Codeforces Round 891 (Div. 3)
A. Array Coloring
题目
给你一个由 n n n个整数组成的数组。您的任务是确定是否可以将其所有元素着色为两种颜色,使得两种颜色的元素之和具有相同的奇偶性,并且每种颜色至少有一个元素着色。
例如,如果数组为[ 1 , 2 , 4 , 3 , 2 , 3 , 5 , 4 1,2,4,3,2,3,5,4 1,2,4,3,2,3,5,4],我们可以将其着色为:[ 1 , 2 , 4 , 3 , 2 , 3 , 5 , 4 \color{blue}{1},\color{blue}{2},\color{red}{4},\color{blue}{3},\color{red}{2},\color{red}{3},\color{red}{5},\color{red}{4} 1,2,4,3,2,3,5,4],其中蓝色元素的总和为 6 6 6,红色元素的总和为【 18 18 18。
思路
如果数组总和为奇数,那么显然分成的两组中必定有一组为奇数,另一组为偶数, 因为如果两组都是偶数或者奇数,那么总和一定是偶数。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl;
#define no cout << "NO" << endl;
#define IOS cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0), ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
#define cxk 1
#define debug(s, x) if (cxk) cout << "#debug:(" << s << ")=" << x << endl;
using namespace std;
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) sum += a[i];
if (sum % 2 == 0) yes else no
}
signed main() {
IOS
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("../test.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("../test.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
B. Maximum Rounding
题目
给定一个自然数 x x x。您可以执行以下操作:
- 选择一个正整数 k k k并将 x x x舍入到第 k k k位数字
请注意,位置从右到左编号,从零开始。如果数字有 k k k位,则认为第 k k k位的数字等于 0 0 0。
舍入按如下方式完成:
-
若第 ( k − 1 ) (k-1) (k−1)位的数字大于或等于 5 5 5,则第 k k k位的数字增加 1 1 1,否则为 k k k位的数字-th 位置保持不变(使用数学舍入)。
-
如果运算前第 k k k位的数字是 9 9 9,应该增加 1 1 1,那么我们就查找最小的位置 k ′ k' k′( k ′ > k k'>k k′>k),其中的数字第 k ′ k' k′位的数字小于 9 9 9,在第 k ′ k' k′位的数字上加 1 1 1。然后我们分配 k = k ′ k=k' k=k′。
-
之后,位置小于 k k k的所有数字都被替换为零。
如果您可以根据需要多次执行该操作,您的任务就是使 x x x尽可能大。
例如 x x x等于 3451 3451 3451,那么如果连续选择:
-
k
=
1
k=1
k=1,那么操作后
x
x
x将变成
3450
3450
3450
-
k
=
2
k=2
k=2,则操作后
x
x
x将变成
3500
3500
3500
-
k
=
3
k=3
k=3,那么操作后
x
x
x将变成
4000
4000
4000
-
k
=
4
k=4
k=4,那么操作后
x
x
x将变成
0
0
0
为了使答案最大化,您需要先选择 k = 2 k=2 k=2,然后选择 k = 3 k=3 k=3,那么数字就会变成 4000 4000 4000。
思路
从左往右找第一个大于等于5的数,显然从这里可以开始往前进位是最优的,这时前面的数只要满足>=4就可以继续进位,因为5可以给它带来1,一直模拟直到不可以继续进位。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl;
#define no cout << "NO" << endl;
#define IOS cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0), ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
#define cxk 1
#define debug(s, x) if (cxk) cout << "#debug:(" << s << ")=" << x << endl;
using namespace std;
void solve() {
string x;
cin >> x;
int n = x.size();
x = "0" + x;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (x[i] >= '5') {
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && x[j] >= '4') j--;
x[j]++;
for (j = j+1; j <= n; j++) x[j] = '0';
if (x[0] != '0') cout << x[0];
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) cout << x[j];
cout << endl;
return;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cout << x[i];
}
cout << endl;
}
signed main() {
IOS
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("../test.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("../test.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
C. Assembly via Minimums
题目
Sasha 有一个包含 n n n个整数的数组 a a a。他觉得无聊,对于 i i i、 j j j( i < j i < j i<j),他写下了 a i a_i ai和 a j a_j aj的最小值。他获得了一个新的数组 b b b,大小为 n ⋅ ( n − 1 ) 2 \frac{n\cdot (n-1)}{2} 2n⋅(n−1)。
例如,如果 a = a= a=[ 2 , 3 , 5 , 1 2,3,5,1 2,3,5,1],他会写[ min ( 2 , 3 ) , min ( 2 , 5 ) , min ( 2 , 1 ) , min ( 3 , 5 ) , min ( 3 , 1 ) , m i n ( 5 , 1 ) \min(2, 3), \min(2, 5), \min(2, 1), \min(3, 5), \min(3, 1), min(5, 1) min(2,3),min(2,5),min(2,1),min(3,5),min(3,1),min(5,1)] = = =[ 2 , 2 , 1 , 3 , 1 , 1 2, 2, 1, 3, 1, 1 2,2,1,3,1,1]。
然后,他将数组 b b b的所有元素随机洗牌。
不幸的是,他忘记了数组 a a a,而你的任务是恢复任何可能获得数组 b b b的数组 a a a。
数组 a a a的元素应在 [ − 1 0 9 , 1 0 9 ] [-10^9,10^9] [−109,109]范围内。
思路
可以先开一个map来记录每个数字出现的次数
显然最小值一定会在b数组中出现n-1次,接下来是第2小的数一定会在b中出现n-2次,一直模拟下去即可。最后需要加一个比数组中最大的数还要大的数,因为这个数不会出现在b中,只要>=max(b[i])就行。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl;
#define no cout << "NO" << endl;
#define IOS cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0), ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
#define cxk 1
#define debug(s, x) if (cxk) cout << "#debug:(" << s << ")=" << x << endl;
using namespace std;
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
int m = n * (n - 1) / 2;
vector<int> a(n + 1), b(m + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) cin >> b[i];
map<int, int> mp;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
mp[b[i]]++;
}
vector<int> res;
int t = n - 1;
for (auto [x, y]: mp) {
while (y > 0) {
y -= t;
t--;
res.push_back(x);
}
}
res.push_back(res.back());
for (auto i: res) cout << i << " ";
cout << endl;
}
signed main() {
IOS
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("../test.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("../test.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
D. Strong Vertices
题目
给定两个数组 a a a和 b b b,长度均为 n n n。两个数组的元素索引从 1 1 1到 n n n。您正在构建一个有向图,如果 a u − a v ≥ b u − b v a_u-a_v \ge b_u-b_v au−av≥bu−bv,则存在从 u u u到 v v v( u ≠ v u\neq v u=v)的边。
如果存在从 V V V到所有其他顶点的路径,则顶点 V V V被称为强顶点。
有向图中的路径是由若干个顶点组成的链,通过边连接,从顶点 u u u出发,沿着边的方向,可以到达顶点 v v v。
你的任务是找到所有强顶点。
例如,如果 a = [ 3 , 1 , 2 , 4 ] a=[3,1,2,4] a=[3,1,2,4]和 b = [ 4 , 3 , 2 , 1 ] b=[4,3,2,1] b=[4,3,2,1],图表将如下所示:
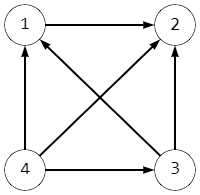
该图只有一个强顶点,编号为 4 4 4
思路
转换一下题目意思就容易了:
a u − a v > = b u − b v a_u-a_v>=b_u-b_v au−av>=bu−bv可以变为: a u − b u > = a v − b v a_u-b_u>=a_v-b_v au−bu>=av−bv,
也就是满足题意的点一定需要满足对于其他所有顶点来说,它的 a [ i ] − b [ i ] a[i]-b[i] a[i]−b[i]一定要大于其他的点,即最大值因此本题只需要统计 a [ i ] − b [ i ] a[i]-b[i] a[i]−b[i]的最大值的数有多少个即可。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl;
#define no cout << "NO" << endl;
#define IOS cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0), ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
#define cxk 1
#define debug(s, x) if (cxk) cout << "#debug:(" << s << ")=" << x << endl;
using namespace std;
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n + 1), b(n + 1), c(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> b[i], c[i] = a[i] - b[i];
int t = *std::max_element(c.begin() + 1, c.end());
vector<int> res;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) if (c[i] == t) res.push_back(i);
cout << res.size() << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); i++) cout << res[i] << " \n"[i == res.size() - 1];
}
signed main() {
IOS
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("../test.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("../test.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
E. Power of Points
题目
给你 n n n个带有整数坐标 x 1 , … x n x_1,\dots x_n x1,…xn的点,它们位于数轴上。
对于某个整数 s s s,我们构造线段[ s , x 1 s,x_1 s,x1]、[ s , x 2 s,x_2 s,x2]、 … \dots …、[ s , x n s,x_n s,xn]。请注意,如果是 x i < s x_i<s xi<s,那么该段将看起来像[ x i , s x_i,s xi,s]。线段[ a , b a, b a,b]覆盖了所有整数点 a , a + 1 , a + 2 , … , b a, a+1, a+2, \dots, b a,a+1,a+2,…,b。
我们将点 p p p的幂定义为与坐标 p p p的点相交的线段数,记为 f p f_p fp。
你的任务是计算每个 s ∈ { x 1 , … , x n } s \in \{x_1,\dots,x_n\} s∈{x1,…,xn}的 ∑ p = 1 1 0 9 f p \sum\limits_{p=1}^{10^9}f_p p=1∑109fp,即 1 1 1到 1 0 9 10^9 109所有整数点的 f p f_p fp之和。
例如,如果初始坐标为 [ 1 , 2 , 5 , 7 , 1 ] [1,2,5,7,1] [1,2,5,7,1],我们选择 s = 5 s=5 s=5,那么线段将是: [ 1 , 5 ] [1,5] [1,5], [ 2 , 5 ] [2,5] [2,5], [ 5 , 5 ] [5,5] [5,5], [ 5 , 7 ] [5,7] [5,7], [ 1 , 5 ] [1,5] [1,5]。各点的幂为: f 1 = 2 , f 2 = 3 , f 3 = 3 , f 4 = 3 , f 5 = 5 , f 6 = 1 , f 7 = 1 , f 8 = 0 , … , f 1 0 9 = 0 f_1=2, f_2=3, f_3=3, f_4=3, f_5=5, f_6=1, f_7=1, f_8=0, \dots, f_{10^9}=0 f1=2,f2=3,f3=3,f4=3,f5=5,f6=1,f7=1,f8=0,…,f109=0。他们的总和是 2 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 5 + 1 + 1 = 18 2+3+3+3+5+1+1=18 2+3+3+3+5+1+1=18。
思路
因为点的顺序不影响答案,可以先对x数组排序,例如样例里面的
1 1 2 5 7
现在计算5这个点:
如果按照题目里面的计算方式太复杂,可以考虑计算长度,例如区间 [ 1 , 5 ] [1,5] [1,5]就是把区间1-5的点全部加1,最后再统计每个点的权值,
可以转换为计算这个区间的长度即可。

代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl;
#define no cout << "NO" << endl;
#define IOS cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0), ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
#define cxk 1
#define debug(s, x) if (cxk) cout << "#debug:(" << s << ")=" << x << endl;
using namespace std;
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<pair<int, int>> a(n + 1);
vector<int> pre(n + 10), suf(n + 10);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i].first, a[i].second = i;
std::sort(a.begin() + 1, a.end());
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) pre[i] = pre[i - 1] + a[i].first;
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--) suf[i] = suf[i + 1] + a[i].first;
vector<int> res(n + 10);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int t = 1;
t += a[i].first * (i - 1) + (i - 1) - pre[i - 1];
t += suf[i + 1] + (n - i) - a[i].first * (n - i);
res[a[i].second] = t;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cout << res[i] << " \n"[i == n];
}
signed main() {
IOS
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("../test.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("../test.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
F. Sum and Product
题目
您有一个长度为 n n n的数组 a a a。
你的任务是回答 q q q个查询:给定 x , y x,y x,y,找到 a i + a j = x a_i + a_j = x ai+aj=x和 a i ⋅ a j = y a_i \cdot a_j = y ai⋅aj=y同时存在的 i i i和 j j j( 1 < = i < j < = n 1 <= i < j <= n 1<=i<j<=n)对的数量。
也就是说,对于数组 [ 1 , 3 , 2 ] [1,3,2] [1,3,2]并要求 x = 3 , y = 2 x=3,y=2 x=3,y=2,答案是 1 1 1:
- i = 1 i=1 i=1和 j = 2 j=2 j=2失败,因为 1 + 3 = 4 1 + 3 = 4 1+3=4而不是 3 , 3, 3,,也是 1 ⋅ 3 = 3 1 \cdot 3=3 1⋅3=3而不是 2 2 2;
- i = 1 i=1 i=1和 j = 3 j=3 j=3满足两个条件;
- i = 2 i=2 i=2和 j = 3 j=3 j=3失败,因为 3 + 2 = 5 3 + 2 = 5 3+2=5而不是 3 , 3, 3,,也是 3 ⋅ 2 = 6 3 \cdot 2=6 3⋅2=6而不是 2 2 2;
思路
可以先用map记录每个数字出现的次数
a [ i ] + a [ j ] = x a[i]+a[j]=x a[i]+a[j]=x
a [ i ] ∗ a [ j ] = y a[i]*a[j]=y a[i]∗a[j]=y
可以把 a [ i ] , a [ j ] a[i],a[j] a[i],a[j]看成是方程 t 2 − x t + y = 0 t^2-xt+y=0 t2−xt+y=0的两个解,这一步可以使用韦达定理,或者直接把 a [ i ] = y / a [ j ] a[i]=y/a[j] a[i]=y/a[j]带入第一个式子计算得到
韦达定理: a x 2 + b x + c = 0 ax^2+bx+c=0 ax2+bx+c=0如果有解,则满足
x 1 + x 2 = − b a x_1+x_2=-\frac{b}{a} x1+x2=−ab
x 1 ∗ x 2 = c a x_1*x_2=\frac{c}{a} x1∗x2=ac
于是题目就转换为求解满足方程的解有多少组
d e l t a = b 2 − 4 a c = x 2 − 4 y delta=b^2-4ac=x^2-4y delta=b2−4ac=x2−4y
-
如果 d e l t a < 0 delta<0 delta<0方程无解
-
如果 d e l t a = 0 delta=0 delta=0,方程有两个相同的解 x 1 = x 2 x1=x2 x1=x2,此时只需要从map中选择两个 = x 1 =x_1 =x1的数,即 C c n t 2 C_{cnt}^2 Ccnt2(cnt为=x1的个数)
-
如果 d e l t a > 0 delta>0 delta>0,需要判断是否有两个不同的整数解, x = x + − d e l t a 2 x=\frac{x+-\sqrt{delta}}{2} x=2x+−delta,判断是否为整数,为答案的贡献为 c n t 1 ∗ c n t 2 cnt1*cnt2 cnt1∗cnt2
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl;
#define no cout << "NO" << endl;
#define IOS cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0), ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
#define cxk 1
#define debug(s, x) if (cxk) cout << "#debug:(" << s << ")=" << x << endl;
using namespace std;
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
std::sort(a.begin() + 1, a.end());
map<int, int> mp;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) mp[a[i]]++;
int q;
cin >> q;
while (q--) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
int delta = x * x - 4 * y;
if (delta < 0) {
cout << 0 << endl;
} else if (delta == 0) {
cout << mp[x / 2] * (mp[x / 2] - 1) / 2 << " ";
} else {
int sq = sqrt(delta);
if (sq * sq != delta) {
cout << 0 << " ";
} else {
if ((x + sq) % 2 != 0 || (x - sq) % 2 != 0) {
cout << 0 << " ";
} else {
int x1 = (x + sq) / 2;
int x2 = (x - sq) / 2;
cout << mp[x1] * mp[x2] << " ";
}
}
}
}
cout << endl;
}
signed main() {
IOS
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("../test.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("../test.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
G. Counting Graphs
题目
给定一棵由 n n n个顶点组成的树。树是无环的连通无向图。树的每条边都有其重量, w i w_i wi。
您的任务是计算满足所有四个条件的不同图表的数量:
1、图不存在自环和重边。
2、图边的权重为整数且不超过
S
S
S。
3. 该图恰好有一个 最小生成树。
4. 图的最小生成树是给定的树。
如果两个图的边集不同,则考虑到边的权重,则认为两个图不同。
答案可以很大,输出对 998244353 998244353 998244353取模。
思路
假设现在已经有了一个最小生成树,我们现在考虑要往上面进行加边操作,显然这条加的边一定是要比两个点 x , y x,y x,y之前的权值要大,否则最小生成树就可以选择刚刚加的这条边,那么最小生成树就要变了。因为边的权值上限为 S S S,因此加的边的取值范围为 w ~ S w~S w~S,即有 S − w + 1 S-w+1 S−w+1中选择
模拟克鲁思卡尔算法求最小生成树的过程,对于两个点 x , y x,y x,y,如果他们不在同一个集合,假设左边 x x x集合的大小为 s 1 s_1 s1, y y y集合的大小为 s 2 s_2 s2,显然我可以从 x x x里面任意选一个点,从 y y y里面任意选一个点,然后这两个点之间可以加任意一条 w ~ S w~S w~S的边,都不会影响到最小生成树。
选点的组合有 s 1 ∗ s 2 − 1 s1*s2-1 s1∗s2−1个组合,,每个组合都可以选择 S − w + 1 S-w+1 S−w+1个边,方案数为: ( S − w + 1 ) s 1 ∗ s 2 − 1 (S-w+1)^{s1*s2-1} (S−w+1)s1∗s2−1
S1*s2-1的减1是因为x和y这两个点是最小生成树的点,他们之间已经有一条边为w了,不可以再加边了,否则就是重边了
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl;
#define no cout << "NO" << endl;
#define IOS cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0), ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
#define cxk 1
#define debug(s, x) if (cxk) cout << "#debug:(" << s << ")=" << x << endl;
using namespace std;
const int mod = 998244353;
struct DSU {
std::vector<int> f, siz;
DSU(int n) {
f.resize(n + 1);
siz.resize(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
f[i] = i;
siz[i] = 1;
}
}
int find(int x) {
if (x != f[x]) f[x] = find(f[x]);
return f[x];
}
bool same(int x, int y) {
return find(x) == find(y);
}
bool merge(int x, int y) {
x = find(x);
y = find(y);
if (x == y) {
return false;
}
siz[x] += siz[y];
f[y] = x;
return true;
}
int size(int x) {
return siz[find(x)];
}
};
int qmi(int a, int b) {
int res = 1;
while (b) {
if (b & 1) res = res * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
void solve() {
int n, s;
cin >> n >> s;
vector<array<int, 3>> edge(n - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) cin >> edge[i][0] >> edge[i][1] >> edge[i][2];
sort(edge.begin(), edge.end(), [](array<int, 3> a, array<int, 3> b) { return a[2] < b[2]; });
DSU dsu(n);
int res = 1;
for (auto [x, y, w]: edge) {
int s1 = dsu.size(x), s2 = dsu.size(y);
res = (res * qmi(s + 1 - w, s1 * s2 - 1)) % mod;
dsu.merge(x, y);
}
cout << res << endl;
}
signed main() {
IOS
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("../test.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("../test.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}