文章目录
- 一、题目
- 二、解法
- 三、完整代码
所有的LeetCode题解索引,可以看这篇文章——【算法和数据结构】LeetCode题解。
一、题目
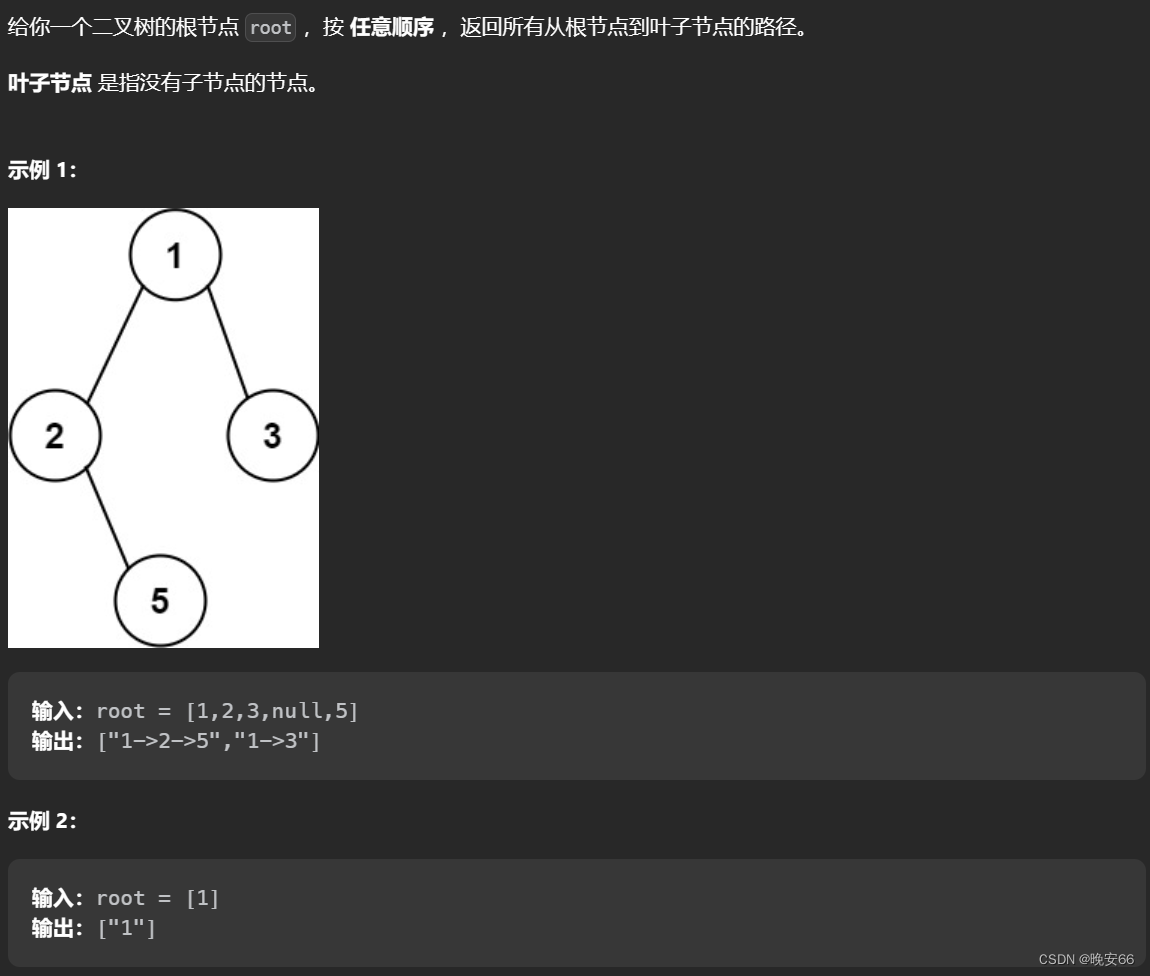
二、解法
思路分析:首先看这道题的输出结果,是前序遍历。然后需要找到从根节点到叶子节点的所有路径,涉及回溯,因此很容易想到用递归+回溯的方法(前序遍历按中左右顺序访问节点,在访问完左节点后返回中节点,接着返回右节点)。递归法有三个要素:
- 1.输入参数和返回值:输入参数为根节点(递归的时候就是中间节点),单个路径,以及结果数组。
- 2.终止条件:遇到叶子节点就终止,同时将path中的节点按要求连接成字符串,插入结果数组。
- 3.单层递归逻辑:如果左/右节点不为空,则递归左/右节点,递归结束后需要删除左/右节点(因为已经遍历过了,换一个路径),然后进行下一个递归,这个操作就是回溯。
程序如下:
class Solution {
public:
// 前序遍历递归法/回溯法
void traversal(TreeNode* root, vector<int> &path, vector<string> &result) { // 1.输入参数和返回值
path.push_back(root->val); // 中间节点先加入path
if (!root->left && !root->right) { // 2.终止条件:遇到叶子节点
string spath;
for (int i = 0; i < path.size() - 1; ++i) {
spath += to_string(path[i]);
spath += "->";
}
spath += to_string(path[path.size() - 1]);
result.push_back(spath);
return;
}
// 3.单层递归逻辑
if (root->left) {
traversal(root->left, path, result); // 递归
path.pop_back(); // 回溯
}
if (root->right) {
traversal(root->right, path, result);
path.pop_back();
}
}
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
vector<string> result;
vector<int> path;
if (!root) return result;
traversal(root, path, result);
return result;
}
};
思路分析:我们对以上代码进行精简,将递归和回溯浓缩要一行代码当中,将path + "->"作为参数输入,因为并没有改变path的数值,执行完递归函数之后,path依然是之前的数值(相当于回溯了)。省去回溯操作,同时每次递归都在修改path的值,也省去将路径节点转换为字符串的操作。
class Solution2 {
public:
// 前序遍历递归法:精简版本
void traversal(TreeNode* root, string path, vector<string>& result) { // 1.输入参数和返回值
path += to_string(root->val); // 中间节点先加入path
if (!root->left && !root->right) { // 2.终止条件:遇到叶子节点
result.push_back(path);
return;
}
// 3.单层递归逻辑:递归+回溯
if (root->left) traversal(root->left, path + "->", result); // 左
if (root->right) traversal(root->right, path + "->", result); // 右
}
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
vector<string> result;
string path;
if (!root) return result;
traversal(root, path, result);
return result;
}
};
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2),n表示节点数量。遍历所有节点复杂度为 O ( n ) O(n) O(n),每一次会对 path 变量进行拷贝构造 O ( n ) O(n) O(n),时间复杂度为总时间复杂度为 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2)。
- 空间复杂度: O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2),考虑最坏的情况下,树的每个节点都只有一个孩子,整棵树呈现链状,递归层数为n层,此时每一层的 path 变量的空间代价的总和为 O ( ∑ i = 1 n i ) = O ( n 2 ) O(\sum^n_{i=1}i)=O(n^2) O(∑i=1ni)=O(n2)。
三、完整代码
# include <iostream>
# include <vector>
# include <queue>
# include <string>
# include <algorithm>
# include <stack>
using namespace std;
// 树节点定义
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
// 前序遍历递归法/回溯法
void traversal(TreeNode* root, vector<int> &path, vector<string> &result) { // 1.输入参数和返回值
path.push_back(root->val); // 中间节点先加入path
if (!root->left && !root->right) { // 2.终止条件:遇到叶子节点
string spath;
for (int i = 0; i < path.size() - 1; ++i) {
spath += to_string(path[i]);
spath += "->";
}
spath += to_string(path[path.size() - 1]);
result.push_back(spath);
return;
}
// 3.单层递归逻辑
if (root->left) {
traversal(root->left, path, result); // 递归
path.pop_back(); // 回溯
}
if (root->right) {
traversal(root->right, path, result);
path.pop_back();
}
}
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
vector<string> result;
vector<int> path;
if (!root) return result;
traversal(root, path, result);
return result;
}
};
class Solution2 {
public:
// 前序遍历递归法:精简版本
void traversal(TreeNode* root, string path, vector<string>& result) { // 1.输入参数和返回值
path += to_string(root->val); // 中间节点先加入path
if (!root->left && !root->right) { // 2.终止条件:遇到叶子节点
result.push_back(path);
return;
}
// 3.单层递归逻辑:递归+回溯
if (root->left) traversal(root->left, path + "->", result); // 左
if (root->right) traversal(root->right, path + "->", result); // 右
}
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
vector<string> result;
if (!root) return result;
traversal(root, "", result);
return result;
}
};
template<typename T>
void my_print(T &v, const string msg)
{
cout << msg << endl;
for (class T ::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
template<class T1, class T2>
void my_print2(T1 & v, const string str) {
cout << str << endl;
for (class T1::iterator vit = v.begin(); vit < v.end(); ++vit) {
for (class T2::iterator it = (*vit).begin(); it < (*vit).end(); ++it) {
cout << *it << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
}
// 前序遍历迭代法创建二叉树,每次迭代将容器首元素弹出(弹出代码还可以再优化)
void Tree_Generator(vector<string>& t, TreeNode*& node) {
if (!t.size() || t[0] == "NULL") return; // 退出条件
else {
node = new TreeNode(stoi(t[0].c_str())); // 中
if (t.size()) {
t.assign(t.begin() + 1, t.end());
Tree_Generator(t, node->left); // 左
}
if (t.size()) {
t.assign(t.begin() + 1, t.end());
Tree_Generator(t, node->right); // 右
}
}
}
// 层序遍历
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
vector<vector<int>> result;
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size(); // size必须固定, que.size()是不断变化的
vector<int> vec;
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
vec.push_back(node->val);
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
result.push_back(vec);
}
return result;
}
int main()
{
vector<string> t = { "1", "2", "NULL", "5", "NULL", "NULL", "3", "NULL", "NULL" }; // 前序遍历
my_print(t, "目标树");
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode();
Tree_Generator(t, root);
vector<vector<int>> tree = levelOrder(root);
my_print2<vector<vector<int>>, vector<int>>(tree, "目标树:");
Solution s1;
vector<string> result = s1.binaryTreePaths(root);
my_print(result, "所有路径为:");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
end