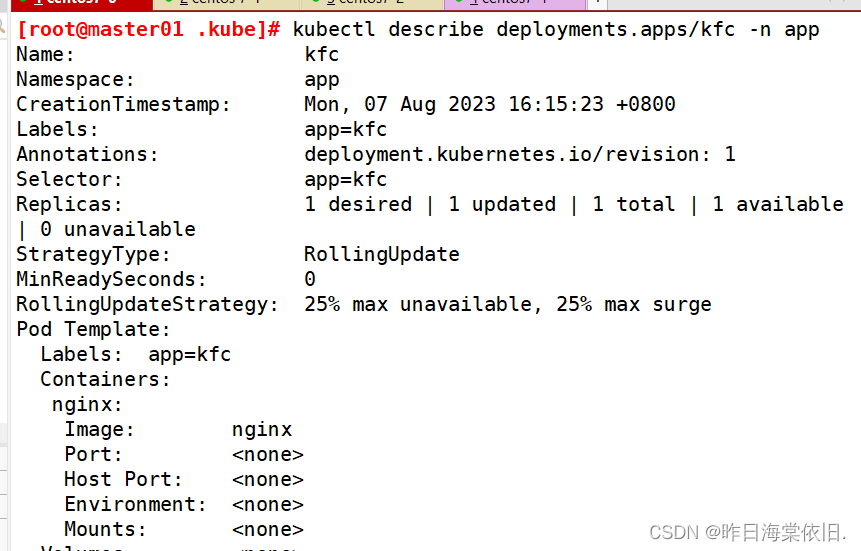
目录
专栏导读
1. JSON数据格式简介
1.1 示例JSON数据
1.2 JSON文件的特点
2 json模块的常用操作
2.1 读写JSON文件的示例
2.2 解析JSON字符串
2.3 修改JSON数据
2.4 查询和操作嵌套数据
2.5 处理包含特殊字符的JSON文件
2.6 处理日期和时间
2.7 处理大型JSON文件
2.8 格式化输出
2.9 处理嵌套结构和深层次的JSON
2.10 JSON文件读取失败如何处理
3 json 文件格式转换
3.1 JSON转换为CSV
3.2 JSON转换为XML
3. 3 JSON转换为YAML
3.4 CSV/XML/YAML转换为JSON
4 CSV/XML/YAML转换为JSON
4.1 CSV转换为JSON
4.2 XML转换为JSON
4.3 YAML转换为JSON
专栏导读
专栏订阅地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35831906/category_12375510.html

1. JSON数据格式简介
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,广泛用于数据的存储和交流。它易于人类阅读和编写,同时也易于机器解析和生成。JSON的主要特点包括:
基本结构:JSON由键值对构成,键和值之间使用冒号分隔,不同的键值对之间使用逗号分隔。JSON的数据结构可以嵌套,从而构建出复杂的数据结构。
数据类型:JSON支持多种数据类型,包括:
- 对象(Object):由花括号
{}包裹,包含键值对,键是字符串,值可以是字符串、数字、布尔值、对象、数组等。- 数组(Array):由方括号
[]包裹,包含多个值,值可以是字符串、数字、布尔值、对象、数组等。- 字符串(String):使用双引号
"包裹,可以包含任何Unicode字符。- 数字(Number):可以是整数或浮点数。
- 布尔值(Boolean):表示真或假。
- 空值(Null):表示空值或缺失数据。
1.1 示例JSON数据
{
"name": "John",
"age": 30,
"is_student": false,
"hobbies": ["reading", "swimming"],
"address": {
"street": "123 Main St",
"city": "Cityville"
}
}
1.2 JSON文件的特点
易于阅读:JSON的结构清晰,容易阅读和理解,适用于人类和机器之间的交互。
跨平台性:JSON是一种与编程语言和平台无关的格式,因此适用于不同语言和操作系统之间的数据交换。
用途广泛:JSON在网络传输、配置文件、API交互、日志记录等领域都有广泛的应用。
JSON的简洁性和可读性使其成为当今应用程序和系统之间数据交换的首选格式之一。无论是在前端和后端的开发中,还是在数据处理和存储中,都可以使用JSON来方便地表示和传递数据。
2 json模块的常用操作
json模块提供了两个主要函数:json.dumps()用于将Python对象转换为JSON格式的字符串,json.loads()用于将JSON格式的字符串解析为Python对象。此外,还有用于读写JSON文件的函数:json.dump()用于将Python对象写入JSON文件,json.load()用于从JSON文件读取数据并将其转换为Python对象。
2.1 读写JSON文件的示例
下面是一个简单的示例,演示如何使用json模块读写JSON文件:
import json
# 要写入JSON文件的数据
data = {
"name": "Alice",
"age": 25,
"is_student": True,
"hobbies": ["painting", "gardening"],
"address": {
"street": "456 Elm St",
"city": "Townsville"
}
}
# 将数据写入JSON文件
with open("data.json", "w") as json_file:
json.dump(data, json_file, indent=4) # indent用于美化输出
# 从JSON文件读取数据
with open("data.json", "r") as json_file:
loaded_data = json.load(json_file)
# 打印读取的数据
print(loaded_data)
在这个示例中,我们首先将一个Python字典写入名为"data.json"的JSON文件中,然后再从该文件中读取数据并将其加载为Python对象。加载的数据与原始数据相同,以字典的形式存储在loaded_data变量中。
2.2 解析JSON字符串
使用json.loads()函数可以将JSON格式的字符串解析为Python字典或列表。
import json
json_string = '{"name": "Bob", "age": 30}'
data = json.loads(json_string)
2.3 修改JSON数据
读取JSON数据后,你可以对其进行修改,然后再写回JSON文件。
import json
with open("data.json", "r") as json_file:
data = json.load(json_file)
# 修改数据
data["age"] = 28
with open("data.json", "w") as json_file:
json.dump(data, json_file, indent=4)
2.4 查询和操作嵌套数据
当JSON数据有嵌套结构时,你可以使用字典或列表的方式查询和操作内部数据。
import json
with open("data.json", "r") as json_file:
data = json.load(json_file)
# 查询嵌套数据
city = data["address"]["city"]
hobbies = data["hobbies"]
# 修改嵌套数据
data["address"]["city"] = "New City"
data["hobbies"].append("cooking")
2.5 处理包含特殊字符的JSON文件
有时,JSON文件中可能包含特殊字符(如Unicode转义字符)或不可打印字符。在读取和处理这些文件时,你可能需要进行解码和处理。
import json
with open("special_chars.json", "r", encoding="utf-8") as json_file:
raw_data = json_file.read()
cleaned_data = raw_data.encode("utf-8").decode("unicode_escape")
parsed_data = json.loads(cleaned_data)
print(parsed_data)
2.6 处理日期和时间
import json
from datetime import datetime
data_with_dates = {
"event": "birthday",
"date": "2023-08-07T15:30:00Z"
}
date_string = data_with_dates["date"]
parsed_date = datetime.strptime(date_string, "%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ")
print(parsed_date)
2.7 处理大型JSON文件
对于大型JSON文件,可能需要逐行读取和处理,以减少内存占用。
import json
with open("large_data.json", "r") as json_file:
for line in json_file:
data = json.loads(line)
# 处理每一行的数据
2.8 格式化输出
使用json.dump()时,可以设置indent参数来美化输出,使其更易读。
import json
data = {
"name": "Alice",
"age": 25,
"hobbies": ["painting", "gardening"]
}
with open("output.json", "w") as json_file:
json.dump(data, json_file, indent=4)
2.9 处理嵌套结构和深层次的JSON
当JSON数据具有深层次的嵌套结构时,访问和处理特定数据可能变得复杂。你可以使用递归方法来处理深层次的嵌套结构。
def get_value(data, target_key):
if isinstance(data, dict):
for key, value in data.items():
if key == target_key:
return value
if isinstance(value, (dict, list)):
result = get_value(value, target_key)
if result is not None:
return result
elif isinstance(data, list):
for item in data:
result = get_value(item, target_key)
if result is not None:
return result
return None
# 示例JSON数据
nested_data = {
"person": {
"name": "Alice",
"address": {
"street": "123 Elm St",
"city": "Townsville"
}
}
}
target_value = get_value(nested_data, "city")
print(target_value) # 输出:Townsville
2.10 JSON文件读取失败如何处理
无法成功读取JSON文件内容,导致json.load()函数报错。
确保文件路径正确,文件存在且可读。检查文件编码是否正确,通常使用utf-8编码。
import json
try:
with open("data.json", "r", encoding="utf-8") as json_file:
data = json.load(json_file)
except FileNotFoundError:
print("JSON file not found.")
except json.JSONDecodeError:
print("Error decoding JSON data.")
3 json 文件格式转换
3.1 JSON转换为CSV
CSV(Comma-Separated Values)是一种以逗号分隔字段的文本文件格式。你可以使用Python的csv模块将JSON数据转换为CSV格式。
import json
import csv
with open("data.json", "r") as json_file:
data = json.load(json_file)
with open("data.csv", "w", newline="") as csv_file:
csv_writer = csv.writer(csv_file)
# 写入表头
csv_writer.writerow(data[0].keys())
# 写入数据
for item in data:
csv_writer.writerow(item.values())
3.2 JSON转换为XML
XML(eXtensible Markup Language)是一种标记语言,用于表示结构化数据。你可以使用Python的第三方库(如xmltodict)将JSON数据转换为XML格式。
import json
import xmltodict
with open("data.json", "r") as json_file:
data = json.load(json_file)
xml_data = xmltodict.unparse({"root": data})
with open("data.xml", "w") as xml_file:
xml_file.write(xml_data)
3. 3 JSON转换为YAML
YAML(YAML Ain't Markup Language)是一种可读性高的数据序列化格式。你可以使用Python的pyyaml库将JSON数据转换为YAML格式。
import json
import yaml
with open("data.json", "r") as json_file:
data = json.load(json_file)
with open("data.yaml", "w") as yaml_file:
yaml.dump(data, yaml_file, default_flow_style=False)
3.4 CSV/XML/YAML转换为JSON
同样地,你可以将CSV、XML和YAML文件转换为JSON格式,具体方法取决于所用的库。例如,使用csv、xmltodict和pyyaml等库可以进行相应的转换。
4 CSV/XML/YAML转换为JSON
4.1 CSV转换为JSON
import csv
import json
csv_file_path = "data.csv"
json_file_path = "data_from_csv.json"
data = []
with open(csv_file_path, "r") as csv_file:
csv_reader = csv.DictReader(csv_file)
for row in csv_reader:
data.append(row)
with open(json_file_path, "w") as json_file:
json.dump(data, json_file, indent=4)
4.2 XML转换为JSON
假设你有一个XML文件 data.xml:
<root>
<item>
<name>John</name>
<age>30</age>
</item>
<item>
<name>Alice</name>
<age>25</age>
</item>
</root>
下面是将XML转换为JSON的示例代码:
import xmltodict
import json
xml_file_path = "data.xml"
json_file_path = "data_from_xml.json"
with open(xml_file_path, "r") as xml_file:
xml_data = xml_file.read()
json_data = json.dumps(xmltodict.parse(xml_data), indent=4)
with open(json_file_path, "w") as json_file:
json_file.write(json_data)
4.3 YAML转换为JSON
假设你有一个YAML文件 data.yaml:
- name: John
age: 30
- name: Alice
age: 25
下面是将YAML转换为JSON的示例代码:
import yaml
import json
yaml_file_path = "data.yaml"
json_file_path = "data_from_yaml.json"
with open(yaml_file_path, "r") as yaml_file:
yaml_data = yaml.safe_load(yaml_file)
json_data = json.dumps(yaml_data, indent=4)
with open(json_file_path, "w") as json_file:
json_file.write(json_data)


![[CKA]考试之查看pod的cpu](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9fe6ab939c344c4488afd104a6b9f3ae.png)