前言
本文记录个人使用MySQL插入大数据总结较实用的方案,通过对常用插入大数据的4种方式进行测试,
- for循环单条
- 拼接SQL
- 批量插入saveBatch()
- 循环 + 开启批处理模式
最近趁空闲之余,在对MySQL数据库进行插入数据测试
准备工作
测试环境:SpringBoot项目、MyBatis-Plus框架、MySQL5.7、JDK8
前提:SpringBoot项目集成MyBatis-Plus上述文章有配置过程,同时实现IService接口用于进行批量插入数据操作saveBatch()方法
创建springboot项目和数据库
github:demo代码地址
maven依赖
pom
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>springboot-demo</artifactId>
<groupId>com.cainiao</groupId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>springboot-save-batch</artifactId>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>springboot-save-batch</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.34</version>
</dependency>
<!--mybatisPlus-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-generator</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.freemarker</groupId>
<artifactId>freemarker</artifactId>
<version>2.3.28</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<!--lombok :getter/setter方法以及构造器的生成 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<!-- 引入阿里数据库连接池 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
applocation.yml
# 配置端口
server:
port: 8089
servlet:
context-path: /caimiao
spring:
# 配置数据源
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/cainiao?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&sessionVariables=sql_mode=NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION
username: root
password: 123456
# type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
# druid:
# initialSize: 5 #初始化连接大小
# minIdle: 5 #最小连接池数量
# maxActive: 20 #最大连接池数量
# maxWait: 60000 #获取连接时最大等待时间,单位毫秒
# timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000 #配置间隔多久才进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接,单位是毫秒
# minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000 #配置一个连接在池中最小生存的时间,单位是毫秒
# validationQuery: SELECT 1 from DUAL #测试连接
# testWhileIdle: true #申请连接的时候检测,建议配置为true,不影响性能,并且保证安全性
# testOnBorrow: false #获取连接时执行检测,建议关闭,影响性能
# testOnReturn: false #归还连接时执行检测,建议关闭,影响性能
# poolPreparedStatements: false #是否开启PSCache,PSCache对支持游标的数据库性能提升巨大,oracle建议开启,mysql下建议关闭
# maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20 #开启poolPreparedStatements后生效
# filters: stat,wall,log4j #配置扩展插件,常用的插件有=>stat:监控统计 log4j:日志 wall:防御sql注入
# connectionProperties: 'druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=5000' #通过connectProperties属性来打开mergeSql功能;慢SQL记录
# mybatis-plus相关配置
mybatis-plus:
# xml扫描,多个目录用逗号或者分号分隔(告诉 Mapper 所对应的 XML 文件位置)
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
# 以下配置均有默认值,可以不设置
global-config:
db-config:
#主键类型 AUTO:"数据库ID自增" INPUT:"用户输入ID",ID_WORKER:"全局唯一ID (数字类型唯一ID)", UUID:"全局唯一ID UUID";
id-type: auto
#字段策略 IGNORED:"忽略判断" NOT_NULL:"非 NULL 判断") NOT_EMPTY:"非空判断"
field-strategy: NOT_EMPTY
#数据库类型
db-type: MYSQL
configuration:
# 是否开启自动驼峰命名规则映射:从数据库列名到Java属性驼峰命名的类似映射
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
# 如果查询结果中包含空值的列,则 MyBatis 在映射的时候,不会映射这个字段
call-setters-on-nulls: true
# 这个配置会将执行的sql打印出来,在开发或测试的时候可以用
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
swagger:
enable: true
实验数据库表创建
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`addr` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
开始测试
简明:完成准备工作后,即对for循环、拼接SQL语句、批量插入saveBatch()、循环插入+开启批处理模式,该4种插入数据的方式进行测试性能。
向数据库中插入5w条数据
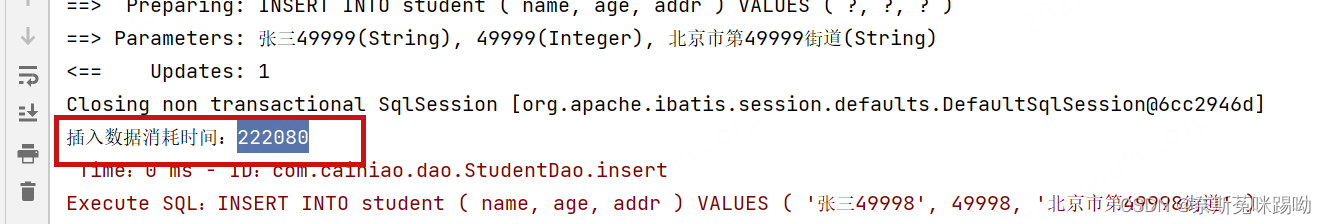
for循环
@GetMapping("for")
public void saveStudent(){
// 开始时间
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++){
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("张三" + i);
student.setAge(i);
student.setAddr("北京市第"+i+"街道");
studentDao.insert(student);
}
// 结束时间
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("插入数据消耗时间:" + (endTime - startTime));
}
执行耗时:222080 大约222秒
拼接sql
简明:拼接格式:insert into student(xxxx) value(xxxx),(xxxx),(xxxxx)…
@ApiOperation("sql批量插入")
@GetMapping("sql")
public void saveSqlStudent(){
// 开始时间
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++){
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("李四" + i);
student.setAge(i);
student.setAddr("北京市第"+i+"街道");
studentList.add(student);
}
studentDao.saveList(studentList);
// 结束时间
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("插入数据消耗时间:" + (endTime - startTime));
}
Dao:
void saveList(@Param("list") List<Student> studentList);
mapper.xml
<insert id="saveList">
INSERT INTO student(name,age,addr) VALUES
<foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index" separator=",">
(#{item.name},
#{item.age},
#{item.addr})
</foreach>
</insert>
执行时间:2971 大约2.9秒
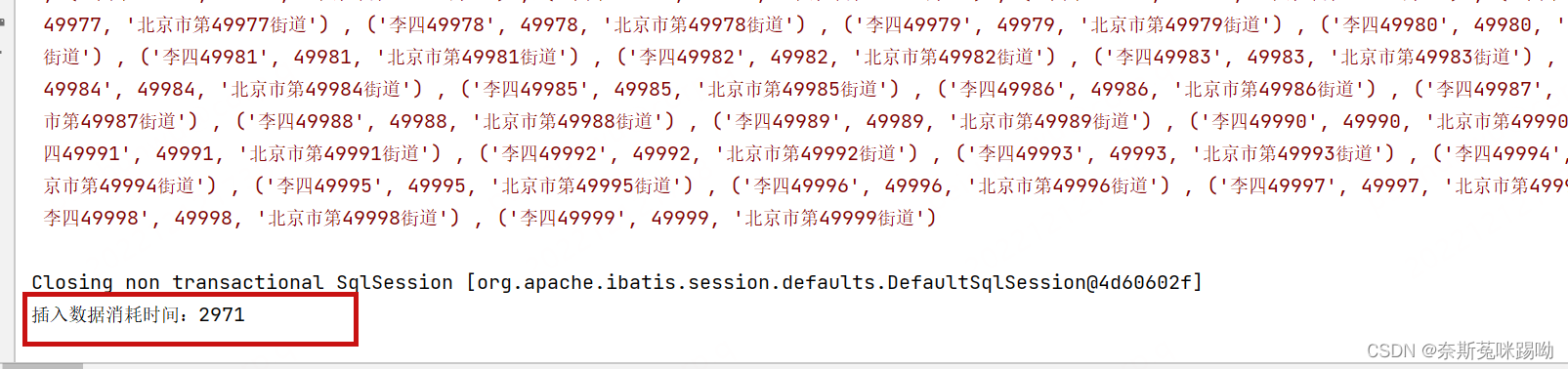
总结:拼接结果就是将所有的数据集成在一条SQL语句的value值上,其由于提交到服务器上的insert语句少了,网络负载少了,性能也就提上去。
但是当数据量上去后,可能会出现内存溢出、解析SQL语句耗时等情况,但与第一点相比,提高了极大的性能。
批量插入saveBatch
简明:使用MyBatis-Plus实现IService接口中批处理saveBatch()方法,对底层源码进行查看时,可发现其实是for循环插入,但是与第一点相比,为什么性能上提高了呢?因为利用分片处理(batchSize = 1000) + 分批提交事务的操作,从而提高性能,并非在Connection上消耗性能。
@ApiOperation("batch批量插入")
@GetMapping("batch")
public void saveBatchStudent(){
// 开始时间
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++){
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("李四" + i);
student.setAge(i);
student.setAddr("北京市第"+i+"街道");
studentList.add(student);
}
studentDao.saveList(studentList);
// 结束时间
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("插入数据消耗时间:" + (endTime - startTime));
}
执行时间:118409秒 约118秒

重点注意:MySQL JDBC驱动默认情况下忽略saveBatch()方法中的executeBatch()语句,将需要批量处理的一组SQL语句进行拆散,执行时一条一条给MySQL数据库,造成实际上是分片插入,即与单条插入方式相比,有提高,但是性能未能得到实质性的提高。
所以需要数据库链接开启rewriteBatchedStatements = true
我们开启之后再执行一遍:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/cainiao?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&rewriteBatchedStatements=true&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&sessionVariables=sql_mode=NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION
执行时间:85155 约85秒
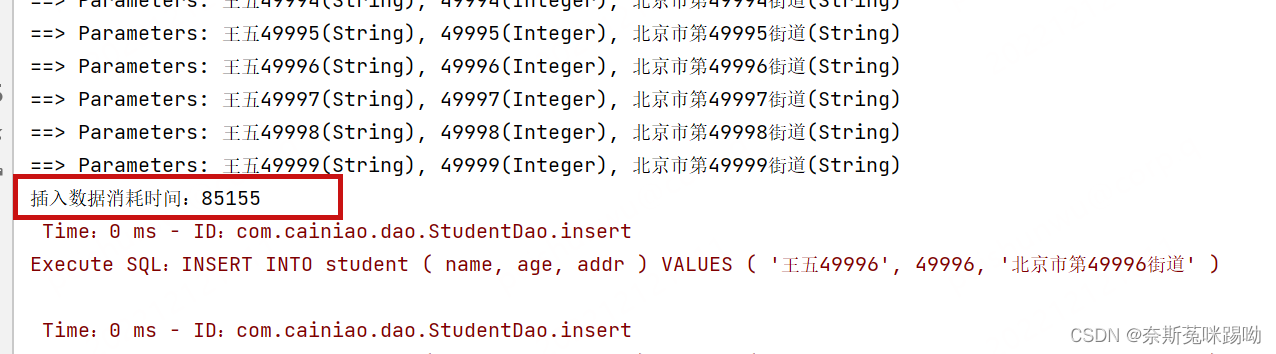
循环插入 + 开启批处理模式(总耗时:1.7秒)(重点:一次性提交)
@ApiOperation("forSaveBatch批量插入")
@GetMapping("/forSaveBatch")
public void forSaveBatch(){
// 开启批量处理模式 BATCH 、关闭自动提交事务 false
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(ExecutorType.BATCH,false);
// 反射获取,获取Mapper
StudentDao studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0 ; i < 50000 ; i++){
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("王五" + i);
student.setAge(i);
student.setAddr("北京市第"+i+"街道");
studentMapper.insert(student);
}
// 一次性提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
// 关闭资源
sqlSession.close();
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("总耗时: " + (endTime - startTime));
}
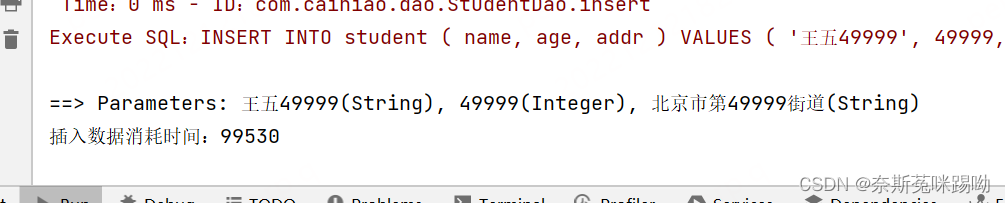
执行时间:99530 约99秒
总结
MySQL插入大数据一些方案心得,可得知主要是在获取连接、关闭连接、释放资源和提交事务等方面较耗能,其中最需要注意是开启批处理模式,即URL地址的参数:rewriteBatchedStatements = true,否则也无法发挥作用。





![[附源码]Node.js计算机毕业设计大学生专业实习管理系统Express](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3359d3627318414bbf610987b5339a6a.png)



![[附源码]Node.js计算机毕业设计大学体育馆预约系统Express](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/940f01914e5f48b5b7d47ede3f96e9fc.png)