- Python scipy Moudle 中的 optimize 方法
scipy Moudle 中的 optimize 方法
minimize
- 最小化一个函数
- 它提供了多种算法,如 BFGS、Nelder-Mead、Powell
可选参数
- fun:要最小化的目标函数
- x0:函数的初始猜测值。可以是一个数组或列表
- method:优化算法的名称或方法对象
- 默认为 'BFGS',可选的值包括 'Nelder-Mead'、'Powell'、'CG' 等
- - 'Nelder-Mead'
- cannot handle constraints
- - 'Powell'
- cannot handle constraints
- - 'CG'
- cannot handle constraints nor bounds
- - 'BFGS'
- cannot handle constraints nor bounds
- - 'Newton-CG'
- - 'L-BFGS-B'
- cannot handle constraints
- - 'TNC'
- cannot handle constraints
- - 'COBYLA'
- Constraints of type 'eq' not handled by COBYLA
- cannot handle bounds
- - 'SLSQP'
- - 'trust-constr'
- - 'dogleg'
- - 'trust-ncg'
- - 'trust-exact'
- - 'trust-krylov'
- jac:目标函数的梯度函数
- 可以是一个布尔值或函数对象
- 输入为布尔值则自动计算目标函数的梯度
- 或者为目标函数的梯度函数
- bounds:定义变量的上下界限制
- constraints:约束条件
- tol:优化算法的终止容忍度
- options:一个字典,用于设置其他特定优化算法的参数
BFGS
- Method BFGS cannot handle constraints nor bounds.
import numpy as np
from scipy.optimize import minimize
def objective(x):
return x[0]**2 + x[1]**2 - x[0]*x[1]*x[2]
def constraint1(x):
return x[0] + x[1] + x[2] - 10
def constraint2(x):
return x[0] - x[1] - 2
def constraint3(x):
return - x[1] - x[2] + 5
x0 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
bounds = [(-5, 5), (-5, 5), (-5, 5)]
constraints = [{'type': 'eq', 'fun': constraint1},
{'type': 'ineq', 'fun': constraint2},
{'type': 'ineq', 'fun': constraint3}]
result = minimize(objective, x0, method='BFGS', bounds=bounds, constraints=constraints, tol=1e-6)
print("Optimization Result:")
print("x:", result.x)
print("fun:", result.fun)
print("success:", result.success)
print("message:", result.message)
Warning (from warnings module):
File "C:\Users\LX\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python310\lib\site-packages\scipy\optimize\_minimize.py", line 559
warn('Method %s cannot handle constraints nor bounds.' % method,
RuntimeWarning: Method BFGS cannot handle constraints nor bounds.
Optimization Result:
x: [1512.43480791 204.93489864 1118.04026935]
fun: -344207877.7418728
success: False
message: Desired error not necessarily achieved due to precision loss.
min=x1^2 + x2^2 - x1*x2*x3;
x1+x2+x3=10;
x1-x2>2;
x2+x3<5;
@bnd(-5, x1, 5);
@bnd(-5, x2, 5);
@bnd(-5, x3, 5);
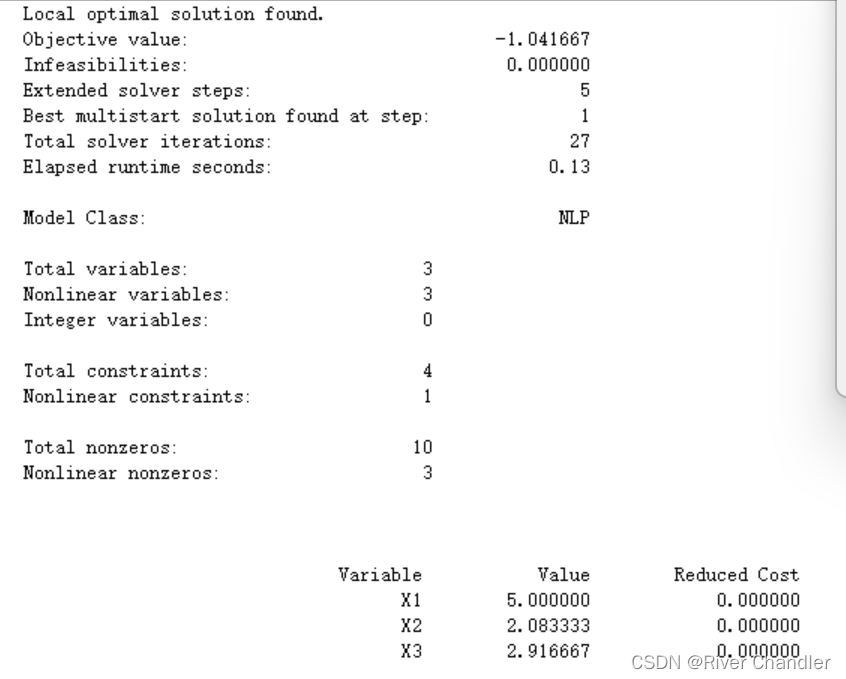
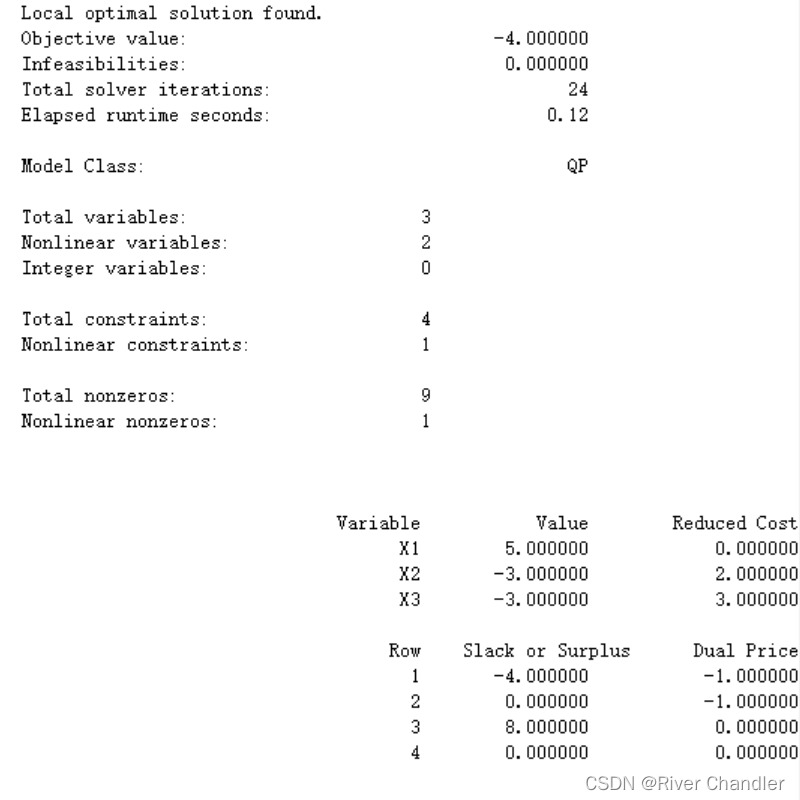
SLSQP
import numpy as np
from scipy.optimize import minimize
def objective(x):
return x[0] - x[1] * x[2]
def constraint1(x):
return x[0] + x[1] - 2
def constraint2(x):
return 2 - x[2] - x[1]
def constraint3(x):
return x[2] + x[0] - 2
x0 = np.array([5, -2, 3])
bounds = [(-5, 5), (-5, 5), (-5, 5)]
constraints = [{'type': 'ineq', 'fun': constraint1},
{'type': 'ineq', 'fun': constraint2},
{'type': 'ineq', 'fun': constraint3}]
result = minimize(objective, x0, method="SLSQP", bounds=bounds, constraints=constraints, tol=1e-6)
print("Optimization Result:")
print("x:", result.x)
print("fun:", result.fun)
print("success:", result.success)
print("message:", result.message)
root
- 用于求解非线性方程组的根。它提供了多种算法,如 Broyden、Newton-Krylov、Anderson 等。
- 大多数方法为迭代方法,必须传入猜测着
- method:指定求解非线性方程组的方法
- 'lm'(Levenberg-Marquardt)
- 'broyden1'(Broyden's first method)
- 'broyden2'(Broyden's second method)
- 'anderson'(Anderson mixing)
- 'linearmixing'(linear mixing)
- 'diagbroyden'(diagonal Broyden)
- 'excitingmixing'(exciting mixing)
- 默认值为None
- jac:指定计算雅可比矩阵的函数。默认值为False
- tol:指定求解器的容差。默认值为1e-12
from scipy.optimize import root
def equation(x):
return x**3 - 2*x - 5
sol = root(equation, 0)
print(sol.x)
least_squares
- 用于最小二乘问题的求解。它提供了多种算法,如 Levenberg-Marquardt、Trust Region Reflective 等
import numpy as np
from scipy.optimize import least_squares
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#目标函数
def func(x, p):
return p[0] * np.exp(p[1] / x) - p[2] * x**2
f = lambda x:5*np.e**(2/x) - 4*x**2
#残差函数
def residual(p, x, y):
return func(x, p) - y
x = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
y = f(x)
noise = np.random.uniform(-0.6, 0.6, len(x))
y += noise
#猜测值
p0 = np.array([1., 2., 3.])
result = least_squares(residual, p0, args=(x, y))
print("拟合参数:", result.x)
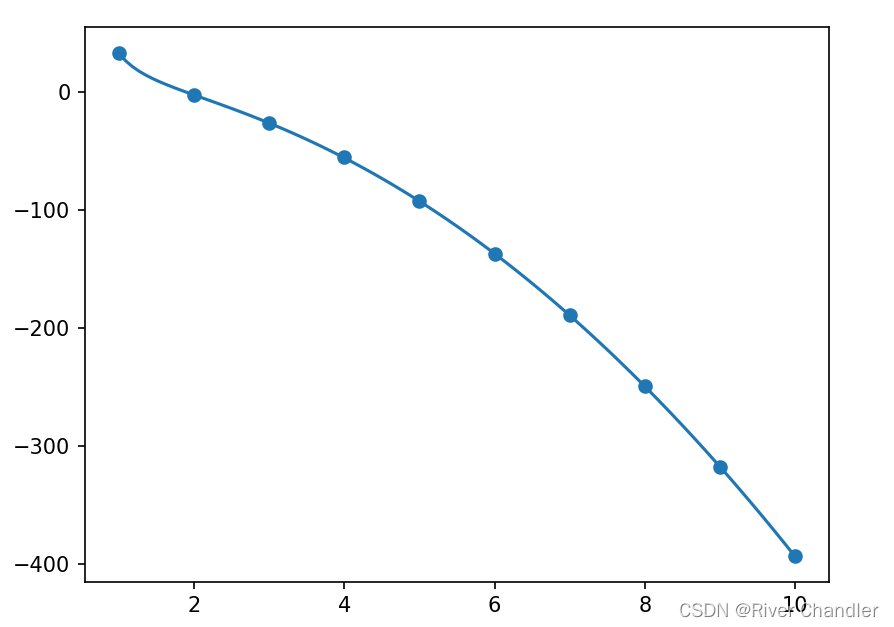
X = np.linspace(1, 10, 100)
Y = f(X)
plt.plot(X, Y, label="function")
plt.scatter(x, y, label="points")
plt.pause(0.01)