一、ReentrantLock
特点:独占、可重入、公平/非公平、可中断、支持多个条件变量
1、常用api
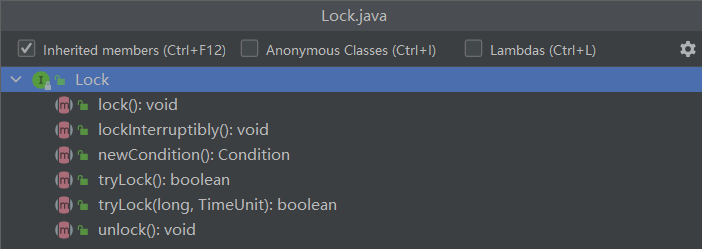
ReentrantLock实现了Lock接口,Lock类规范定义了如下方法
- lock():获取锁,调用该方法的线程会获取锁,当锁获得后,该方法返回
- lockInterruptibly():可中断得获取锁,和lock()方法不同之处在于该方法会响应中断,即在锁的获取中可以中断当前线程
- tryLock():尝试非阻塞的获取锁,调用该方法后立即返回。如果能够获取到返回true,否则返回false
- tryLock(long, TimeUnit):超时获取锁,当前线程在三种情况下会被返回(1、当前线程在超时时间内获取了锁 2、当前线程在超时时间内被中断 3、超时时间结束,返回false)
- unLock():释放锁
- newCondition():获取等待通知组件,该组件和当前的锁绑定,当前线程只有获取了锁,才能调用该组件的await()方法,而调用后,当前线程将释放锁
2、使用
使用范式:
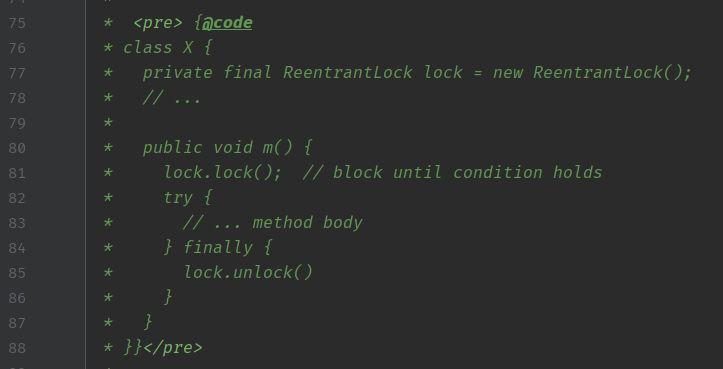
如果把lock.lock()加锁操作放在try里面,可能try里面其它代码导致加锁失败,最后lock.unlock()解锁操作时由于没加锁成功抛出IllegalMonitorStateException异常
public class ReentrantLockTest {
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 库存数量
private static int inventoryQuantity = 5;
// 减库存方法
private void reduceInventory() {
lock.lock();
try {
if (inventoryQuantity > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"购买了商品,剩余库存数:"+--inventoryQuantity);
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":已经没有库存了");
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ReentrantLockTest lockTest = new ReentrantLockTest();
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
lockTest.reduceInventory();
}).start();
}
}
}打印结果:
Thread-0购买了商品,剩余库存数:4
Thread-1购买了商品,剩余库存数:3
Thread-2购买了商品,剩余库存数:2
Thread-3购买了商品,剩余库存数:1
Thread-5购买了商品,剩余库存数:0
Thread-4:已经没有库存了
Thread-6:已经没有库存了
Thread-9:已经没有库存了
Thread-7:已经没有库存了
Thread-8:已经没有库存了
3、公平锁和非公平锁
ReentrantLock支持公平锁和非公平锁,默认是非公平锁
- 公平锁:线程在获取锁时,按照等待的先后顺序获取锁
- 非公平锁:线程在获取锁时,不按照等待的先后顺序获取锁,而是随机获取锁
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); //参数默认false,非公平锁
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true); //公平锁


非公平锁在加锁允许先进行CAS操作判断一次,公平锁则直接进入acquire()方法
4、可重入锁
可重入锁又名递归锁,是指在同一个线程在外层方法获取锁的时候,再进入该线程的内层方法会自动获取锁(前提锁对象得是同一个),不会因为之前已经获取过还没释放而阻塞。ReentrantLock和synchronized都是可重入锁,可重入锁可一定层度避免死锁。在实际开发中,可重入锁常常 应用于递归操作、调用同一个类中的其他方法、锁嵌套等场景中
public class ReentrantLockRecursiveTest {
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
/**
* 递归调用5次
* @param num
*/
public void recursiveCall(int num) {
lock.lock();
try {
if (num > 5) {
return;
}
System.out.println("执行递归调用第"+num+"次");
recursiveCall(++num);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLockRecursiveTest lockRecursiveTest = new ReentrantLockRecursiveTest();
lockRecursiveTest.recursiveCall(1);
}
}打印结果:
执行递归调用第1次
执行递归调用第2次
执行递归调用第3次
执行递归调用第4次
执行递归调用第5次
5、基于Condition的等待唤醒机制
java.util.concurrent类库中提供Condition类实现线程之间的协调。调用Condition.await()方法使线程等待,其它线程调用Condition.signal()或Condition.signalAll()方法唤醒等待的线程
注意:调用Condition的await()和signal()方法,都必须在lock保护之内
案例:基于ReentrantLock和Condition实现一个简单队列
public class ReentrantLockConditionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue queue = new Queue(5);
// 创建生产者线程
new Thread(new Producer(queue)).start();
// 创建消费者线程
new Thread(new Customer(queue)).start();
}
}
class Queue {
private Object[] items;
int size = 0;
int takeIndex;
int putIndex;
private ReentrantLock lock;
public Condition notEmpty;
public Condition notFull;
public Queue(int capacity) {
this.items = new Object[capacity];
lock = new ReentrantLock();
notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
notFull = lock.newCondition();
}
/**
* 生产者方法
* @param value
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public void put(Object value) throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (size == items.length) {
// 队列满了 进入等待
notFull.await();
}
items[putIndex] = value;
if (++putIndex == items.length) {
putIndex = 0;
}
size++;
notEmpty.signal();// 队列中只要添加一个对象就唤醒消费者线程
} finally {
System.out.println("producer生产:"+value);
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* 消费者方法
* @return
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public Object take() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
// 队列空了就让消费者等待
while (size == 0) {
notEmpty.await();
}
Object value = items[takeIndex];
items[takeIndex] = null;
if (++takeIndex == items.length) {
takeIndex = 0;
}
size--;
notFull.signal();// 队列中只要消费一个对象就唤醒生产者线程
return value;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
class Producer implements Runnable {
private Queue queue;
public Producer(Queue queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
Thread.sleep(1000);
queue.put(new Random().nextInt(1000));
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class Customer implements Runnable {
private Queue queue;
public Customer (Queue queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("consumer消费:" + queue.take());
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}6、应用场景总结
ReentrantLock具体应用场景如下:
- 解决多线程竞争资源的问题,例如多个线程同时对同一个数据库进行写操作,可以使用ReentrantLock保证每次只有一个线程能够写入。
- 实现多线程任务的顺序执行,例如在一个线程执行完某个任务后,再让另一个线程执行任务。
- 实现多线程等待/通知机制,例如在某个线程执行完某个任务后,通知其他线程继续执行任务。
二、Semaphore
Semaphore(信号量)是一种用于多线程编程的同步工具,用于控制同时访问某个资源的线程数量。
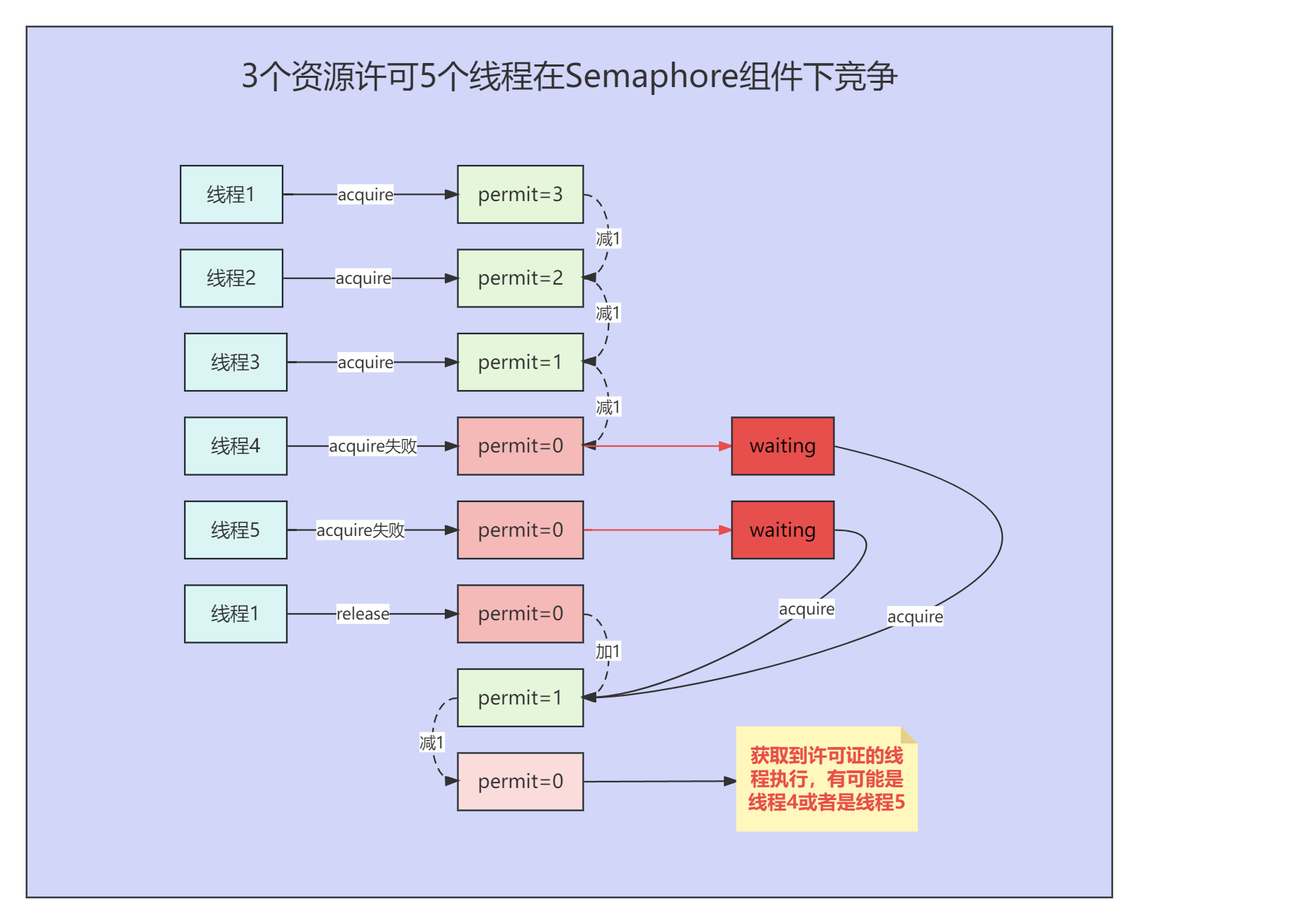
Semaphore维护了一个计数器,线程可以通过调用acquire()方法来获取Semaphore中的许可证,当计数器为0时,调用acquire()的线程将被阻塞,直到有其他线程释放许可证;线程可以通过调用release()方法来释放Semaphore中的许可证,这会使Semaphore中的计数器增加,从而允许更多的线程访问共享资源。
1、常用api
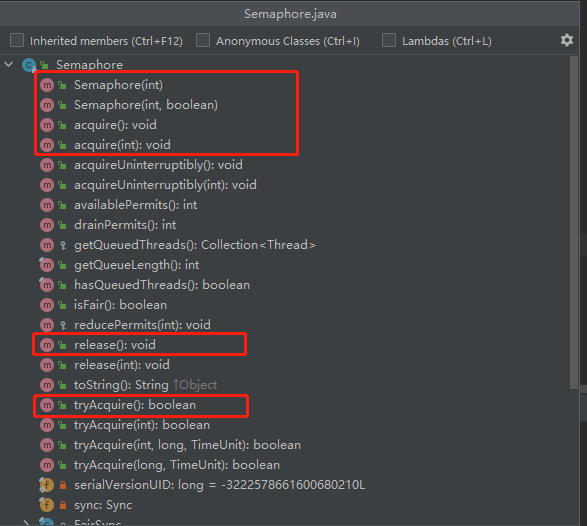
- permits 表示许可证的数量(资源数)
- fair 表示公平性,如果这个设为 true 的话,下次执行的线程会是等待最久的线程
- acquire() 表示阻塞并获取许可
- tryAcquire() 方法在没有许可的情况下会立即返回 false,要获取许可的线程不会阻塞
- release() 表示释放许可
2、使用
public class SemaphoreTest {
// 定义两个资源数
private static Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(2);
private static Executor executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
executor.execute(() -> fluidControl());
}
}
public static void fluidControl2() {
try {
// acquire()会构建同步等待队列
semaphore.acquire();
System.out.println("请求服务成功");
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
semaphore.release();
}
}
public static void fluidControl() {
// tryAcquire()直接CAS返回
if (!semaphore.tryAcquire()) {
System.out.println("请求被流控了");
return;
}
try {
System.out.println("请求服务成功");
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
semaphore.release();
}
}
}3、应用场景
以下是一些使用Semaphore的常见场景:
- 限流:Semaphore可以用于限制对共享资源的并发访问数量,以控制系统的流量。
- 资源池:Semaphore可以用于实现资源池,以维护一组有限的共享资源。
三、CountDownLatch
CountDownLatch(闭锁)是一个同步协助类,允许一个或多个线程等待,直到其他线程完成操作集。

CountDownLatch使用给定的计数值(count)初始化。await方法会阻塞直到当前的计数值(count),由于countDown方法的调用达到0,count为0之后所有等待的线程都会被释放,并且随后对await方法的调用都会立即返回。这是一个一次性现象 —— count不会被重置。
1、常用api
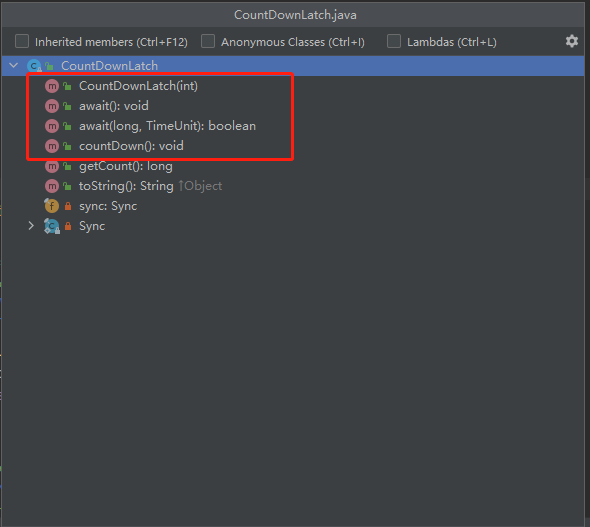
- CountDownLatch(int):构造方法初始化count数
- await():等待count减到0后继续往后执行
- await():等待指定时长,count值还没减到0,不再等待继续执行
- countDown():每调用一次count就会减1,减到0为止
2、使用
public class CountDownLatchTest {
private static int[] values = {30, 20, 65, 23, 45};
private static int result = 0;
private static CountDownLatch coming = new CountDownLatch(values.length);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++) {
int tempI = i;
new Thread(() -> {
result += values[tempI];
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程计算的结果集是:"+result);
coming.countDown();
}, "Thread_"+i).start();
}
coming.await();
System.out.println("汇总结果集是:"+result);
}
}3、应用场景
以下是使用CountDownLatch的常见场景:
- 并行任务同步:CountDownLatch可以用于协调多个并行任务的完成情况,确保所有任务都完成后再继续执行下一步操作。
- 多任务汇总:CountDownLatch可以用于统计多个线程的完成情况,以确定所有线程都已完成工作。
- 资源初始化:CountDownLatch可以用于等待资源的初始化完成,以便在资源初始化完成后开始使用。
四、CyclicBarrier
CyclicBarrier(回环栅栏或循环屏障),是 Java 并发库中的一个同步工具,通过它可以实现让一组线程等待至某个状态(屏障点)之后再全部同时执行。叫做回环是因为当所有等待线程都被释放以后,CyclicBarrier可以被重用。
1、常用api
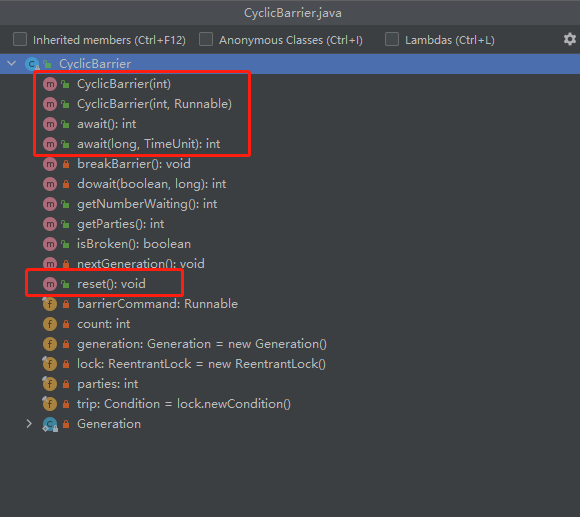
// parties表示屏障拦截的线程数量,每个线程调用 await 方法告诉 CyclicBarrier 我已经到达了屏障,然后当前线程被阻塞。
public CyclicBarrier(int parties)
// 用于在线程到达屏障时,优先执行 barrierAction,方便处理更复杂的业务场景(该线程的执行时机是在到达屏障之后再执行)
public CyclicBarrier(int parties, Runnable barrierAction)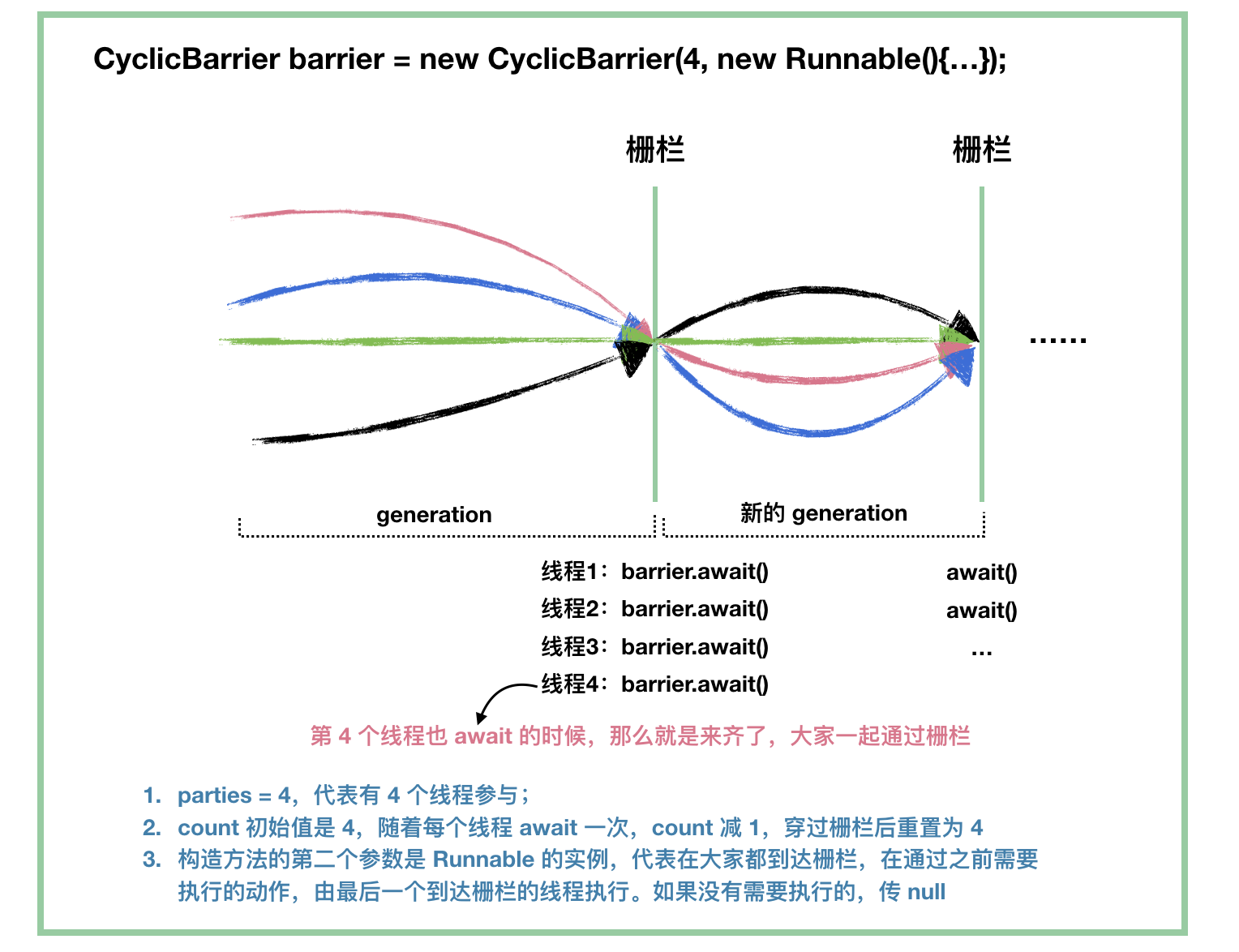
//指定数量的线程全部调用await()方法时,这些线程不再阻塞
// BrokenBarrierException 表示栅栏已经被破坏,破坏的原因可能是其中一个线程 await() 时被中断或者超时
public int await() throws InterruptedException, BrokenBarrierException
public int await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, BrokenBarrierException, TimeoutException
//循环 通过reset()方法可以进行重置
public void reset()2、使用
public class CyclicBarrierTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(5,
() -> System.out.println("人齐了,准备发车"));
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
final int id = i+1;
executorService.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(id+"号马上就到");
int sleepMills = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(2000);
Thread.sleep(sleepMills);
System.out.println(id + "号到了,上车");
cyclicBarrier.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(BrokenBarrierException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
}
3、应用场景
以下是一些常见的 CyclicBarrier 应用场景:
- 多线程任务:CyclicBarrier 可以用于将复杂的任务分配给多个线程执行,并在所有线程完成工作后触发后续操作。
- 数据处理:CyclicBarrier 可以用于协调多个线程间的数据处理,在所有线程处理完数据后触发后续操作。
4、CyclicBarrier 与 CountDownLatch 区别
- CountDownLatch 是一次性的,CyclicBarrier 是可循环利用的
- CountDownLatch 参与的线程的职责是不一样的,有的在倒计时,有的在等待倒计时结束。CyclicBarrier 参与的线程职责是一样的。
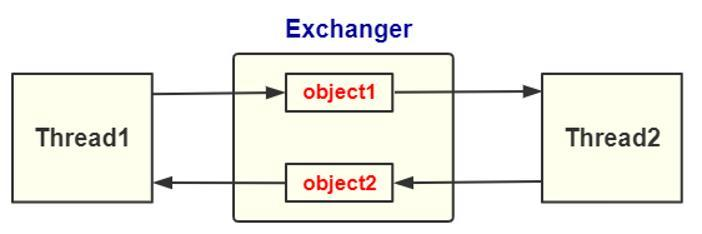
五、Exchanger
Exchanger是一个用于线程间协作的工具类,用于两个线程间交换数据。具体交换数据是通过exchange方法来实现的,如果一个线程先执行exchange方法,那么它会同步等待另一个线程也执行exchange方法,这个时候两个线程就都达到了同步点,两个线程就可以交换数据。
1、常用api
public V exchange(V x) throws InterruptedException
public V exchange(V x, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, TimeoutException- V exchange(V v):等待另一个线程到达此交换点(除非当前线程被中断),然后将给定的对象传送给该线程,并接收该线程的对象。
- V exchange(V v, long timeout, TimeUnit unit):等待另一个线程到达此交换点,或者当前线程被中断——抛出中断异常;又或者是等候超时——抛出超时异常,然后将给定的对象传送给该线程,并接收该线程的对象。
2、使用
public class ExchangerTest {
private static Exchanger exchanger = new Exchanger();
static String goods = "电脑";
static String money = "$4000";
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("准备交易,一手交钱一手交货...");
// 卖家
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("卖家到了,已经准备好货:" + goods);
try {
String money = (String) exchanger.exchange(goods);
System.out.println("卖家收到钱:" + money);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
Thread.sleep(3000);
// 买家
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("买家到了,已经准备好钱:" + money);
String goods = (String) exchanger.exchange(money);
System.out.println("买家收到货:" + goods);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
}3、应用场景
Exchanger 可以用于各种应用场景,具体取决于具体的 Exchanger 实现。常见的场景包括:
- 数据交换:在多线程环境中,两个线程可以通过 Exchanger 进行数据交换。
- 数据采集:在数据采集系统中,可以使用 Exchanger 在采集线程和处理线程间进行数据交换。
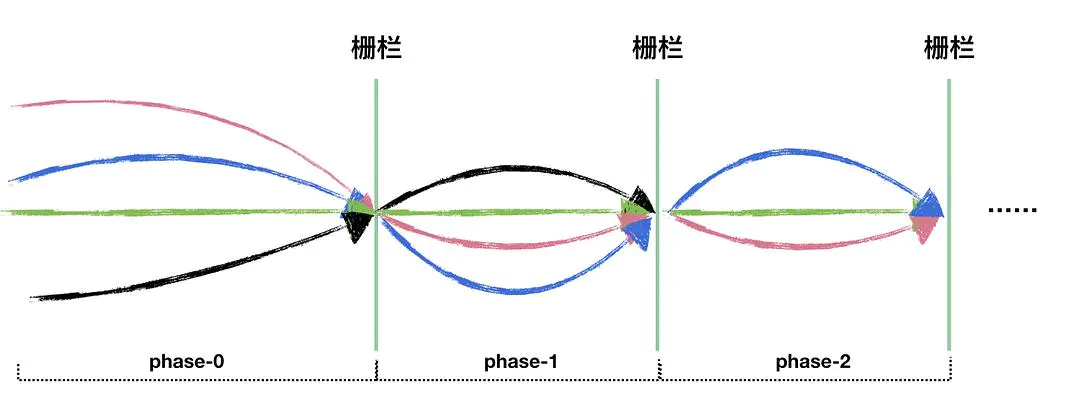
六、Phaser
Phaser(阶段协同器)是一个Java实现的并发工具类,用于协调多个线程的执行。它提供了一些方便的方法来管理多个阶段的执行,可以让程序员灵活地控制线程的执行顺序和阶段性的执行。Phaser可以被视为CyclicBarrier和CountDownLatch的进化版,它能够自适应地调整并发线程数,可以动态地增加或减少参与线程的数量。所以Phaser特别适合使用在重复执行或者重用的情况。
1、常用api
构造方法
- Phaser(): 参与任务数0
- Phaser(int parties) :指定初始参与任务数
- Phaser(Phaser parent) :指定parent阶段器, 子对象作为一个整体加入parent对象, 当子对象中没有参与者时,会自动从parent对象解除注册
- Phaser(Phaser parent,int parties) : 集合上面两个方法
增减参与任务数方法
- int register() 增加一个任务数,返回当前阶段号。
- int bulkRegister(int parties) 增加指定任务个数,返回当前阶段号。
- int arriveAndDeregister() 减少一个任务数,返回当前阶段号。
到达、等待方法
- int arrive() 到达(任务完成),返回当前阶段号。
- int arriveAndAwaitAdvance() 到达后等待其他任务到达,返回到达阶段号。
- int awaitAdvance(int phase) 在指定阶段等待(必须是当前阶段才有效)
- int awaitAdvanceInterruptibly(int phase) 阶段到达触发动作
- int awaitAdvanceInterruptiBly(int phase,long timeout,TimeUnit unit)
- protected boolean onAdvance(int phase,int registeredParties)类似CyclicBarrier的触发命令,通过重写该方法来增加阶段到达动作,该方法返回true将终结Phaser对象。
2、使用
public class PhaserBatchProcessorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Phaser phaser = new Phaser() {
//重写该方法来增加阶段到达动作
@Override
protected boolean onAdvance(int phase, int registeredParties) {
// 参与者数量,去除主线程
int staffs = registeredParties - 1;
switch (phase) {
case 0:
System.out.println("大家都到公司了,出发去公园,人数:" + staffs);
break;
case 1:
System.out.println("大家都到公园门口了,出发去餐厅,人数:" + staffs);
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("大家都到餐厅了,开始用餐,人数:" + staffs);
break;
}
// 判断是否只剩下主线程(一个参与者),如果是,则返回true,代表终止
return registeredParties == 1;
}
};
// 注册主线程 ———— 让主线程全程参与
phaser.register();
final StaffTask staffTask = new StaffTask();
// 3个全程参与团建的员工
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
// 添加任务数
phaser.register();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
staffTask.step1Task();
//到达后等待其他任务到达
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
staffTask.step2Task();
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
staffTask.step3Task();
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
staffTask.step4Task();
// 完成了,注销离开
phaser.arriveAndDeregister();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
// 两个不聚餐的员工加入
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
phaser.register();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
staffTask.step1Task();
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
staffTask.step2Task();
System.out.println("员工【" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "】回家了");
// 完成了,注销离开
phaser.arriveAndDeregister();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
while (!phaser.isTerminated()) {
int phase = phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
if (phase == 2) {
// 到了去餐厅的阶段,又新增4人,参加晚上的聚餐
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
phaser.register();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
staffTask.step3Task();
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
staffTask.step4Task();
// 完成了,注销离开
phaser.arriveAndDeregister();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
}
}
}
static final Random random = new Random();
static class StaffTask {
public void step1Task() throws InterruptedException {
// 第一阶段:来公司集合
String staff = "员工【" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "】";
System.out.println(staff + "从家出发了……");
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(5000));
System.out.println(staff + "到达公司");
}
public void step2Task() throws InterruptedException {
// 第二阶段:出发去公园
String staff = "员工【" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "】";
System.out.println(staff + "出发去公园玩");
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(5000));
System.out.println(staff + "到达公园门口集合");
}
public void step3Task() throws InterruptedException {
// 第三阶段:去餐厅
String staff = "员工【" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "】";
System.out.println(staff + "出发去餐厅");
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(5000));
System.out.println(staff + "到达餐厅");
}
public void step4Task() throws InterruptedException {
// 第四阶段:就餐
String staff = "员工【" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "】";
System.out.println(staff + "开始用餐");
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(5000));
System.out.println(staff + "用餐结束,回家");
}
}
}3、应用场景
以下是一些常见的 Phaser 应用场景:
- 多线程任务分配:Phaser 可以用于将复杂的任务分配给多个线程执行,并协调线程间的合作。
- 多级任务流程:Phaser 可以用于实现多级任务流程,在每一级任务完成后触发下一级任务的开始。
- 模拟并行计算:Phaser 可以用于模拟并行计算,协调多个线程间的工作。
- 阶段性任务:Phaser 可以用于实现阶段性任务,在每一阶段任务完成后触发下一阶段任务的开始。