Background
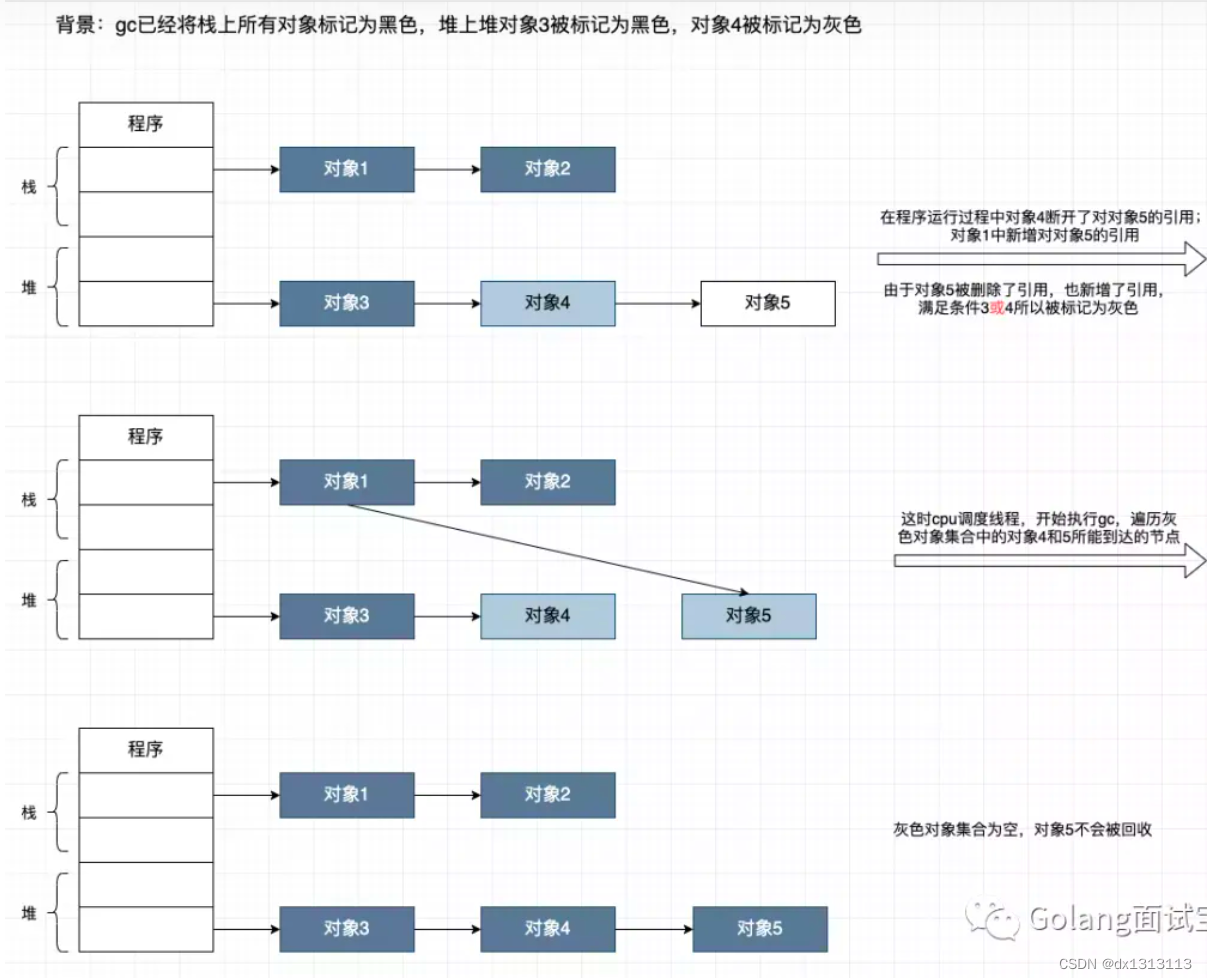
首先完成这个实验我们需要理清线程怎么启动的和切换的
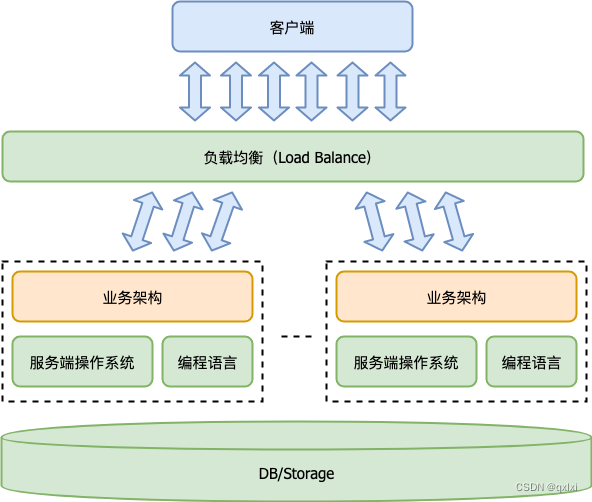
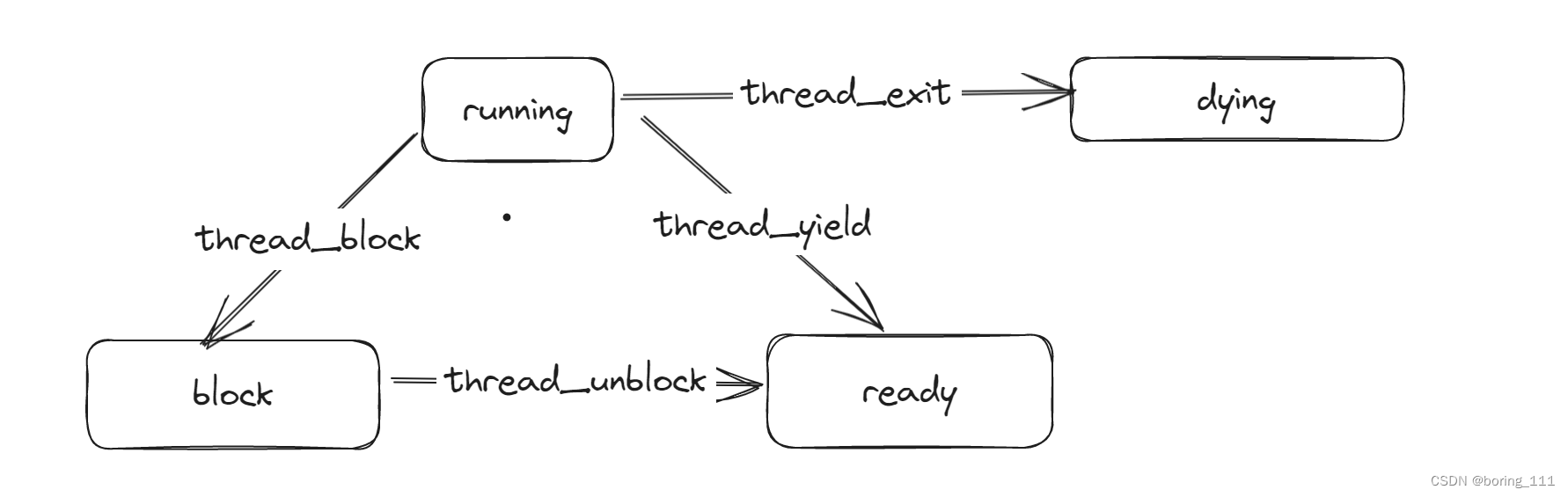
下面这张图可以大体表示线程状态的切换
让我们看看thread init的前世今生吧(:
从start.S汇编调用了一个c函数

pintos_init初始化了一堆东西,当然里面也包括了thread啦
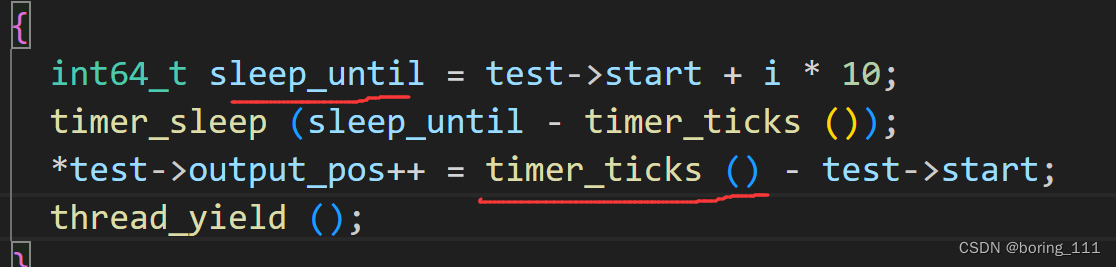
int
pintos_init (void)
{
char **argv;
/* Clear BSS. */
bss_init ();
/* Break command line into arguments and parse options. */
argv = read_command_line ();
argv = parse_options (argv);
/* Initialize ourselves as a thread so we can use locks,
then enable console locking. */
thread_init ();
console_init ();
/* Greet user. */
printf ("Pintos booting with %'"PRIu32" kB RAM...\n",
init_ram_pages * PGSIZE / 1024);
/* Initialize memory system. */
palloc_init (user_page_limit);
malloc_init ();
paging_init ();
/* Segmentation. */
#ifdef USERPROG
tss_init ();
gdt_init ();
#endif
/* Initialize interrupt handlers. */
intr_init ();
timer_init ();
kbd_init ();
input_init ();
#ifdef USERPROG
exception_init ();
syscall_init ();
#endif
/* Start thread scheduler and enable interrupts. */
thread_start ();
serial_init_queue ();
timer_calibrate ();
#ifdef FILESYS
/* Initialize file system. */
ide_init ();
locate_block_devices ();
filesys_init (format_filesys);
#endif
printf ("Boot complete.\n");
if (*argv != NULL) {
/* Run actions specified on kernel command line. */
run_actions (argv);
} else {
//...
}
//...
} 初始化init线程也叫main线程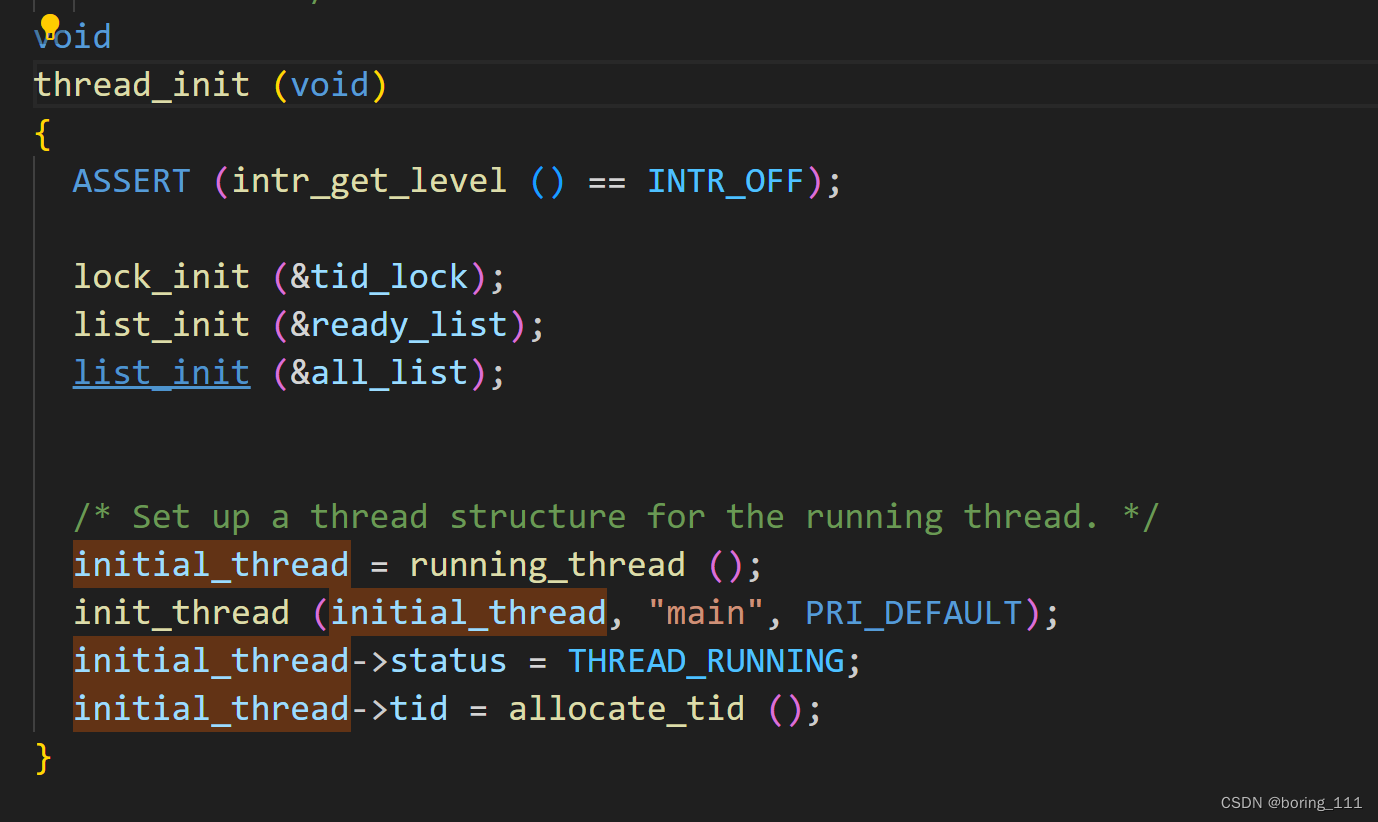
让我们从最开始开始,我们还要初始化一个init_thread, idel_thread放到ready_list里面,为了即使一个线程也可以做tswith.有点链表哑结点那味。
void
thread_start (void)
{
/* Create the idle thread. */
struct semaphore idle_started;
sema_init (&idle_started, 0);
thread_create ("idle", PRI_MIN, idle, &idle_started);
/* Start preemptive thread scheduling. */
intr_enable ();
/* Wait for the idle thread to initialize idle_thread. */
sema_down (&idle_started);
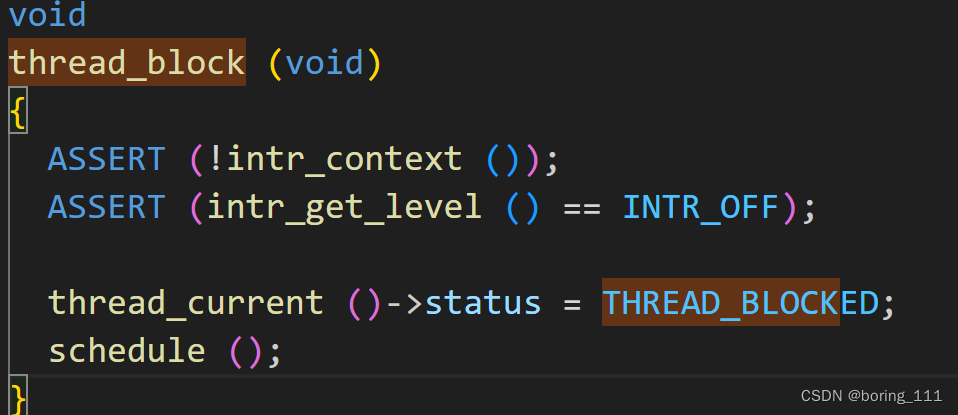
}然后就是thread_unblock,thread_block
一般是sleep,或者lock阻塞才用到,把状态变为block
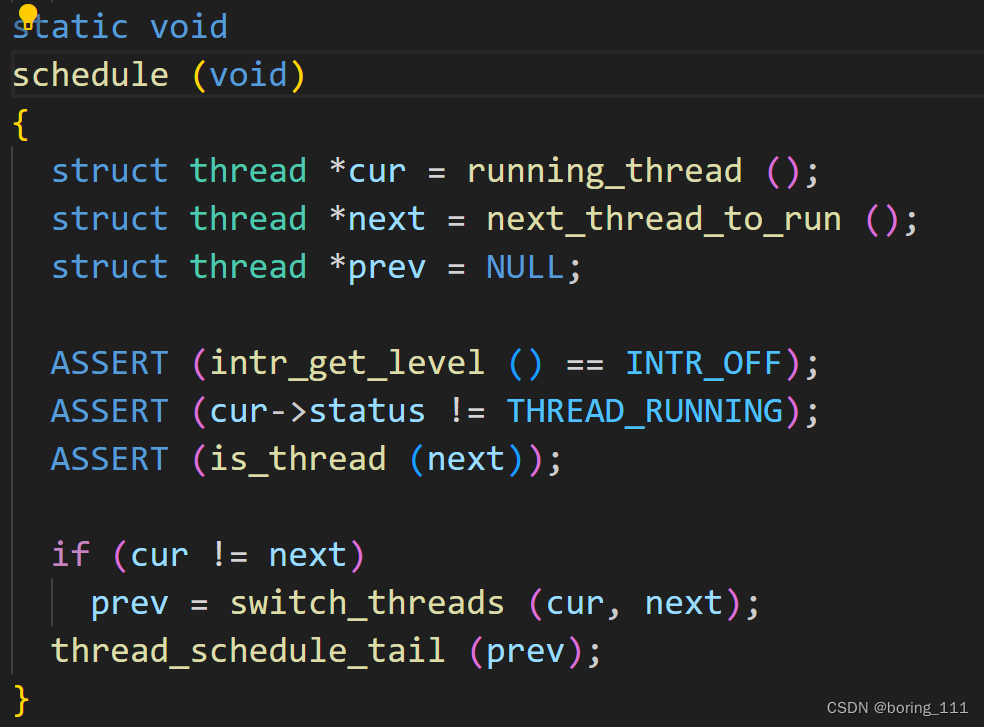
在ready_list里面选择优先级最高的,然后切换线程上下文
然后就是thread_schedule_tail:Completes a thread switch by activating the new thread's page
tables, and, if the previous thread is dying, destroying it。还有就是设置一下struct thread*的状态
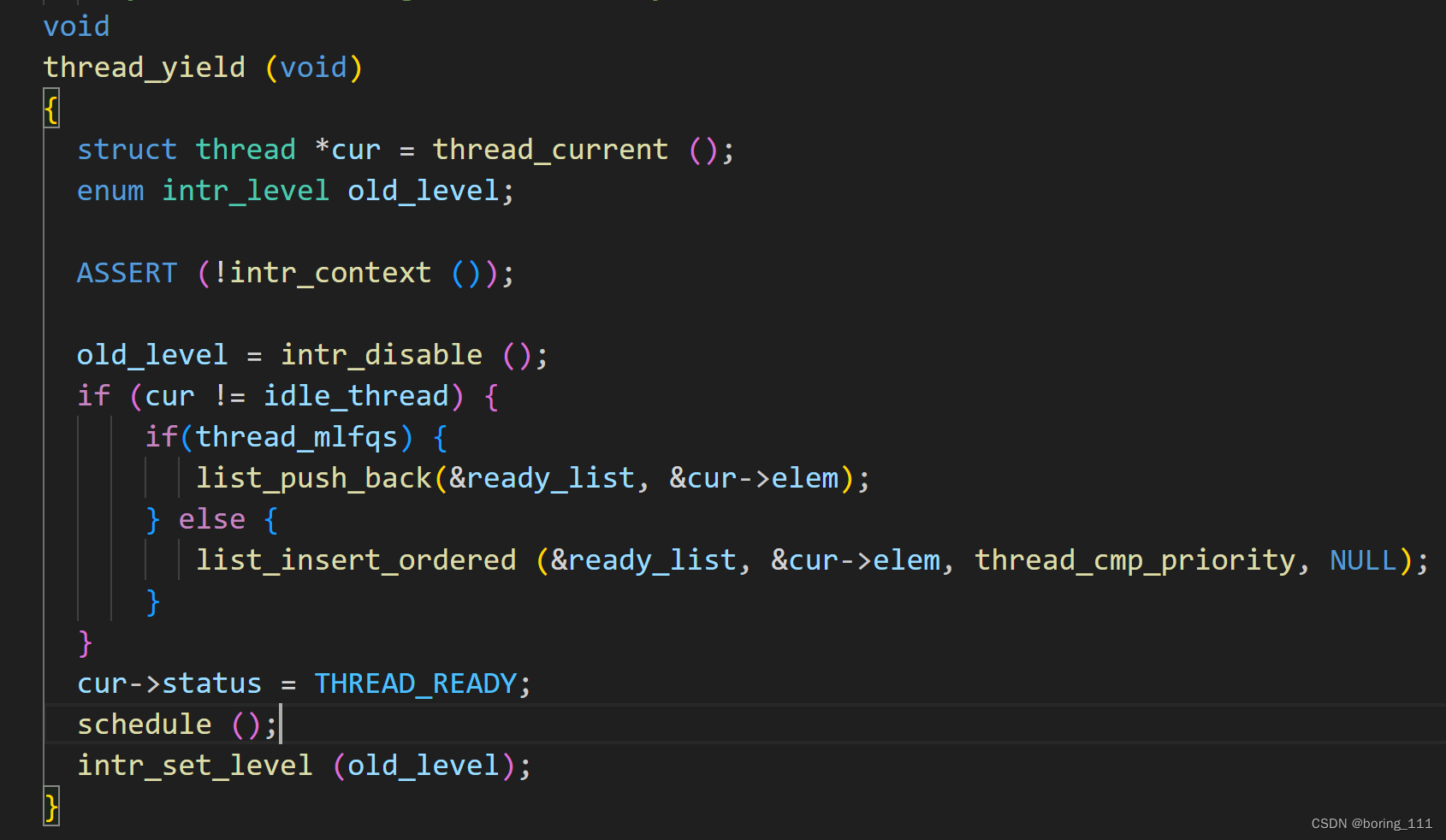
thread_unblock就是把线程插入到ready_list里面等待调度。
thread_yield就是出让cpu给别的线程,自己放入ready_list里面
thread_exit不言自明

然后关于时间片这个概念,我们要先从一个硬件中断定时器说起,实际上这个也是单核上能做到并发假象的关键,如果我们关中断的话,就是一个串行程序了,这个debug时可以用的一个trick
注册一个中断函数。

中断函数来做提高时间,可能这个时间就是本地时钟吧,sleep_tick来唤醒sleep的线程
thread_tick 来做一个时间片耗尽后的出让,也就是thread_yiled()

大体背景也就是这样,实际上说到这,后面的lab也就是修修补补
分三个部分来讲吧
lab内容
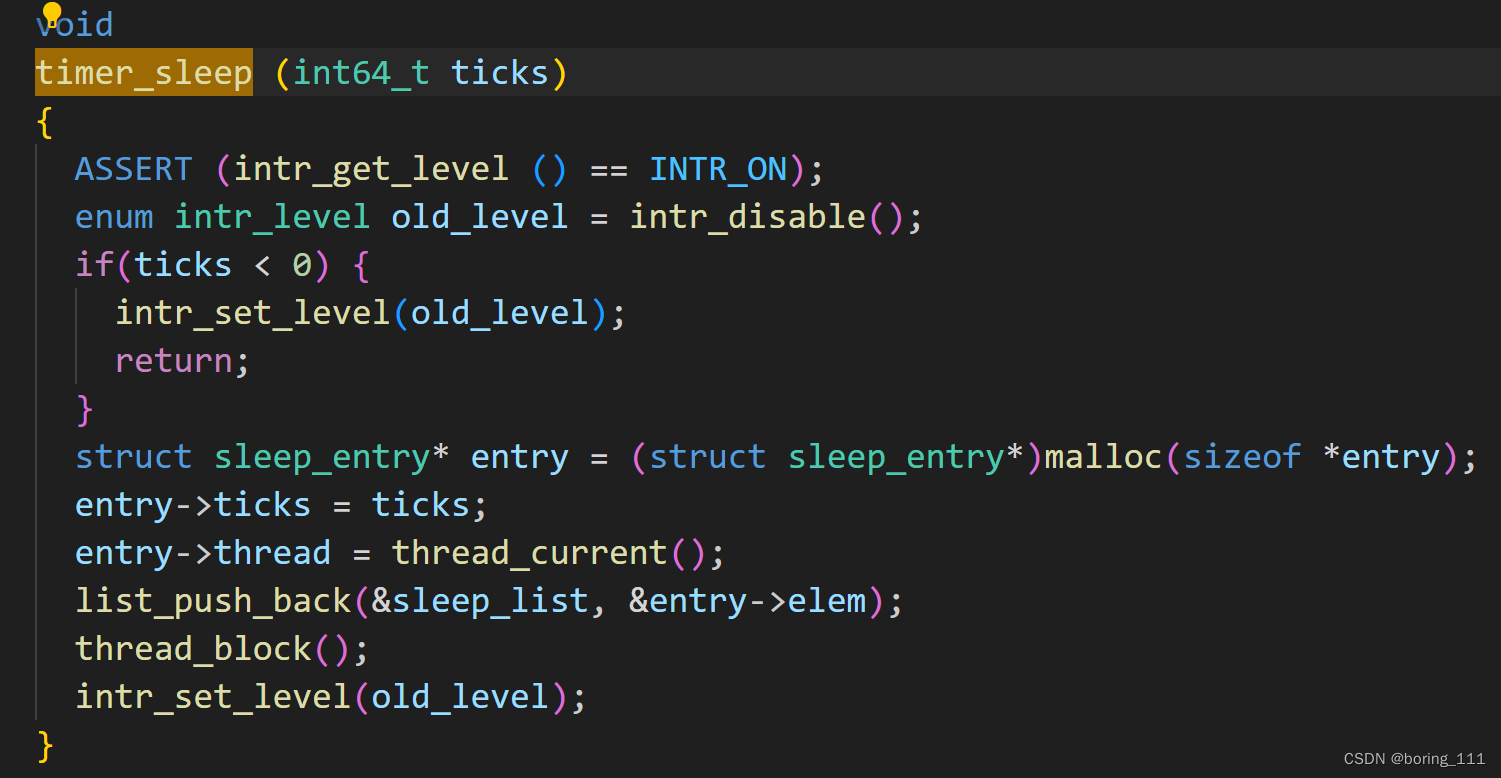
lab1.1 实现 sleep
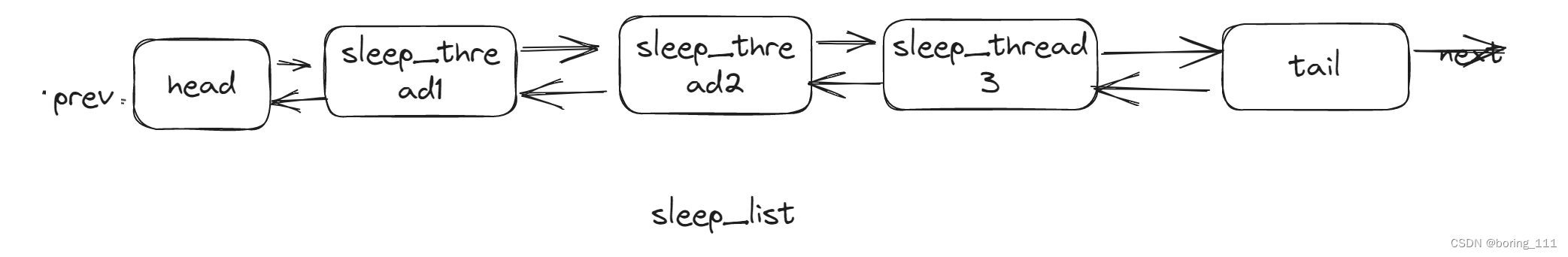
然后记录下ticks,然后等中断时,遍历减一
lab1.2 实现优先级调度和优先级捐赠
优先级调度就是ready_list按thread priority做排序,然后每次run_next_thread的时,取优先级最大的
但是在持有锁的情况下,可能发生不符合我们预期的事,这就是优先级翻转,解决办法就是优先级捐赠
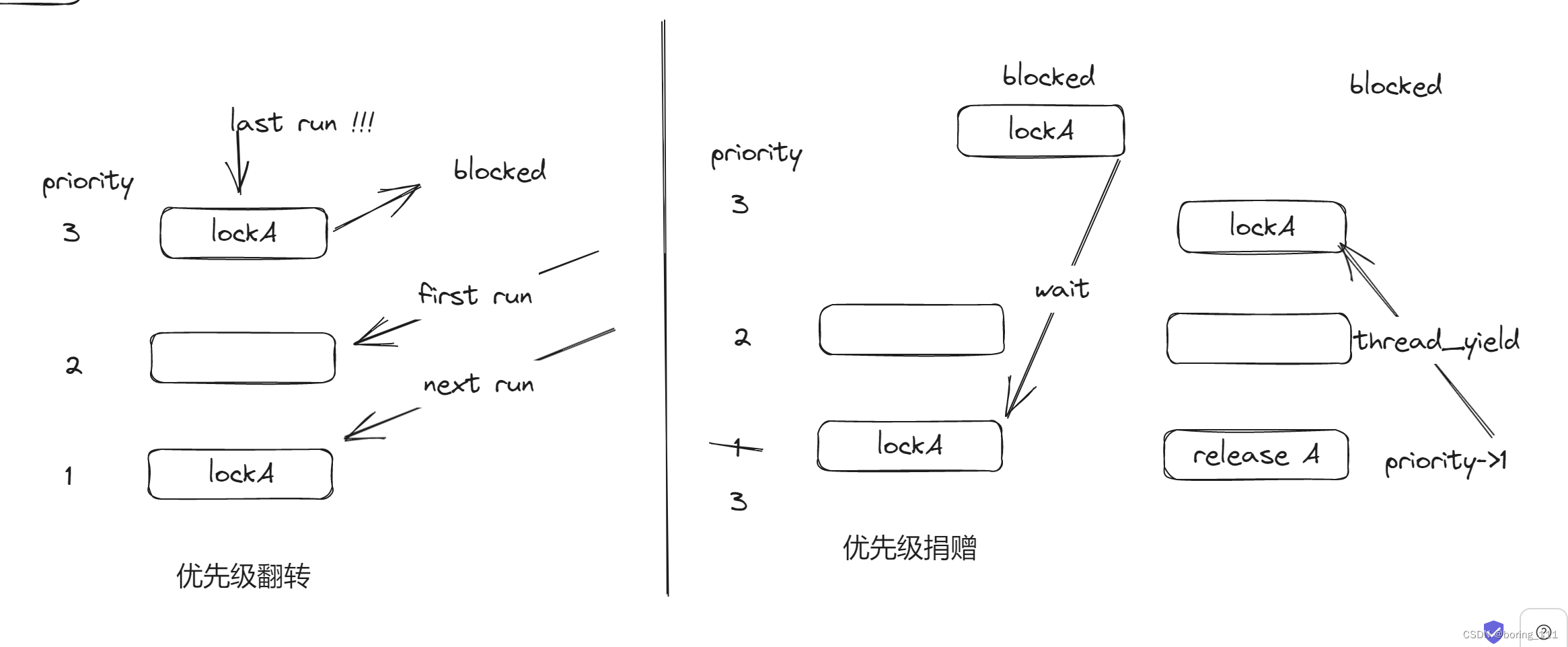
还有一个挑战就是优先级捐赠有传递性,多重性(持有多个锁,优先级取最高的)
举个例子
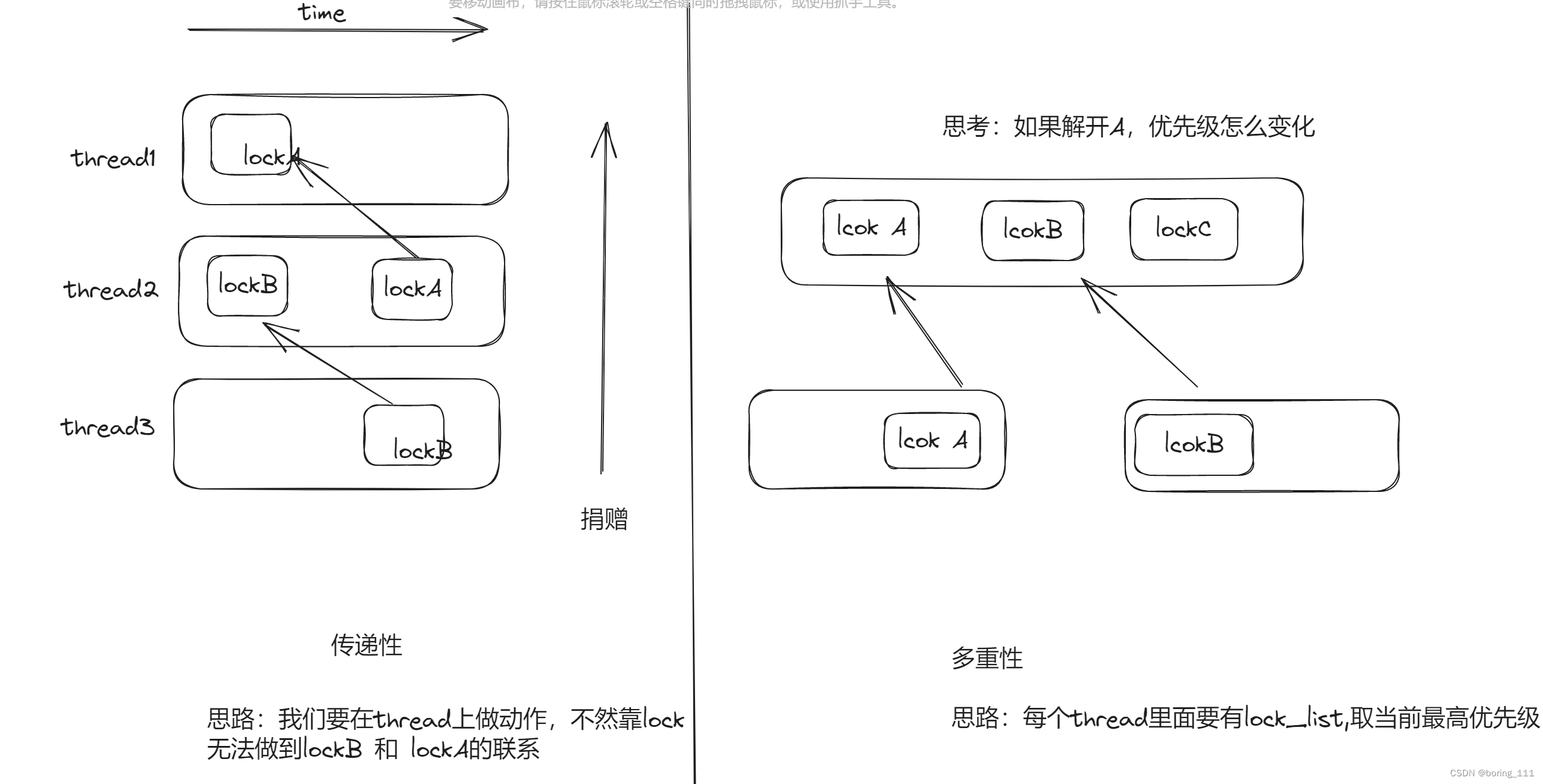
那么我们的实现也就很正常水到渠成了
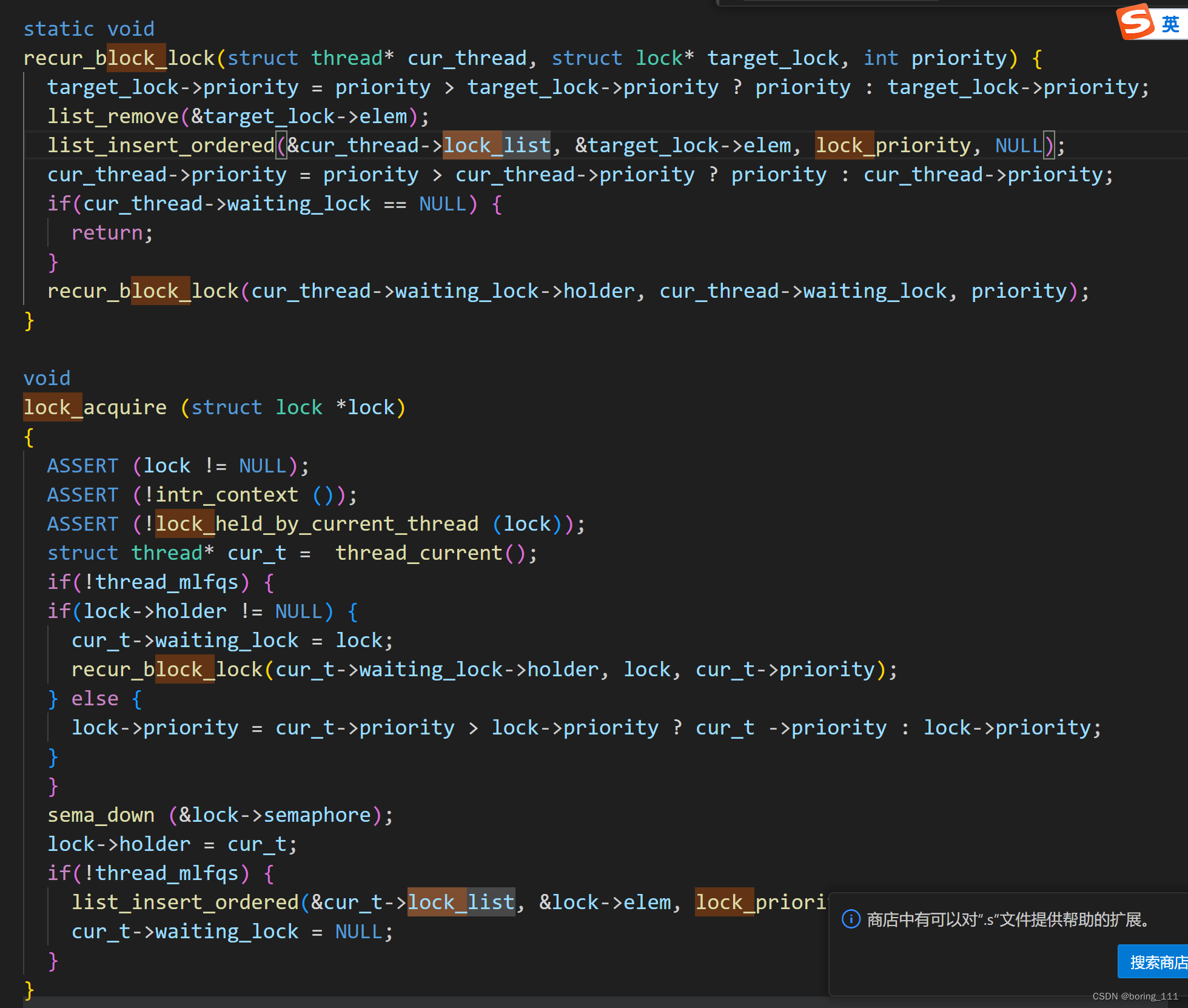
就是thread里面做一个wait_lockomg因为一个thread只能被一个lock阻塞,然后我们传递优先级也是传递到这个wait_locking,lock->holder可以定位到那个thread,然后递归做就行了。
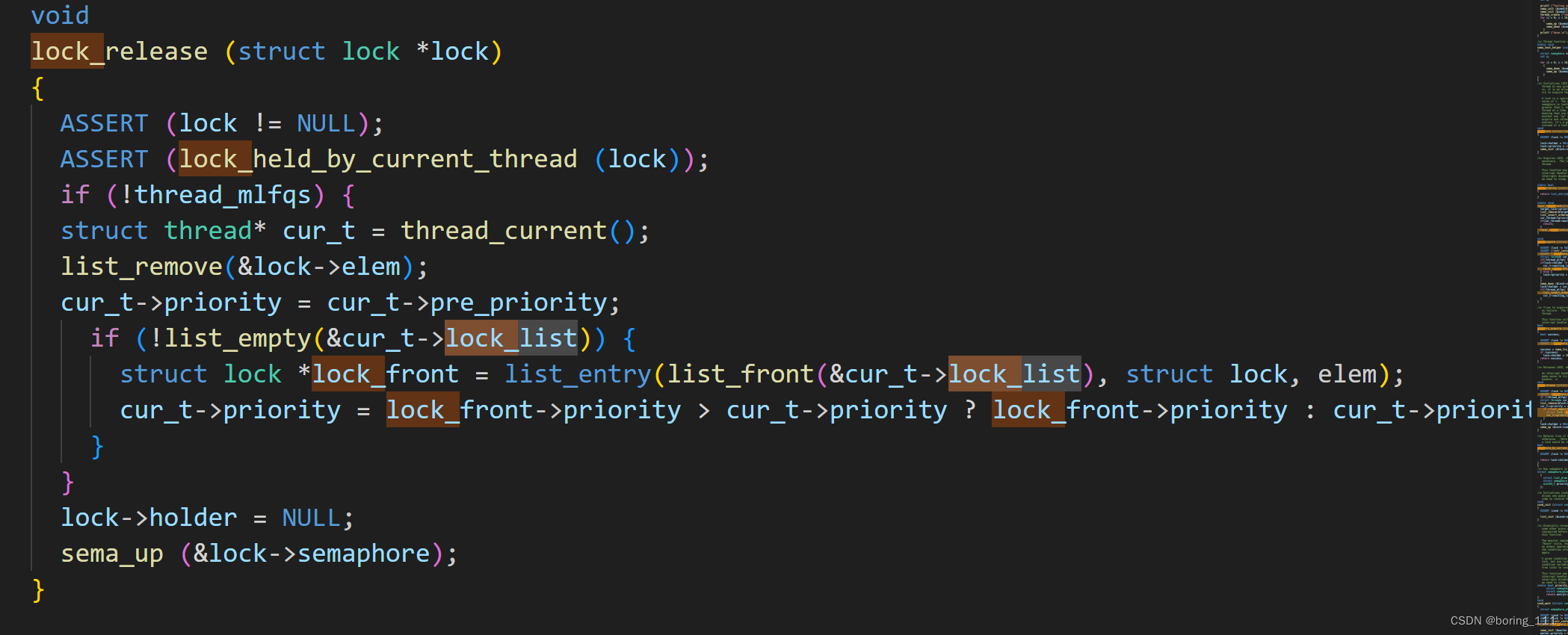
然后lock_release时,要减低优先级。
让我们看看lock_acquire和lock_release的实现吧
lab1,3 高级调度
就是实现一个类似BSD4.4 的调度器
有什么优势吗?


我们看到recent_cpu和load_avg有一个系数,实际上也就是说更近的recent_cpu和load_avg有着更大的权重。

pintos通过解析参数来选择调度器,如果选择的是mlqfs就是这个调度器,同时也学习了要static(如果不是全局的话,最好加一下,不然可能会重复定义)和external(全局,一个共享,一个是只声明)具体可以看看这篇bloghttps://www.cnblogs.com/honernan/p/13431431.html
然后pintos内核不支持浮点运算,因为Pintos does not support floating-point arithmetic in the kernel, because it would complicate and slow the kernel.
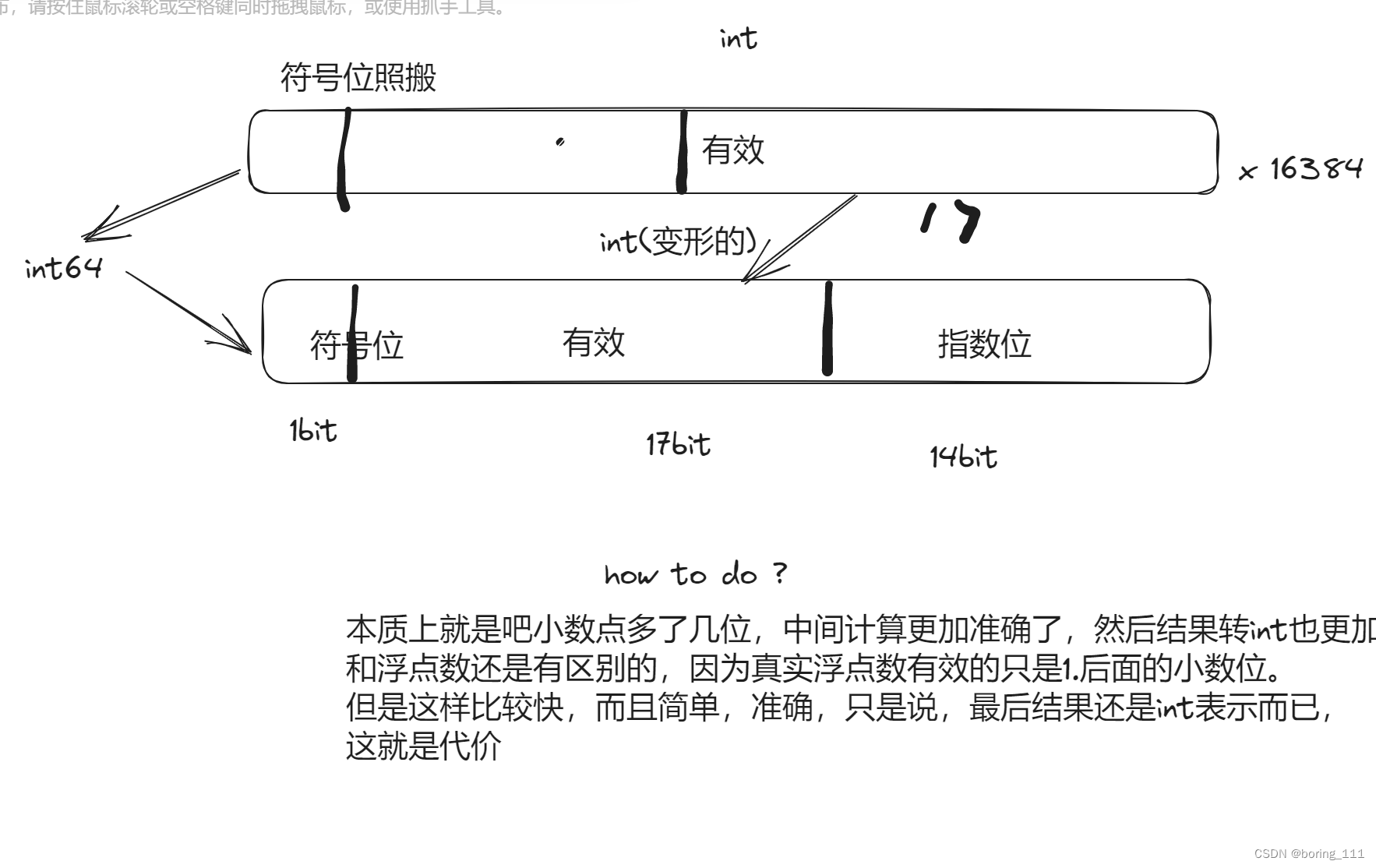
最后也是放大100倍在float里面,然后我们就可以这样观察到小数点后面的东西了,小数点后面两位就不会被转化抹掉。因为我们最终还是int,没有int表示浮点,没有float类型!


结果

fail了一个点,但是这个中断好像无法避免?因为可能时间刚好卡的比较准,tick+1了,导致这两个点不相等