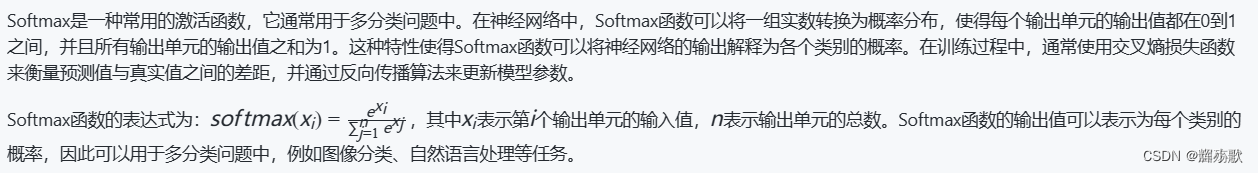
目录
一、定义接口、实体类、创建XML文件实现接口)
二、MyBatis的增删改查
🍅1、MyBatis传递参数查询
🎈写法一
🎈写法二
🎈两种方式的区别
🍅2、删除操作
🍅3、根据id修改用户名
🍅4、添加用户操作
🎈返回受影响的行数
🎈返回自增id
🍅5、like查询
🍅6、多表查询
三、注意
🍅1、mybatisx插件报错
🍅2、数据回滚
🍅 3、查询某字段结果为null时
一、定义接口、实体类、创建XML文件实现接口)
注意包名:
实体类
package com.example.demo.model;
import lombok.Data;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
@Data
public class UserInfo {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String photo;
private LocalDateTime updatatime;
private LocalDateTime createtime;
private int state;
}
接口
package com.example.demo.dao;
import com.example.demo.model.UserInfo;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper //数据持久层的标志
public interface UserMapper {
List<UserInfo> getAll();
}
XML文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.demo.dao.UserMapper">
<!-- id是UserMapper的方法名-->
<select id="getAll" resultType="com.example.demo.model.UserInfo">
-- 不写分号
select * from userinfo
</select>
</mapper>二、MyBatis的增删改查
🍅1、MyBatis传递参数查询
🎈写法一
@Param("id")与${id}相互匹配 (及时执行)
使用id去查询某条数据(传参数)
UserInfo getUserById(@Param("id") Integer uid);-- 这里应该写${id},而不是uid
<select id="getUserById" resultType="com.example.demo.model.UserInfo">
select * from userinfo where id=${id}
</select>测试类:
@Test
void getUserById() {
UserInfo userInfo = userMapper.getUserById(1);
System.out.println(userInfo.toString());
}🎈写法二
@Param("id")与#{id}相互匹配 (预执行)
<select id="getUserById" resultType="com.example.demo.model.UserInfo">
select * from userinfo where id=#{id}
</select>🎈两种方式的区别
1.${}是直接替换;而#{}是预执行
2.使用${}是不安全的,存在SQL注入;而#{}是安全的,不存在SQL注入
3.${}使用场景:当业务需要传递SQL语句时,只能使用${},不能使用#{}。
SQL注入:将SQL代码插入或添加到应用(用户)的输入参数中的攻击,之后再将这些参数传递给后台的sql服务器加以解析和执行。
🍅2、删除操作
UserInfo getUserById(@Param("id") Integer uid);<!-- delete操作不需要设置返回类型-->
<delete id="delById">
delete from userinfo where id=#{id}
</delete>测试类
@Transactional //数据回滚:使用该注解,会执行下面操作,但是不会真的操作数据库中的内容
@Test
void testGetUserById() {
int id = 1;
UserInfo result = userMapper.getUserById(id);
System.out.println("受影响的行数:"+result);
}🍅3、根据id修改用户名
// 根据id修改用户名
// 返回受影响行数
int update(UserInfo userInfo);<!-- 默认返回受影响的行数,不需要设置resultType-->
<update id="update" >
update userinfo set username=#{username} where id=#{id}
</update>
@Transactional
@Test
void update() {
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setId(1);
userInfo.setUsername("管理员");
int result = userMapper.update(userInfo);
System.out.println("受影响行数"+ result);
}运行结果:

🍅4、添加用户操作
🎈返回受影响的行数
//返回受影响字段
int add(UserInfo userInfo);<insert id="add">
insert into userinfo(username,password,photo)
values (#{username},#{password},#{photo})
</insert>//测试类
@Test
void add() {
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUsername("张三");
userInfo.setPassword("11111");
userInfo.setPhoto("/image/default.png");
int result = userMapper.add(userInfo);
System.out.println("受影响的行数:"+ result);
} 运行结果:
🎈返回自增id
int insert(UserInfo userInfo);
<insert id="insert" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyColumn="id" keyProperty="id">
insert into userinfo(username,password,photo) values (#{username},#{password},#{photo})
</insert>//测试类
@Test
void insert() {
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUsername("李四");
userInfo.setPassword("111111");
userInfo.setPhoto("");
int result = userMapper.insert(userInfo);
System.out.println("受影响的行数:" + result +
"| id:"+ userInfo.getId());
} 运行结果:
对应关系:
🍅5、like查询
List<UserInfo> getListByLike(@Param("username")String username);
<select id="getListByLike" resultType="com.example.demo.model.UserInfo">
select * from userinfo where username like concat('%',#{username},'%')
</select>@Test
void getListByLike() {
String username = "三";
List<UserInfo> list = userMapper.getListByLike(username);
System.out.println(list);
}运行结果:

🍅6、多表查询
使用注解将sql语句和接口连接起来。
之前是,写一个接口就要写一个对应的xml文件编写sql语句。现在可以不使用这种方法
可以直接在接口中通过注解编写查询语句:
@Mapper
public interface ArticleMapper{
@Select("select a.*,u.username from articleinfo a" +
"left join userinfo u on a.uid=u.id")
List<Articleinfo> getAll();
}测试类:
class ArticleMapperTest {
@Autowired
private ArticleMapper articleMapper;
@Test
void getAll() {
List<Articleinfo> list = articleMapper.getAll();
System.out.println(list);
}
}
三、注意
🍅1、mybatisx插件报错

以上并非系统报错,而是插件在报错,告诉我们没有设置返回的技术类型,高版本的idea遇到这种情况运行是不会报错的。
🍅2、数据回滚
@Transactional //数据回滚:使用该注解,会执行下面操作,但是不会真的操作数据库中的内容
🍅 3、查询某字段结果为null时
原因是:实体类中的属性和数据库表中的字段名不一致。
解决方案:
1.将实体类中的属性和表中的字段名保持一致(最简单的解决方案)
2.使用sql语句中的as进行列名(字段名)重命名,让列名(字段名)等于属性名
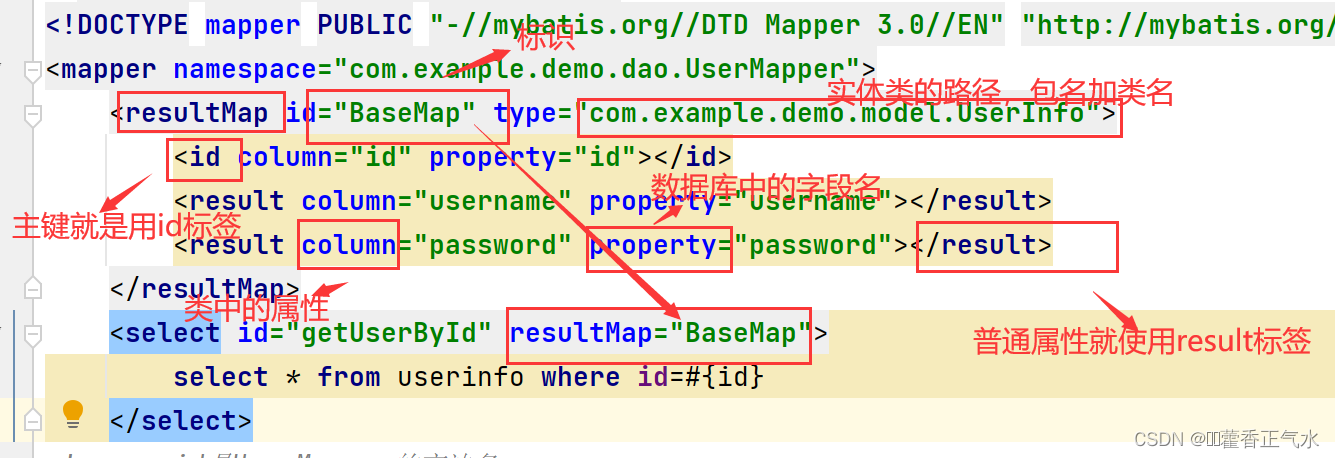
<!-- 加入要查询的字段名应该是name,对name进行重命名 --> <selet id="getUserById" resultType="com.example.demo.model.UserInfo"> select username as name from userinfo where id=#{id}c </select>3.定义一个resultMap,将属性名和字段名进行手动映射
resultMap放入mapper.xml的<mapper></mapper>中
<resultMap id="UserMapper" type="com.example.demo.model.UserInfo"> <id column="id" property="id"></id> <result column="username" property="username"></result> <result column="password" property="password"></result> </resultMap> <select id="getUserById" resultMap="BaseMap"> select * from userinfo where id=#{id} </select>以下是对应关系:尽量把全部属性映射上,否则多表查询时可能会报错。
上图有个错误!!! colum是表里面的字段名,property是实体类里的属性,写反了。