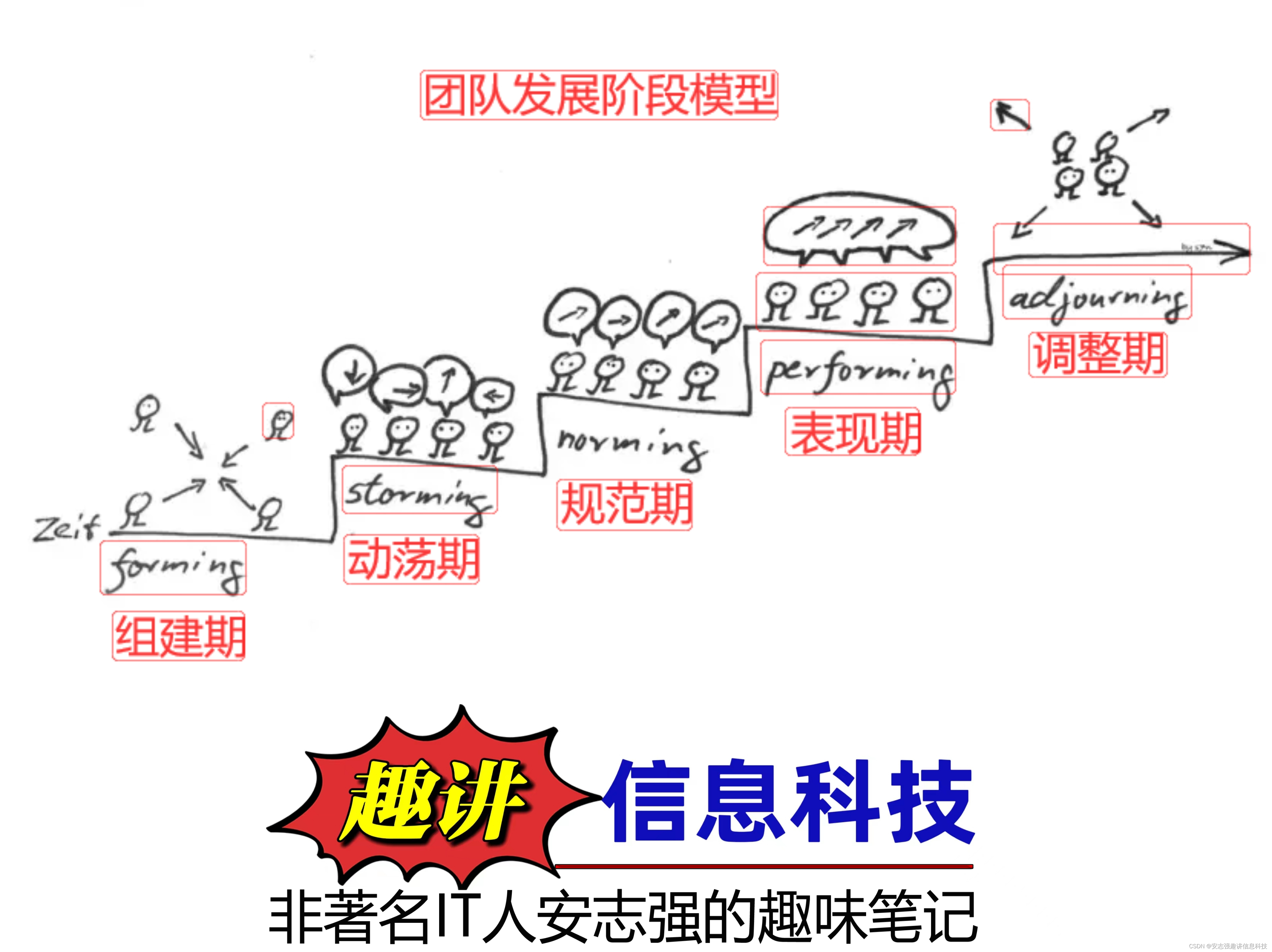
本文主要讨论在系统磁盘分区空间不足时,如何使用gpart命令在线对磁盘分区进行调整和扩容。主要包括以下几个步骤:
- 备份文件系统
- 删除不用的分区
- 对目标分区进行扩容
- 调整目标文件系统
- 划分剩余磁盘空间
本文使用的软件版本:
- FreeBSD 13.2-RELEASE
- gpart 系统自带磁盘工具
一直以来,对磁盘进行分区都是一个技术活。分几个区,每个区分多少空间大概是每个人拿到一个新电脑以后首先要考虑的问题。然而,即使在最开始时规划得再精细,用上几年之后总会有几个磁盘让人感觉捉襟见肘。这时,如果不打算换硬盘,那么使用工具对磁盘分区进行调整可能就是接下来必须要考虑的问题了。
Windows操作系统自带的“磁盘管理器”可以查看和管理磁盘分区,也可以对磁盘分区进行扩展和压缩等操作;Linux操作系统中有一个GParted磁盘分区工具,以图形化的方式对磁盘进行管理操作;gpart是FreeBSD操作系统提供的针对磁盘分区GEOM类的控制实用程序,可用于对磁盘分区进行创建、删除、调整、修改、备份、恢复、显示、查看等操作。
0 磁盘分区与文件系统现状
在一个8G的USB磁盘上安装操作系统时,对空间使用量估计不足,分出一个4G的分区作为根分区,正常情况下使用率大概在60%左右,基本算是够用了。昨天在系统中安装tomcat 10时,依赖安装了openjdk 11和llvm(Low Level Virtual Machine) 15,磁盘一下子就不够用了,可用空间为负数,使用率也飙升到了105%,看来得想点办法给这个分区扩一下容了。
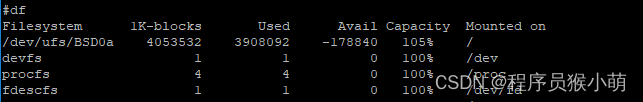
使用gpart查看磁盘信息如下:
# gpart list da0
Geom name: da0
modified: false
state: OK
fwheads: 255
fwsectors: 63
last: 15630335
first: 0
entries: 8
scheme: BSD
Providers:
1. Name: da0a
Mediasize: 4294967296 (4.0G)
Sectorsize: 512
Mode: r1w1e2
rawtype: 7
length: 4294967296
offset: 0
type: freebsd-ufs
index: 1
end: 8388607
start: 0
2. Name: da0b
Mediasize: 536870912 (512M)
Sectorsize: 512
Stripesize: 0
Stripeoffset: 4294967296
Mode: r0w0e0
rawtype: 1
length: 536870912
offset: 4294967296
type: freebsd-swap
index: 2
end: 9437183
start: 8388608
3. Name: da0d
Mediasize: 3170893824 (3.0G)
Sectorsize: 512
Stripesize: 0
Stripeoffset: 4831838208
Mode: r1w1e2
rawtype: 7
length: 3170893824
offset: 4831838208
type: freebsd-ufs
index: 4
end: 15630335
start: 9437184
Consumers:
1. Name: da0
Mediasize: 8002732032 (7.5G)
Sectorsize: 512
Mode: r2w2e6可以看到,da0为挂载的USB磁盘,可用空间为7.5G,共有3个分区。第一个分区为da0a,4G,根分区;第2个分区为da0b,512M,交换分区;第3个分区为da0d,3.0G,/var分区,暂时未用。
根据目前的使用情况,要想对第一个分区扩容,就需要压缩第3个分区的容量。幸好第3个分区当前未使用,可以对其进行删除操作。所以此次在线扩容调整的步骤就是:
(1)备份文件系统
(2)删除不用的分区
(3)对目标分区进行扩容
(4)调整目标文件系统
(5)划分剩余磁盘空间
现在就开始吧。
1 备份
(1)备份文件系统
在开始操作之前,一定要注意,备份数据!数据很重要,一旦丢失就再也找不回来了。即使有一定的把握,也不要忘记备份,切记!切记!切记!
tar zcvf /BACKUP_DEVICE/da0a-backup-20230805.tar.gz /
注意:这里的BACKUP_DEVICE一定不要是将要操作的USB磁盘,不然备份就没有意义了。
(2)备份磁盘分区表
除了备份文件系统之外,磁盘分区表也非常重要,需要进行备份,以便在误操作后可以及时恢复。
gpart的backup命令选项可以用来将分区表转储到标准输出,这种特殊格式的输出可以保存到文件中,记录了分区的类型和每个分区的起始扇区,方便restore命令进行恢复操作,命令格式如下:
gpart backup geom
backup Dump a partition table to standard output in a special
format used by the restore action.磁盘分区备份结果如下:

2 删除不用的分区
(1)删除分区
gpart 工具的delete命令选项可以用来删除不用的分区,命令格式如下:
gpart delete -i index [-f flags] geom
delete Delete a partition from geom geom and further identified by
the -i index option. The partition cannot be actively used
by the kernel.
The delete command accepts these options:
-f flags Additional operational flags. See the section
entitled OPERATIONAL FLAGS below for a
discussion about its use.
-i index Specifies the index of the partition to be
deleted.其中,-i选项用于指定要删除的分区的索引,一般从1开始(程序员们要注意了,不是从0开始)。特别是使用BSD分区模式时,3号分区是永远都不会出现的,所以da0d对应的是4号分区,da0b对应的是2号分区。
#gpart delete -i 4 da0
da0d deleted
#gpart delete -i 2 da0
da0b deleted(2)查看删除后的磁盘分区信息
使用gpart list命令查看新磁盘信息:
#gpart list
Geom name: da0
modified: false
state: OK
fwheads: 255
fwsectors: 63
last: 15630335
first: 0
entries: 8
scheme: BSD
Providers:
1. Name: da0a
Mediasize: 4294967296 (4.0G)
Sectorsize: 512
Mode: r1w1e2
rawtype: 7
length: 4294967296
offset: 0
type: freebsd-ufs
index: 1
end: 8388607
start: 0
Consumers:
1. Name: da0
Mediasize: 8002732032 (7.5G)
Sectorsize: 512
Mode: r1w1e3可以看到,这个7.5G的USB盘只剩下一个da0a分区了,其编号为1。
3 对目标分区进行扩容
(1)分区扩容
gpart工具的resize命令选项可以对分区容量进行修改,命令格式如下:
gpart resize -i index [-a alignment] [-s size] [-f flags] geom
resize Resize a partition from geom geom and further identified by
the -i index option. If the new size is not specified it
is automatically calculated to be the maximum available
from geom.
The resize command accepts these options:
-a alignment If specified, then the gpart utility tries to
align partition size to be a multiple of the
alignment value.
-f flags Additional operational flags. See the
section entitled OPERATIONAL FLAGS below for
a discussion about its use.
-i index Specifies the index of the partition to be
resized.
-s size Specifies the new size of the partition, in
logical blocks. A SI unit suffix is allowed.
其中-i选项用于指定分区,一定要注意核对,以避免错误。-s选项用于指定分区大小,如果新的分区大小未指定,则会自动计算并分配最大的空间给这个分区。
使用resize命令将da0磁盘的第一个分区扩容到6G:
#gpart resize -i 1 -s 6G da0
da0a resized(2)查看扩容后的磁盘分区信息
使用gpart list命令查看扩容后的磁盘信息:
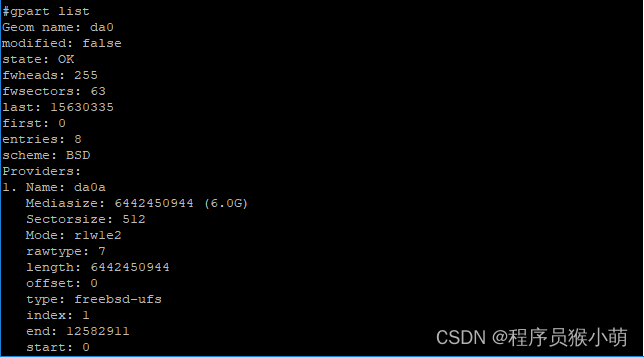
可以看到,当前磁盘的第1个分区已经被扩容到了6G。
(3)查看文件系统信息
前面我们知道,这个扩容后的da0a分区被挂载为根分区,查看文件挂载信息如下:
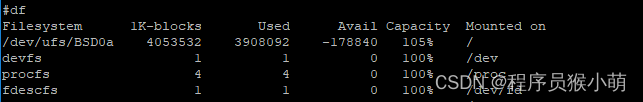
可以看到,虽然分区已被扩容到6G,但是在其上创建文件系统却依然保持不变,也就是说,扩容出来的空间并没有文件系统被利用。扩容工作还没有完成,下一步就该让这些扩出来的空间被文件系统识别和利用。
4 调整目标文件系统
FreeBSD文件系统提供了一个growfs命令,用于扩展一个存在的UFS文件系统,命令格式如下:
growfs [-Ny] [-s size] special | filesystem
DESCRIPTION
The growfs utility makes it possible to expand an UFS file system.
Before running growfs the partition or slice containing the file system
must be extended using gpart(8). If you are using volumes you must
enlarge them by using gvinum(8). The growfs utility extends the size of
the file system on the specified special file. The following options are
available:
-N “Test mode”. Causes the new file system parameters to be printed
out without actually enlarging the file system.
-y Causes growfs to assume yes as the answer to all operator
questions.
-s size
Determines the size of the file system after enlarging in
sectors. Size is the number of 512 byte sectors unless suffixed
with a b, k, m, g, or t which denotes byte, kilobyte, megabyte,
gigabyte and terabyte respectively. This value defaults to the
size of the raw partition specified in special (in other words,
growfs will enlarge the file system to the size of the entire
partition).其中,-s选项用到确定增大后的文件系统,其默认值为所在分区的大小,也就是全部占用这个磁盘分区。
使用growfs命令时,注意参数不能写成未挂载文件系统的磁盘分区名。我们知道磁盘的第一个分区da0a里面确实是根文件系统,使用growfs扩容da0a时
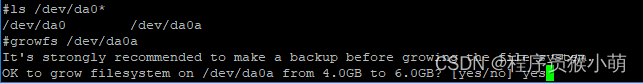
则会给出操作不允许的提示:
growfs: /dev/da0a: Operation not permitted这个磁盘与其他磁盘稍微有点不一样,文件系统都是按照UFS名称挂载的,如根文件系统其实是挂在/dev/ufs/BSD0a这个设备上的,使用这个设备名来扩容文件系统:
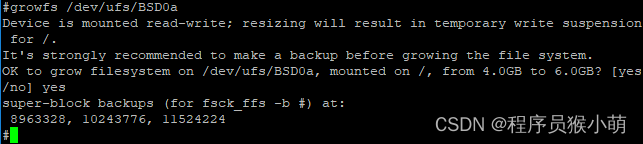
可以看到,文件系统被成功扩容到了6.0G。
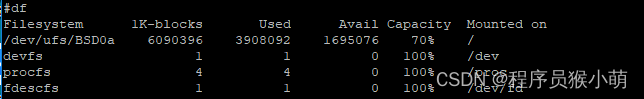
这时,分区使用率也降到了70%,可用空间也不再是负数了。根分区的扩容成功了!
5 划分剩余磁盘空间
根分区扩容成功后,整个USB磁盘还剩下约1.5G的空间未使用,可通过如下命令重建两个分区:
# gpart add -a 4K -t freebsd-swap -s 512M da0
da0b added
# gpart add -a 4K -t freebsd-ufs da0
da0d added然后,使用newfs命令分别在这两个分区上创建文件系统:
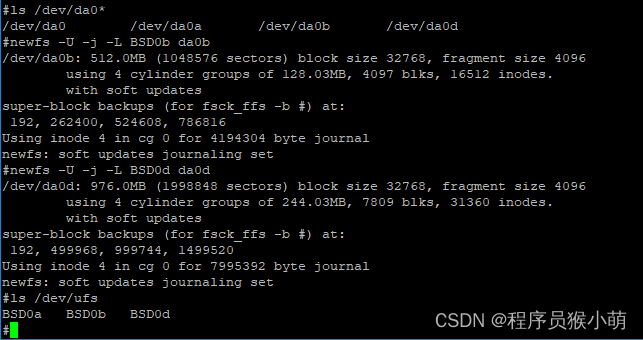
至此,大功告成!
声明:本文是作者在自有USB磁盘上的一次操作记录,用于帮助大家更好地了解gpart、growfs和newfs等系统操作命令,对于未按要求进行备份而导致数据丢失等意外情况不承担任何责任。