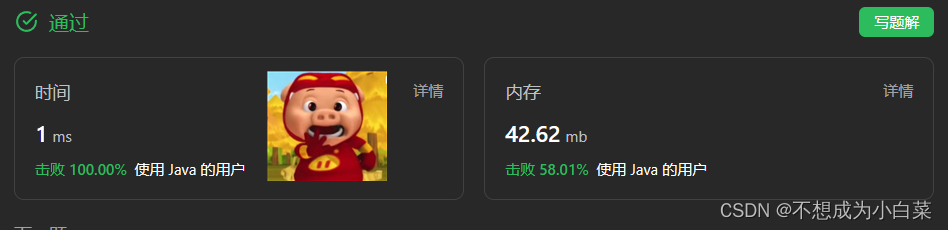
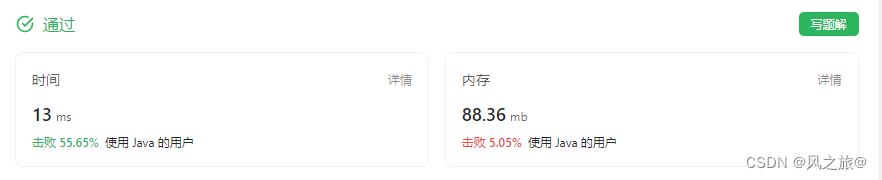
目录
- 弹性盒子模型
- flex-direction 排列方式 主轴方向
- 换行
- 排序
- 控制子元素缩放比例
- 缩放是如何实现的?
- 控制子元素的对其方式
- justify-content 横向 对齐方式
- align-items 纵向 对齐方式
- align-content 多行 对齐方式
弹性盒子模型
flex-direction 排列方式 主轴方向
flex-direction: row; 横向布局,默认从左向右。
flex-direction: row-reverse; 横向布局,从右向左。
flex-direction: column; 纵向布局,从上到下。
flex-direction: column-reverse; 纵向布局,从下到上。
.top{
width:800px;
background: yellow;
display:flex;
flex-direction: row-reverse;
}
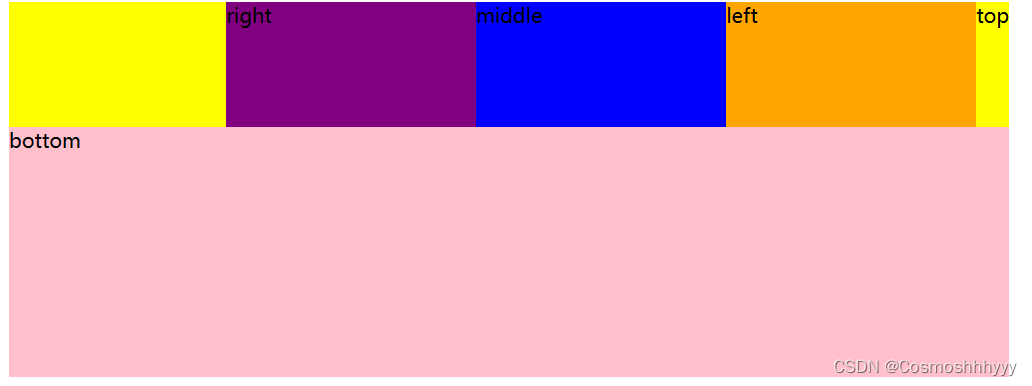
换行
flex-wrap: wrap; 换行
flex-wrap: nowrap; 不换行
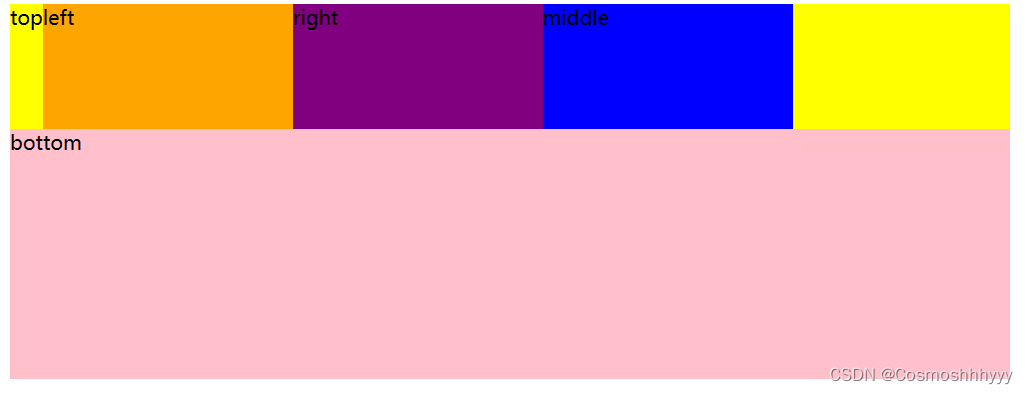
排序
给子级加上 order: 编号
值越小越考前,值越大越向后排。
.top{
width:800px;
background: yellow;
display:flex;
flex-direction: row;
}
.bottom{
width:800px;
height:200px;
background:pink;
}
.left{
width:200px;
height:100px;
background:orange;
float:left;
order:1;
}
.middle{
width:200px;
height:100px;
background:blue;
float:left;
order:3;
}
.right{
width:200px;
height:100px;
background: purple;
float:left;
order:2;
}
控制子元素缩放比例
作用于子级元素。
flex-shrink: 压缩因子。
flex-grow: 拉伸因子。
flex-grow: 基准因子,一般用宽度代替。
.top{
width:800px;
background: yellow;
display:flex;
flex-direction: row;
}
.bottom{
width:800px;
height:200px;
background:pink;
}
.left{
width:200px;
height:100px;
background:orange;
flex-grow: 8;
}
.middle{
width:200px;
height:100px;
background:blue;
flex-grow:5;
}
.right{
width:200px;
height:100px;
background: purple;
flex-grow:1;
}
三个比例的拉伸效果:

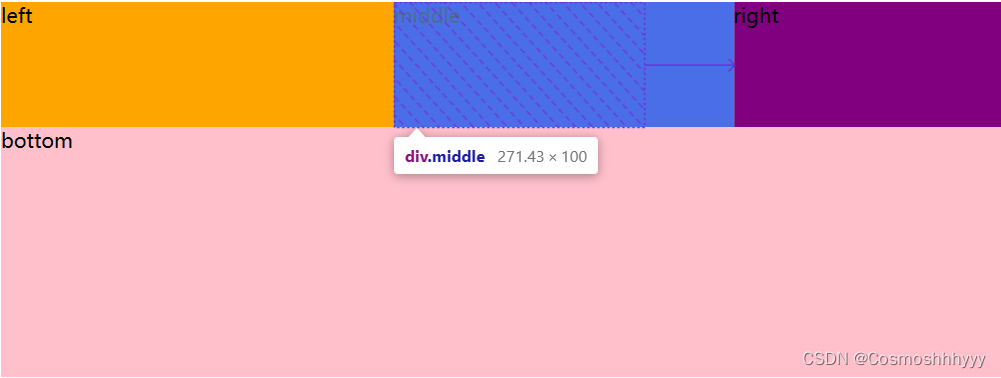
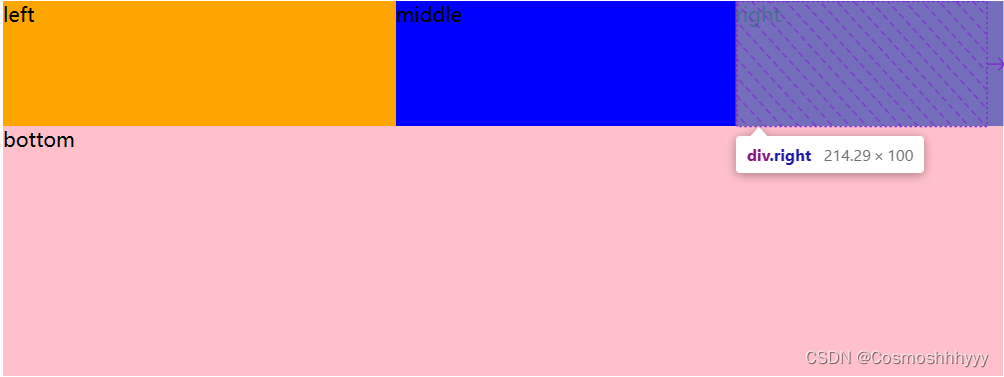
缩放是如何实现的?
拉伸:把所有flex-gorw求和,在把未占满的位置分为总和个份数,根据每个子集的比例分给子集。
缩小:根据子集宽度按比例比例自动缩小。
控制子元素的对其方式
justify-content 横向 对齐方式
其实是和主轴方向有关系,不一定是横向的,这里用横向举例展示。
justify-content: flex-start; 默认左对其
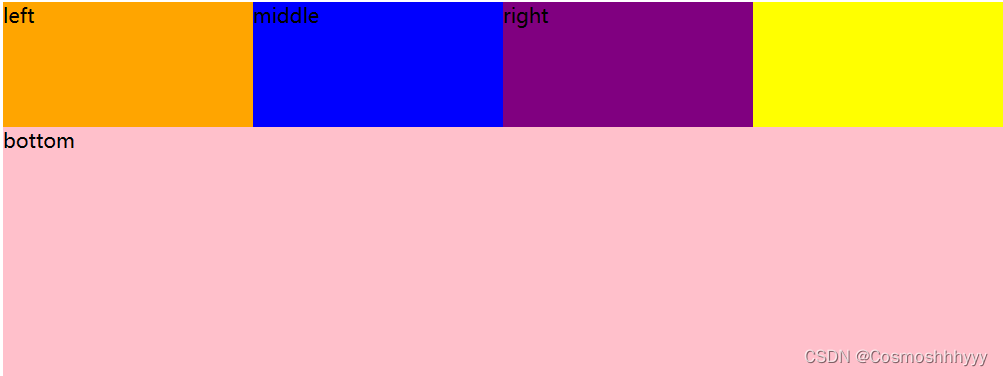
justify-content: flex-end; 右
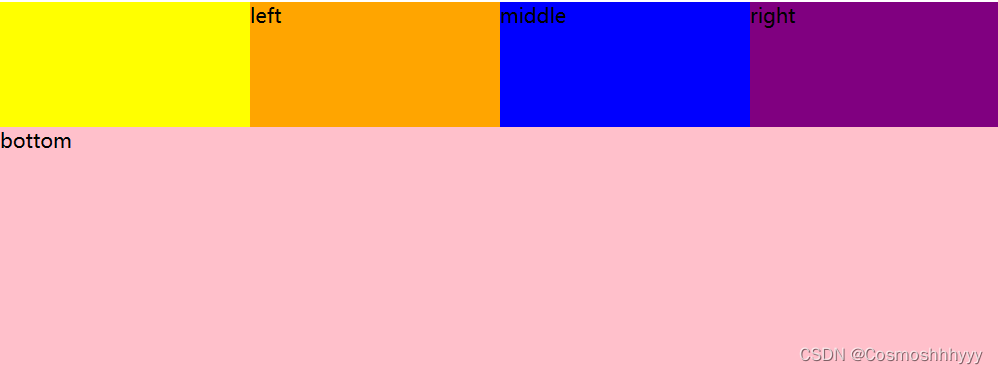
justify-content: center; 中间

justify-content: space-between; 空白放中间
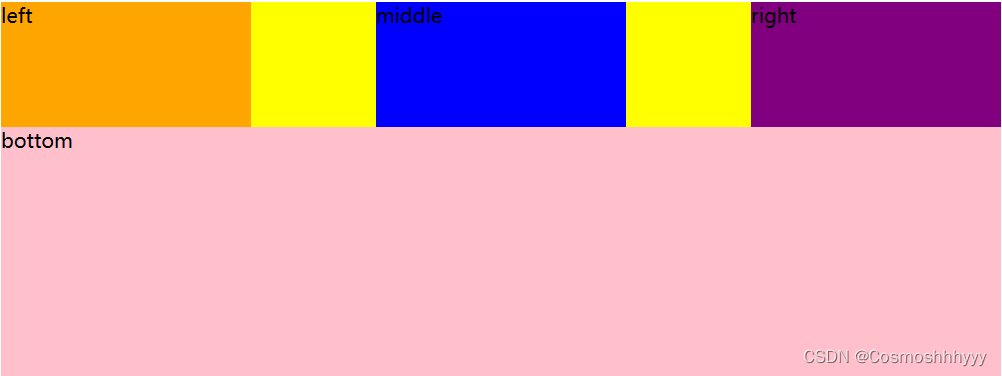
justify-content: space-around; 空白放周围
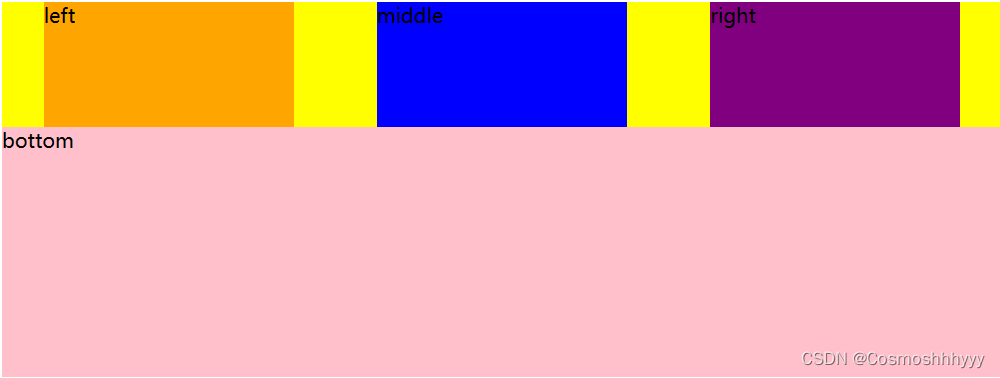
justify-content: space-evenly; 空白均匀分布
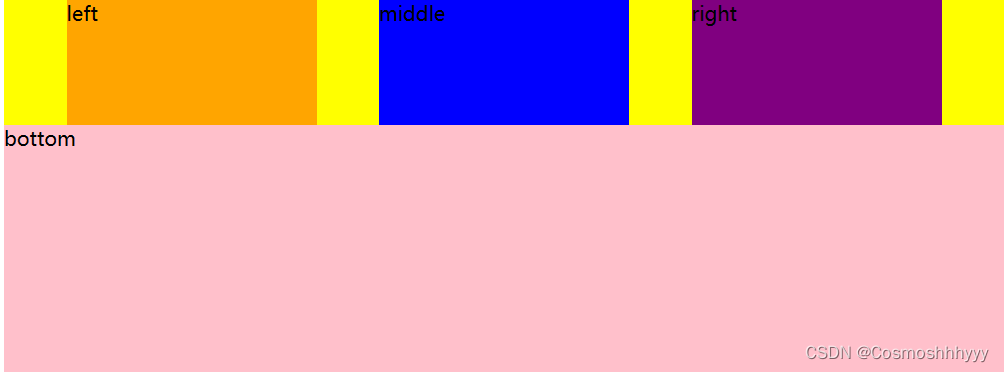
align-items 纵向 对齐方式
align-items: flex-start; 默认顶端对齐
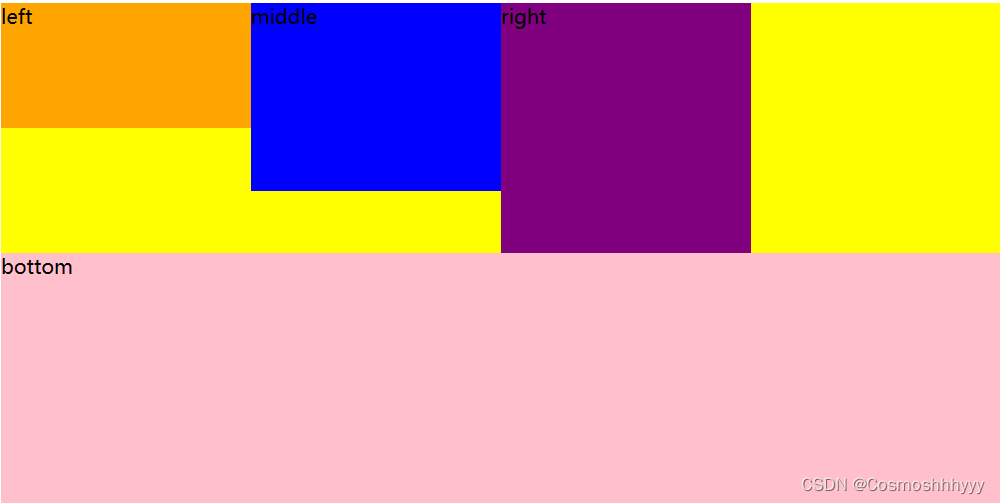
align-items: flex-end; 底端对齐
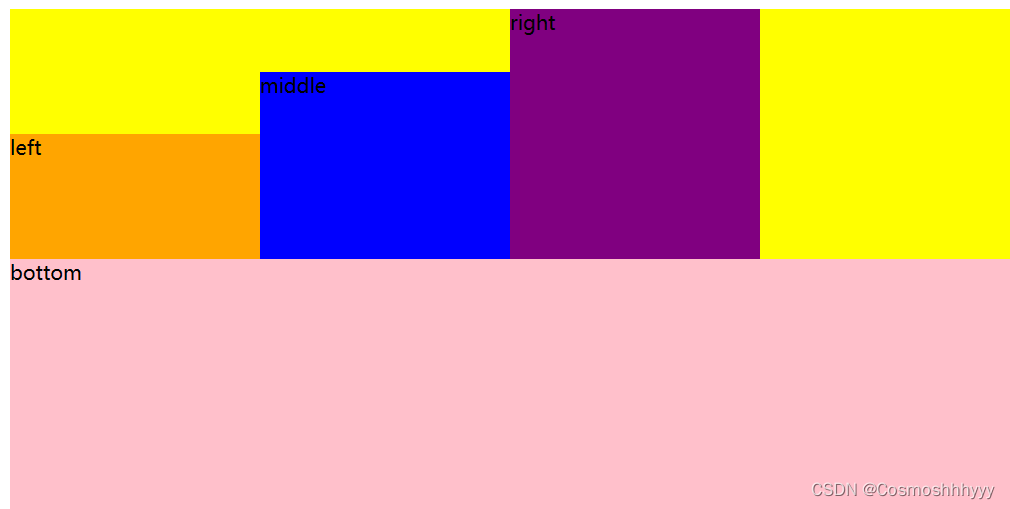
align-items: center; 居中对齐
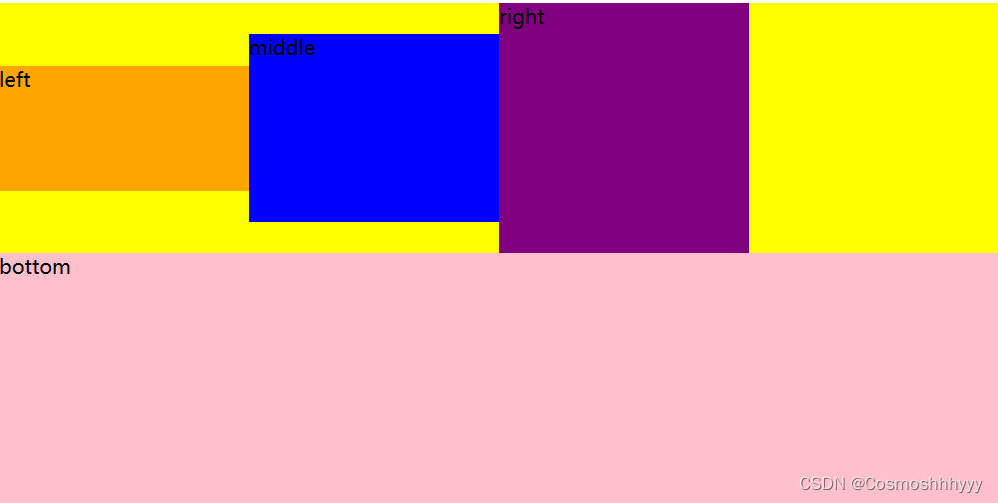
align-items: baseline; 首行底端对齐
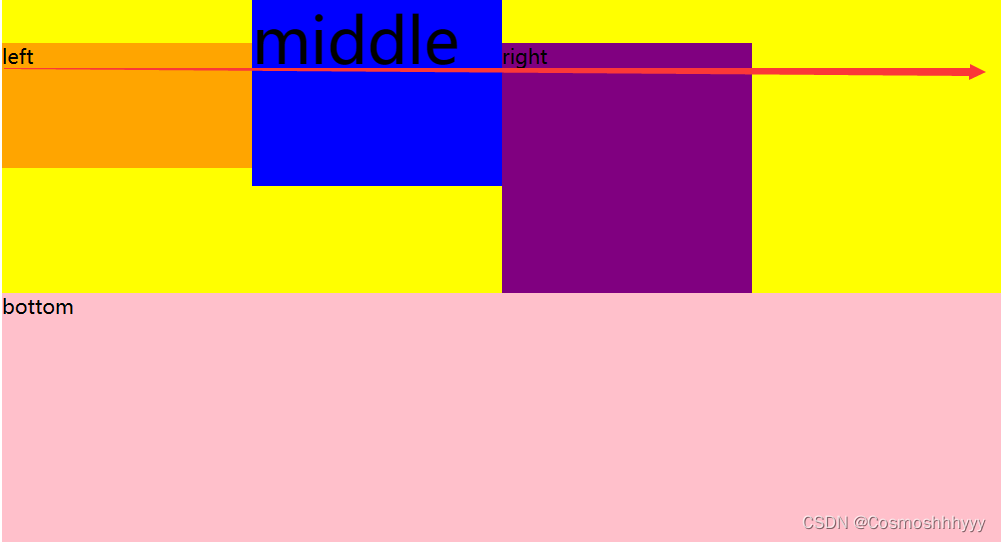
align-content 多行 对齐方式
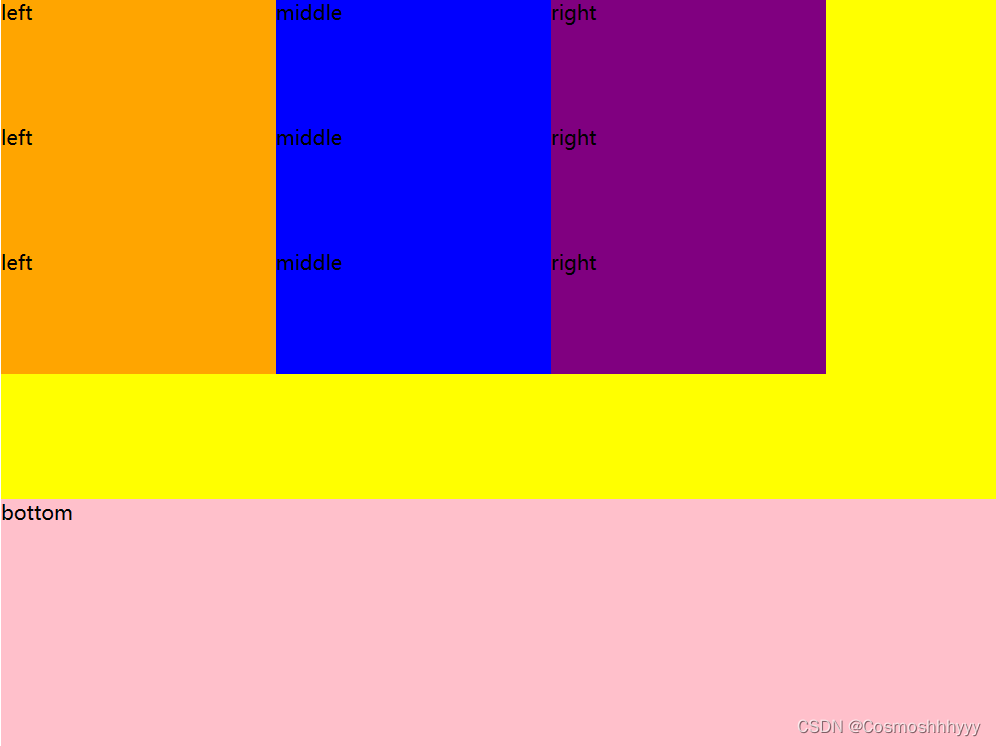
align-content: flex-start; 所有行都在顶端
我们先给给父级加上高度,好用来展示效果。
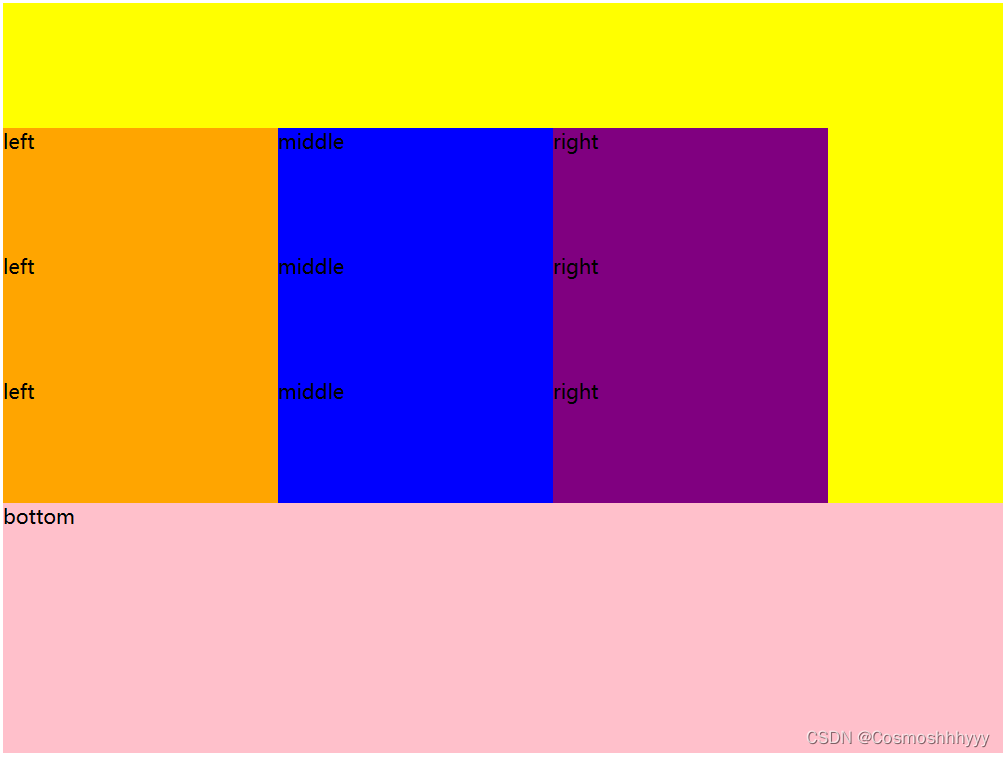
align-content: flex-end; 底部
align-content: center; 中间
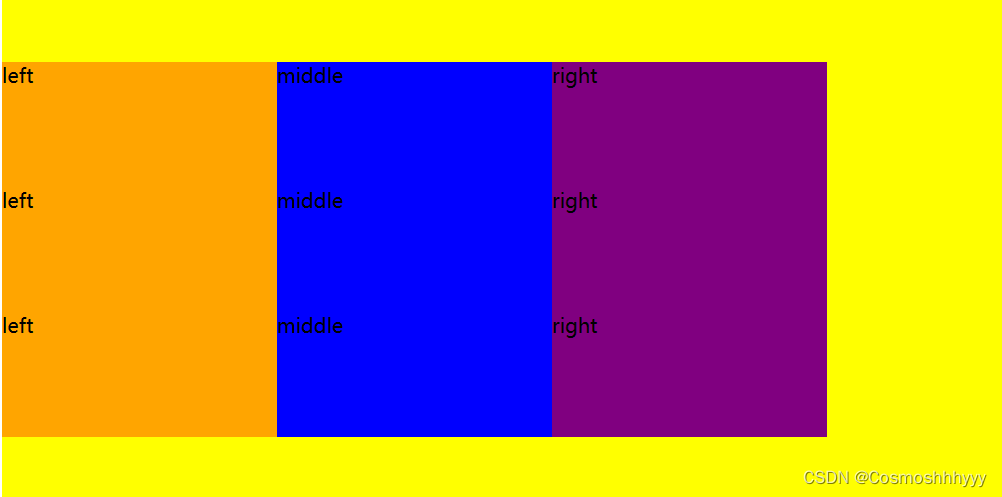
align-content: space-betwween; 空白放中间
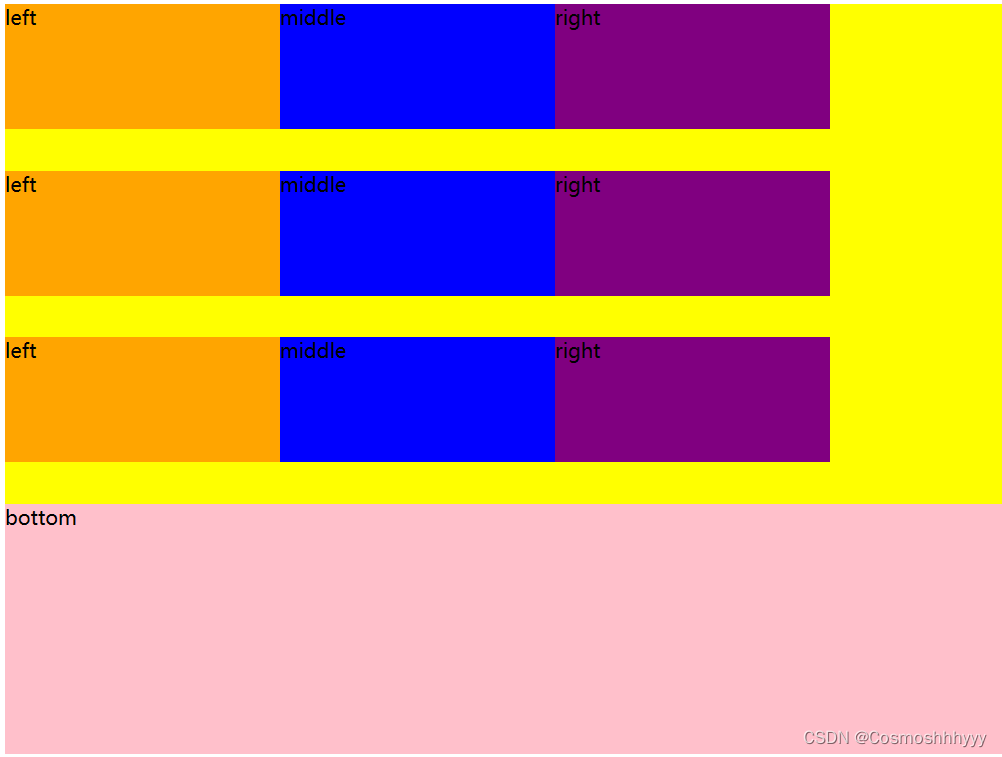
align-content: space-around; 空白放周围
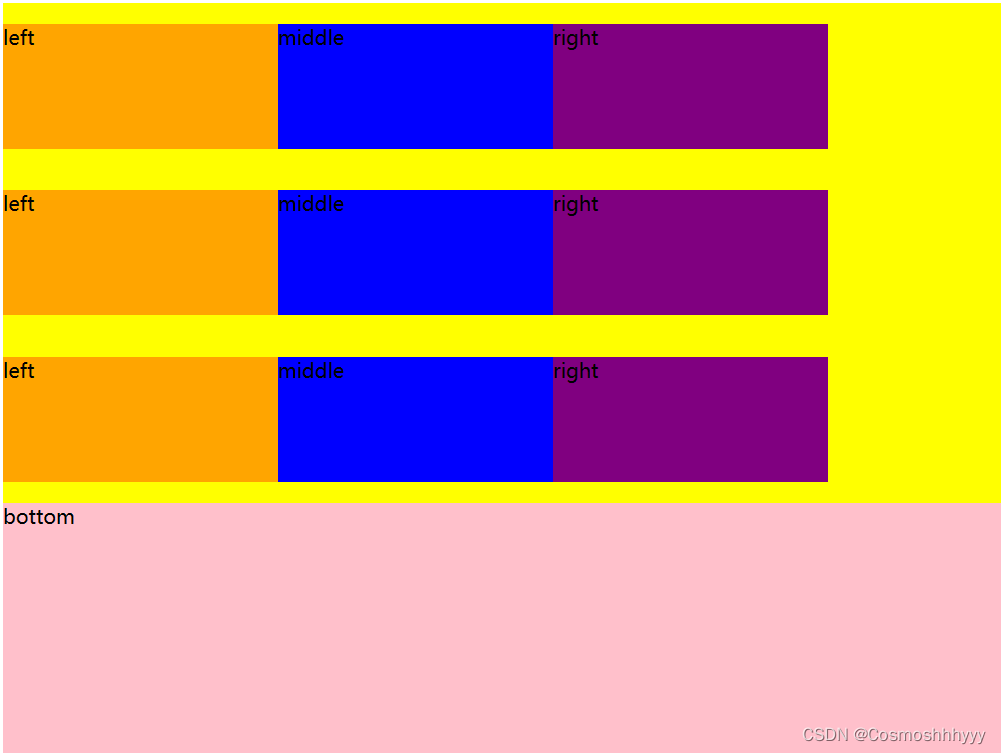
align-content: space-evenly; 空白均匀分布




![加入[无人驾驶吕同学]Apollo专属课程领礼品啦!](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e7371cb516fd43ab86cae490e19808fb.jpeg#pic_center)