实验任务
(1) 掌握顺序循环队列及其C语言的表示;
(2) 掌握入队、出队等基本算法的实现;
(3) 掌握顺序循环队列的基本应用(求解迷宫通路)。
实验内容
- 使用C语言实现顺序循环队列的类型定义与算法函数;
- 编写main()函数并根据需要修改、补充相关的类型定义与函数,以实现“求解迷宫通路”问题:
- 求解迷宫通路问题描述:
- 给定一个M×N的迷宫图,指定一个入口与一个出口;
- 规定行走规则为:按“上右下左”优先顺序向相邻空位移动1格,用(i,j)表示迷宫中的第i行第j列的一个方块
- 在迷宫外围加上围墙;
- 实现指定入口和出口的固定迷宫;
- 实现随机入口和出口的固定迷宫;
- 实现障碍、入口和出口都随机的迷宫。
实验源码
注意:必须在Dos窗口下运行,并且以管理员身份打开Dos窗口最佳
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include "windows.h"
#define MAXSIZE 1000
#define ROW 15
#define LINE 15
#define RATIO 0.6875 // 44/64的比例
#define COORDINATE -1 // 坐标默认 值
#define DISTOP 5 // 迷宫距离顶端距离格数
#define PASS 0 // 通路
#define WALL 1 // 墙
#define ENTRY 2 // 入口
#define EXIT 3 // 出口
#define DEAD 5 // 死路
// 延时设置
int walkDelay = 500;
int dirDelay = 1000;
typedef struct Box {
int x; // 点的横坐标(行)
int y; // 点的纵坐标(列)
int pre; // 上一个点的下标
} Box;
typedef struct {
Box *base;
int front;
int rear;
} SqQueue;
void Map(int map[][LINE]); // 生成地图
void KnuthShuffle(int map[], int length); // 洗牌算法
void swapInt(int *a, int *b); // 辅助洗牌算法 交换
void PrintMap(int map[][LINE]); // 打印迷宫地图
boolean InitQueue(SqQueue *queue); // 循环队列的初始化
void Walk(SqQueue *queue, int in_x, int in_y, int map[][LINE]); // 移动迷宫
boolean EnQueue(SqQueue *queue, Box node); // 循环队列入队列
boolean IsFull(SqQueue *queue); // 判队满
boolean IsEmpty(SqQueue *queue); // 判队空
Box DeQueue(SqQueue *queue); // 循环队列出队列
void ShowPath(SqQueue *queue, int end); // 求解最短路径
void Color(short x); // 自定义函根据参数改变颜色
void DirTest(int map[][LINE], int dir, int j, int k); // 方向试探
void DeadPath(int j, int k); // 置为死路
void GotoXY(int x, int y); // 将光标移至屏幕 第x列,第y行 处
void DisplayQueue(SqQueue *queue); // 队列动态展示
void HideCursor(void); // 隐藏光标
/**
* <h2>顺序队列实验</h2>
* <h3>随机迷宫问题</h3>
* <h3>注意:请在Dos窗口下运行</h3>
* <h4>非循环队列,并不是真的退出队列</h4>
* @return 0
*/
int main() {
GotoXY(0, 0);
Color(9);
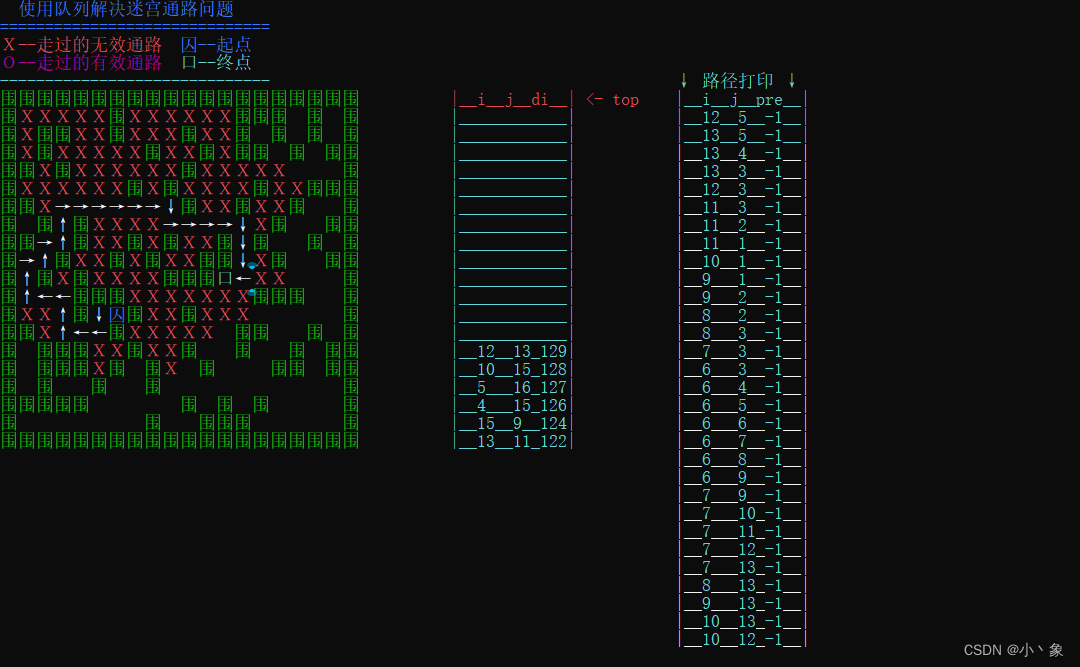
printf(" 使用队列解决迷宫通路问题 \n");
GotoXY(0, 1);
printf("==============================\n");
GotoXY(0, 2);
Color(12);
printf("X--走过的无效通路");
Color(9);
printf(" 囚--起点\n");
GotoXY(0, 3);
Color(13);
printf("O--走过的有效通路");
Color(11);
printf(" 口--终点\n");
GotoXY(0, 4);
printf("------------------------------\n");
srand(time(NULL));
int map[ROW][LINE];
Map(map);
PrintMap(map);
SqQueue queue;
if (!(InitQueue(&queue))) {
printf("队列初始化失败~~\n");
return 0;
}
int in_x, in_y;
for (int i = 0; i < ROW; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < LINE; j++) {
if (map[i][j] == ENTRY) {
in_x = i;
in_y = j;
}
}
}
HideCursor();
DisplayQueue(&queue);
Walk(&queue, in_x, in_y, map);
getchar();
}
void Map(int map[][LINE]) {
int length = (ROW - 2) * (LINE - 2); // 8 * 8 内区域
int randArr[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
randArr[i++] = ENTRY;
randArr[i++] = EXIT;
}
if (i < (length * RATIO) + 2) {
randArr[i] = PASS;
} else {
randArr[i] = WALL;
}
}
KnuthShuffle(randArr, length); // 打乱 内区域
// 赋值整张地图
for (int i = 0; i < ROW; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < LINE; j++) {
// 这里一个小技巧:只要前面四个表达式一个为假,说明未到边界赋值,保证Length不会越界
if (i != 0 && i != ROW - 1 && j != 0 && j != LINE - 1 && length--) {
map[i][j] = randArr[length];
} else {
map[i][j] = WALL;
}
}
}
}
void KnuthShuffle(int map[], int length) {
for (int i = length - 1; i >= 1; i--) {
swapInt(&map[i], &map[rand() % (i + 1)]);
}
}
void swapInt(int *a, int *b) {
int t;
t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
void PrintMap(int map[][LINE]) {
for (int i = 0; i < ROW; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < LINE; j++) {
GotoXY(j * 2, i + DISTOP);
switch (map[i][j]) {
case PASS:
printf(" ");
break;
case WALL:
Color(10);
printf("围");
break;
case ENTRY:
Color(9);
printf("囚");
break;
case EXIT:
Color(11);
printf("口");
break;
}
}
printf("\n");
}
Sleep(3000);
}
boolean InitQueue(SqQueue *queue) {
queue->base = (Box *) malloc(sizeof(Box) * MAXSIZE);
if (!(queue->base)) {
return FALSE;
}
queue->front = queue->rear = 0;
return TRUE;
}
void Walk(SqQueue *queue, int in_x, int in_y, int map[][LINE]) {
// 起点先入队列
Box node; // 生成当前位置(起点)
node.x = in_x;
node.y = in_y;
node.pre = COORDINATE; // 起点位置下标 -1
EnQueue(queue, node); // 起点入队列
while (!(IsEmpty(queue))) { // 无路可走的情况,回到起点
node = DeQueue(queue); // 取出队头位置 队头指针front++
if (map[node.x][node.y] == EXIT) { // 判断当前位置是否是终点
ShowPath(queue, queue->front);
return;
}
int dir; // 装方向
Box tNode; // 生成下一个位置
for (dir = 0; dir < 4; dir++) { // 判断当前位置各个方向是否可走
switch (dir) {
case 0:
tNode.x = node.x - 1;
tNode.y = node.y;
DirTest(map, dir, node.x, node.y);
break;
case 1:
tNode.x = node.x;
tNode.y = node.y + 1;
DirTest(map, dir, node.x, node.y);
break;
case 2:
tNode.x = node.x + 1;
tNode.y = node.y;
DirTest(map, dir, node.x, node.y);
break;
case 3:
tNode.x = node.x;
tNode.y = node.y - 1;
DirTest(map, dir, node.x, node.y);
break;
}
if (map[tNode.x][tNode.y] == PASS || map[tNode.x][tNode.y] == EXIT) { // 判断这个方向 是否可走
tNode.pre = queue->front - 1; // 把节点位置的下标给 新位置
EnQueue(queue, tNode); // 入队
if (map[tNode.x][tNode.y] == PASS) {
map[tNode.x][tNode.y] = DEAD;
DeadPath(tNode.x, tNode.y);
}
}
}
}
// 这里加二号条件的原因是:此程序使用的是终点出队列即停止,但是也不排除 到终点即为空
if (IsEmpty(queue) && map[node.x][node.y] != EXIT) {
GotoXY(0, ROW + DISTOP + 2);
Color(12);
printf("\t无路可走,死翘翘了~~\n");
}
}
boolean EnQueue(SqQueue *queue, Box node) {
if (IsFull(queue)) {
return FALSE;
}
queue->base[queue->rear] = node; // 新元素插入队尾
queue->rear = queue->rear + 1; // 队尾指针加 1
DisplayQueue(queue);
return TRUE;
}
boolean IsFull(SqQueue *queue) {
return queue->rear + 1 == queue->front; // 非循环队列
}
boolean IsEmpty(SqQueue *queue) {
return queue->rear == queue->front;
}
Box DeQueue(SqQueue *queue) {
Box box = queue->base[queue->front++];
DisplayQueue(queue);
return box; // 取出队头元素,并把其出队列
}
void ShowPath(SqQueue *queue, int end) {
int i, tmp;
for (i = end - 1; i >= 0;) {
tmp = queue->base[i].pre;
queue->base[i].pre = COORDINATE;
i = tmp;
}
int count = 0, ti;
for (i = 1; i < end; i++) { // i = 1, 保证不是终点即可
if (queue->base[i].pre == COORDINATE) {
if (count == 0) {
GotoXY(LINE * 2 + 35, DISTOP - 1);
printf("↓ 路径打印 ↓");
GotoXY(LINE * 2 + 35, DISTOP);
printf("|__i__j__pre__|");
}
count++;
GotoXY(LINE * 2 + 35, DISTOP + count);
printf("|_____________|\n");
Color(11);
GotoXY(LINE * 2 + 35 + 3, DISTOP + count);
printf("%d", queue->base[i].x);
GotoXY(LINE * 2 + 35 + 7, DISTOP + count);
printf("%d", queue->base[i].y);
GotoXY(LINE * 2 + 35 + 10, DISTOP + count);
printf("%d", queue->base[i].pre);
if (count == 1) {
ti = i;
continue;
}
GotoXY(queue->base[ti].y * 2, queue->base[ti].x + DISTOP);
Color(15);
if (queue->base[i].x - queue->base[ti].x == -1 &&
queue->base[i].y - queue->base[ti].y == 0) {
printf("↑");
} else if (queue->base[i].x - queue->base[ti].x == 0 &&
queue->base[i].y - queue->base[ti].y == 1) {
printf("→");
} else if (queue->base[i].x - queue->base[ti].x == 1 &&
queue->base[i].y - queue->base[ti].y == 0) {
printf("↓");
} else {
printf("←");
}
ti = i;
}
}
}
void Color(short x) {
if (x >= 0 && x <= 15) { // 参数在0-15的范围颜色
SetConsoleTextAttribute( // 调用设置控制台文本属性函数(调用获取句柄函数(不理解), 不理解)
GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), x); // 只有一个参数,改变字体颜色
} else { // 默认的颜色白色
SetConsoleTextAttribute(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), 7);
}
}
void DirTest(int map[][LINE], int dir, int j, int k) {
GotoXY(k * 2, j + DISTOP);
Color(15);
switch (dir) {
case 0:
printf("↑");
break;
case 1:
printf("→");
break;
case 2:
printf("↓");
break;
case 3:
printf("←");
break;
}
Sleep(dirDelay);
GotoXY(k * 2, j + DISTOP);
Color(13);
switch (map[j][k]) {
case ENTRY:
Color(9);
printf("囚");
break;
case DEAD:
Color(12);
printf("X");
break;
}
}
void DeadPath(int j, int k) {
GotoXY(k * 2, j + DISTOP);
Color(12);
printf("X");
Sleep(walkDelay);
}
void GotoXY(int x, int y) {
COORD pos = {x, y}; // 坐标
HANDLE hOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE); // 获取句柄(标准输出句柄)
SetConsoleCursorPosition(hOut, pos); // 设置控制台光标位置
}
void DisplayQueue(SqQueue *queue) {
int len = ROW - 1;
Color(12);
GotoXY(LINE * 2 + 10, DISTOP);
printf("|__i__j__di__| <- top");
for (int j = 1; j <= len; j++) {
GotoXY(LINE * 2 + 10, DISTOP + j);
printf("|____________|\n");
}
int length = queue->rear;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++, len--) {
if (len == 0) {
len = ROW - 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= len; j++) {
GotoXY(LINE * 2 + 10, DISTOP + j);
printf("|____________|\n");
}
}
Color(11);
GotoXY(LINE * 2 + 10 + 3, DISTOP + len);
printf("%d", queue->base[i].x);
GotoXY(LINE * 2 + 10 + 7, DISTOP + len);
printf("%d", queue->base[i].y);
GotoXY(LINE * 2 + 10 + 10, DISTOP + len);
printf("%d", queue->base[i].pre);
}
}
void HideCursor(void) {
CONSOLE_CURSOR_INFO cursor_info = {1, 0};
SetConsoleCursorInfo(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), &cursor_info);
}
实验结果




![[护网杯 2018]easy_tornado1](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7d74e541d821473898cd24323f5e24da.png)