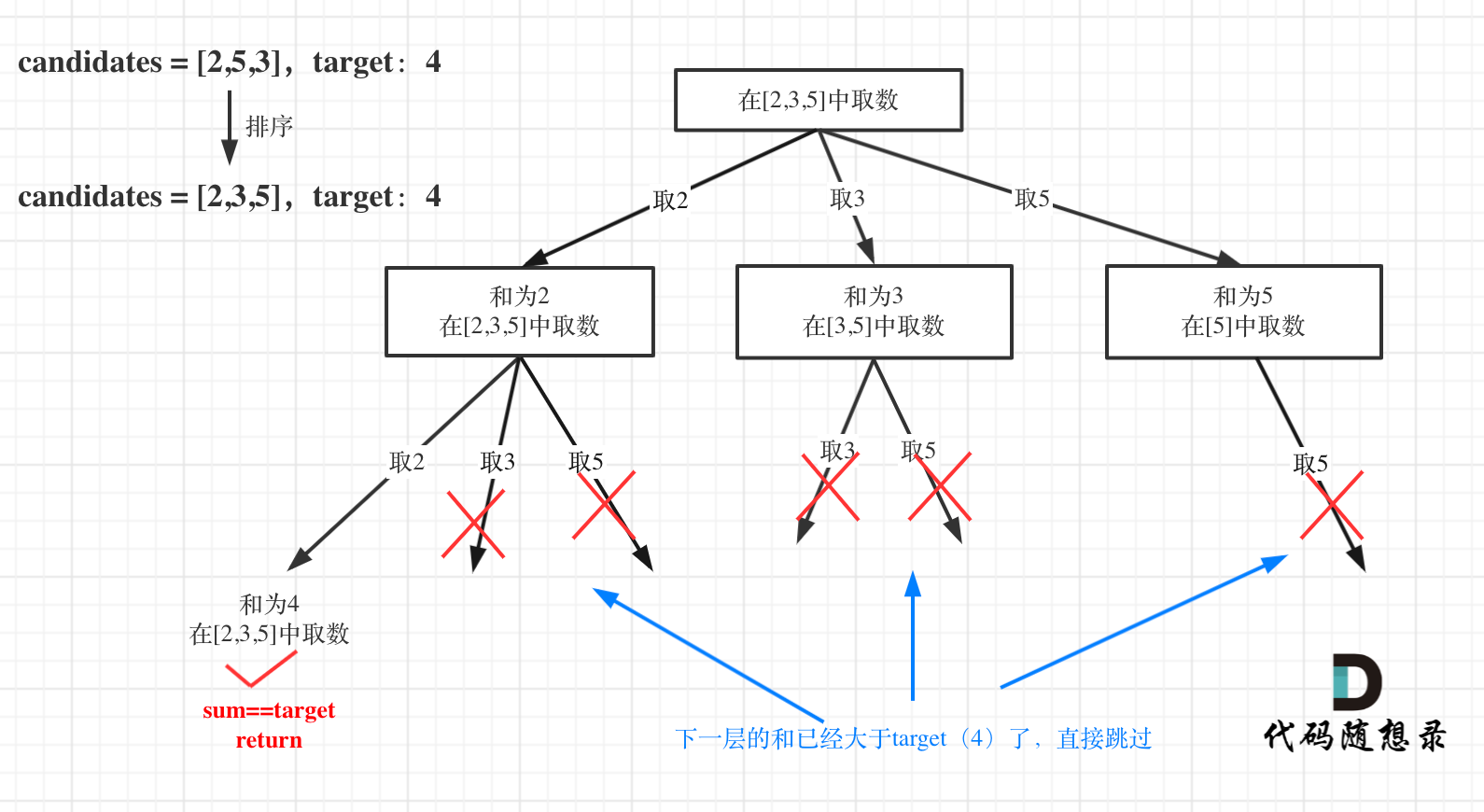
先给数组排序,是为了后续的剪枝操作;
代码:
class Solution {
private List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
private List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
private int sum = 0;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
if (candidates.length == 0) {
return ans;
}
// 排序
Arrays.sort(candidates);
backtracking(candidates, target, 0);
return ans;
}
public void backtracking(int[] candidates, int target, int startIndex) {
// if (sum > target) {
// return;
// }
if (sum == target) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
// 剪枝操作:sum + candidates[i] <= target,若超过target,不需要进入下一层递归判断
for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (sum + candidates[i] > target) {
break;
}
sum += candidates[i];
path.add(candidates[i]);
backtracking(candidates, target, i);
sum -= candidates[i];
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}- 时间复杂度: O(n * 2^n),注意这只是复杂度的上界,因为剪枝的存在,真实的时间复杂度远小于此
- 空间复杂度: O(target)
40. 组合总和 II
难度:medium
类型:回溯
思路:
本题的特点是:集合中有重复元素,集合每个元素在每个组合只能使用一次;
集合中有重复元素:进行去重操作;避免递归树中同一层有重复元素,同一层的元素会出现在path的相同位置,会造成重复的组合(去重前先要排序)
1.使用startIndex方法去重
i>0无法确定candidates[i]和candidates[i - 1]是同层还是同枝;而i>startIndex可以确定是同层;
if (i > startIndex && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]) {
continue;
2.使用used数组去重
if (i > 0 && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false) {
continue;
}· 在candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]相同的情况下:
- used[i - 1] == true,说明同一树枝candidates[i - 1]使用过
- used[i - 1] == false,说明同一树层candidates[i - 1]使用过
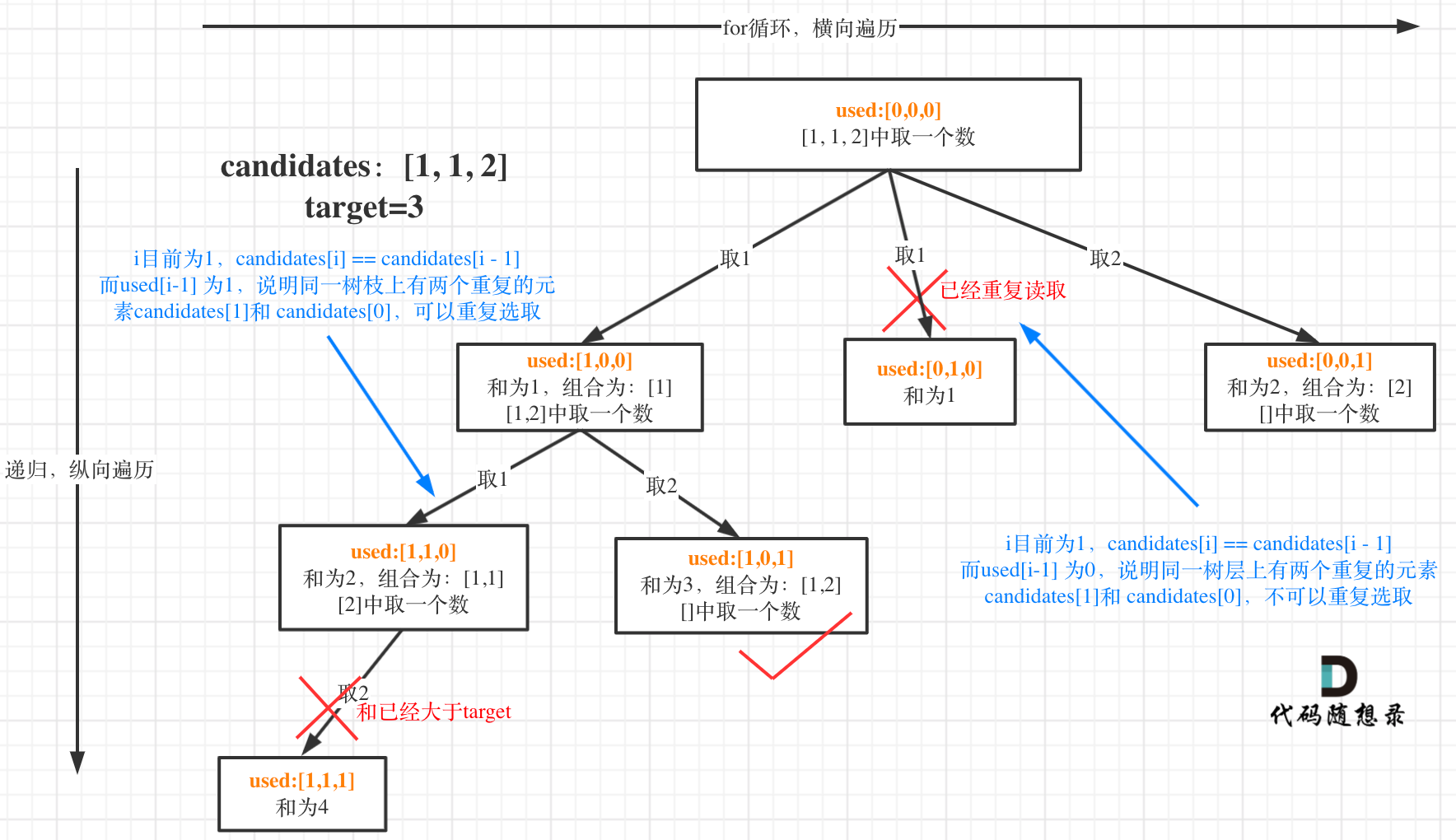
集合每个元素在每个组合只能使用一次:调用递归时,startIndex为i+1
代码:
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
private int sum = 0;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
if (candidates.length == 0) {
return ans;
}
Arrays.sort(candidates);
backtracking(candidates, target, 0);
return ans;
}
public void backtracking(int[] candidates, int target, int startIndex) {
if (sum == target) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length && sum + candidates[i] <= target; i++) {
// 避免递归树中同一层有重复元素,同一层的元素会出现在path的相同位置,会造成重复的组合
// 例如candidates = [1,2,2,2,2,3,3,3,3],target = 6
if (i > startIndex && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
sum += candidates[i];
path.add(candidates[i]);
backtracking(candidates, target, i + 1);
sum -= candidates[i];
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
// 使用used数组方法
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
private boolean[] used;
// used[i - 1] == true,说明同一树枝candidates[i - 1]使用过
// used[i - 1] == false,说明同一树层candidates[i - 1]使用过
private int sum = 0;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
if (candidates.length == 0) {
return ans;
}
Arrays.sort(candidates);
used = new boolean[candidates.length];
backtracking(candidates, target, 0);
return ans;
}
public void backtracking(int[] candidates, int target, int startIndex) {
if (sum == target) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length && sum + candidates[i] <= target; i++) {
// 这里是关键区别,除了对used[i-1]判定外,i>0也不同于上面的i>startIndex
// 因为i>0无法确定candidates[i]和candidates[i - 1]是同层还是同枝;而i>startIndex可以确定是同层
if (i > 0 && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false) {
continue;
}
sum += candidates[i];
path.add(candidates[i]);
used[i] = true;
backtracking(candidates, target, i + 1);
sum -= candidates[i];
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
- 时间复杂度: O(n * 2^n)
- 空间复杂度: O(n)
131. 分割回文串
难度:medium
类型:回溯
思路:
本题为切割问题,也是组合的一种。
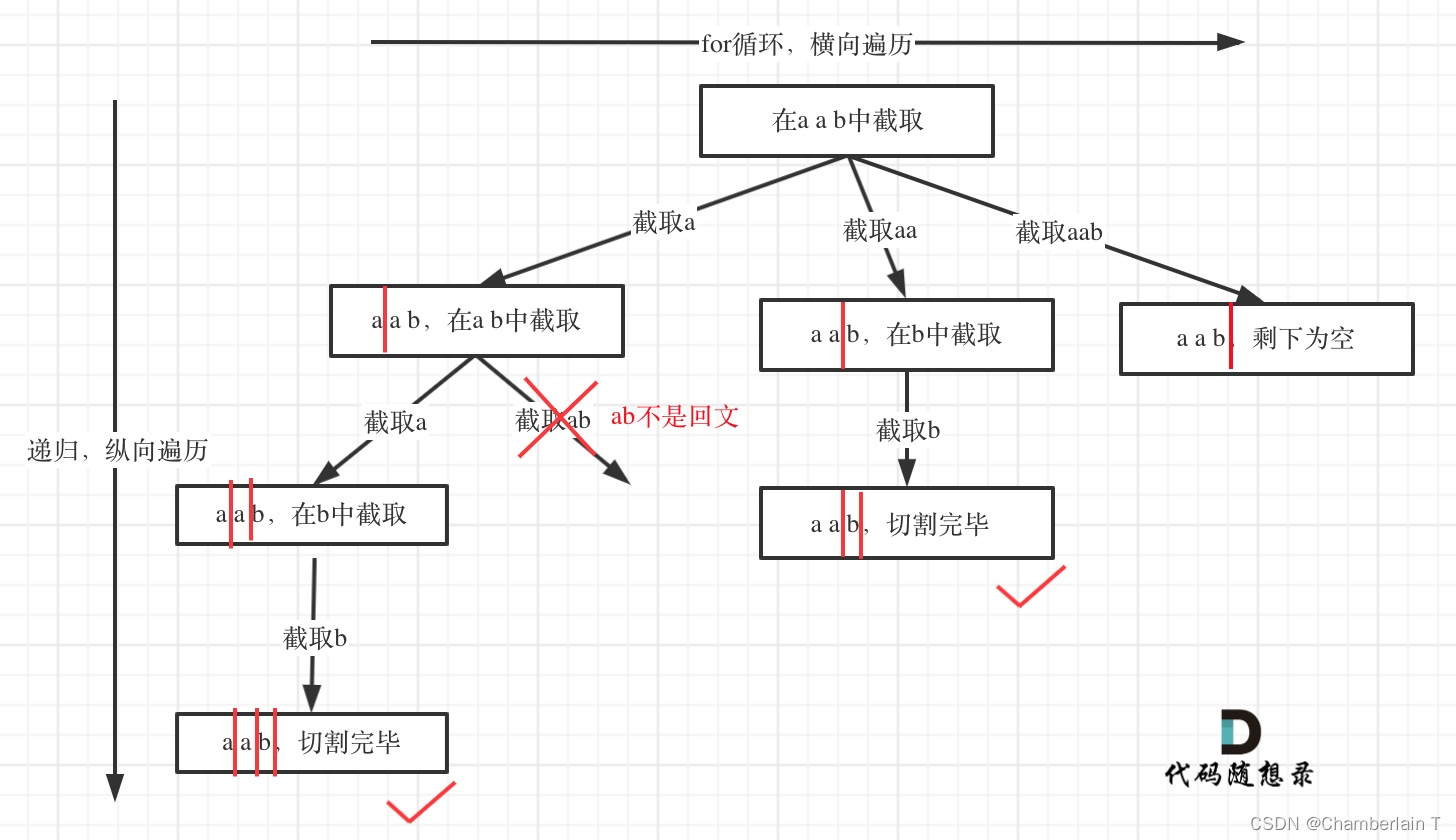


代码:
class Solution {
private List<List<String>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
private List<String> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
backtracking(s, 0);
return ans;
}
public void backtracking(String s, int startIndex) {
if (startIndex == s.length()) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++) {
// substring()方法为左闭右开
String str = s.substring(startIndex, i + 1);
if (judge(str)) {
path.add(str);
backtracking(s, i + 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
public boolean judge(String s) {
int left = 0;
int right = s.length() - 1;
while (left < right) {
if (s.charAt(left) != s.charAt(right)) {
return false;
}
left++;
right--;
}
return true;
}
}- 时间复杂度: O(n * 2^n)
- 空间复杂度: O(n^2)