21. Merge Two Sorted Lists合并两个排序列表
You are given the heads of two sorted linked lists
list1andlist2.
Merge the two lists in a one sorted list. The list should be made by splicing together the nodes of the first two lists.
Return the head of the merged linked list.
给你两个排序的链表list1 和list2 的头。
将两个列表合并到一个排序列表中。
返回合并链表的头部。
Example 1:
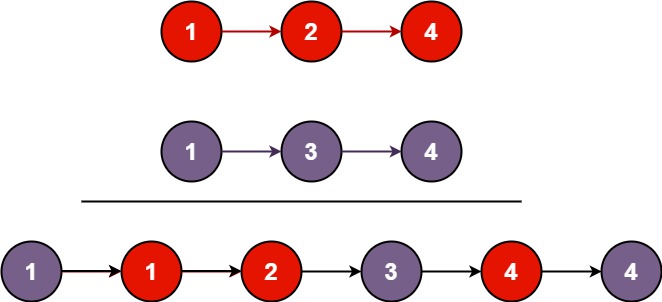
Input: list1 = [1,2,4], list2 = [1,3,4]
Output: [1,1,2,3,4,4]
Example 2:
Input: list1 = [], list2 = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: list1 = [], list2 = [0]
Output: [0]
代码实现
package com.xu.leecode.practise1;
import practise7.Stack;
public class MergeTwoSortedLists {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建第一个链表
ListNode l1 = new ListNode(1);
l1.next = new ListNode(2);
l1.next.next = new ListNode(4);
//创建第二个链表
ListNode l2 = new ListNode(1);
l2.next = new ListNode(3);
l2.next.next = new ListNode(4);
MergeTwoSortedLists mergeTwoSortedLists = new MergeTwoSortedLists();
ListNode mergedList = mergeTwoSortedLists.mergeTwoLists(l1, l2);
// 打印合并列表
while (mergedList != null) {
System.out.print(mergedList.val + " -> ");
mergedList = mergedList.next;
}
System.out.println("null");
}
//单向链表的定义
public static class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {}
ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
}
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
// 创建一个新的ListNode作为合并后链表的头部
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1);
// 创建一个对当前添加到合并链表的节点的引用
ListNode curr = head;
// 当l1和l2中仍有元素时
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
// 如果l1的当前元素比l2的当前元素小
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
// 将l1的当前元素添加到合并链表中
curr.next = l1;
// 移动到l1的下一个元素
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
// 将l2的当前元素添加到合并链表中
curr.next = l2;
// 移动到l2的下一个元素
l2 = l2.next;
}
// 移动到合并链表的下一个元素
curr = curr.next;
}
// 如果在遍历完l2后l1中还有剩余元素
if (l1 != null) {
// 将l1中剩余的元素添加到合并链表中
curr.next = l1;
}
// 如果在遍历完l1后l2中还有剩余元素
if (l2 != null) {
// 将l2中剩余的元素添加到合并链表中
curr.next = l2;
}
// 返回合并链表,排除虚拟头节点
return head.next;
}
}
结果:
1 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 4 -> null
首先,在两个链表都不为空的情况下,判断两个链表当前元素的大小,将值较小的元素添加到合并链表中,并将当前元素后移。然后递归地调用 mergeTwoLists() 函数,直到两个链表中有一个为空。
如果在遍历完一个链表后,另一个链表中还有剩余元素,则将剩余的元素添加到合并链表的末尾。
最后,返回合并链表的头部。
class Solution {
// 合并两个有序链表
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
// 如果list1为空,则返回list2
if(list1 == null) return list2;
// 如果list2为空,则返回list1
if(list2 == null) return list1;
// 如果list1的当前元素比list2的当前元素小
if(list1.val < list2.val){
// 将list1的下一个元素和list2中的元素合并
list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next, list2);
// 返回list1
return list1;
} else{
// 将list1和list2的下一个元素合并
list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list1, list2.next);
// 返回list2
return list2;
}
}
}
26. Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array从排序数组中删除重复项
Given an integer array
numssorted in non-decreasing order, remove the duplicates in-place such that each unique element appears only once. The relative order of the elements should be kept the same.
Since it is impossible to change the length of the array in some languages, you must instead have the result be placed in the first part of the arraynums. More formally, if there arekelements after removing the duplicates, then the firstkelements ofnumsshould hold the final result. It does not matter what you leave beyond the firstkelements.
Returnkafter placing the final result in the firstkslots ofnums.
Do not allocate extra space for another array. You must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.
给定一个按非递减顺序排序的整数数组 nums,就地删除重复项,使每个唯一元素只出现一次。元素的相对顺序应保持不变。
由于在某些语言中无法更改数组的长度,因此您必须将结果放在数组 nums 的第一部分。更正式地说,如果删除重复项后有 k 个元素,则 nums 的前 k 个元素应该保存最终结果。在前 k 个元素之外留下什么并不重要。
将最终结果放入 nums 的前 k 个槽后返回 k。
不要为另一个数组分配额外的空间。您必须通过使用 O(1) 额外内存就地修改输入数组来做到这一点。
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,1,2]
Output: 2, nums = [1,2,_]
Explanation: Your function should return k = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 1 and 2 respectively.
It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4]
Output: 5, nums = [0,1,2,3,4,_,_,_,_,_]
Explanation: Your function should return k = 5, with the first five elements of nums being 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively.
It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
代码实现:
public class RemoveDuplicates {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5};
RemoveDuplicates solution = new RemoveDuplicates();
int length = solution.removeDuplicates(nums);
System.out.println(length);
}
public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
// 如果数组为空或者数组长度为1,则无需处理,直接返回数组长度
if (nums == null || nums.length == 1) return nums.length;
// 从第2个元素开始遍历数组
int i = 1;
for (int j = 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
// 如果当前元素与上一个元素不相同
if (nums[j] != nums[j - 1]) {
// 将当前元素复制到第i个位置,并将i后移1
nums[i] = nums[j];
i++;
}
}
// 返回不重复的元素的个数
return i;
}
}
Leecode代码:
class Solution {
public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) { // 定义一个方法,接收一个整数数组,返回一个整数
if (nums.length == 0) return 0; // 如果数组长度为0,则直接返回0
int i = 0; // 定义变量i,表示当前可插入的位置
for (int j = 1; j < nums.length; j++) { // 从1开始循环到数组末尾
if (nums[j] != nums[i]) { // 如果nums[j]和nums[i]不同
i++; // 当前可插入的位置向后移一位
nums[i] = nums[j]; // 将nums[j]插入到当前位置
}
}
return i + 1; // 返回数组长度
}
运行结果:
5
27. Remove Element移除元素
Given an integer array
numsand an integerval, remove all occurrences ofvalinnumsin-place. The relative order of the elements may be changed.
Since it is impossible to change the length of the array in some languages, you must instead have the result be placed in the first part of the arraynums. More formally, if there arekelements after removing the duplicates, then the firstkelements ofnumsshould hold the final result. It does not matter what you leave beyond the firstkelements.
Returnkafter placing the final result in the firstkslots ofnums.
Do not allocate extra space for another array. You must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 val,就地删除 nums 中所有出现的 val。元素的相对顺序可能会改变。
由于在某些语言中无法更改数组的长度,因此您必须将结果放在数组 nums 的第一部分。更正式地说,如果删除重复项后有 k 个元素,则 nums 的前 k 个元素应该保存最终结果。在前 k 个元素之外留下什么并不重要。
将最终结果放入 nums 的前 k 个槽后返回 k。
不要为另一个数组分配额外的空间。您必须通过使用 O(1) 额外内存就地修改输入数组来做到这一点。
Custom Judge:
The judge will test your solution with the following code:
int[] nums = [...]; // Input array
int val = ...; // Value to remove
int[] expectedNums = [...]; // The expected answer with correct length.
// It is sorted with no values equaling val.
int k = removeElement(nums, val); // Calls your implementation
assert k == expectedNums.length;
sort(nums, 0, k); // Sort the first k elements of nums
for (int i = 0; i < actualLength; i++) {
assert nums[i] == expectedNums[i];
}
If all assertions pass, then your solution will be accepted.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,2,2,3], val = 3
Output: 2, nums = [2,2,_,_]
Explanation: Your function should return k = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 2.
It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0,1,2,2,3,0,4,2], val = 2
Output: 5, nums = [0,1,4,0,3,_,_,_]
Explanation: Your function should return k = 5, with the first five elements of nums containing 0, 0, 1, 3, and 4.
Note that the five elements can be returned in any order.
It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
代码实现:
package com.xu.leecode.practise1;
public class RemoveElement {
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) return 0;
// 从头开始遍历数组
for (int j = 0; j < nums.length; j++) {
// 如果当前元素与指定值不相同
if (nums[j] != val) {
// 将当前元素复制到第i个位置,并将i后移1
nums[i] = nums[j];
i++;
}
}
// 返回新数组的长度
return i;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,9};
RemoveElement solution = new RemoveElement();
int length = solution.removeElement(nums, 9);
System.out.println("新数组长度:" + length);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
System.out.print(nums[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
Leecode代码实现:
class Solution {
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) { // 定义一个方法,接收一个整数数组和一个要移除的整数值,返回一个整数
int i = 0; // 定义变量i,表示当前可插入的位置
for (int j = 0; j < nums.length; j++) { // 从0开始循环到数组末尾
if (nums[j] != val) { // 如果nums[j]不等于val
nums[i] = nums[j]; // 将nums[j]插入到当前位置
i++; // 当前可插入的位置向后移一位
}
}
return i; // 返回数组长度
}
}
运行结果:
新数组长度:8
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
28. Implement strStr()实现 strStr()
Given two strings
needleandhaystack, return the index of the first occurrence ofneedleinhaystack, or-1ifneedleis not part ofhaystack.
Clarification:
What should we return whenneedleis an empty string? This is a great question to ask during an interview.
For the purpose of this problem, we will return 0 whenneedleis an empty string. This is consistent to C’s strstr() and Java’s
indexOf().
给定两个字符串 needle 和 haystack,返回 haystack 中第一次出现 needle 的索引,如果 needle 不是 haystack 的一部分,则返回 -1。
当 needle 为空字符串时,我们应该返回什么?
针对这个问题,当needle为空字符串时,我们将返回0,这与C的strstr()和Java的indexOf()是一致的。
Example 1:
Input: haystack = "hello", needle = "ll"
Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: haystack = "aaaaa", needle = "bba"
Output: -1
代码实现:
package com.xu.leecode.practise1;
public class strStr {
public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
if (haystack == null || needle == null) return -1;
// 计算needle长度
int needleLength = needle.length();
// 如果needle为空串,则直接返回0
if (needleLength == 0) return 0;
// 计算haystack长度
int haystackLength = haystack.length();
// 如果needle长度大于haystack长度,则一定无法找到needle
if (needleLength > haystackLength) return -1;
// 循环遍历haystack
for (int i = 0; i < haystackLength; i++) {
// 如果当前字符不是needle的第一个字符,则继续循环
if (haystack.charAt(i) != needle.charAt(0)) continue;
// 如果当前字符刚好是haystack末尾,则无法找到needle
if (i == haystackLength - 1) return -1;
// 如果haystack剩下的长度小于needle的长度,则无法找到needle
if (haystackLength - i < needleLength) return -1;
// 比较haystack[i+1]到haystack[i+needleLength]与needle[1]到needle[needleLength]是否相同
boolean found = true;
for (int j = 1; j < needleLength; j++) {
if (haystack.charAt(i + j) != needle.charAt(j)) {
found = false;
break;
}
}
// 如果找到了,则返回needle在haystack中出现的位置
if (found) return i;
}
// 没找到,返回-1
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
strStr solution = new strStr();
String haystack = "aaaaa";
String needle = "bba";
int result = solution.strStr(haystack, needle);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
Leecode代码实现:
class Solution {
public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) { // 定义一个方法,接收两个字符串,返回一个整数
if (needle.equals("") || needle.equals(haystack)) return 0; // 如果needle为空或者等于haystack,则返回0
int hLen = haystack.length(), nLen = needle.length(); // 取出两个字符串的长度
if (nLen > hLen) return -1; // 如果needle长度大于haystack,则返回-1
for (int i = 0; i <= hLen - nLen; i++) { // 从0开始循环到haystack末尾
if (haystack.substring(i, i + nLen).equals(needle)) return i; // 如果haystack的i到i+nLen的子串等于needle,则返回i
}
return -1; // 否则返回-1
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
String haystack = "hello";
String needle = "ll";
int result = solution.strStr(haystack, needle);
System.out.println(result);
haystack = "aaaaa";
needle = "bba";
result = solution.strStr(haystack, needle);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
运行结果:
-1
35. Search Insert Position搜索插入位置
Given a sorted array of distinct integers and a target value, return the index if the target is found. If not, return the index where it would be if it were inserted in order.
You must write an algorithm withO(log n)runtime complexity.
给定一个由不同整数组成的排序数组和一个目标值,如果找到目标,则返回索引。
如果不是,则返回按顺序插入的索引。
您必须编写一个具有 O(log n) 运行时复杂度的算法。
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 5
Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 2
Output: 1
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 7
Output: 4
代码实现:
package com.xu.leecode.practise1;
public class SearchInsertPosition {
public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) return -1; // 如果nums为null或者长度为0,则返回-1
int left = 0; // 定义搜索区间的左端点
int right = nums.length - 1; // 定义搜索区间的右端点
while (left <= right) { // 当左端点小于等于右端点时,继续循环
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2; // 计算搜索区间的中间位置
if (nums[mid] == target) return mid; // 如果nums[mid]等于target,则直接返回mid
else if (nums[mid] < target) left = mid + 1; // 如果nums[mid]小于target,则搜索区间缩小到[mid + 1, right]
else right = mid - 1; // 如果nums[mid]大于target,则搜索区间缩小到[left, mid - 1]
}
// 如果没有找到,则返回应该插入的位置
return left;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SearchInsertPosition solution = new SearchInsertPosition();
int[] nums = new int[]{1, 3, 5, 6}; // 定义排好序的整数数组
int target = 5; // 定义查询的目标值
int result = solution.searchInsert(nums, target); // 查询并获得结果
System.out.println(result); // 输出结果
target = 1; // 定义查询的目标值
result = solution.searchInsert(nums, target); // 查询并获得结果
System.out.println(result); // 输出结果
}
}
Leecode代码实现:
class Solution {
public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) { // 定义一个方法,接收一个整数数组和一个目标整数,返回一个整数
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { // 从0开始循环到数组末尾
if (nums[i] >= target) return i; // 如果nums[i]大于等于target,则返回i
}
return nums.length; // 否则返回数组长度
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
int[] nums = new int[] {1, 3, 5, 6};
int target = 5;
int result = solution.searchInsert(nums, target);
System.out.println(result);
nums = new int[] {1, 3, 5, 6};
target = 2;
result = solution.searchInsert(nums, target);
System.out.println(result);
nums = new int[] {1, 3, 5, 6};
target = 7;
result = solution.searchInsert(nums, target);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
运行结果:
2
0
![[附源码]计算机毕业设计基于人脸识别的社区防疫管理系统Springboot程序](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c0d349988c734addbac9e643657b1bda.png)