文章目录
- 前言
- 一、Redission是什么?
- 二、使用场景
- 三、代码实战
- 1.项目结构
- 2.类图
- 3.maven依赖
- 4.yml
- 5.config
- 6.annotation
- 7.aop
- 8.model
- 9.service
- 四、单元测试
- 总结
前言
在集群环境下非单体应用存在的问题:JVM锁只能控制本地资源的访问,无法控制多个JVM间的资源访问,所以需要借助第三方中间件来控制整体的资源访问,redis是一个可以实现分布式锁,保证AP的中间件,可以采用setnx命令进行实现,但是在实现细节上也有很多需要注意的点,比如说获取锁、释放锁时机、锁续命问题,而redission工具能够有效降低实现分布式锁的复杂度,看门狗机制有效解决锁续命问题。
一、Redission是什么?
Redisson是一个用于Java的Redis客户端,它提供了许多分布式对象和服务,使得在Java应用中使用Redis变得更加便捷。Redisson提供了对Redis的完整支持,并附带了一系列的功能,如分布式锁、分布式集合、分布式对象、分布式队列等。
二、使用场景
- 分布式锁:Redisson提供了强大的分布式锁机制,通过基于Redis的分布式锁,可以保证在分布式环境下的数据一致性。常见的使用场景包括分布式任务调度、防止重复操作、资源竞争控制等。
- 分布式集合:Redisson提供了一系列的分布式集合实现,如Set、List、Queue、Deque等。这些集合的特点是数据分布在多台机器上,并且支持并发访问,适用于需要在多个节点之间共享数据的场景。
- 分布式对象:Redisson支持将普通Java对象转换为可在Redis中存储和操作的分布式对象。这些对象可以跨JVM进行传输,并保持一致性。使用分布式对象,可以方便地实现分布式缓存、会话管理等功能。
- 分布式队列:Redisson提供了高级的分布式队列实现,支持公平锁和非公平锁的排队方式。分布式队列可以在多个线程和多个JVM之间进行数据传输,适用于消息队列、异步任务处理等场景。
- 分布式信号量、锁定和闭锁:Redisson提供了分布式信号量、可重入锁和闭锁等机制,用于实现更复杂的并发控制需求。这些工具能够有效地管理并发访问,确保在分布式环境下的数据操作的正确性。
除了以上提到的功能,Redisson还提供了许多其他的分布式应用场景所需的功能组件,如分布式BitSet、分布式地理位置、分布式发布/订阅等。
三、代码实战
通过aop切面编程,可以降低与业务代码的耦合度,便于拓展和维护
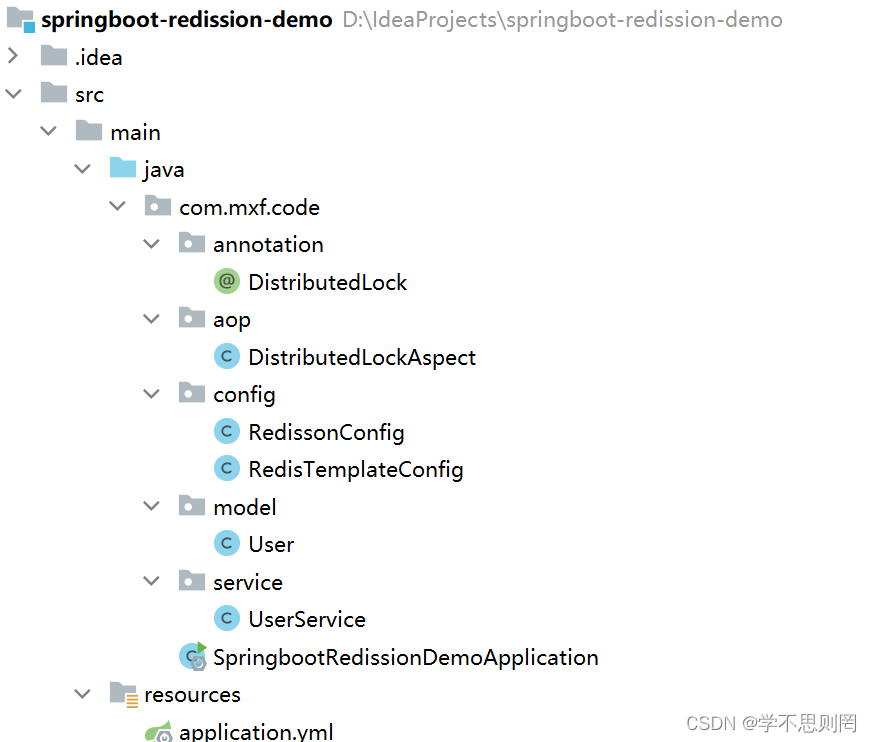
1.项目结构
2.类图

3.maven依赖
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Boot -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Redisson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.20.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring AOP -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Expression Language (SpEL) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
4.yml
dserver:
port: 8081
spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
# 如果需要密码认证,请使用以下配置
# password: your_password
5.config
import org.redisson.Redisson;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.redisson.config.Config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author 28382
*/
@Configuration
public class RedissonConfig {
@Value("${spring.redis.host}")
private String redisHost;
@Value("${spring.redis.port}")
private int redisPort;
// 如果有密码认证,请添加以下注解,并修改相应的配置:
//@Value("${spring.redis.password}")
//private String redisPassword;
@Bean(destroyMethod = "shutdown")
public RedissonClient redissonClient() {
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://" + redisHost + ":" + redisPort);
// 如果有密码认证,请添加以下配置:
//config.useSingleServer().setPassword(redisPassword);
return Redisson.create(config);
}
}
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
/**
* @author 28382
*/
@Configuration
public class RedisTemplateConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.setValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
template.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.setHashValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
template.afterPropertiesSet();
return template;
}
}
6.annotation
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @author 28382
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface DistributedLock {
// 自定义业务keys
String[] keys() default {};
// 租赁时间 单位:毫秒
long leaseTime() default 30000;
// 等待时间 单位:毫秒
long waitTime() default 3000;
}
7.aop
支持解析 SpEL
import com.mxf.code.annotation.DistributedLock;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.redisson.api.RLock;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.core.DefaultParameterNameDiscoverer;
import org.springframework.core.ParameterNameDiscoverer;
import org.springframework.expression.EvaluationContext;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.common.LiteralExpression;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.SpelEvaluationException;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.support.StandardEvaluationContext;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class DistributedLockAspect {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@Around("@annotation(distributedLock)")
public Object lockMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, DistributedLock distributedLock) throws Throwable {
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = methodSignature.getMethod();
// 获取自定义业务keys
String[] keys = distributedLock.keys();
// 租赁时间
long leaseTime = distributedLock.leaseTime();
// 等待时间
long waitTime = distributedLock.waitTime();
// 创建参数名发现器
ParameterNameDiscoverer parameterNameDiscoverer = new DefaultParameterNameDiscoverer();
// 获取方法参数名
String[] parameterNames = parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(method);
// 创建 SpEL 解析器
ExpressionParser expressionParser = new SpelExpressionParser();
// 创建 SpEL 上下文
EvaluationContext evaluationContext = new StandardEvaluationContext();
// 设置方法参数值到 SpEL 上下文中
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
if (parameterNames != null && args != null && parameterNames.length == args.length) {
for (int i = 0; i < parameterNames.length; i++) {
evaluationContext.setVariable(parameterNames[i], args[i]);
}
}
// 构建完整的锁键名
StringBuilder lockKeyBuilder = new StringBuilder();
if (keys.length > 0) {
for (String key : keys) {
if (StringUtils.hasText(key)) {
try {
// 解析 SpEL 表达式获取属性值
Object value = expressionParser.parseExpression(key).getValue(evaluationContext);
lockKeyBuilder.append(value).append(":");
} catch (SpelEvaluationException ex) {
// 如果解析失败,则使用原始字符串作为属性值
LiteralExpression expression = new LiteralExpression(key);
lockKeyBuilder.append(expression.getValue()).append(":");
}
}
}
}
// 使用方法名作为最后一部分键名
lockKeyBuilder.append(methodSignature.getName());
String fullLockKey = lockKeyBuilder.toString();
// 获取 Redisson 锁对象
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(fullLockKey);
// 尝试获取分布式锁
// boolean tryLock(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit)
boolean success = lock.tryLock(waitTime, leaseTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (success) {
try {
// 执行被拦截的方法
return joinPoint.proceed();
} finally {
// 释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
} else {
log.error("Failed to acquire distributed lock");
// 获取锁超时,抛出异常
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to acquire distributed lock");
}
}
}
8.model
import lombok.Data;
/**
* @author 28382
*/
@Data
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String address;
public User(Long id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
}
9.service
import com.mxf.code.annotation.DistributedLock;
import com.mxf.code.model.User;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author 28382
*/
@Service
public class UserService {
int i = 0;
@DistributedLock
public void test01() {
System.out.println("执行方法1 , 当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "执行的结果是:" + ++i);
sleep();
}
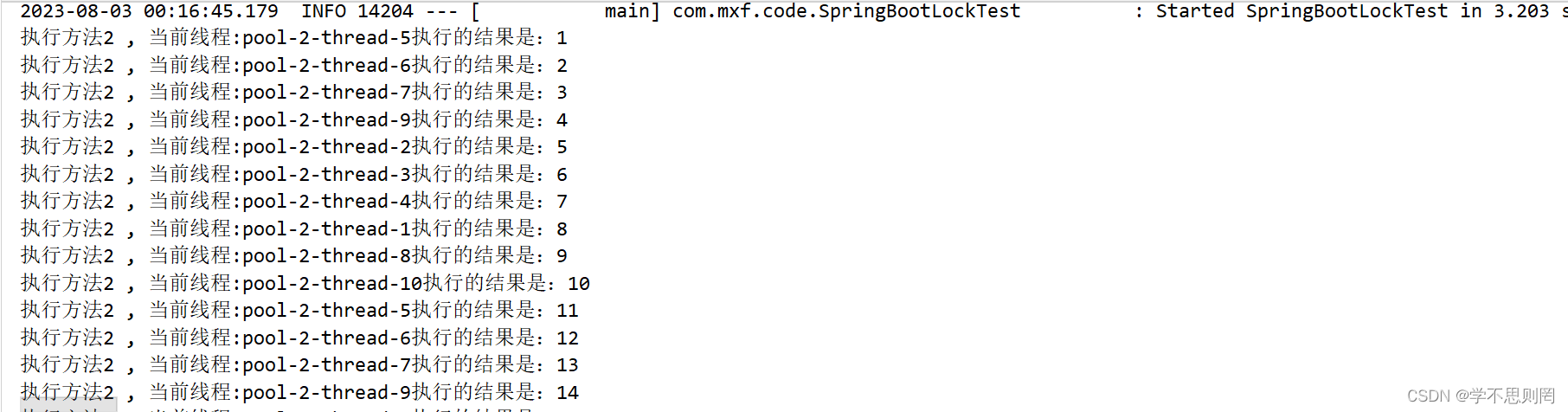
@DistributedLock(keys = "myKey",leaseTime = 30L)
public void test02() {
System.out.println("执行方法2 , 当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "执行的结果是:" + ++i);
sleep();
}
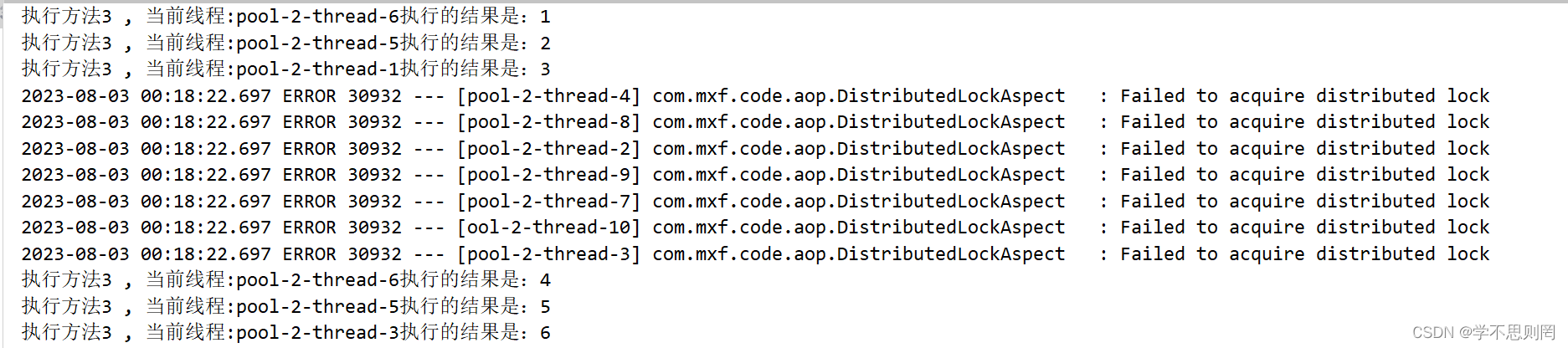
@DistributedLock(keys = "#user.id")
public User test03(User user) {
System.out.println("执行方法3 , 当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "执行的结果是:" + ++i);
sleep();
return user;
}
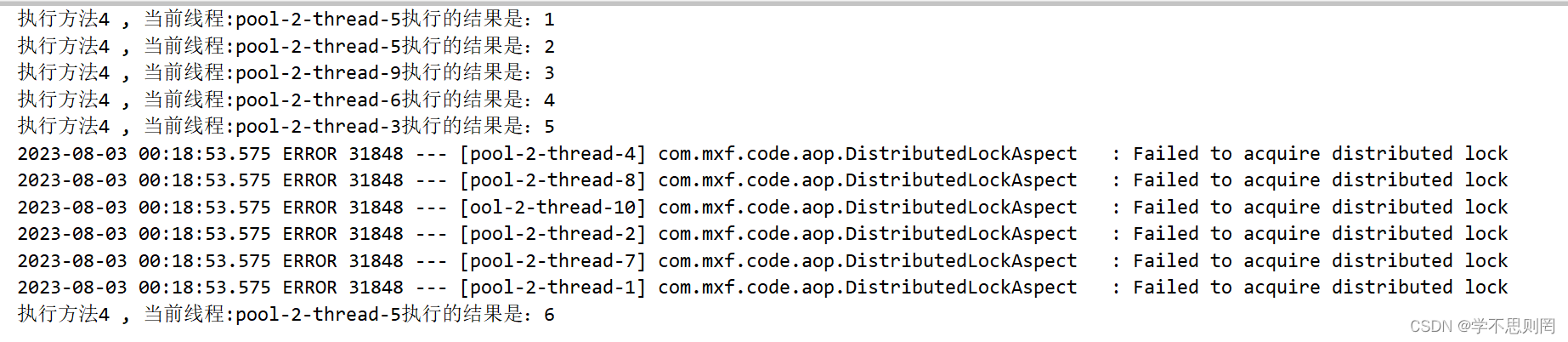
@DistributedLock(keys = {"#user.id", "#user.name"}, leaseTime = 5000, waitTime = 5000)
public User test04(User user) {
System.out.println("执行方法4 , 当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "执行的结果是:" + ++i);
sleep();
return user;
}
private void sleep() {
// 模拟业务耗时
try {
Thread.sleep(1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
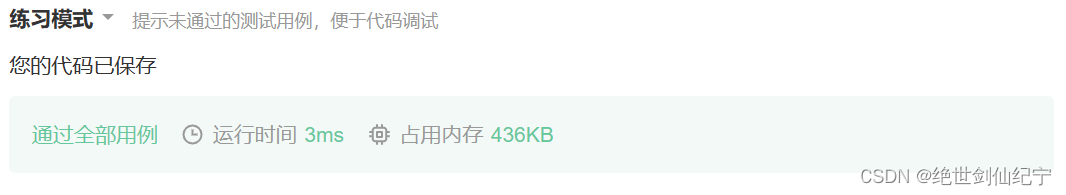
四、单元测试
import com.mxf.code.model.User;
import com.mxf.code.service.UserService;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
@SpringBootTest(classes = SpringBootLockTest.class)
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootLockTest {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
private static final Random RANDOM = new Random();
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootLockTest.class, args);
}
@Test
public void test01() throws Exception {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
Runnable task = () -> userService.test01();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
executorService.submit(task);
}
Thread.sleep(10000);
}
@Test
public void test02() throws Exception {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
Runnable task = () -> userService.test02();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
executorService.submit(task);
}
Thread.sleep(10000L);
}
@Test
public void test03() throws Exception {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
Runnable task = () -> userService.test03(new User(1L, "name"));
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
executorService.submit(task);
}
Thread.sleep(10000L);
}
@Test
public void test04() throws Exception {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
Runnable task = () -> userService.test04(new User(1L, "name"));
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
executorService.submit(task);
}
Thread.sleep(100000L);
}
}
test01
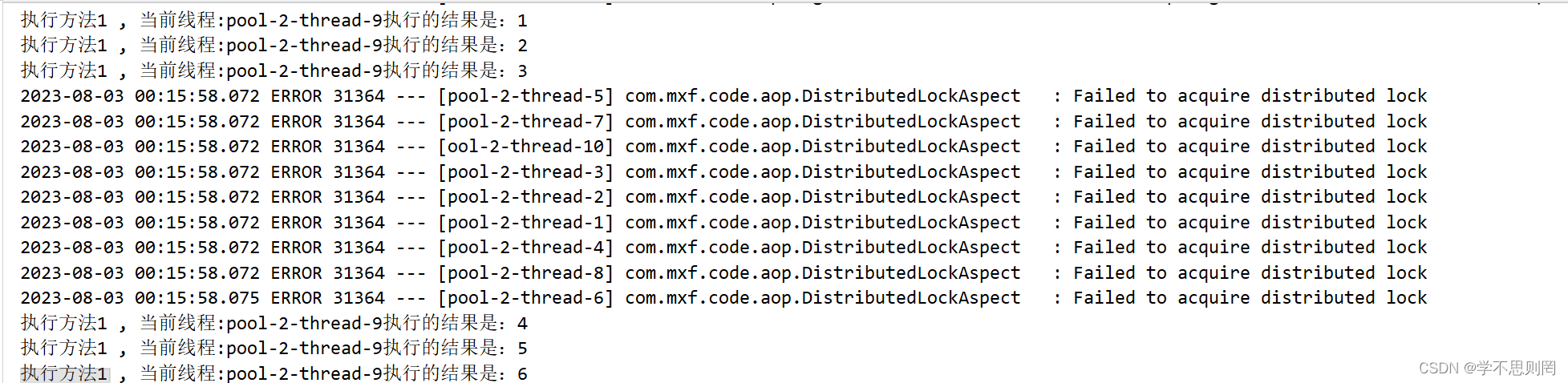
test02
test03
test04
总结
可以在项目中单独建立一个Module,需要的子系统直接引入,在需要加分布式的业务代码方法上添加注解及配注解属性值即可,存在一个潜在的问题就是如果redis使用主从架构,在主节点和从节点同步加锁信息时主节点挂掉,这时选取一个暂未同步完整节点信息的从节点作为主节点时,存在一定锁失效的问题,这是可以考虑红锁或者zookeeper实现强一致性。