前言:
邻接矩阵是数学和计算机科学中常用的一种表示方式,用来表述有向图或无向图,一张图由一组顶点(或结点)和一组表组成,用邻接矩阵就能表示这些顶点间存在的边的关系
1.图的概念
对于图而言,是数据结构中最复杂的结构,而是在做题的过程中,最大的难点在于BFS和DFS的过程,图从两个维度划分可以有:有向图、无权图、带权图。
1.有向图和无向图:
在无向图中,边没有方向,表示的是双向关系,换句话来说,如果两个顶点(或结点)之间存在边,那么这两个顶点就互相连接
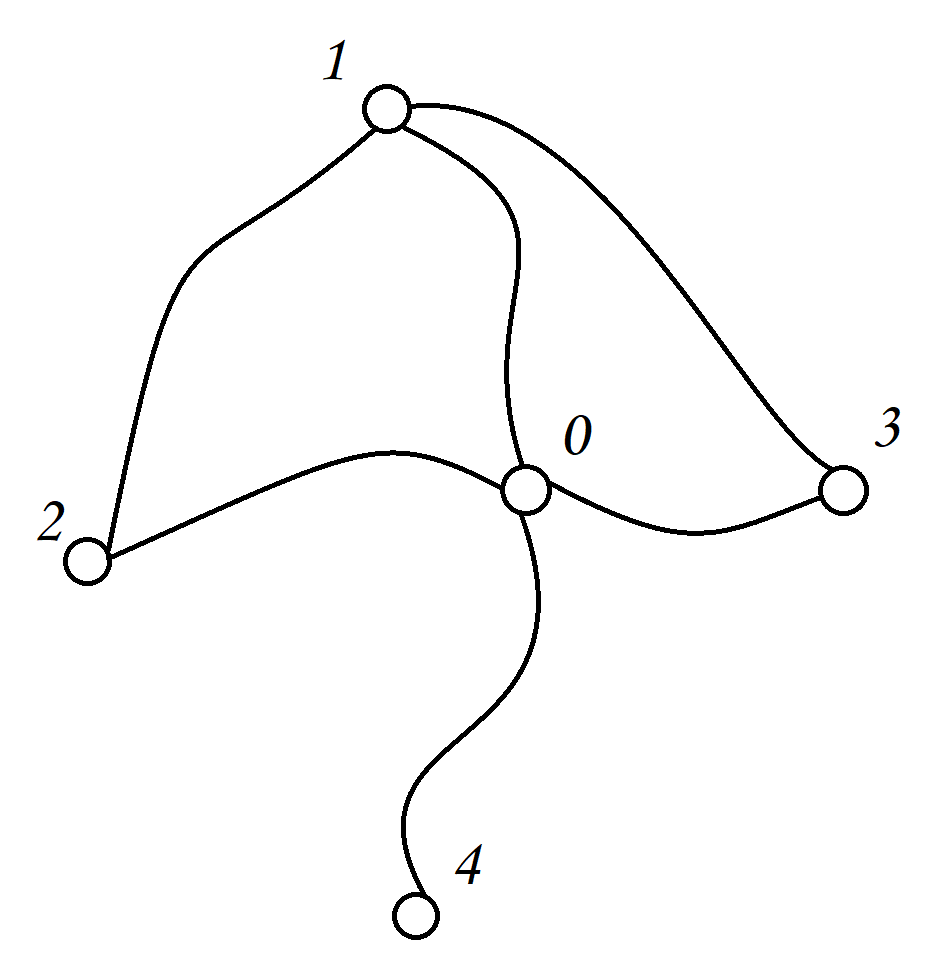
例如,如果你正在建模一个社交网络,你可能会使用无向图,因为友谊是双向,如果1是2的朋友,那么2也是1的朋友,如图示:

有向图:与无向图相反,有向图的边有方向,表示单向关系,在这种图中,如果存在从1到2的边,那不一定存在从2到1的边,如图所示:

2.无权图和带权图
在图论中,图可以是无权的也可以是带权的,这主要取决于边是否具有与其关联的值(权重)
无权图:
在无权图中,边没有权重,或者说所有边的权重都是相同的,你只关心两个节点(顶点)之间是否存在边,而不是关心边的长度或者是成本,比如,社交网络的人际关心就可以用无权图来表示,如果两个人是朋友,就有一条边连接它们,所有的边都被视为相等
带权图:
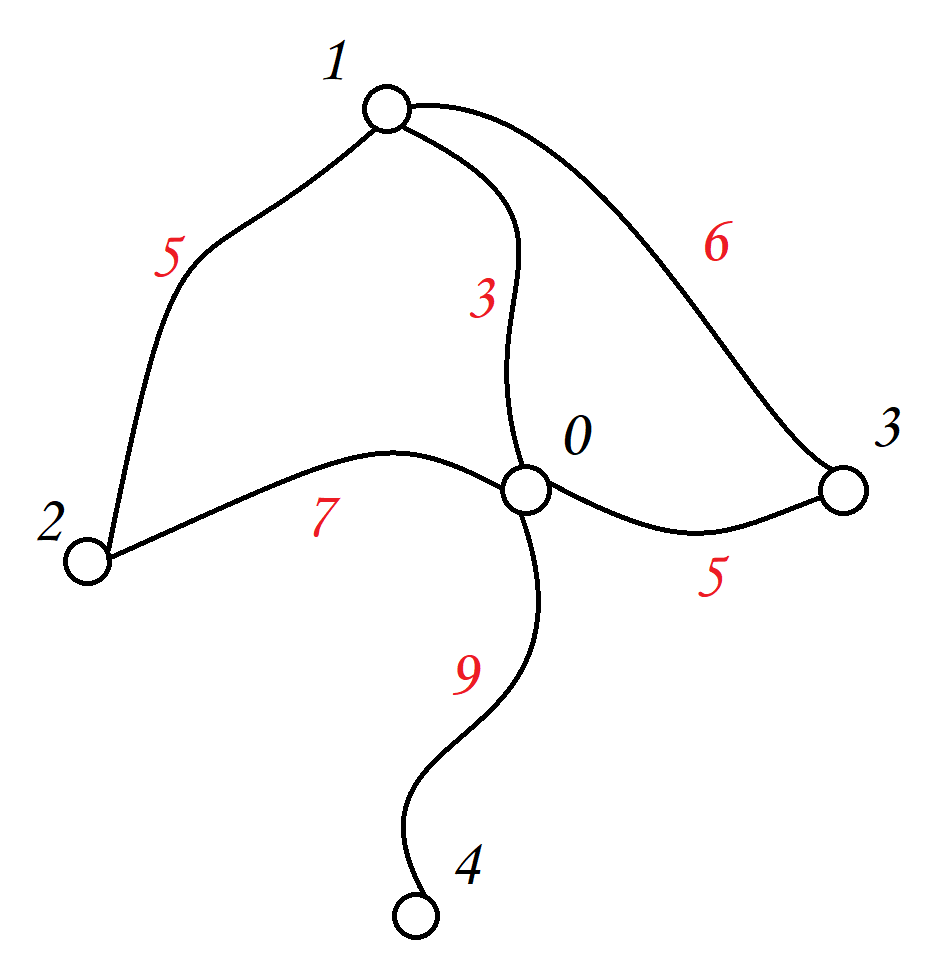
与无权图相对,带权图中的边有各自的权重,这个权重可以表示很多的意义,如距离、时间、成本等等,取决于你要了解的问题,比如,在导航应用中,每个结点可以代表一个结点,边的权重就可以代表两个地点之间的距离或者是行驶时间,在这种情况下,你不仅关心结点之间是否存在边,还关心这个边的权重是多少
2.邻接矩阵的概念
注意:对于邻接矩阵而言 ,不需要去考虑是有向的还是无向的,统一都可以理解成有向的,因为有向图可以兼容无向图,对于无向图而言,只不过这个矩阵按照主对角线对称,因为A到B有变,则必然B到A有边
1.无权图的邻接矩阵
在这样一个矩阵里:
1.矩阵中的行和列都是对应图中的一个顶点
2.如果顶点A到顶点B有一条边(这里是单向的),则对应矩阵单元为1
3.如果顶点A到顶点B没有边,则对应的矩阵单元就为0
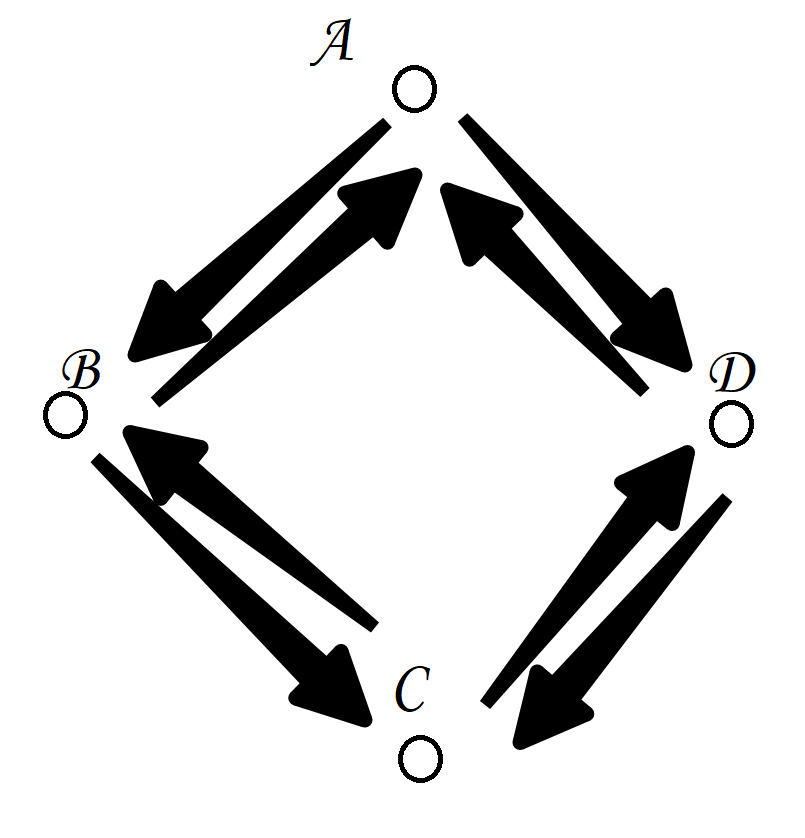
如下图所示:
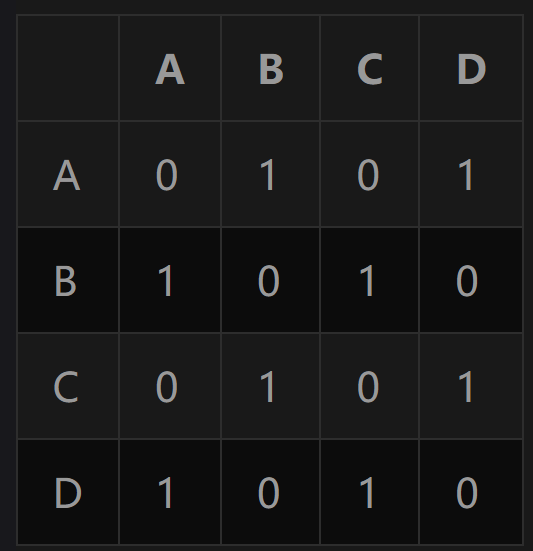
从这个矩阵中我们可以看出,A节点能够到达B、D节点,B节点能够到达A、C节点,C节点能够到达B、D节点,D节点能够到达A、C节点,所以如图所示:
2.带权图的邻接矩阵
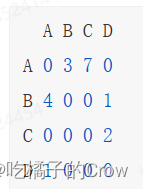
在带权图的邻接矩阵中,每个矩阵元素表示一个有向边的权值,如果不存在从一个结点到另一个节点的边,则通常将其表示为特殊的值(0、-1均可)
- A->B 权重为3
- A->C 权重为7
- B->A 权重为4
- B->D 权重为1
- C->D 权重为2
- D->A 权重为1
该邻接矩阵为:
3.邻接矩阵的代码实现
/**
* 图的表示--使用邻接矩阵
*/
public class Graph01 {
private char[] V;//顶点上的值
private Vertex[] vertexs;//顶点数组
private int N;
//邻接矩阵
private int[][] adj;
//图的构造函数
public Graph01(char[] arr) {//{'A','E','F','G','H','P'}
//拿到数组的长度
int length = arr.length;
this.N = length;
V = new char[length];
//arr元素赋值 到V
this.V = Arrays.copyOf(arr, length);
//构建图中的结点
vertexs = new Vertex[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
vertexs[i] = new Vertex(i,this.V[i]);//
}
this.adj = new int[length][length];
}
//打印邻接矩阵
public void show() {
System.out.print(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < this.N; i++) {
System.out.format("%4c", this.V[i]);
}
System.out.println();
for (int i = 0; i < this.N; i++) {
System.out.format("%4c",this.V[i]);
for (int j = 0; j < this.N; j++) {
System.out.format("%4s", this.adj[i][j] > 0?(this.adj[i][j]):"-");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
/**
* 创建顶点类
*/
private class Vertex {
char v;//值
int index;//索引
public Vertex(int index, char c) {
this.index = index;
this.v = v;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
char arr[] = {'A', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'P'};
//构建graph01
Graph01 graph01 = new Graph01(arr);
//进行连接
int[][] adjMatrix = graph01.adj;
adjMatrix[0][1]=1;
adjMatrix[0][2]=1;
adjMatrix[0][3]=1;
adjMatrix[1][0]=1;
adjMatrix[1][3]=1;
adjMatrix[1][4]=1;
adjMatrix[2][0]=1;
adjMatrix[3][0]=1;
adjMatrix[3][1]=1;
adjMatrix[3][4]=1;
adjMatrix[3][5]=1;
adjMatrix[4][1]=1;
adjMatrix[4][3]=1;
adjMatrix[4][5]=1;
adjMatrix[5][3]=1;
adjMatrix[5][4]=1;
graph01.show();
}**
* 图的表示--使用邻接矩阵
*/
public class Graph02 {
private char[] V;//顶点上的值
private Vertex[] vertexs;//顶点数组
private int N;
//邻接矩阵
private List<Integer>[] adj;
//图的构造函数
public Graph02(char[] arr) {//{'A','E','F','G','H','P'}
//拿到数组的长度
int length = arr.length;
this.N = length;
V = new char[length];
//arr元素赋值 到V
this.V = Arrays.copyOf(arr, length);
//构建图中的结点
vertexs = new Vertex[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
vertexs[i] = new Vertex(i, this.V[i]);
}
this.adj = new List[length];
for (int i = 0; i < this.N; i++) {
this.adj[i]=new ArrayList<>();
}
}
//打印邻接矩阵
public void show() {
System.out.println(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < this.N; i++) {
System.out.format("%-4c", this.V[i]);
//拿到邻接表相邻结点的集合
List<Integer> linkedList = this.adj[i];
for (int j = 0; j < linkedList.size(); j++) {
System.out.print(this.V[linkedList.get(j)] + "---->");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.format("%-4d",vertexs[i].index);
for (int j = 0; j < linkedList.size(); j++) {
System.out.print(vertexs[linkedList.get(j)].index + "---->");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
/**
* 创建顶点类
*/
private class Vertex {
char v;//值
int index;//索引
int weight;//权值
public Vertex(int index, char c) {
this.index = index;
this.v = v;
this.weight = weight;
}
public Vertex(int index) {
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
char arr[] = {'A', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'P'};
//构建graph01
Graph02 graph02 = new Graph02(arr);
//邻接表
List<Integer>[] adj = graph02.adj;
adj[0].add(1);
adj[0].add(2);
adj[0].add(3);
adj[1].add(0);
adj[1].add(3);
adj[1].add(4);
adj[2].add(0);
adj[3].add(0);
adj[3].add(1);
adj[3].add(4);
adj[3].add(5);
adj[4].add(1);
adj[4].add(3);
adj[4].add(5);
adj[5].add(3);
adj[5].add(4);
graph02.show();
}leetcode题单:
省份数量
//进行广度优先搜索
public int findCircleNum(int[][] isConnected) {
if(isConnected==null||isConnected.length==0){
return 0;
}
int privice=0;
Queue<Integer> queue=new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] visited=new boolean[isConnected.length];
Arrays.fill(visited,false);
//对每一个城市进行遍历,得到每一个城市与相连的城市表
for (int i = 0; i <isConnected.length; i++) {
//如果是没有遍历过的城市,则进行如下操作
if(!visited[i]){
queue.offer(i);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int index=queue.poll();
visited[index]=true;
for (int j = 0; j <isConnected.length; j++) {
if(isConnected[index][j]==1&&!visited[j]){
queue.offer(j);
}
}
}
privice++;
}
}
return privice;
}矩阵中的最长递增路径
LCP07.传递信息