给定两个整数数组 inorder 和 postorder ,其中 inorder 是二叉树的中序遍历, postorder 是同一棵树的后序遍历,请你构造并返回这颗 二叉树 。
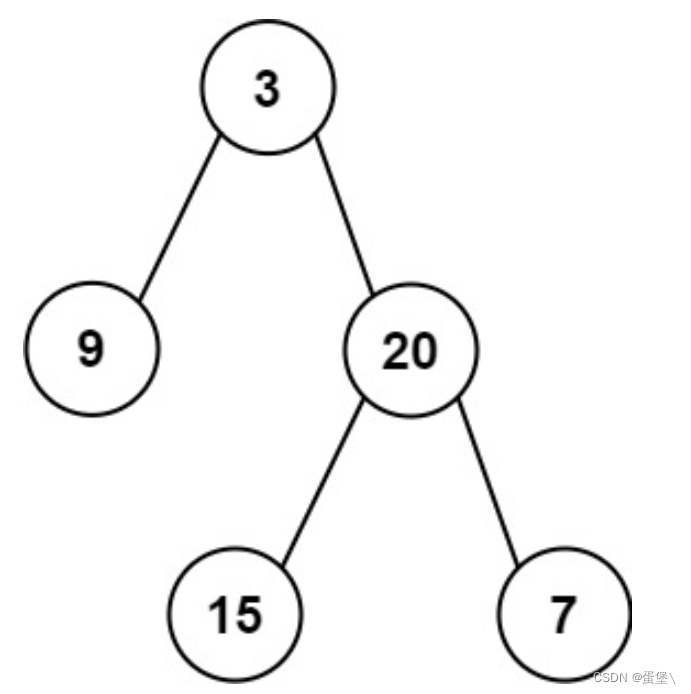
输入:inorder = [9,3,15,20,7], postorder = [9,15,7,20,3] 输出:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
//递归:
/* 解题思路:
1.通过后序遍历的特点我们可以确定地是根节点永远是后序序列的最后一个值
2.先分别划分左子树和右子树节点在后序序列和中序序列中的下标范围
3.因为我们要在中序序列中找到根节点的下标,所以我们通过哈希表建立中序序列中的节点值和下标的映射关系
//index[inorder[i]]=i;
4.在中序遍历中找到根节点的位置后,可以确定的是根节点之前的节点都是左子树上的节点,根节点之后的节点是右子树上的节点,所以我们根据下标关系确认左子树的节点总数leftnode
5.不断更新左子树在后序和中序序列中的左右边界和右子树在后序和中序序列中的左右边界
6.左子树上的所有节点的下标范围(后序序列中):[post_left,post_right]
左子树上的所有节点的下标范围(中序序列中):[ino_left,ino_right]
7.右子树也是同理
8.递归地构造节点的左子树和右子树
*/
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<int,int> index;
TreeNode* dfs(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder,int in_left,int in_right,int post_left,int post_right)
{
if(in_left>in_right) return nullptr;
TreeNode* root=new TreeNode(postorder[post_right]);//先建立根节点
int root_index=index[postorder[post_right]];//在中序序列中找到根节点的下标
int leftnode=root_index-in_left;//计算左子树上节点的个数
root->left=dfs(inorder,postorder,in_left,root_index-1,post_left,post_left+leftnode-1);
root->right=dfs(inorder,postorder,root_index+1,in_right,post_left+leftnode,post_right-1);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
int n=inorder.size();
//建立中序序列中下标与节点值的映射关系
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
index[inorder[i]]=i;
}
return dfs(inorder,postorder,0,n-1,0,n-1);
}
};迭代:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
int n=postorder.size();
if(n==0) return nullptr;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* root=new TreeNode(postorder[n-1]);//根节点是后序序列的最后一个值
st.push(root);//根节点入栈
int root_index=n-1;//后序序列从后往前遍历
int in_index=n-1;//中序序列从后往前遍历
for(int i=root_index-1;i>=0;i--)
{
TreeNode* node=st.top();
//判断栈顶元素与后序序列当前的值是否相等,不相等则说明是右子树
if(inorder[in_index]!=node->val)
{
//构建右子树
node->right=new TreeNode(postorder[i]);
//同时入栈
st.push(node->right);
}
//相等,说明找到了根节点
else
{
//找到一个有左子树的节点
while(!st.empty()&&st.top()->val==inorder[in_index])
{
node=st.top();
st.pop();
in_index--;
}
//构建左子树
node->left=new TreeNode(postorder[i]);
//同时入栈
st.push(node->left);
}
}
return root;
}
};