😏★,°:.☆( ̄▽ ̄)/$:.°★ 😏
这篇文章主要介绍AStar规划算法原理与实现。
学其所用,用其所学。——梁启超
欢迎来到我的博客,一起学习,共同进步。
喜欢的朋友可以关注一下,下次更新不迷路🥞
文章目录
- :smirk:1. AStar介绍
- :satisfied:2. 应用示例
- :satisfied:3. 其他常用算法示例
😏1. AStar介绍
A* 算法是一种常用的启发式搜索算法,用于解决图形中的路径规划问题。它是一种通用的图搜索算法,适用于各种离散空间搜索问题,包括游戏中的路径规划、机器人运动规划等。
A* 算法结合了广度优先搜索和贪婪最佳优先搜索的优点。它在搜索过程中利用了一个启发式函数(称为估价函数)来估计从当前节点到目标节点的代价。这个估价函数通常使用欧氏距离、曼哈顿距离等来度量节点之间的距离。
A* 算法的基本思想如下:
- 创建一个开放列表(open list)和一个关闭列表(closed list),以及一个存储每个节点的代价的数据结构。
- 将起始节点添加到开放列表,并将其代价设置为从起始节点到目标节点的估计代价。
- 当开放列表不为空时,执行以下步骤:
从开放列表中选择具有最低代价的节点作为当前节点。
如果当前节点是目标节点,则已找到路径,结束搜索。
将当前节点移入关闭列表。
对当前节点周围的每个相邻节点执行以下步骤:
1.如果相邻节点不可通过或者已经在关闭列表中,则忽略它。
2.如果相邻节点不在开放列表中,则将其添加到开放列表,并计算从起始节点到该节点的代价。
3,如果相邻节点在开放列表中,则比较当前路径是否更好(代价更低)。如果是,则更新相邻节点的代价值和父节点。
- 如果开放列表为空,表示无法到达目标节点,搜索失败。
A* 算法通过启发式函数来引导搜索,使其更加高效。通过不断选择估计代价最低的节点进行扩展,A* 算法倾向于沿着代价最低的路径搜索,从而更快地接近目标节点。
😆2. 应用示例
学习Github项目地址(仅学习用):https://github.com/JokerEyeAdas/AStarShellMapSearch
编译运行:g++ CAstar.cpp AStarTest.cpp -o AstarShellMapTest

该案例实现了在shell终端中显示10*10的地图,设置起点和终点,用寻路函数执行,若能找到全局路径,则用绿色的块表示路径,否则不显示并提示有障碍物。
由这个文件组成:ShellMap.hpp、CAstar.h、CAstar.cpp和AStarTest.cpp组成。
CAstar.h定义了障碍类型和openlist&closelist,以及f=g+h评价函数:
#ifndef __Astar__CAstar__
#define __Astar__CAstar__
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include "ShellMap.hpp"
using namespace std;
//地图最大值
#define MAX_X 10
#define MAX_Y 10
enum class AType
{
ATYPE_UNKNOWN,
ATYPE_CLOSED,
ATYPE_OPENED,
ATYPE_BARRIER //障碍
};
class APoint
{
public:
APoint();
~APoint();
int x;
int y;
AType type; //类型:障碍、开放列表、关闭列表
int f; //f = g+h
int g;
int h;
APoint *parent;
bool operator == (const APoint& po)
{
if (x == po.x && y == po.y)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
class CAstar
{
vector<APoint*> _openList; //开放列表
vector<APoint*> _closeList; //关闭列表
vector<APoint*> _neighbourList; //周边节点
APoint* _endPoint;
APoint* _curPoint;
vector< vector<APoint*> > _allPoints;
ShellMap shellMap_;
public:
CAstar();
~CAstar();
APoint* findWay(APoint* beginPoint,APoint* endPoint,vector< vector<APoint*> >& allPoints);
ShellMap& GetMap() {return shellMap_;};
// APoint* findWay(int beginX,int beginY,int endX,int endY);
private:
int getF(APoint *point);
int getH(APoint *point);
vector<APoint*> getNeighboringPoint(APoint* point);
};
#endif
CAstar.cpp主要是启发函数的实现:
#include "CAstar.h"
bool mySort(const APoint* p1,const APoint* p2)
{
return p1->f < p2->f;
}
APoint::APoint():x(0)
,y(0)
,h(0)
,f(0)
,g(0)
,parent(nullptr)
,type(AType::ATYPE_UNKNOWN)
{
}
APoint::~APoint()
{
}
#pragma mark------CAstar-------
CAstar::CAstar():_endPoint(nullptr)
,_curPoint(nullptr)
{
shellMap_.GenMap(MAX_X, MAX_Y);
//shellMap_.SetStartEndPoint(Point(1, 1), Point(6, 6));
}
CAstar::~CAstar()
{
_openList.clear();
_closeList.clear();
_neighbourList.clear();
_allPoints.clear();
}
APoint* CAstar::findWay(APoint *beginPoint, APoint *endPoint,vector< vector<APoint*> >& allPoints)
{
shellMap_.SetStartEndPoint(Point(beginPoint->x, beginPoint->y), Point(endPoint->x, endPoint->y));
shellMap_.ShowMap();
//传递地图
_allPoints = allPoints;
_endPoint = endPoint;
if (_endPoint->type == AType::ATYPE_BARRIER)
{
cout<<"ERR the final point is barrier!!"<<endl;
return nullptr;
}
if (*_endPoint == *beginPoint)
{
cout<<"起始点相同"<<endl;
return nullptr;
}
_openList.push_back(beginPoint);
beginPoint->type = AType::ATYPE_OPENED;
beginPoint->f = getF(beginPoint);
do
{
//获取最小值的节点
_curPoint = _openList[0];
_openList.erase(_openList.begin());
_curPoint->type = AType::ATYPE_CLOSED;
_closeList.push_back(_curPoint);
//GetMap().GetMapPtr()[_curPoint->y * MAX_X + _curPoint->x] = CUR;
if (*_curPoint == *_endPoint)
{
cout<<"have find way"<<endl;
return _curPoint;
}
//获取相邻的节点
vector<APoint*> neVec = getNeighboringPoint(_curPoint);
for (int i = 0; i<neVec.size(); i++)
{
auto tmpoint = neVec[i];
if (tmpoint->type == AType::ATYPE_CLOSED)
{
//GetMap().GetMapPtr()[tmpoint->y * MAX_X + tmpoint->x] = CLOSE;
continue;
}
//是否在开放列表里
if (tmpoint->type != AType::ATYPE_OPENED)
{
tmpoint->parent = _curPoint;
tmpoint->g = _curPoint->g + 10;
//计算H值
tmpoint->h = getH(tmpoint);
//添加到开放列表里
_openList.push_back(tmpoint);
tmpoint->type = AType::ATYPE_OPENED;
//GetMap().GetMapPtr()[tmpoint->y * MAX_X + tmpoint->x] = OPEN;
}
else
{
//已经在开放列表里
if (tmpoint->h < _curPoint->h)
{
tmpoint->parent = _curPoint;
tmpoint->g = _curPoint->g + 10;
//GetMap().GetMapPtr()[tmpoint->y * MAX_X + tmpoint->x] = OPEN;
}
}
}
//排序 F值最小的排在前面
sort(_openList.begin(), _openList.end(), mySort);
//GetMap().ShowMap();
//sleep(500);
} while (_openList.size()>0);
cout<<"---can not find way---"<<endl;
return nullptr;
}
int CAstar::getF(APoint *point)
{
return (point->g + getH(point));
}
int CAstar::getH(APoint *point)
{
//曼哈顿城市街区估算法
return (abs(_endPoint->y - point->y) + abs(_endPoint->x - point->x))*10;
}
vector<APoint*> CAstar::getNeighboringPoint(APoint *point)
{
_neighbourList.clear();
// cout<<"nei size:"<<_neighbourList.size()<<endl;
if (point->x < MAX_X-1)
{
if (_allPoints[point->x+1][point->y]->type != AType::ATYPE_BARRIER)
{
_neighbourList.push_back(_allPoints[point->x+1][point->y]);
}
}
if (point->x >0)
{
if (_allPoints[point->x-1][point->y]->type != AType::ATYPE_BARRIER)
{
_neighbourList.push_back(_allPoints[point->x-1][point->y]);
}
}
if (point->y < MAX_Y-1)
{
if (_allPoints[point->x][point->y+1]->type != AType::ATYPE_BARRIER)
{
_neighbourList.push_back(_allPoints[point->x][point->y+1]);
}
}
if (point->y >0)
{
if (_allPoints[point->x][point->y-1]->type != AType::ATYPE_BARRIER)
{
_neighbourList.push_back(_allPoints[point->x][point->y-1]);
}
}
return _neighbourList;
}
AStarTest.cpp是测试示例:
#include "CAstar.h"
int main()
{
/*ShellMap map(10, 10);
map.SetStartEndPoint(Point(1, 1), Point(8, 8));
map.ShowMap();
*/
auto star = new CAstar();
vector< vector<APoint*> > map;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_X; i++)
{
vector<APoint*> tmp;
for (int j = 0; j < MAX_Y; j++)
{
APoint *point = new APoint();
point->x = i;
point->y = j;
if (star->GetMap().GetMapPtr()[j * MAX_X + i] == BLOCK)
{
point->type = AType::ATYPE_BARRIER;
}
tmp.push_back(point);
}
map.push_back(tmp);
}
//开始寻路
auto point = star->findWay(map[0][0], map[9][9], map);
if (!point)
{
return 0;
}
while (point)
{
if (star->GetMap().GetMapPtr()[point->y * MAX_X + point->x] == START || star->GetMap().GetMapPtr()[point->y * MAX_X + point->x] == END) {
;
} else {
star->GetMap().GetMapPtr()[point->y * MAX_X + point->x] = PATH;
}
point = point->parent;
}
star->GetMap().ShowMap();
//-------------释放内存----------
delete star;
for (int i = 0; i<MAX_X; i++)
{
for (int j = 10; j<MAX_Y; j++)
{
delete map[i][j];
map[i][j] = nullptr;
}
}
return 0;
}
😆3. 其他常用算法示例
项目Github地址:https://github.com/czjaixuexi/path_planning
该项目实现了astar、dijkstra、rrt规划算法和bezier、b-spline曲线生成,并用matplotlibcpp.h调用python的matplot库实现了图形化显示,清楚地展示了规划算法和曲线的生成过程,可以学习。
EMPlanner项目Github地址:https://github.com/reflector-li/EMplanner
EM planner是百度Apollo自动驾驶系统的路径规划算法。通过将非凸轨迹规划问题分解为路径规划和速度规划两个子问题,并基于matplotlibcpp.h实现可视化显示规划器的基本功能。
相关库的安装可参考:http://t.csdn.cn/UoWsg
运行如下:
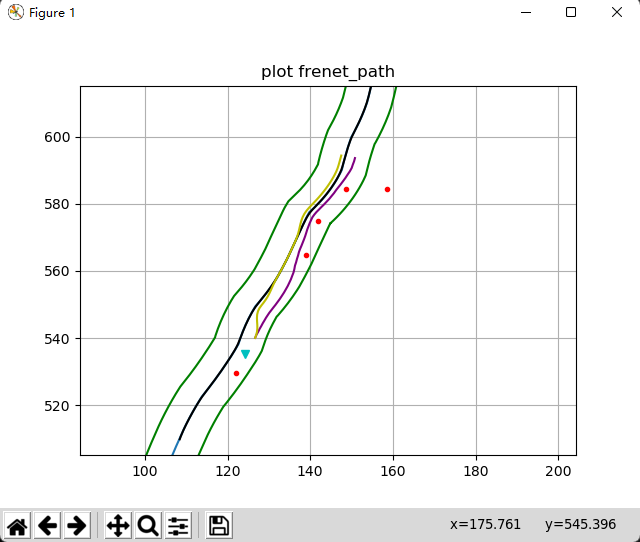

以上。








![[OnWork.Tools]系列 06-屏幕水印](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/97b96824b1f7096a5d9f5840e9e5d64a.gif)