适配器的官方解释:openTCS 支持自定义车辆驱动程序的集成,这些驱动程序实现特定于车辆的通信协议,从而在内核和车辆之间进行调解。 由于其功能,车辆驾驶员也称为通信适配器。 openTCS适配器。欢迎随时沟通
1、源码下载
github下载:openTCS源码
2、源码运行
源码在Idea中打开,依次运行kernel,editor,desk,controller模块,依次双击运行。
运行后的页面和使用方法和上一篇说的完全一致,可以参考利用openTCS实现车辆调度系统(二)openTCS下载部署
3、车辆适配器
车辆适配器是我们通过tcs控制车辆的关键组成,适配器为我们提供了一组很有用的方法,我们只要实现这些方法,就可以实现自己的设备控制。具体可以参考官方API车辆适配器接口文档
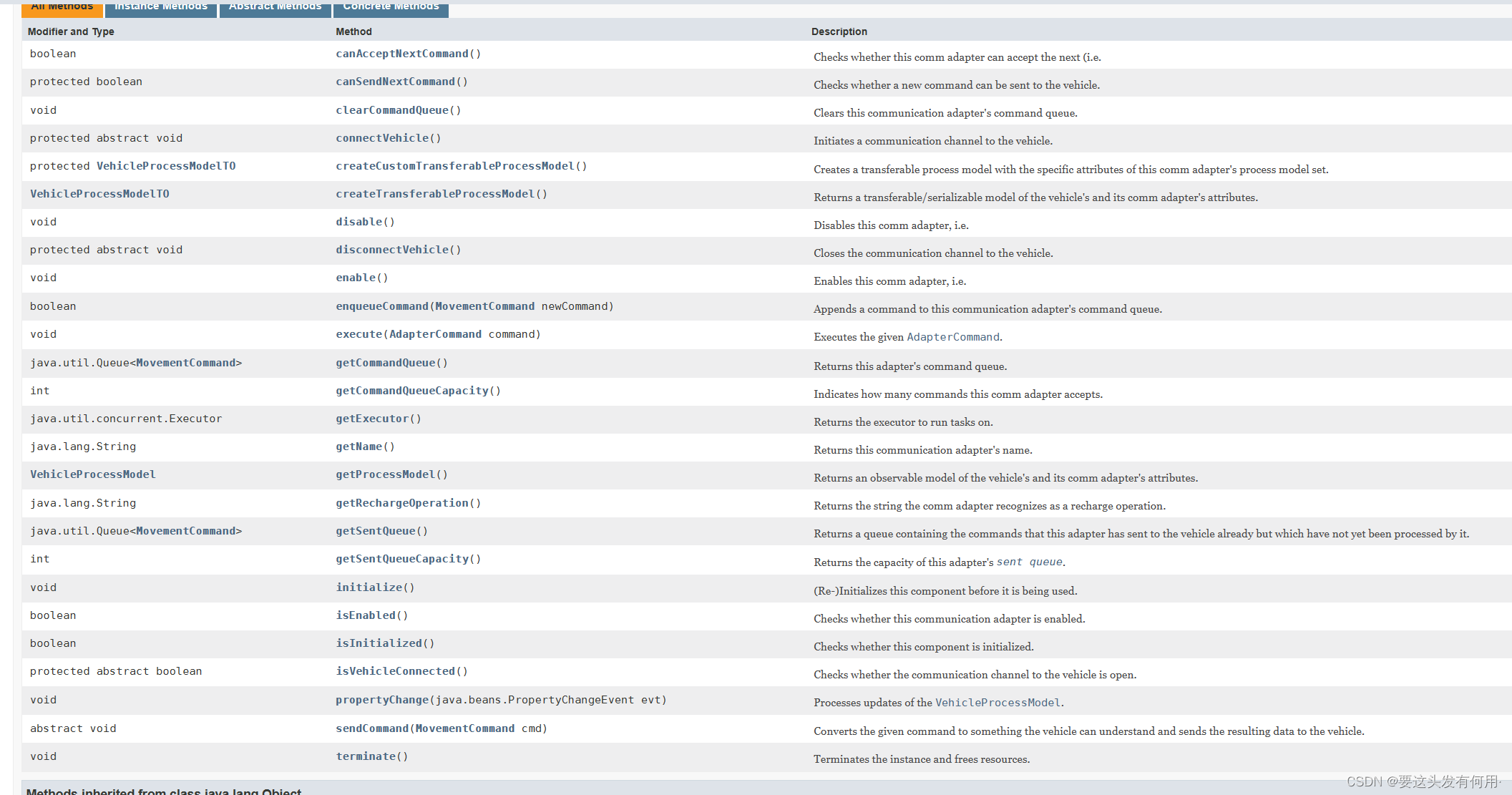
我们说几个最主要的方法,实现了这几个方法就可以让我们的车动起来。
1、enable/disable:控制车辆开启和关闭,一般开启时,我们会通过网络协议建立适配器与车辆的连接,更新连接状态。关闭时断开连接。
2、execute:执行指令,这里的指令指的是单步的调试指令,比如车辆前进、后退、顶升、充电等指令。
3、sendCommand:发送指令,这里的指令指的是订单指令,这里的指令是连续的,有前后关联的。比如我们的订单是让车辆到达地图中的某个点送货,openTCS的内核会把一整条规划路径拆分成每一步,分别发给适配器。比如下图,小车在Point-0001时,openTCS会通过sendCommand把Point-0003、Point-0004…这些点依次发给适配器。适配器将这些指令发给车辆,高速车辆去往物理中的Point-0003点。

默认适配器中,这一步是模拟执行的,适配器并没有给任何真实物理设备发信号,只是在一段时间后默认执行事件完成了。将当前步骤完成,更新地图中车辆的位置和状态等。代码如下:
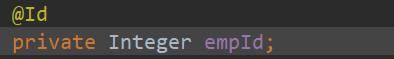
@Override
public synchronized void sendCommand(MovementCommand cmd) {
requireNonNull(cmd, "cmd");
LOG.info("==CommandQueue:{}", getCommandQueue());
// Start the simulation task is the single step modus is not active.
if (!getProcessModel().isSingleStepModeEnabled()) {
isSimulationRunning = true;
((ExecutorService) getExecutor()).submit(() -> startVehicleSimulation(cmd));
}
}
private void startVehicleSimulation(MovementCommand command) {
LOG.debug("Starting vehicle simulation for command: {}", command);
Step step = command.getStep();
getProcessModel().setVehicleState(Vehicle.State.EXECUTING);
operationSimulationTimePassed = 0;
if (step.getPath() == null) {
LOG.debug("Starting operation simulation...");
((ScheduledExecutorService) getExecutor()).schedule(() -> operationSimulation(command),
SIMULATION_TASKS_DELAY,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
else {
getProcessModel().getVelocityController().addWayEntry(
new WayEntry(step.getPath().getLength(),
maxVelocity(step),
step.getDestinationPoint().getName(),
step.getVehicleOrientation())
);
LOG.debug("Starting movement simulation...");
((ScheduledExecutorService) getExecutor()).schedule(() -> movementSimulation(command),
SIMULATION_TASKS_DELAY,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
private void movementSimulation(MovementCommand command) {
if (!getProcessModel().getVelocityController().hasWayEntries()) {
return;
}
WayEntry prevWayEntry = getProcessModel().getVelocityController().getCurrentWayEntry();
getProcessModel().getVelocityController().advanceTime(getSimulationTimeStep());
WayEntry currentWayEntry = getProcessModel().getVelocityController().getCurrentWayEntry();
//if we are still on the same way entry then reschedule to do it again
if (prevWayEntry == currentWayEntry) {
((ScheduledExecutorService) getExecutor()).schedule(() -> movementSimulation(command),
SIMULATION_TASKS_DELAY,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
else {
//if the way enties are different then we have finished this step
//and we can move on.
getProcessModel().setVehiclePosition(prevWayEntry.getDestPointName());
LOG.debug("Movement simulation finished.");
if (!command.isWithoutOperation()) {
LOG.debug("Starting operation simulation...");
((ScheduledExecutorService) getExecutor()).schedule(() -> operationSimulation(command),
SIMULATION_TASKS_DELAY,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
else {
finishVehicleSimulation(command);
}
}
}
private void operationSimulation(MovementCommand command) {
operationSimulationTimePassed += getSimulationTimeStep();
if (operationSimulationTimePassed < getProcessModel().getOperatingTime()) {
getProcessModel().getVelocityController().advanceTime(getSimulationTimeStep());
((ScheduledExecutorService) getExecutor()).schedule(() -> operationSimulation(command),
SIMULATION_TASKS_DELAY,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
else {
LOG.debug("Operation simulation finished.");
String operation = command.getOperation();
if (operation.equals(getProcessModel().getLoadOperation())) {
// Update load handling devices as defined by this operation
getProcessModel().setVehicleLoadHandlingDevices(
Arrays.asList(new LoadHandlingDevice(LHD_NAME, true))
);
}
else if (operation.equals(getProcessModel().getUnloadOperation())) {
getProcessModel().setVehicleLoadHandlingDevices(
Arrays.asList(new LoadHandlingDevice(LHD_NAME, false))
);
}
finishVehicleSimulation(command);
}
}
private void finishVehicleSimulation(MovementCommand command) {
//Set the vehicle state to idle
if (getSentQueue().size() <= 1 && getCommandQueue().isEmpty()) {
getProcessModel().setVehicleState(Vehicle.State.IDLE);
}
if (Objects.equals(getSentQueue().peek(), command)) {
// Let the comm adapter know we have finished this command.
getProcessModel().commandExecuted(getSentQueue().poll());
}
else {
LOG.warn("{}: Simulated command not oldest in sent queue: {} != {}",
getName(),
command,
getSentQueue().peek());
}
isSimulationRunning = false;
}
其中getProcessModel().commandExecuted(getSentQueue().poll());是告诉openTCS内核,该指令执行完成。与之对应的有getProcessModel().commandFailed()告诉内核,当前指令执行出错。在实际应用开发中只需要把自己的发送报文业务和接收报文加上即可。
上一篇:利用openTCS实现车辆调度系统(二)openTCS下载部署
下一篇:利用openTCS实现车辆调度系统(四)利用已有RMI接口做二次开发





![[原创]从强化学习的本质推导到PPO](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8a8e2242dc6b4ada9451b51b00015e1e.png)
![ParallelCollectionRDD [0] isEmpty at KyuubiSparkUtil.scala:48问题解决](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/09dcfa699ce941da918f243e63ffcbe0.jpeg)