文章目录
- 一、准备工作
- 二、C语言threadpool实现
- 三、C++ 11标准实现
代码看视频敲的,非原创
一、准备工作
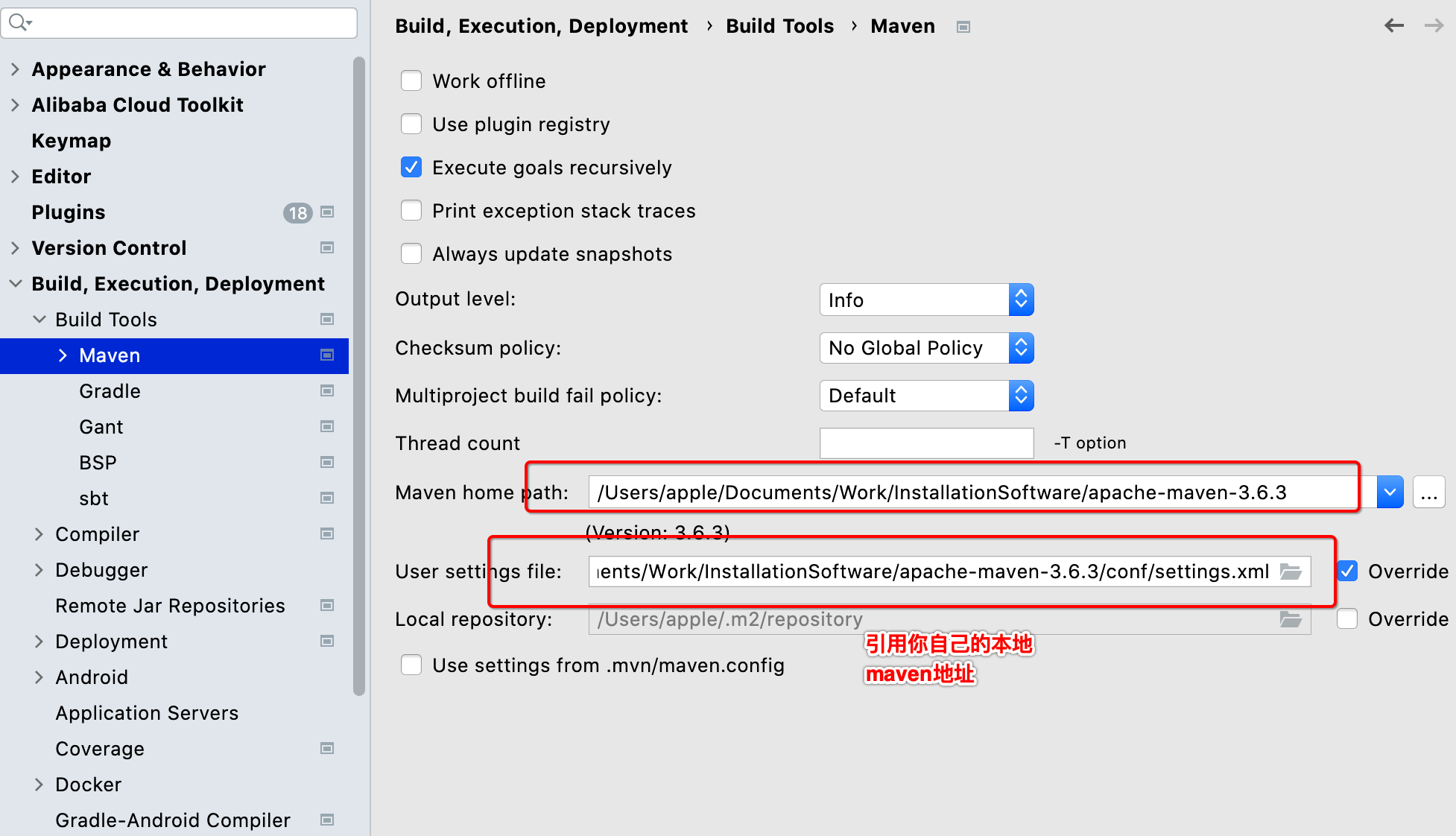
创建项目
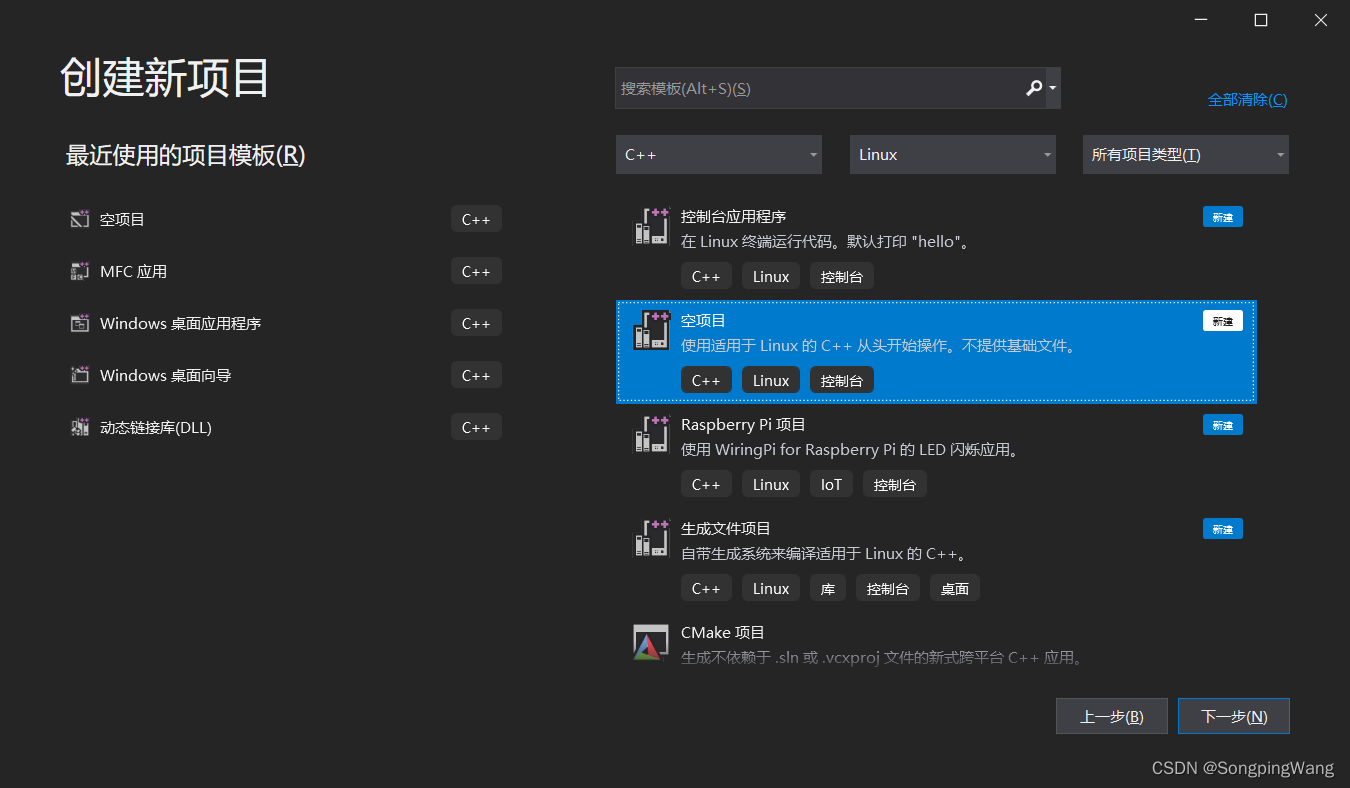
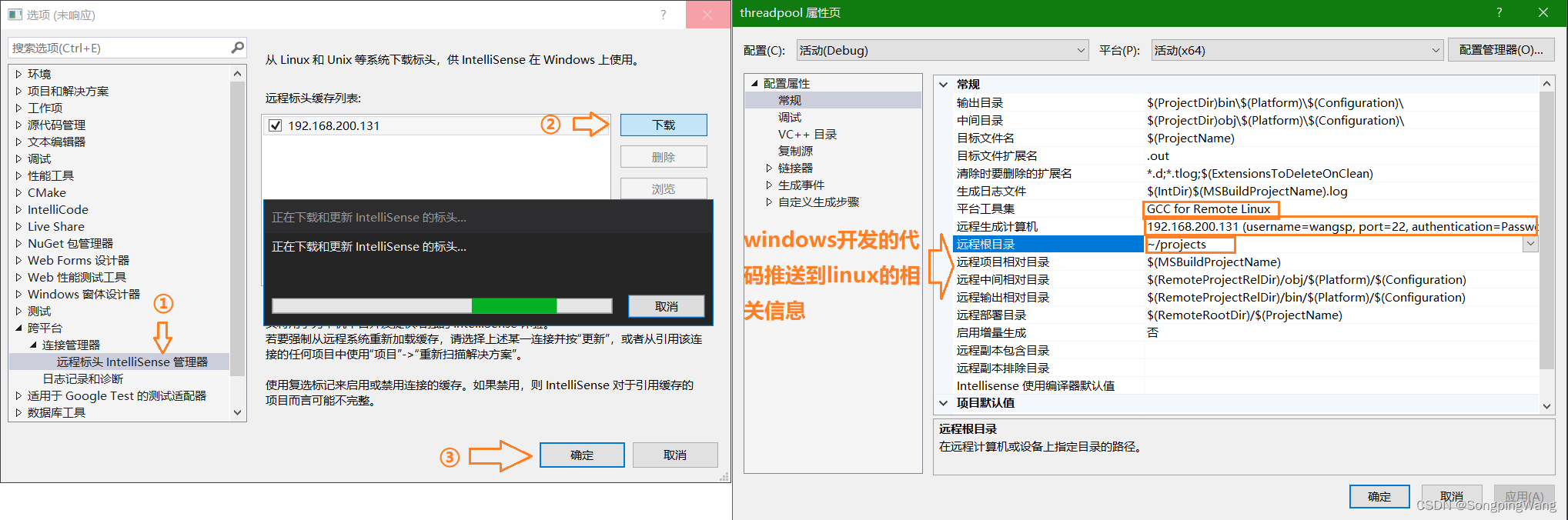
连接linux虚拟机
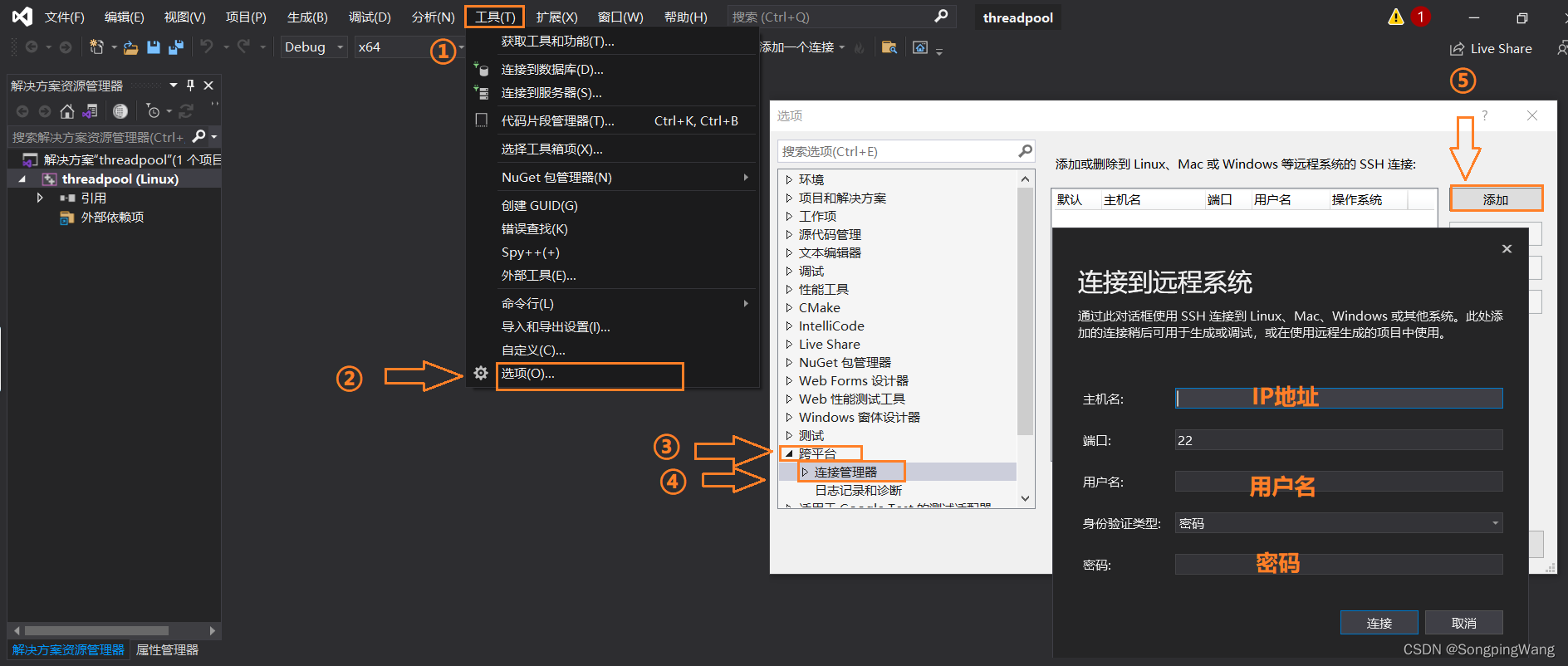
启动测试:VS2019运行Linux程序报错:无法启动gdb。系统中缺少gdb。sudo yum install -y gdb
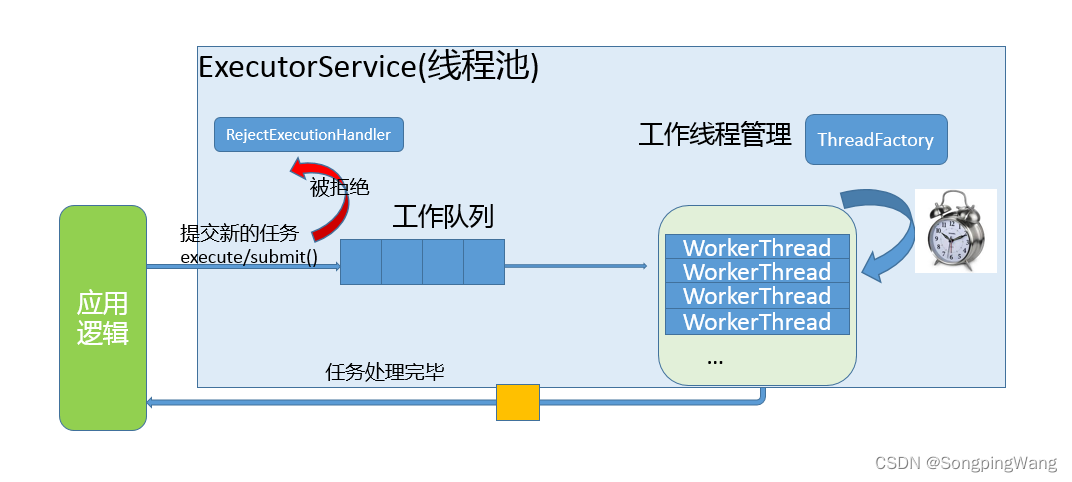
线程池的组成主要分为3个部分,这三部分配合工作就可以得到一个完整的线程池:
- 任务队列,存储需要处理的任务,由工作的线程来处理这些任务
通过线程池提供的API函数,将一个待处理的任务添加到任务队列,或者从任务队列中删除
已处理的任务会被从任务队列中删除
线程池的使用者,也就是调用线程池函数往任务队列中添加任务的线程就是生产者线程 - 工作的线程(任务队列任务的消费者) ,N个
线程池中维护了一定数量的工作线程, 他们的作用是是不停的读任务队列, 从里边取出任务并处理
工作的线程相当于是任务队列的消费者角色,
如果任务队列为空, 工作的线程将会被阻塞 (使用条件变量/信号量阻塞)
如果阻塞之后有了新的任务, 由生产者将阻塞解除, 工作线程开始工作 - 管理者线程(不处理任务队列中的任务),1个
它的任务是周期性的对任务队列中的任务数量以及处于忙状态的工作线程个数进行检测
当任务过多的时候, 可以适当的创建一些新的工作线程
当任务过少的时候, 可以适当的销毁一些工作的线程
二、C语言threadpool实现
threadpool.h
#pragma once
#ifndef _THREADPOOL_H
#define _THREADPOOL_H
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
// 任务结构体
typedef struct Task
{
void (*function)(void* arg);
void* arg;
}Task;
// 线程池结构体
typedef struct ThreadPool
{
// 任务队列
Task* taskQ;
int queueCapacity; // 容量
int queueSize; // 当前任务个数
int queueFront; // 队头 -> 取数据
int queueRear; // 队尾 -> 放数据
pthread_t managerID; // 管理者线程ID
pthread_t* threadIDs; // 工作的线程ID
int minNum; // 最小线程数量
int maxNum; // 最大线程数量
int busyNum; // 忙的线程的个数
int liveNum; // 存活的线程的个数
int exitNum; // 要销毁的线程个数
pthread_mutex_t mutexPool; // 锁整个的线程池
pthread_mutex_t mutexBusy; // 锁busyNum变量
pthread_cond_t notFull; // 任务队列是不是满了
pthread_cond_t notEmpty; // 任务队列是不是空了
int shutdown; // 是不是要销毁线程池, 销毁为1, 不销毁为0
}ThreadPool;
// 创建线程池并初始化
ThreadPool* threadPoolCreate(int min, int max, int queueSize);
// 销毁线程池
int threadPoolDestroy(ThreadPool* pool);
// 给线程池添加任务
void threadPoolAdd(ThreadPool* pool, void(*func)(void*), void* arg);
// 获取线程池中工作的线程的个数
int threadPoolBusyNum(ThreadPool* pool);
// 获取线程池中活着的线程的个数
int threadPoolAliveNum(ThreadPool* pool);
//
// 工作的线程(消费者线程)任务函数
void* worker(void* arg);
// 管理者线程任务函数
void* manager(void* arg);
// 单个线程退出
void threadExit(ThreadPool* pool);
#endif // _THREADPOOL_H
threadpool.c
#include "threadpool.h"
const int NUMBER = 2;
ThreadPool* threadPoolCreate(int min, int max, int queueSize)
{
ThreadPool* pool = (ThreadPool*)malloc(sizeof(ThreadPool));
do
{
if (pool == NULL)
{
printf("malloc threadpool failed...\n");
break;
}
pool->threadIDs = (pthread_t*)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t) * max);
if (pool->threadIDs == NULL)
{
printf("malloc threadIDs failed...\n");
break;
}
memset(pool->threadIDs, 0, sizeof(pthread_t) * max);
pool->minNum = min;
pool->maxNum = max;
pool->busyNum = 0;
pool->liveNum = min; // 和最小个数相等
pool->exitNum = 0;
if (pthread_mutex_init(&pool->mutexPool, NULL) != 0 ||
pthread_mutex_init(&pool->mutexBusy, NULL) != 0 ||
pthread_cond_init(&pool->notEmpty, NULL) != 0 ||
pthread_cond_init(&pool->notFull, NULL) != 0)
{
printf("mutex or condition init fail...\n");
break;
}
// 任务队列
pool->taskQ = (Task*)malloc(sizeof(Task) * queueSize);
pool->queueCapacity = queueSize;
pool->queueSize = 0;
pool->queueFront = 0;
pool->queueRear = 0;
pool->shutdown = 0;
// 创建线程
pthread_create(&pool->managerID, NULL, manager, pool);
for (size_t i = 0; i < min; i++)
{
pthread_create(&pool->threadIDs[i], NULL, worker, pool);
}
return pool;
} while (0);
//释放资源
if (pool && pool->threadIDs) free(pool->threadIDs);
if (pool && pool->taskQ) free(pool->taskQ);
if (pool) free(pool);
return NULL;
}
int threadPoolDestroy(ThreadPool* pool)
{
if (pool == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
//关闭线程池
pool->shutdown = 1;
//阻塞回收管理者线程
pthread_join(pool->managerID, NULL);
//唤醒阻塞消费者线程
for (size_t i = 0; i < pool->liveNum; i++)
{
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->notEmpty);
}
//释放申请的堆内存
if (pool->taskQ) free(pool->taskQ);
if (pool->threadIDs) free(pool->threadIDs);
//释放互斥锁
pthread_mutex_destroy(&pool->mutexBusy);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&pool->mutexPool);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&pool->notEmpty);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&pool->notFull);
free(pool);
return 0;
}
void threadPoolAdd(ThreadPool* pool, void(*func)(void*), void* arg)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool);
while (pool->queueSize == pool->queueCapacity && !pool->shutdown)
{
//阻塞生产者线程
pthread_cond_wait(&pool->notFull, &pool->mutexPool);
}
if (pool->shutdown)
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
return;
}
//添加任务到队尾
pool->taskQ[pool->queueRear].function = func;
pool->taskQ[pool->queueRear].arg = arg;
pool->queueRear = (pool->queueRear + 1) % pool->queueCapacity;
pool->queueSize++;
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->notEmpty);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
}
int threadPoolBusyNum(ThreadPool* pool)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexBusy);
int busyNum = pool->busyNum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexBusy);
return busyNum;
}
int threadPoolAliveNum(ThreadPool* pool)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool);
int Alive = pool->liveNum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
return Alive;
}
void* worker(void* arg)
{
ThreadPool* pool = (ThreadPool*)arg;
while (1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool);
//当前任务队列是否为空
while (pool->queueSize == 0 && !pool->shutdown)
{
//阻塞工作线程
pthread_cond_wait(&pool->notEmpty, &pool->mutexPool);
//判断是不是要销毁线程
if (pool->exitNum > 0)
{
pool->exitNum--;
if (pool->liveNum > pool->minNum)
{
pool->liveNum--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
threadExit(pool);
}
}
}
//判断当前线程是否被关闭了
if (pool->shutdown)
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
threadExit(pool);
}
//从任务队列中取出一个任务
Task task;
task.function = pool->taskQ[pool->queueFront].function;
task.arg = pool->taskQ[pool->queueFront].arg;
//移动头部指针指向下一个节点
pool->queueFront = (pool->queueFront + 1) % pool->queueCapacity;
pool->queueSize--;
//唤醒生产者
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->notFull);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
printf("thread %ld start working...\n", pthread_self());
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexBusy);
pool->busyNum++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexBusy);
task.function(task.arg);
free(task.arg);
task.arg = NULL;
printf("thread %ld end worked...\n", pthread_self());
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexBusy);
pool->busyNum--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexBusy);
}
return NULL;
}
void* manager(void* arg)
{
ThreadPool* pool = (ThreadPool*)arg;
while (!pool->shutdown)
{
//每3s检测一次
sleep(3);
//取出线程池中任务的数量和当前线程的个数
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool);
int queueSize = pool->queueSize;
int liveNum = pool->liveNum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
//取出线程池中忙碌线程的个数
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexBusy);
int busyNum = pool->busyNum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexBusy);
// 添加线程(当前任务个数>存活线程个数 && 存活线程个数< 最大线程数)
if (queueSize > liveNum && liveNum < pool->maxNum)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool);
int counter = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < pool->maxNum
&& counter < NUMBER
&& pool->liveNum < pool->maxNum; i++)
{
if (pool->threadIDs[i] == 0)
{
pthread_create(&pool->threadIDs[i], NULL, worker, pool);
counter++;
pool->liveNum++;
}
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
}
// 销毁线程(忙的线程*2 < 存活的线程数 && 存活的线程数 > 最小的线程数)
if (busyNum * 2 < liveNum && liveNum > pool->minNum)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool);
pool->exitNum = NUMBER;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
//让工作线程自杀
for (size_t i = 0; i < NUMBER; i++)
{
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->notEmpty);
}
}
}
return NULL;
}
void threadExit(ThreadPool* pool)
{
pthread_t tid = pthread_self();
for (size_t i = 0; i < pool->maxNum; i++)
{
if (pool->threadIDs[i] == tid)
{
pool->threadIDs[i] = 0;
printf("threadExit %ld exiting...", tid);
break;
}
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
main.c
#include "threadpool.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void taskFunc(void* arg)
{
int num = *(int*)arg;
printf("thread %ld is working, number = %d\n", pthread_self(), num);
sleep(1);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
printf("%s 向你问好!\n", "windows to linux");
// 创建线程池
ThreadPool* pool = threadPoolCreate(4, 10, 100);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i)
{
int* num = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
*num = i + 100;
threadPoolAdd(pool, taskFunc, num);
}
sleep(10);
threadPoolDestroy(pool);
return 0;
}
https://gitee.com/lc123/thread-pool
三、C++ 11标准实现
三个文件:TaskQueue.hpp, ThreadPool.hpp, main.cpp
TaskQueue.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <mutex>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
typedef function<void(void*)> callback;
template<class T>
class Task {
public:
Task() {
function = nullptr;
arg = nullptr;
}
Task(callback f, void *arg) {
function = f;
this->arg = (T *)arg;
}
callback function;
T *arg;
};
template<class T>
class TaskQueue {
public:
TaskQueue() {};
~TaskQueue() {};
void addTask(const Task<T>& task)
{
lock_guard<mutex> lock(mtx);
taskQueue.push(task);
};
Task<T> takeTask()
{
lock_guard<mutex> lock(mtx);
Task<T> task;
if (!taskQueue.empty()) {
task = taskQueue.front();
taskQueue.pop();
}
return task;
};
inline unsigned int taskNumber()
{
return taskQueue.size();
}
private:
queue<Task<T>> taskQueue;
mutex mtx;
};
ThreadPool.hpp
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<mutex>
#include<thread>
#include<string.h>
#include<atomic>
#include<vector>
#include<condition_variable>
#include"TaskQueue.hpp"
#include<signal.h>
using namespace std;
//线程池结构体
template<class T>
class ThreadPool {
public:
ThreadPool();
explicit ThreadPool(unsigned int min, unsigned int max);
~ThreadPool();
void addTask(const Task<T> &task);
unsigned int getBusyNum(); //忙的线程个数
unsigned int getAliveNum(); //活的线程个数
private:
void threadExit();//线程退出
static void * worker(void *arg);//工作线程调用的任务函数
static void * manager(void *arg);//管理者线程调用的任务函数
const static unsigned int NUMBER = 2;//一次加入的线程数
//任务队列
TaskQueue<T> *taskQueue;
thread *managerThread; //管理者线程
vector<thread> workGroup; //工作线程组
unsigned int minNum; //最小线程数
unsigned int maxNum; //最大线程数
atomic<unsigned int> busyNum; //忙的线程的个数
atomic<unsigned int> liveNum; //存活的线程的个数
atomic<unsigned int> exitNum; //要销毁的线程个数
mutex mutexPool; //锁整个线程池
condition_variable notEmpty; //任务队列是不是空了 利用条件变量通知
bool isShutdown; //线程池销毁 true
};
template<class T>
ThreadPool<T>::ThreadPool() {}
template<class T>
ThreadPool<T>::ThreadPool(unsigned int min, unsigned int max) {
taskQueue = new TaskQueue<T>;
if (nullptr == taskQueue) {
cout << "new taskQueue fail..." << endl;
return;
}
workGroup.reserve(max); //分配最大容量
minNum = min;
maxNum = max;
busyNum = 0;
liveNum = min;
exitNum = 0;
isShutdown = false;
//管理者线程
managerThread = new thread(manager, this);
if (nullptr == managerThread) {
cout << "new managerThread fail..." << endl;
return;
}
//工作线程
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < min; ++i) {
workGroup.push_back(thread(worker, this));
}
}
template<class T>
ThreadPool<T>::~ThreadPool() {
isShutdown = true;
//唤醒工作线程 主动关闭
if (liveNum > 0) {
notEmpty.notify_all();
}
if (taskQueue) {
delete taskQueue;
}
if (managerThread != nullptr) {
//设置managerThread为守护线程时
//c++运行库可以保证managerThread相关资源回收
if (managerThread->joinable()) {
managerThread->join();
}
delete managerThread;
}
if (!workGroup.empty()) {
threadExit();
}
cout << "ThreadPool end!" << endl;
}
template<class T>
void * ThreadPool<T>::worker(void *arg) {
cout << this_thread::get_id() << " worker thread starting..." << endl;
ThreadPool *pool = static_cast<ThreadPool *>(arg);
while (true) {
unique_lock<mutex> poolLock(pool->mutexPool);
while (0 == pool->taskQueue->taskNumber() && !pool->isShutdown) {
cout << this_thread::get_id() << " waiting task..." << endl;
pool->notEmpty.wait(poolLock);//阻塞等待任务,唤醒后自动上锁
//判断是否销毁线程
if (pool->exitNum > 0 && pool->liveNum > pool->minNum) {
pool->exitNum--;
pool->liveNum--;
poolLock.unlock();
cout << this_thread::get_id() << " thread end work" << endl;
return NULL;
}
}
if (pool->isShutdown) {
poolLock.unlock();
cout << this_thread::get_id() << " thread end work" << endl;
return NULL;
}
//取出一个任务
Task<T> task = pool->taskQueue->takeTask();
poolLock.unlock();
pool->busyNum++;
task.function(task.arg);//执行函数
delete task.arg;
pool->busyNum--;
}
}
template<class T>
void * ThreadPool<T>::manager(void *arg) {
cout << this_thread::get_id() << " manager thread starting..." << endl;
ThreadPool *pool = static_cast<ThreadPool *>(arg);
int checkInterval = 3;
while (!pool->isShutdown) {
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds(checkInterval));//每3秒检查
unique_lock<mutex> poolLock(pool->mutexPool);
unsigned int queueSize = pool->taskQueue->taskNumber();
//唤醒等待任务的线程
unsigned int sleepThreadNum = pool->liveNum - pool->busyNum;
if (pool->busyNum < queueSize) {
while (sleepThreadNum > 0) {
pool->notEmpty.notify_one();
sleepThreadNum--;
}
}
//添加线程
if (queueSize > pool->liveNum && pool->liveNum < pool->maxNum) {
for (unsigned int counter = 0; counter < NUMBER
&& pool->liveNum < pool->maxNum; ++counter) {
pool->workGroup.push_back(thread(worker, pool));
pool->liveNum++;
}
}
//检查时间自适应
//还需完善
if ((queueSize * 2 < pool->liveNum || queueSize > 2 * pool->liveNum)
&& checkInterval > 1) {
checkInterval--;
}
poolLock.unlock();
//销毁线程
if (pool->busyNum * 2 < pool->liveNum && pool->liveNum > pool->minNum) {
pool->exitNum = NUMBER;
for (int i = 0; i < NUMBER; ++i) {
pool->notEmpty.notify_one();
}
}
//代表有些线程以经结束了工作,需要从容器中删除,回收资源
if (pool->workGroup.size() > pool->liveNum) {
pool->threadExit();
}
}
return NULL;
}
template<class T>
void ThreadPool<T>::threadExit() {
//清空容器里结束的线程
//thread::id tid = this_thread::get_id();
auto it = workGroup.begin();
while (it != workGroup.end()) {
auto correntTid = (*it).native_handle();//获取线程pthread_id
int kill_rc = pthread_kill(correntTid, 0);//发送信号0,探测线程是否存活
if (kill_rc == ESRCH) {
//the specified thread did not exists or already quit
if ((*it).joinable()) {
(*it).join();//等待线程结束 清理线程存储
}
it = workGroup.erase(it);
cout << "thread " << correntTid << " exit from group" << endl;
}
else {
++it;
}
}
}
template<class T>
void ThreadPool<T>::addTask(const Task<T> &task) {
taskQueue->addTask(task);
}
template<class T>
unsigned int ThreadPool<T>::getBusyNum() {
return this->busyNum;
}
template<class T>
unsigned int ThreadPool<T>::getAliveNum() {
return this->liveNum;
}
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <future>
#include <thread>
#include "TaskQueue.hpp"
#include "ThreadPool.hpp"
using namespace std;
void task(void *arg) {
int num = *(int *)arg;
cout << "corrent id is: " << this_thread::get_id() << " :" << num << endl;
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds(1));
}
void test1() {
cout << "start threadPool test" << endl;
ThreadPool<int> pool(2, 10);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i) {
int *num = new int(i + 100);
pool.addTask(Task<int>(task, num));
}
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds(15));
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i) {
int* num = new int(i + 200);
pool.addTask(Task<int>(task, num));
}
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds(20));
cout << "end threadPool test" << endl;
}
int main() {
test1();
}