苍穹外卖-day07
本项目学自黑马程序员的《苍穹外卖》项目,是瑞吉外卖的Plus版本
功能更多,更加丰富。
结合资料,和自己对学习过程中的一些看法和问题解决情况上传课件笔记
视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1TP411v7v6/?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click
资料:关注黑马程序员公众号---->回复:苍穹外卖
一起学习,一起加油
【可以使用ApiFox代替YApi来导入的接口文档】
🙂 🙃 😉 😌 😍 🥰 😘 😗 😙 😚 😋 😛 😝 😜 🤪 🤨 🧐 🤓 😎 🤩 🥳
1、Redis缓存菜品以及SpringCache缓存套餐
文章目录
- 苍穹外卖-day07
- 1. 缓存菜品
- 1.1 问题说明
- 1.2 实现思路
- 1.3 代码开发
- 1.4 功能测试
- 1.5 代码提交
- 2. 缓存套餐
- 2.1 Spring Cache
- 2.1.1 介绍
- 2.1.2 常用注解
- 2.1.3 入门案例
- 2.2 实现思路
- 2.3 代码开发
- 2.4 功能测试
- 2.5 代码提交
- 3. 添加购物车
- 3.1 需求分析和设计
- 3.1.1 产品原型
- 3.1.2 接口设计
- 3.1.3 表设计
- 3.2 代码开发
- 3.2.1 DTO设计
- 3.2.2 Controller层
- 3.2.3 Service层接口
- 3.2.4 Service层实现类
- 3.2.5 Mapper层
- 3.3 功能测试
- 3.4 代码提交
- 4. 查看购物车
- 4.1 需求分析和设计
- 4.1.1 产品原型
- 4.1.2 接口设计
- 4.2 代码开发
- 4.2.1 Controller层
- 4.2.2 Service层接口
- 4.2.3 Service层实现类
- 4.3 功能测试
- 4.4 代码提交
- 5. 清空购物车
- 5.1 需求分析和设计
- 5.1.1 产品原型
- 5.1.2 接口设计
- 5.2 代码开发
- 5.2.1 Controller层
- 5.2.2 Service层接口
- 5.2.3 Service层实现类
- 5.2.4 Mapper层
- 5.3 功能测试
- 5.4 代码提交
1. 缓存菜品
1.1 问题说明
用户端小程序展示的菜品数据都是通过查询数据库获得,如果用户端访问量比较大,数据库访问压力随之增大。
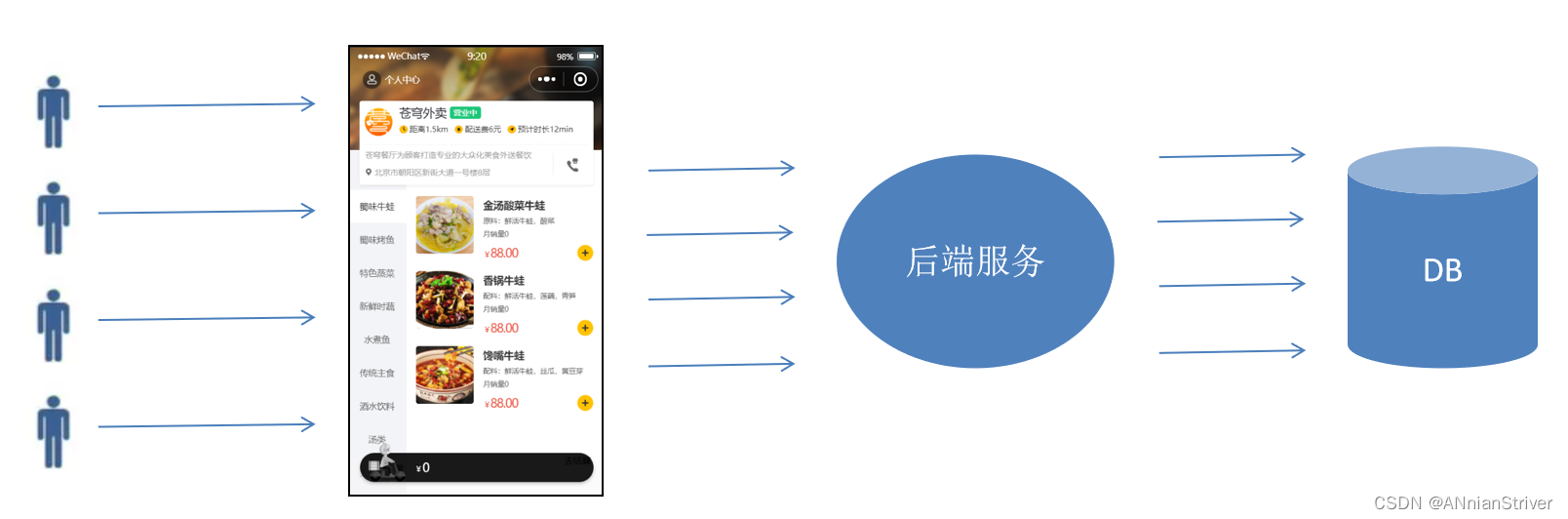
**结果:**系统响应慢、用户体验差
1.2 实现思路
通过Redis来缓存菜品数据,减少数据库查询操作。
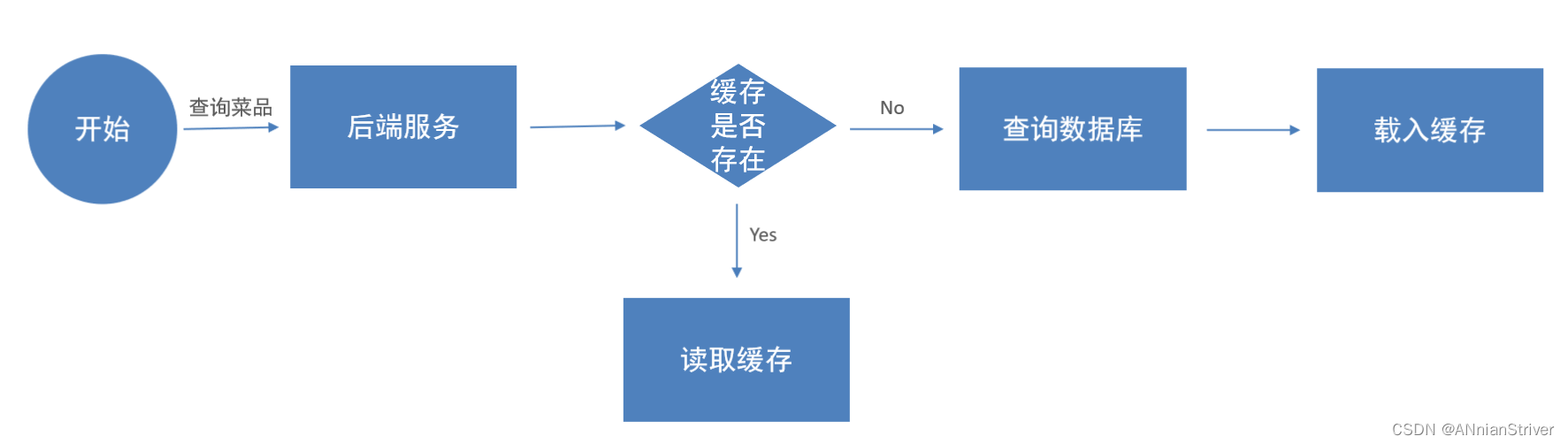
缓存逻辑分析:
- 每个分类下的菜品保存一份缓存数据
- 数据库中菜品数据有变更时清理缓存数据
1.3 代码开发
修改用户端接口 DishController 的 list 方法,加入缓存处理逻辑:
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
/**
* 根据分类id查询菜品
*
* @param categoryId
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/list")
@ApiOperation("根据分类id查询菜品")
public Result<List<DishVO>> list(Long categoryId) {
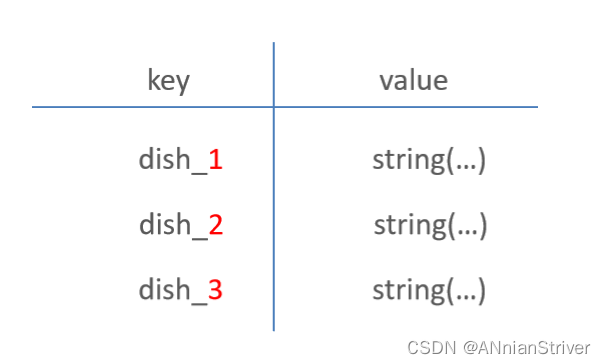
//构造redis中的key,规则:dish_分类id
String key = "dish_" + categoryId;
//查询redis中是否存在菜品数据
List<DishVO> list = (List<DishVO>) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if(list != null && list.size() > 0){
//如果存在,直接返回,无须查询数据库
return Result.success(list);
}
Dish dish = new Dish();
dish.setCategoryId(categoryId);
dish.setStatus(StatusConstant.ENABLE);//查询起售中的菜品
//如果不存在,查询数据库,将查询到的数据放入redis中
list = dishService.listWithFlavor(dish);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, list);
return Result.success(list);
}
为了保证数据库和Redis中的数据保持一致,修改管理端接口 DishController 的相关方法,加入清理缓存逻辑。
需要改造的方法:
- 新增菜品
- 修改菜品
- 批量删除菜品
- 起售、停售菜品
抽取清理缓存的方法:
在管理端DishController中添加
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
/**
* 清理缓存数据
* @param pattern
*/
private void cleanCache(String pattern){
Set keys = redisTemplate.keys(pattern);
redisTemplate.delete(keys);
}
调用清理缓存的方法,保证数据一致性:
1). 新增菜品优化
/**
* 新增菜品
*
* @param dishDTO
* @return
*/
@PostMapping
@ApiOperation("新增菜品")
public Result save(@RequestBody DishDTO dishDTO) {
log.info("新增菜品:{}", dishDTO);
dishService.saveWithFlavor(dishDTO);
//清理缓存数据
String key = "dish_" + dishDTO.getCategoryId();
cleanCache(key);
return Result.success();
}
2). 菜品批量删除优化
/**
* 菜品批量删除
*
* @param ids
* @return
*/
@DeleteMapping
@ApiOperation("菜品批量删除")
public Result delete(@RequestParam List<Long> ids) {
log.info("菜品批量删除:{}", ids);
dishService.deleteBatch(ids);
//将所有的菜品缓存数据清理掉,所有以dish_开头的key
cleanCache("dish_*");
return Result.success();
}
3). 修改菜品优化
/**
* 修改菜品
*
* @param dishDTO
* @return
*/
@PutMapping
@ApiOperation("修改菜品")
public Result update(@RequestBody DishDTO dishDTO) {
log.info("修改菜品:{}", dishDTO);
dishService.updateWithFlavor(dishDTO);
//将所有的菜品缓存数据清理掉,所有以dish_开头的key
cleanCache("dish_*");
return Result.success();
}
4). 菜品起售停售优化
/**
* 菜品起售停售
*
* @param status
* @param id
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/status/{status}")
@ApiOperation("菜品起售停售")
public Result<String> startOrStop(@PathVariable Integer status, Long id) {
dishService.startOrStop(status, id);
//将所有的菜品缓存数据清理掉,所有以dish_开头的key
cleanCache("dish_*");
return Result.success();
}
1.4 功能测试
可以通过如下方式进行测试:
- 查看控制台sql
- 前后端联调
- 查看Redis中的缓存数据
以加入缓存、菜品修改两个功能测试为例,通过前后端联调方式,查看控制台sql的打印和Redis中的缓存数据变化。
1). 加入缓存
当第一次查询某个分类的菜品时,会从数据为中进行查询,同时将查询的结果存储到Redis中,在后绪的访问,若查询相同分类的菜品时,直接从Redis缓存中查询,不再查询数据库。
**登录小程序:**选择蜀味牛蛙(id=17)
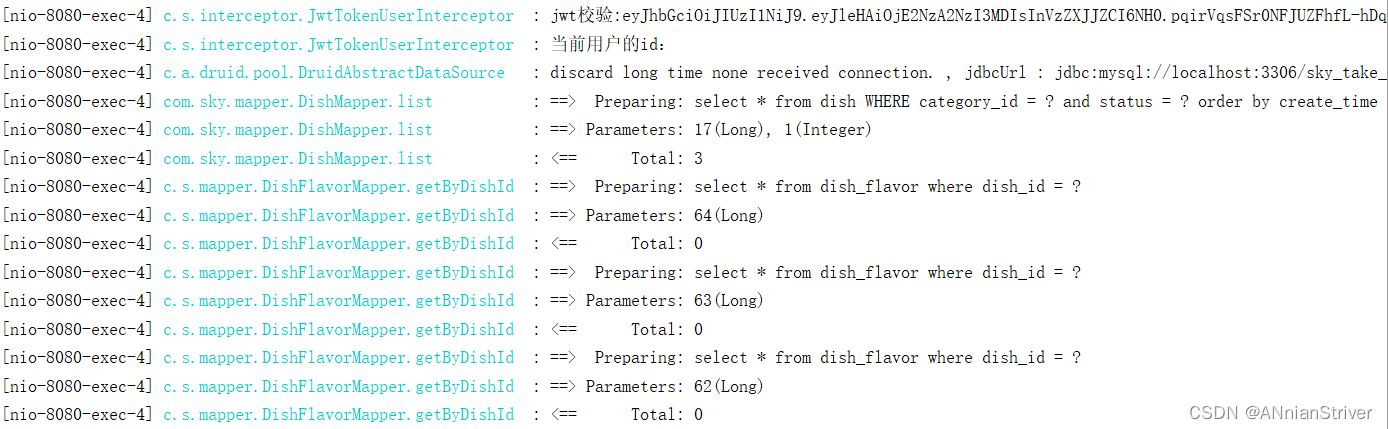
**查看控制台sql:**有查询语句,说明是从数据库中进行查询
**查看Redis中的缓存数据:**说明缓存成功
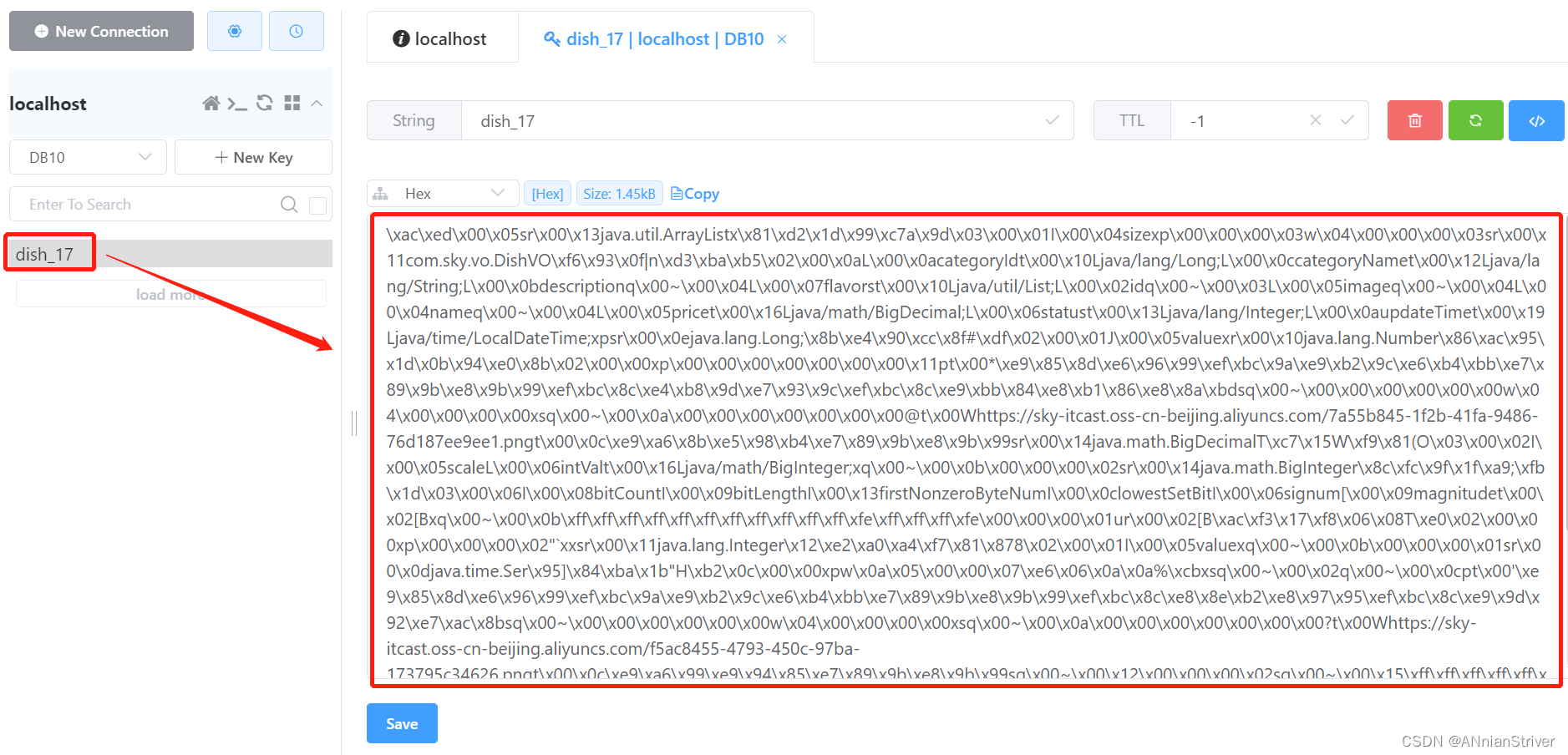
**再次访问:**选择蜀味牛蛙(id=17)
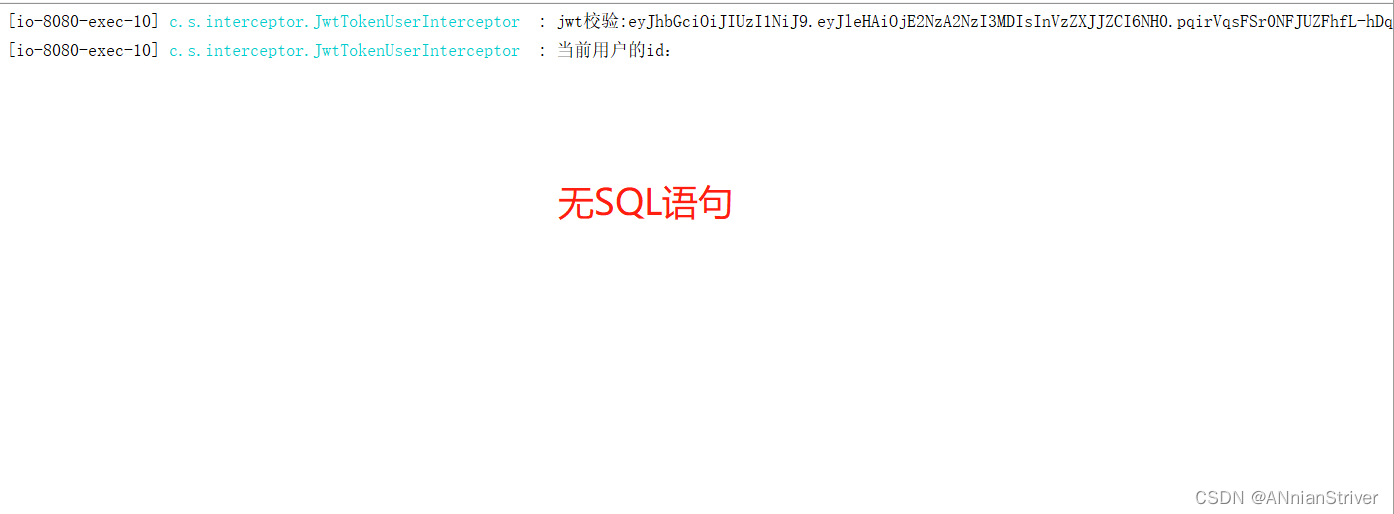
说明是从Redis中查询的数据。
2). 菜品修改
当在后台修改菜品数据时,为了保证Redis缓存中的数据和数据库中的数据时刻保持一致,当修改后,需要清空对应的缓存数据。用户再次访问时,还是先从数据库中查询,同时再把查询的结果存储到Redis中,这样,就能保证缓存和数据库的数据保持一致。
**进入后台:**修改蜀味牛蛙分类下的任意一个菜品,当前分类的菜品数据已在Redis中缓存 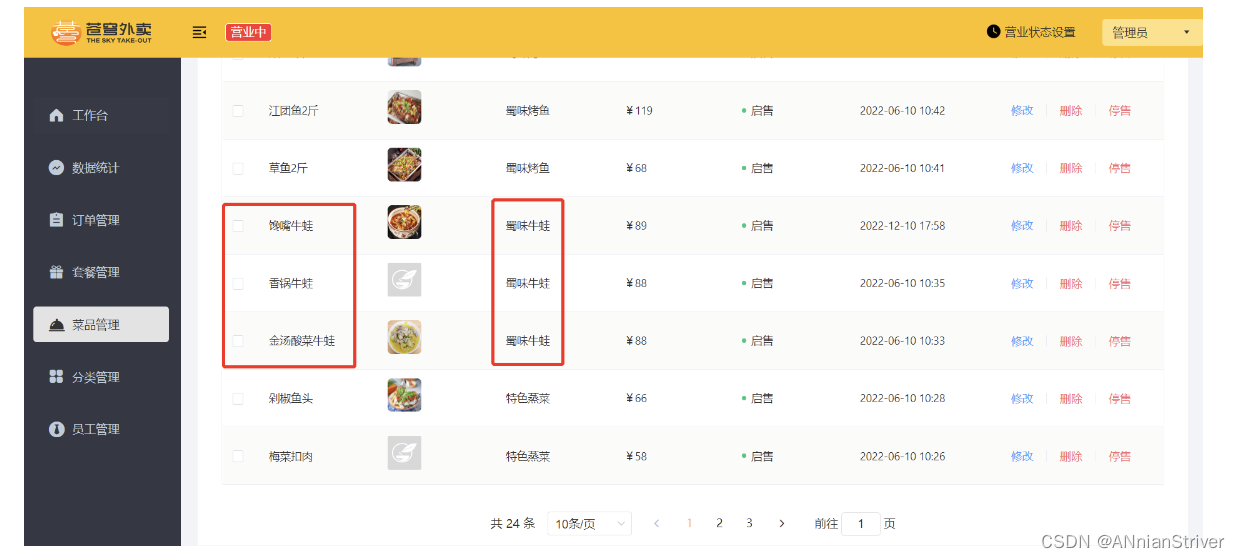
修改:
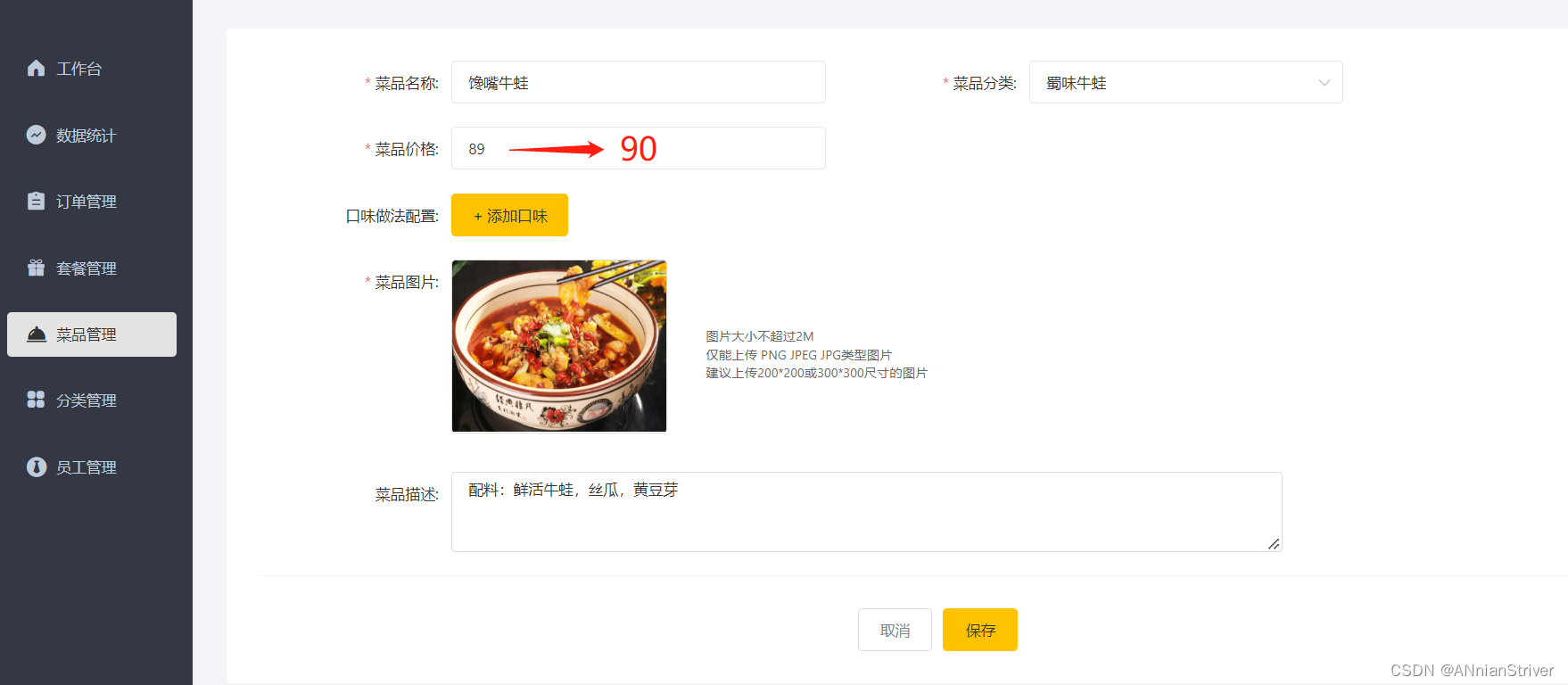
**查看Redis中的缓存数据:**说明修改时,已清空缓存
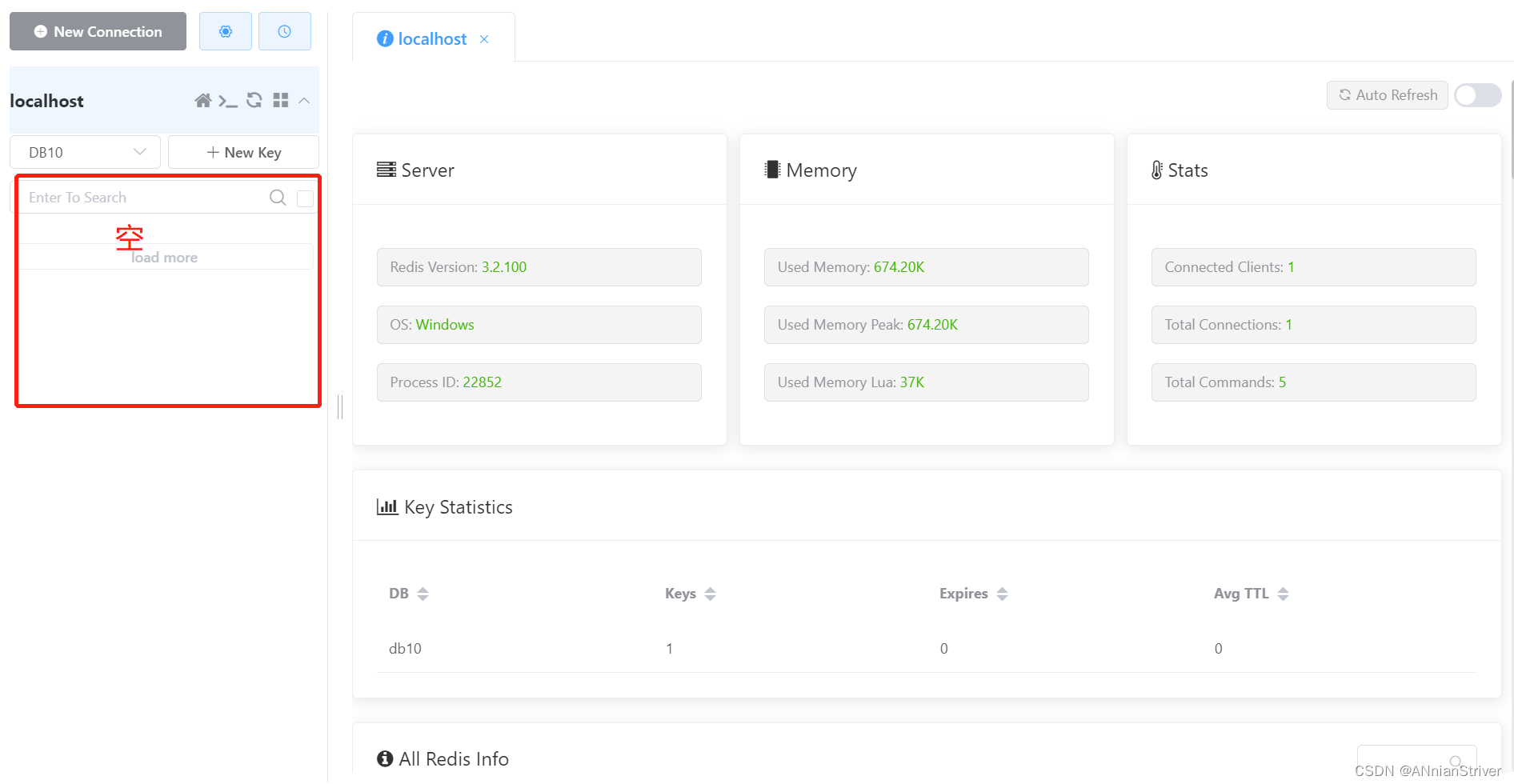
用户再次访问同一个菜品分类时,需要先查询数据库,再把结果同步到Redis中,保证了两者数据一致性。
其它功能测试步骤基本一致,自已测试即可。
1.5 代码提交
2. 缓存套餐
2.1 Spring Cache
2.1.1 介绍
Spring Cache 是一个框架,实现了基于注解的缓存功能,只需要简单地加一个注解,就能实现缓存功能。
Spring Cache 提供了一层抽象,底层可以切换不同的缓存实现,例如:
- EHCache
- Caffeine
- Redis(常用)
起步依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId> <version>2.7.3</version>
</dependency>
2.1.2 常用注解
在SpringCache中提供了很多缓存操作的注解,常见的是以下的几个:
| 注解 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| @EnableCaching | 开启缓存注解功能,通常加在启动类上 |
| @Cacheable | 在方法执行前先查询缓存中是否有数据,如果有数据,则直接返回缓存数据;如果没有缓存数据,调用方法并将方法返回值放到缓存中 |
| @CachePut | 将方法的返回值放到缓存中 |
| @CacheEvict | 将一条或多条数据从缓存中删除 |
在spring boot项目中,使用缓存技术只需在项目中导入相关缓存技术的依赖包,并在启动类上使用@EnableCaching开启缓存支持即可。
例如,使用Redis作为缓存技术,只需要导入Spring data Redis的maven坐标即可。
2.1.3 入门案例
1). 环境准备
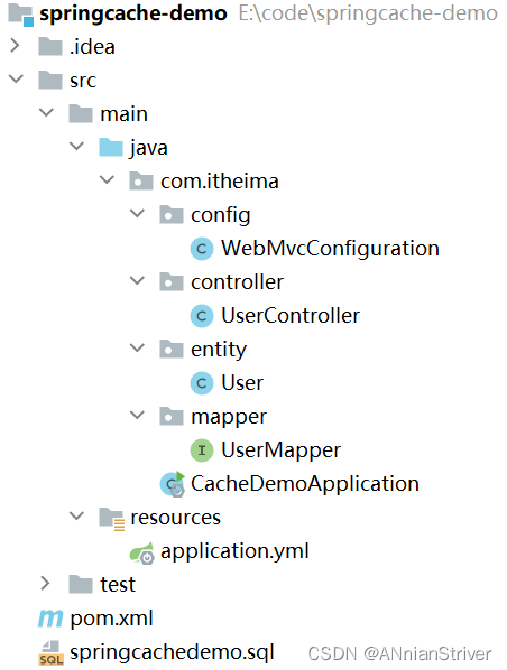
**导入基础工程:**底层已使用Redis缓存实现
基础环境的代码,在我们今天的资料中已经准备好了, 大家只需要将这个工程导入进来就可以了。导入进来的工程结构如下:
数据库准备:
创建名为spring_cache_demo数据库,将springcachedemo.sql脚本直接导入数据库中。

引导类上加@EnableCaching:
package com.itheima;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
@Slf4j
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching//开启缓存注解功能
public class CacheDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CacheDemoApplication.class,args);
log.info("项目启动成功...");
}
}
2). @CachePut注解
@CachePut 说明:
作用: 将方法返回值,放入缓存
value: 缓存的名称, 每个缓存名称下面可以有很多key
key: 缓存的key ----------> 支持Spring的表达式语言SPEL语法
在save方法上加注解@CachePut
当前UserController的save方法是用来保存用户信息的,我们希望在该用户信息保存到数据库的同时,也往缓存中缓存一份数据,我们可以在save方法上加上注解 @CachePut,用法如下:
/**
* CachePut:将方法返回值放入缓存
* value:缓存的名称,每个缓存名称下面可以有多个key
* key:缓存的key
*/
@PostMapping
@CachePut(value = "userCache", key = "#user.id")//key的生成:userCache::1
public User save(@RequestBody User user){
userMapper.insert(user);
return user;
}
**说明:**key的写法如下
#user.id : #user指的是方法形参的名称, id指的是user的id属性 , 也就是使用user的id属性作为key ;
#result.id : #result代表方法返回值,该表达式 代表以返回对象的id属性作为key ;
#p0.id:#p0指的是方法中的第一个参数,id指的是第一个参数的id属性,也就是使用第一个参数的id属性作为key ;
#a0.id:#a0指的是方法中的第一个参数,id指的是第一个参数的id属性,也就是使用第一个参数的id属性作为key ;
#root.args[0].id:#root.args[0]指的是方法中的第一个参数,id指的是第一个参数的id属性,也就是使用第一个参数
的id属性作为key ;
启动服务,通过swagger接口文档测试,访问UserController的save()方法
因为id是自增,所以不需要设置id属性
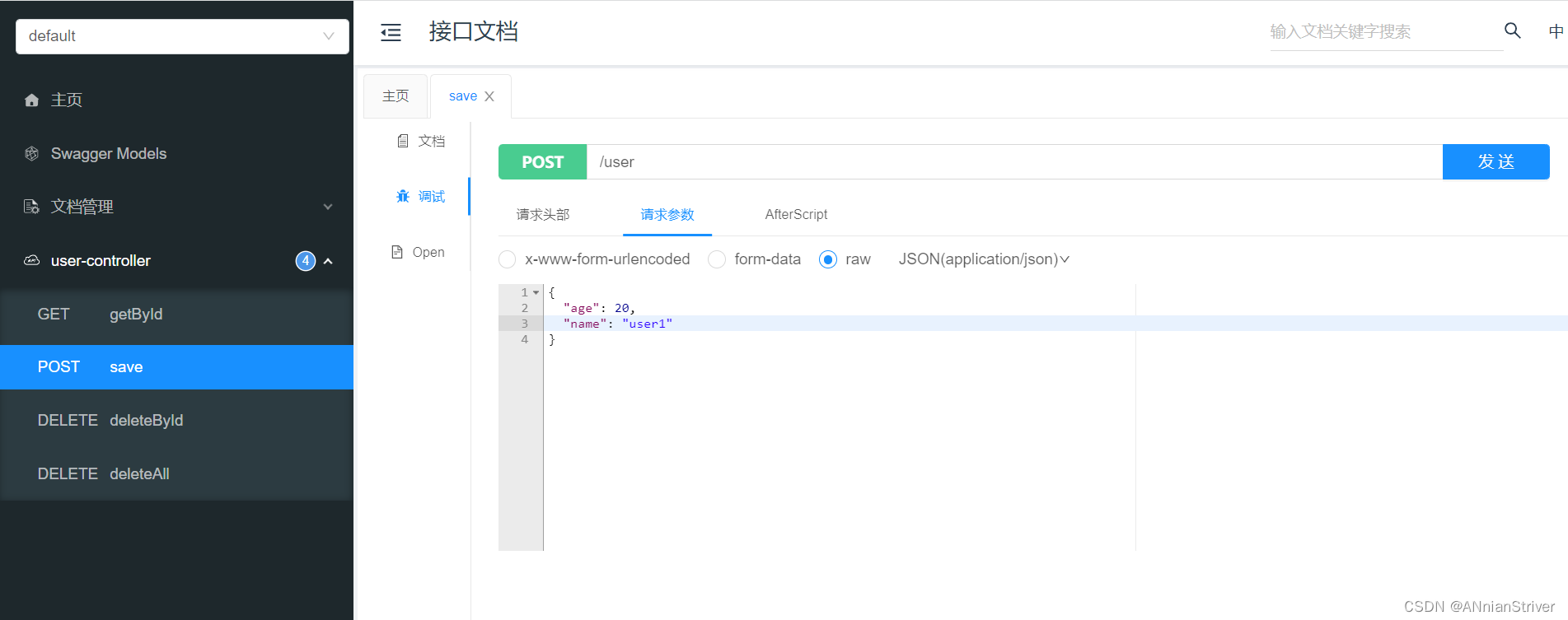
查看user表中的数据
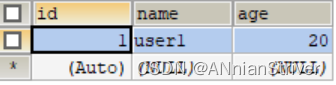
查看Redis中的数据
3). @Cacheable注解
@Cacheable 说明:
作用: 在方法执行前,spring先查看缓存中是否有数据,如果有数据,则直接返回缓存数据;若没有数据,调用方法并将方法返回值放到缓存中
value: 缓存的名称,每个缓存名称下面可以有多个key
key: 缓存的key ----------> 支持Spring的表达式语言SPEL语法
在getById上加注解@Cacheable
/**
* Cacheable:在方法执行前spring先查看缓存中是否有数据,如果有数据,则直接返回缓存数据;若没有数据, *调用方法并将方法返回值放到缓存中
* value:缓存的名称,每个缓存名称下面可以有多个key
* key:缓存的key
*/
@GetMapping
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "userCache",key="#id")
public User getById(Long id){
User user = userMapper.getById(id);
return user;
}
重启服务,通过swagger接口文档测试,访问UserController的getById()方法
第一次访问,会请求我们controller的方法,查询数据库。后面再查询相同的id,就直接从Redis中查询数据,不用再查询数据库了,就说明缓存生效了。
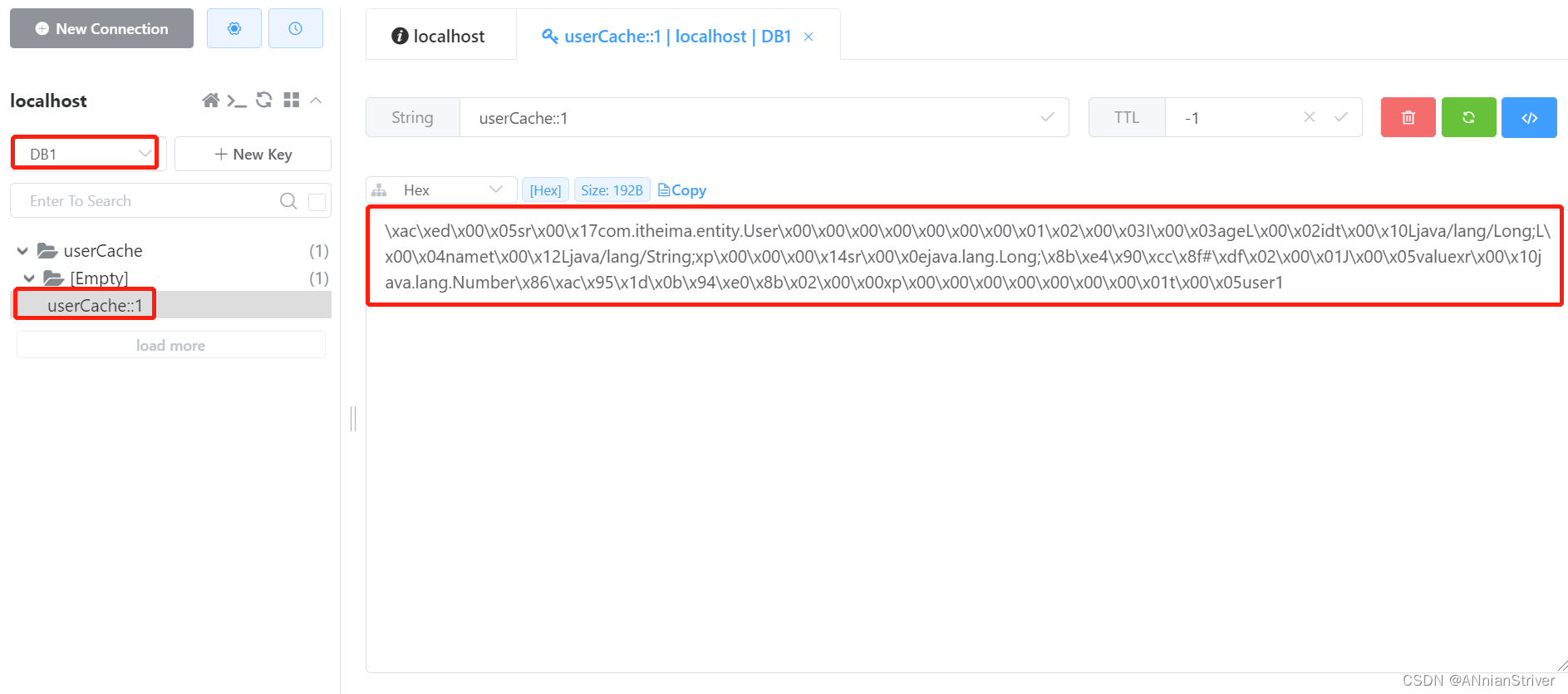
提前在redis中手动删除掉id=1的用户数据
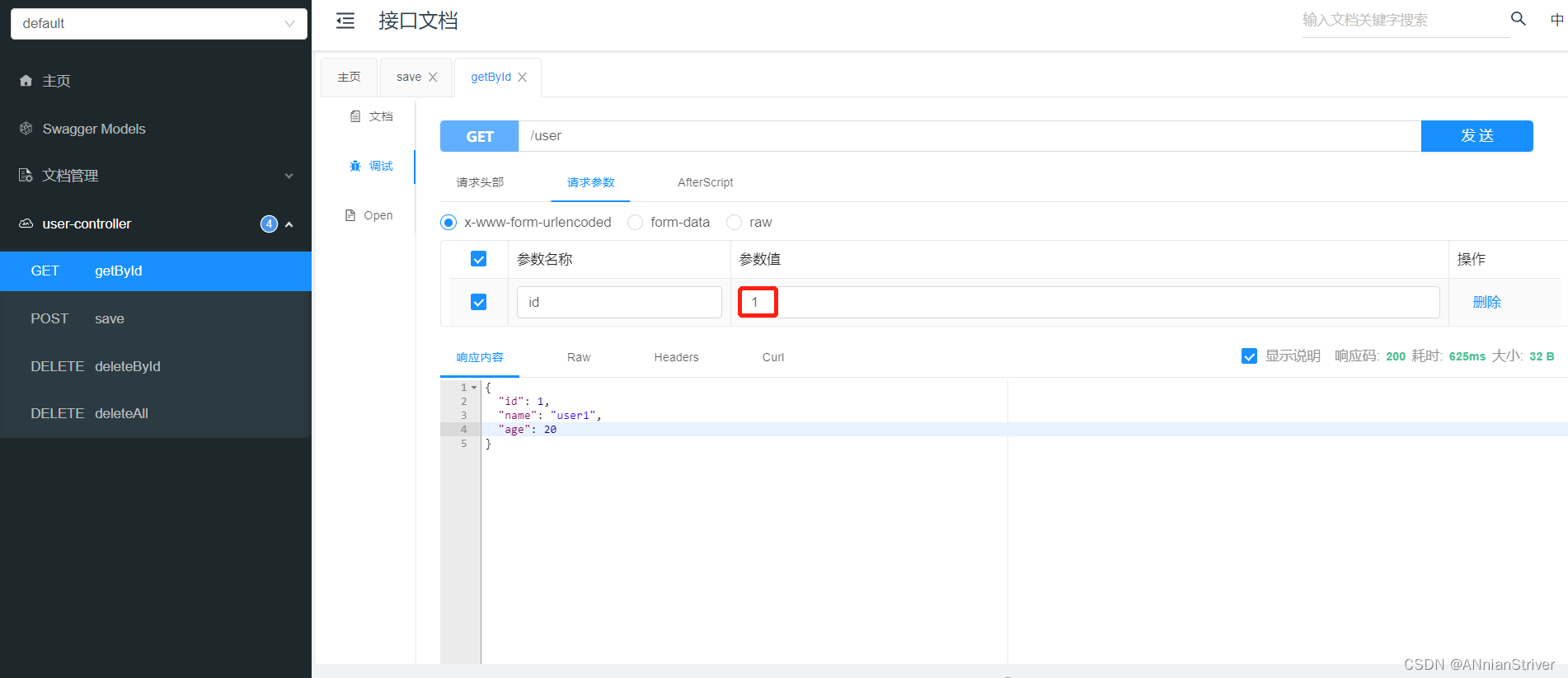
**查看控制台sql语句:**说明从数据库查询的用户数据
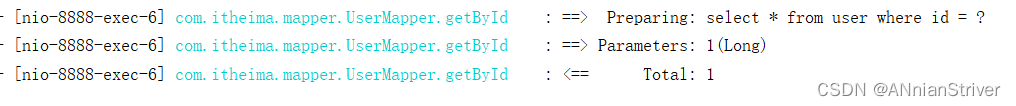
**查看Redis中的缓存数据:**说明已成功缓存
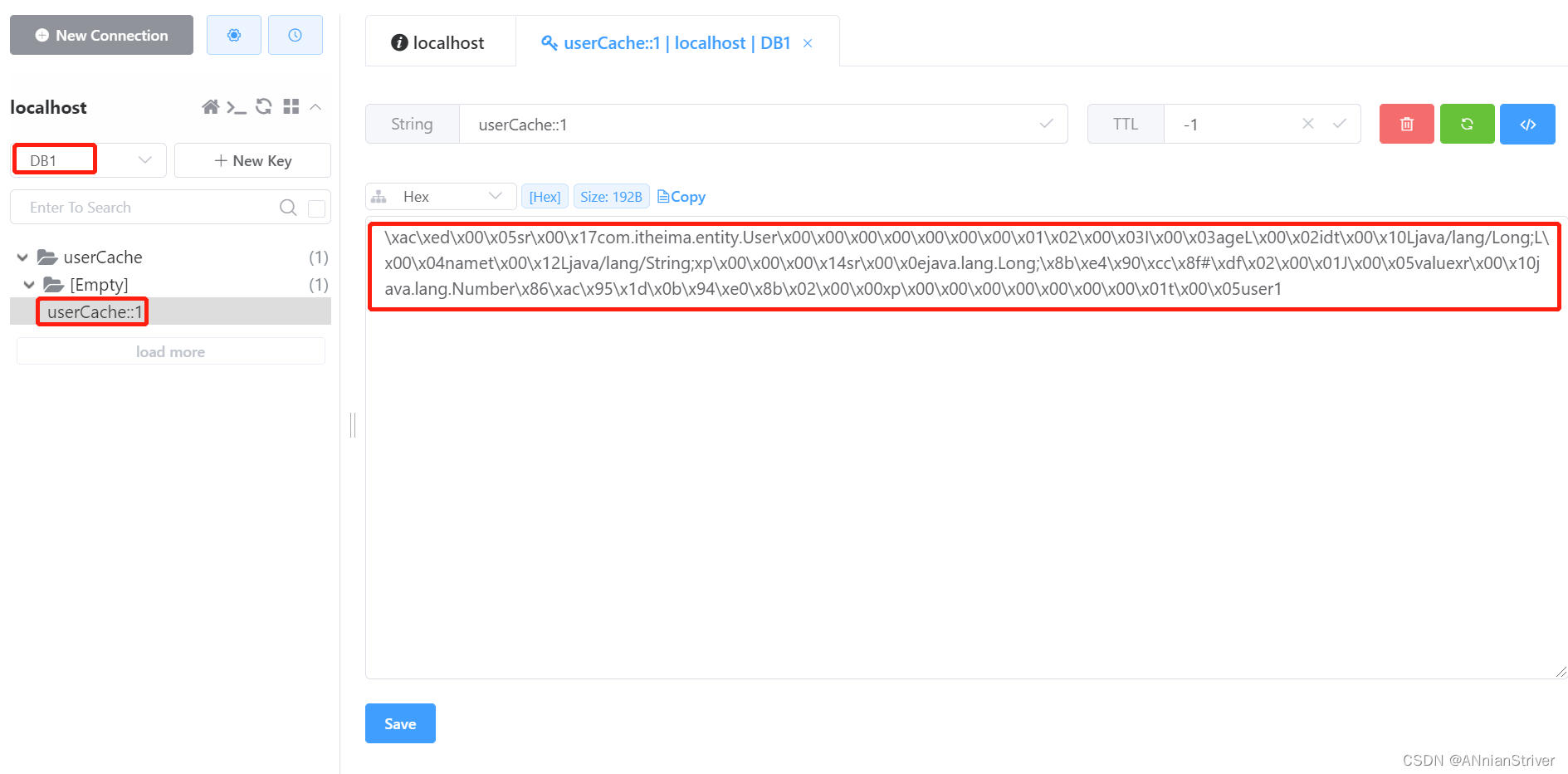
再次查询相同id的数据时,直接从redis中直接获取,不再查询数据库。
4). @CacheEvict注解
@CacheEvict 说明:
作用: 清理指定缓存
value: 缓存的名称,每个缓存名称下面可以有多个key
key: 缓存的key ----------> 支持Spring的表达式语言SPEL语法
在 delete 方法上加注解@CacheEvict
@DeleteMapping
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "userCache",key = "#id")//删除某个key对应的缓存数据
public void deleteById(Long id){
userMapper.deleteById(id);
}
@DeleteMapping("/delAll")
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "userCache",allEntries = true)//删除userCache下所有的缓存数据
public void deleteAll(){
userMapper.deleteAll();
}
重启服务,通过swagger接口文档测试,访问UserController的deleteAll()方法
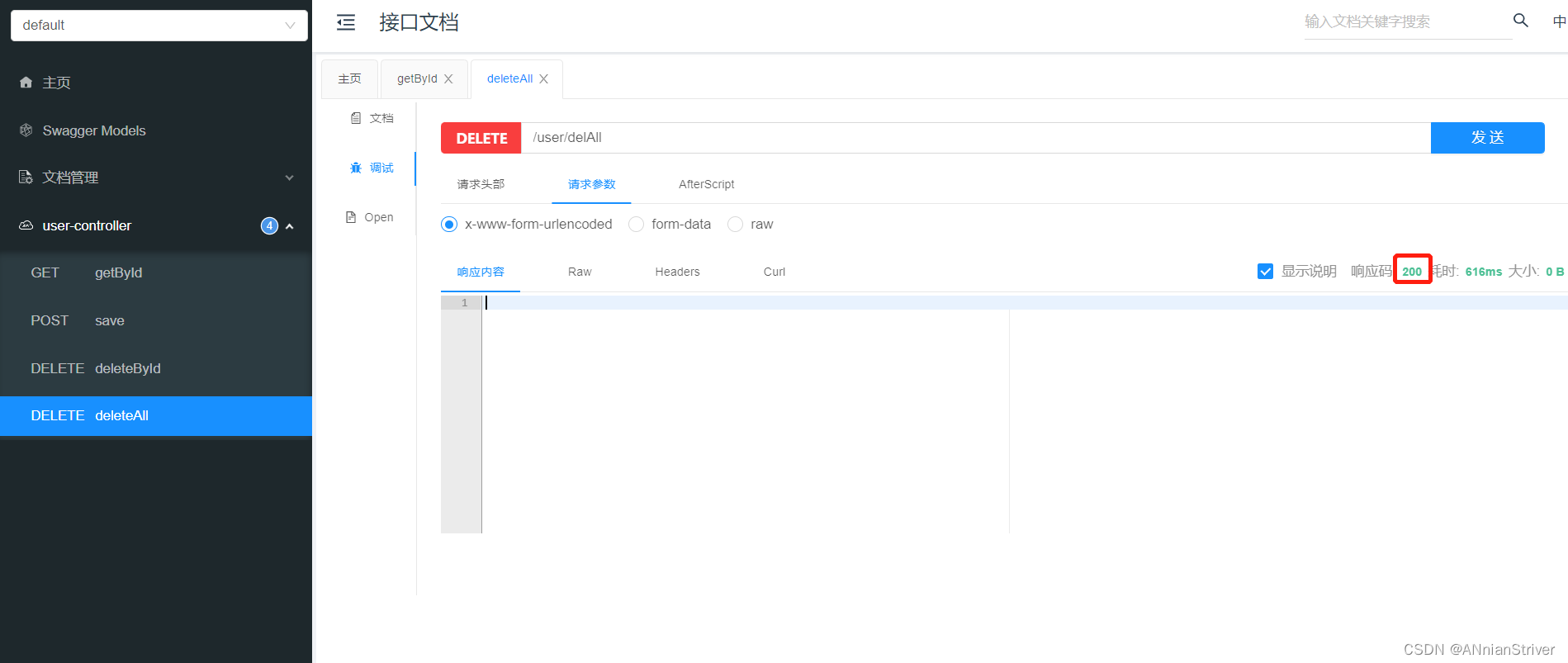
**查看user表:**数据清空
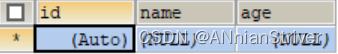
查询Redis缓存数据 
2.2 实现思路
实现步骤:
1). 导入Spring Cache和Redis相关maven坐标
2). 在启动类上加入@EnableCaching注解,开启缓存注解功能
3). 在用户端接口SetmealController的 list 方法上加入@Cacheable注解
4). 在管理端接口SetmealController的 save、delete、update、startOrStop等方法上加入CacheEvict注解
2.3 代码开发
按照上述实现步骤:
1). 导入Spring Cache和Redis相关maven坐标(已实现)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
2). 在启动类上加入@EnableCaching注解,开启缓存注解功能
package com.sky;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableTransactionManagement //开启注解方式的事务管理
@Slf4j
@EnableCaching
public class SkyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SkyApplication.class, args);
log.info("server started");
}
}
3). 在用户端接口SetmealController的 list 方法上加入@Cacheable注解
/**
* 条件查询
*
* @param categoryId
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/list")
@ApiOperation("根据分类id查询套餐")
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "setmealCache",key = "#categoryId") //key: setmealCache::100
public Result<List<Setmeal>> list(Long categoryId) {
Setmeal setmeal = new Setmeal();
setmeal.setCategoryId(categoryId);
setmeal.setStatus(StatusConstant.ENABLE);
List<Setmeal> list = setmealService.list(setmeal);
return Result.success(list);
}
4). 在管理端接口SetmealController的 save、delete、update、startOrStop等方法上加入CacheEvict注解
/**
* 新增套餐
*
* @param setmealDTO
* @return
*/
@PostMapping
@ApiOperation("新增套餐")
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "setmealCache",key = "#setmealDTO.categoryId")//key: setmealCache::100
public Result save(@RequestBody SetmealDTO setmealDTO) {
setmealService.saveWithDish(setmealDTO);
return Result.success();
}
/**
* 批量删除套餐
*
* @param ids
* @return
*/
@DeleteMapping
@ApiOperation("批量删除套餐")
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "setmealCache",allEntries = true)
public Result delete(@RequestParam List<Long> ids) {
setmealService.deleteBatch(ids);
return Result.success();
}
/**
* 修改套餐
*
* @param setmealDTO
* @return
*/
@PutMapping
@ApiOperation("修改套餐")
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "setmealCache",allEntries = true)
public Result update(@RequestBody SetmealDTO setmealDTO) {
setmealService.update(setmealDTO);
return Result.success();
}
/**
* 套餐起售停售
*
* @param status
* @param id
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/status/{status}")
@ApiOperation("套餐起售停售")
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "setmealCache",allEntries = true)
public Result startOrStop(@PathVariable Integer status, Long id) {
setmealService.startOrStop(status, id);
return Result.success();
}
2.4 功能测试
通过前后端联调方式来进行测试,同时观察redis中缓存的套餐数据。和缓存菜品功能测试基本一致,不再赘述。
2.5 代码提交
3. 添加购物车
3.1 需求分析和设计
3.1.1 产品原型
用户可以将菜品或者套餐添加到购物车。对于菜品来说,如果设置了口味信息,则需要选择规格后才能加入购物车;对于套餐来说,可以直接点击 + 将当前套餐加入购物车。在购物车中可以修改菜品和套餐的数量,也可以清空购物车。
效果图: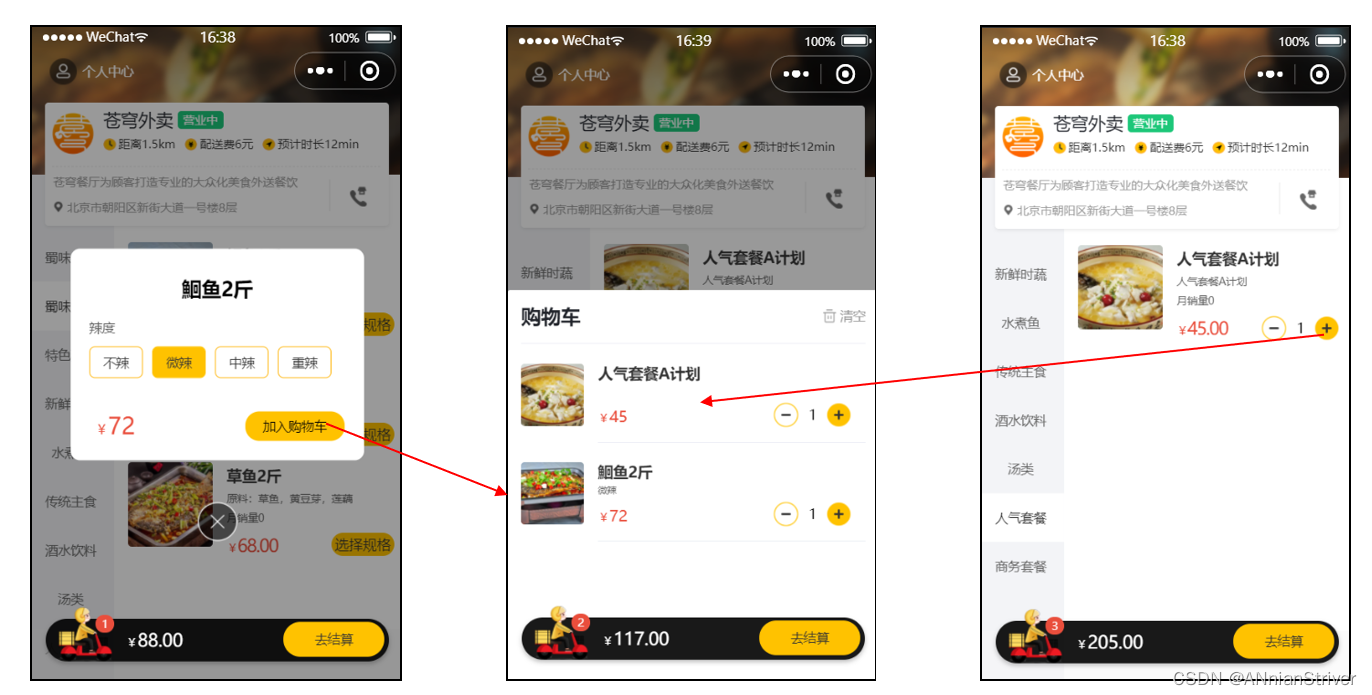
3.1.2 接口设计
通过上述原型图,设计出对应的添加购物车接口。
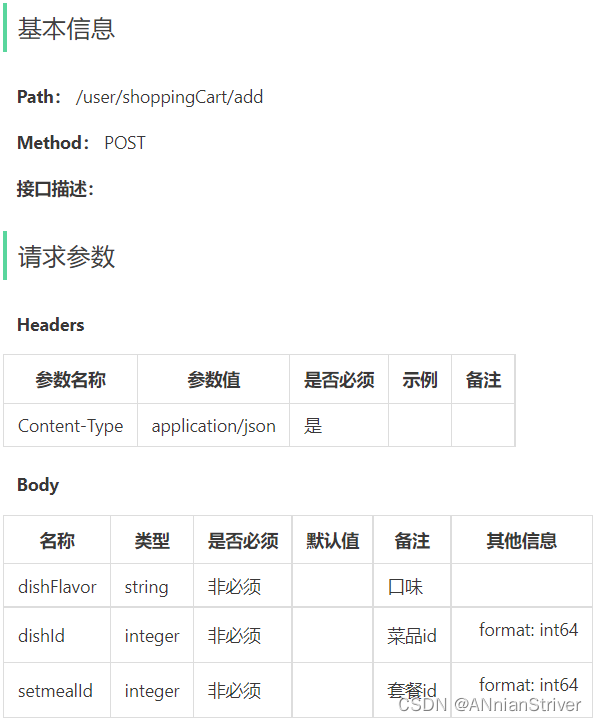
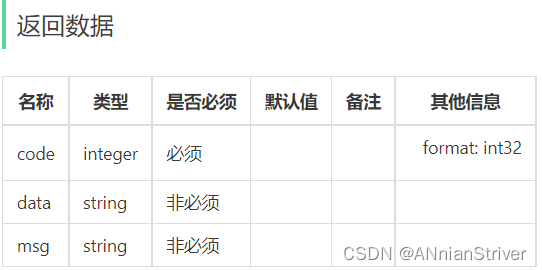
**说明:**添加购物车时,有可能添加菜品,也有可能添加套餐。故传入参数要么是菜品id,要么是套餐id。
3.1.3 表设计
用户的购物车数据,也是需要保存在数据库中的,购物车对应的数据表为shopping_cart表,具体表结构如下:
| 字段名 | 数据类型 | 说明 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | bigint | 主键 | 自增 |
| name | varchar(32) | 商品名称 | 冗余字段 |
| image | varchar(255) | 商品图片路径 | 冗余字段 |
| user_id | bigint | 用户id | 逻辑外键 |
| dish_id | bigint | 菜品id | 逻辑外键 |
| setmeal_id | bigint | 套餐id | 逻辑外键 |
| dish_flavor | varchar(50) | 菜品口味 | |
| number | int | 商品数量 | |
| amount | decimal(10,2) | 商品单价 | 冗余字段 |
| create_time | datetime | 创建时间 |
说明:
- 购物车数据是关联用户的,在表结构中,我们需要记录,每一个用户的购物车数据是哪些
- 菜品列表展示出来的既有套餐,又有菜品,如果用户选择的是套餐,就保存套餐ID(setmeal_id),如果用户选择的是菜品,就保存菜品ID(dish_id)
- 对同一个菜品/套餐,如果选择多份不需要添加多条记录,增加数量number即可
3.2 代码开发
3.2.1 DTO设计
根据添加购物车接口的参数设计DTO:
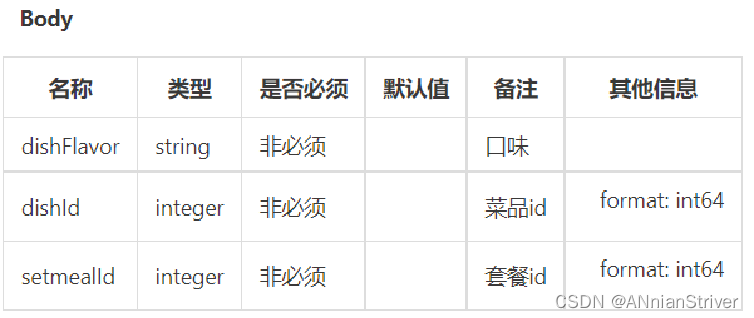
在sky-pojo模块,ShoppingCartDTO.java已定义
package com.sky.dto;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Data
public class ShoppingCartDTO implements Serializable {
private Long dishId;
private Long setmealId;
private String dishFlavor;
}
3.2.2 Controller层
根据添加购物车接口创建ShoppingCartController:
package com.sky.controller.user;
import com.sky.dto.ShoppingCartDTO;
import com.sky.result.Result;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* 购物车
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user/shoppingCart")
@Slf4j
@Api(tags = "C端-购物车接口")
public class ShoppingCartController {
@Autowired
private ShoppingCartService shoppingCartService;
/**
* 添加购物车
* @param shoppingCartDTO
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/add")
@ApiOperation("添加购物车")
public Result<String> add(@RequestBody ShoppingCartDTO shoppingCartDTO){
log.info("添加购物车:{}", shoppingCartDTO);
shoppingCartService.addShoppingCart(shoppingCartDTO);//后绪步骤实现
return Result.success();
}
}
3.2.3 Service层接口
创建ShoppingCartService接口:
package com.sky.service;
import com.sky.dto.ShoppingCartDTO;
import com.sky.entity.ShoppingCart;
import java.util.List;
public interface ShoppingCartService {
/**
* 添加购物车
* @param shoppingCartDTO
*/
void addShoppingCart(ShoppingCartDTO shoppingCartDTO);
}
3.2.4 Service层实现类
创建ShoppingCartServiceImpl实现类,并实现add方法:
package com.sky.service.impl;
import com.sky.context.BaseContext;
import com.sky.dto.ShoppingCartDTO;
import com.sky.entity.Dish;
import com.sky.entity.Setmeal;
import com.sky.entity.ShoppingCart;
import com.sky.mapper.DishMapper;
import com.sky.mapper.SetmealMapper;
import com.sky.service.ShoppingCartService;
import org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class ShoppingCartServiceImpl implements ShoppingCartService {
@Autowired
private ShoppingCartMapper shoppingCartMapper;
@Autowired
private DishMapper dishMapper;
@Autowired
private SetmealMapper setmealMapper;
/**
* 添加购物车
*
* @param shoppingCartDTO
*/
public void addShoppingCart(ShoppingCartDTO shoppingCartDTO) {
ShoppingCart shoppingCart = new ShoppingCart();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(shoppingCartDTO, shoppingCart);
//只能查询自己的购物车数据
shoppingCart.setUserId(BaseContext.getCurrentId());
//判断当前商品是否在购物车中
List<ShoppingCart> shoppingCartList = shoppingCartMapper.list(shoppingCart);
if (shoppingCartList != null && shoppingCartList.size() == 1) {
//如果已经存在,就更新数量,数量加1
shoppingCart = shoppingCartList.get(0);
shoppingCart.setNumber(shoppingCart.getNumber() + 1);
shoppingCartMapper.updateNumberById(shoppingCart);
} else {
//如果不存在,插入数据,数量就是1
//判断当前添加到购物车的是菜品还是套餐
Long dishId = shoppingCartDTO.getDishId();
if (dishId != null) {
//添加到购物车的是菜品
Dish dish = dishMapper.getById(dishId);
shoppingCart.setName(dish.getName());
shoppingCart.setImage(dish.getImage());
shoppingCart.setAmount(dish.getPrice());
} else {
//添加到购物车的是套餐
Setmeal setmeal = setmealMapper.getById(shoppingCartDTO.getSetmealId());
shoppingCart.setName(setmeal.getName());
shoppingCart.setImage(setmeal.getImage());
shoppingCart.setAmount(setmeal.getPrice());
}
shoppingCart.setNumber(1);
shoppingCart.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
shoppingCartMapper.insert(shoppingCart);
}
}
}
3.2.5 Mapper层
创建ShoppingCartMapper接口:
package com.sky.mapper;
import com.sky.entity.ShoppingCart;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Delete;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Update;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper
public interface ShoppingCartMapper {
/**
* 条件查询
*
* @param shoppingCart
* @return
*/
List<ShoppingCart> list(ShoppingCart shoppingCart);
/**
* 更新商品数量
*
* @param shoppingCart
*/
@Update("update shopping_cart set number = #{number} where id = #{id}")
void updateNumberById(ShoppingCart shoppingCart);
/**
* 插入购物车数据
*
* @param shoppingCart
*/
@Insert("insert into shopping_cart (name, user_id, dish_id, setmeal_id, dish_flavor, number, amount, image, create_time) " +
" values (#{name},#{userId},#{dishId},#{setmealId},#{dishFlavor},#{number},#{amount},#{image},#{createTime})")
void insert(ShoppingCart shoppingCart);
}
创建ShoppingCartMapper.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" >
<mapper namespace="com.sky.mapper.ShoppingCartMapper">
<select id="list" parameterType="ShoppingCart" resultType="ShoppingCart">
select * from shopping_cart
<where>
<if test="userId != null">
and user_id = #{userId}
</if>
<if test="dishId != null">
and dish_id = #{dishId}
</if>
<if test="setmealId != null">
and setmeal_id = #{setmealId}
</if>
<if test="dishFlavor != null">
and dish_flavor = #{dishFlavor}
</if>
</where>
order by create_time desc
</select>
</mapper>
3.3 功能测试
进入小程序,添加菜品
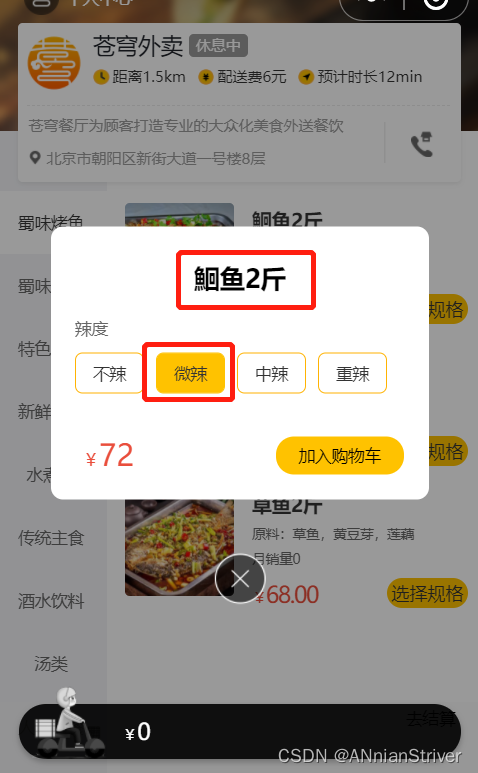
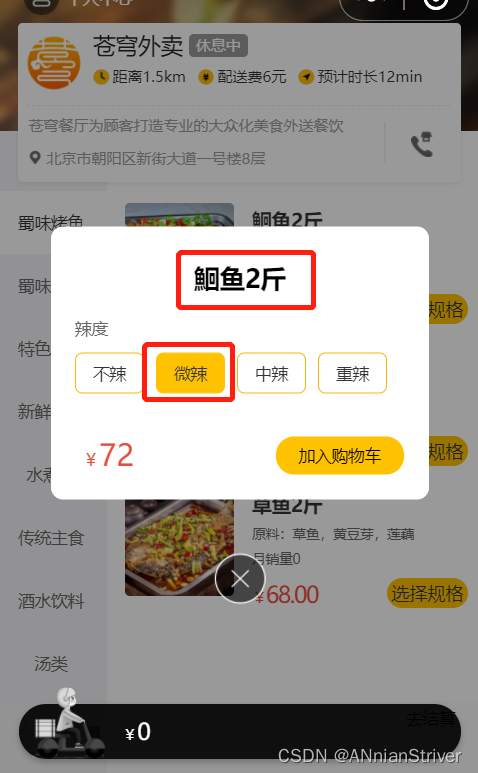
加入购物车,查询数据库

因为现在没有实现查看购物车功能,所以只能在表中进行查看。
在前后联调时,后台可通断点方式启动,查看运行的每一步。
3.4 代码提交
4. 查看购物车
4.1 需求分析和设计
4.1.1 产品原型
当用户添加完菜品和套餐后,可进入到购物车中,查看购物中的菜品和套餐。
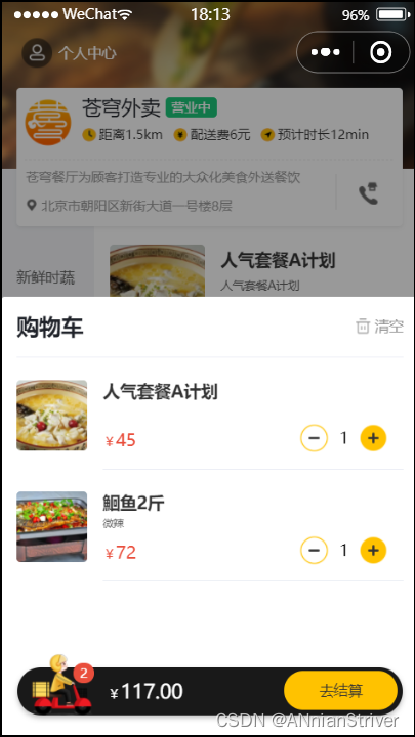
4.1.2 接口设计
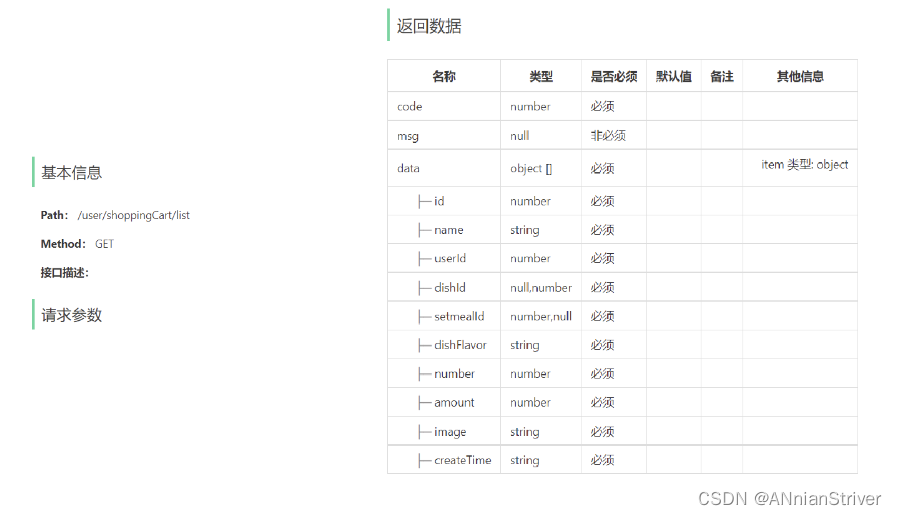
4.2 代码开发
4.2.1 Controller层
在ShoppingCartController中创建查看购物车的方法:
/**
* 查看购物车
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/list")
@ApiOperation("查看购物车")
public Result<List<ShoppingCart>> list(){
return Result.success(shoppingCartService.showShoppingCart());
}
4.2.2 Service层接口
在ShoppingCartService接口中声明查看购物车的方法:
/**
* 查看购物车
* @return
*/
List<ShoppingCart> showShoppingCart();
4.2.3 Service层实现类
在ShoppingCartServiceImpl中实现查看购物车的方法:
/**
* 查看购物车
* @return
*/
public List<ShoppingCart> showShoppingCart() {
return shoppingCartMapper.list(ShoppingCart.
builder().
userId(BaseContext.getCurrentId()).
build());
}
4.3 功能测试
当进入小程序时,就会发起查看购物车的请求
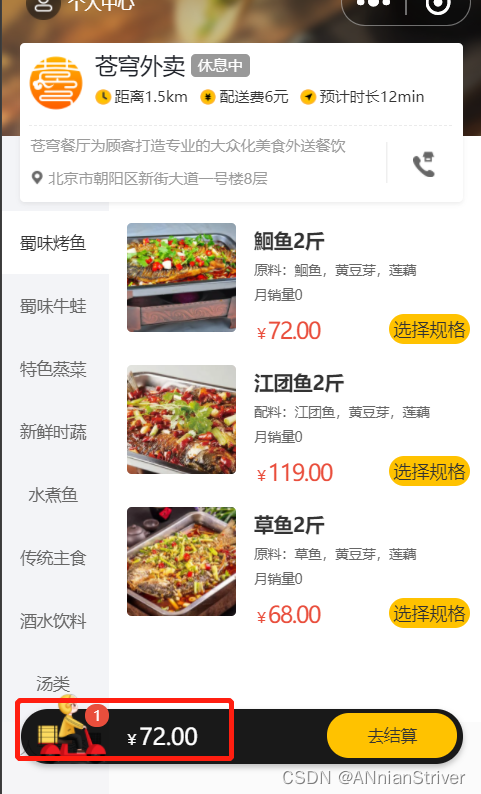
点击购物车图标
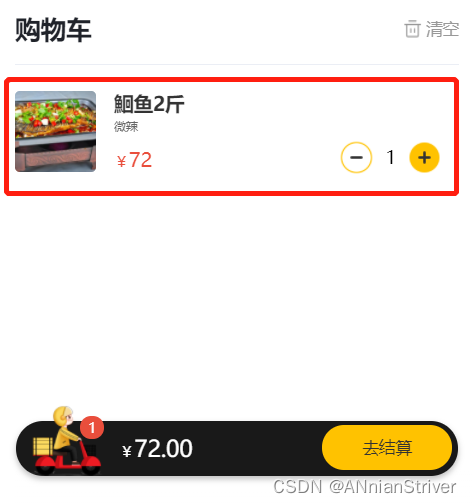
测试成功。
4.4 代码提交
5. 清空购物车
5.1 需求分析和设计
5.1.1 产品原型
当点击清空按钮时,会把购物车中的数据全部清空。
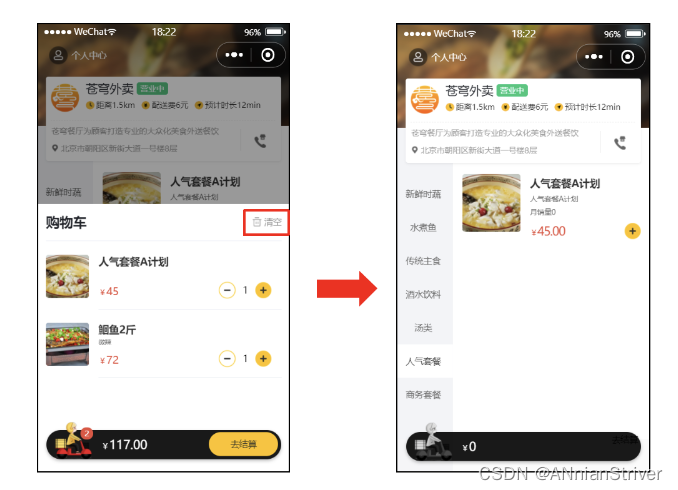
5.1.2 接口设计
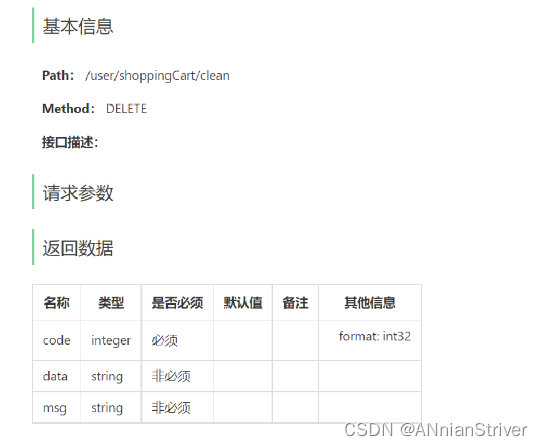
5.2 代码开发
5.2.1 Controller层
在ShoppingCartController中创建清空购物车的方法:
/**
* 清空购物车商品
* @return
*/
@DeleteMapping("/clean")
@ApiOperation("清空购物车商品")
public Result<String> clean(){
shoppingCartService.cleanShoppingCart();
return Result.success();
}
5.2.2 Service层接口
在ShoppingCartService接口中声明清空购物车的方法:
/**
* 清空购物车商品
*/
void cleanShoppingCart();
5.2.3 Service层实现类
在ShoppingCartServiceImpl中实现清空购物车的方法:
/**
* 清空购物车商品
*/
public void cleanShoppingCart() {
shoppingCartMapper.deleteByUserId(BaseContext.getCurrentId());
}
5.2.4 Mapper层
在ShoppingCartMapper接口中创建删除购物车数据的方法:
/**
* 根据用户id删除购物车数据
*
* @param userId
*/
@Delete("delete from shopping_cart where user_id = #{userId}")
void deleteByUserId(Long userId);
5.3 功能测试
进入到购物车页面
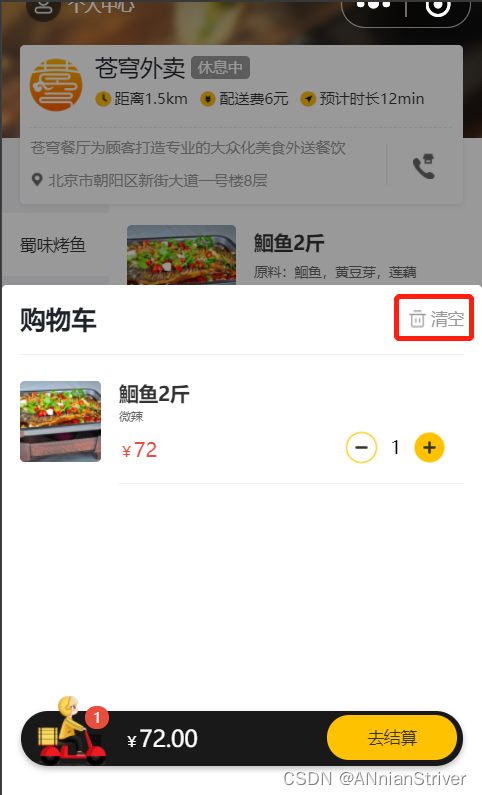
点击清空
查看数据库中的数据

说明当前用户的购物车数据已全部删除。