并行计算(Parallel Computing)是指同时使用多种计算资源解决计算问题的过程,是提高计算机系统计算速度和处理能力的一种有效手段。它的基本思想是用多个处理器来协同求解同一问题,即将被求解的问题分解成若干个部分,各部分均由一个独立的处理机来并行计算。并行计算系统既可以是专门设计的、含有多个处理器的超级计算机,也可以是以某种方式互连的若干台的独立计算机构成的集群。通过并行计算集群完成数据的处理,再将处理的结果返回给用户。
OpenMP是由OpenMP Architecture Review Board牵头提出的,用于共享内存并行系统的多处理器程序设计的一套指导性编译处理方案。OpenMP支持的编程语言包括C、C++和Fortran。OpenMp提供了对并行算法的高层的抽象描述,程序员通过在源代码中加入专用的pragma来指明自己的意图,由此编译器可以自动将程序进行并行化,并在必要之处加入同步互斥以及通信。当选择忽略这些pragma,或者编译器不支持OpenMp时,程序又可退化为通常的程序(一般为串行),代码仍然可以正常运作,只是不能利用多线程来加速程序执行。
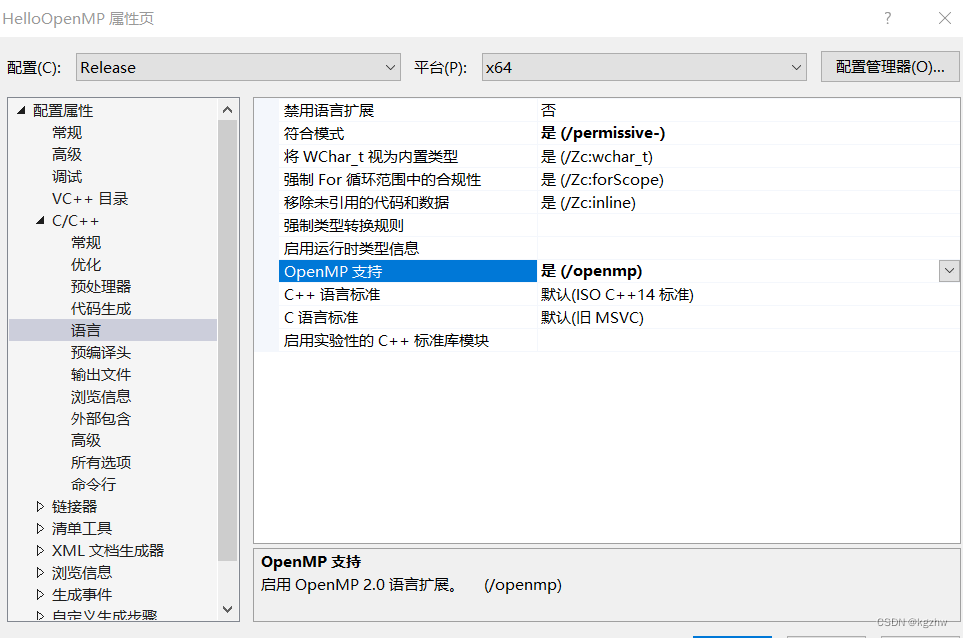
在VS中使用OPENMP需要打开Open MP支持开关,如下图VS2019中打开方式。
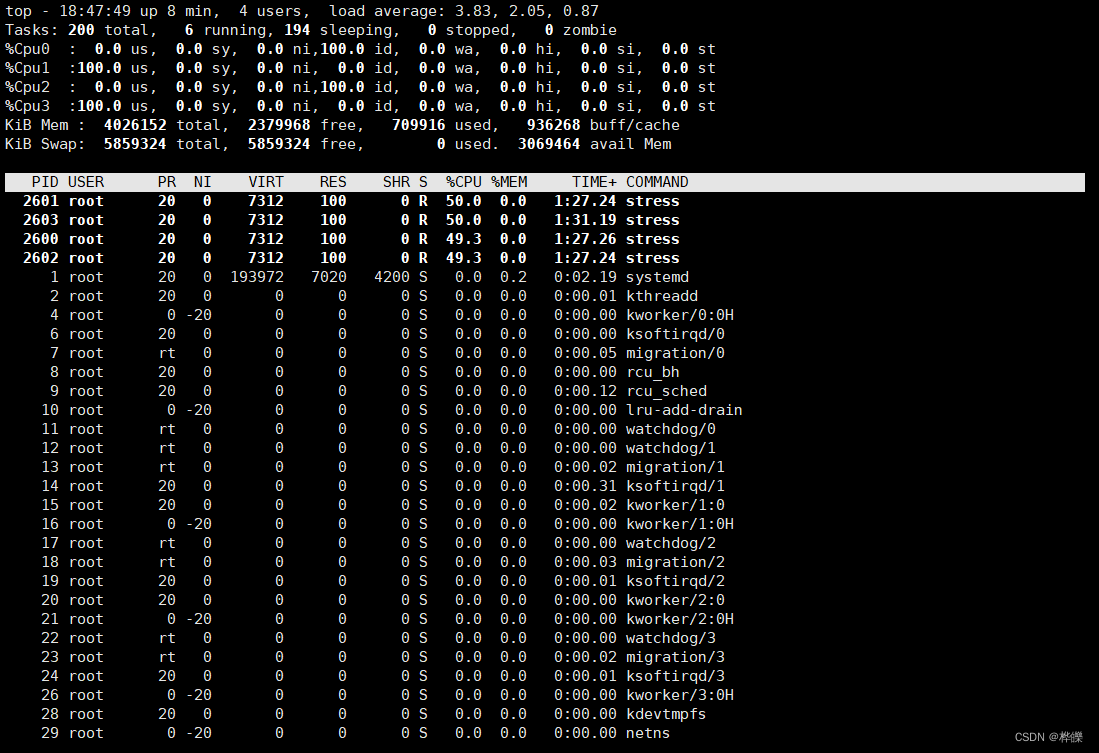
Hello, omp! 如下代码会根据运行机器上的处理器开对应数量的线程进行运行。
#include <iostream>
#include <omp.h>
using namespace std;
#include <windows.h>
int main()
{
#pragma omp parallel
{
DWORD dwThread = GetCurrentThreadId();
printf("ThreadID:%d threadIndex:%d, Hello, omp!\r\n", \
dwThread, omp_get_thread_num());
}
system("pause");
}Open MP函数
| 函数名 | 函数 功能说明 |
| omp_set_num_threads | 设置即将出现的并行区域中的线程数,除非由 num_threads 子句重写。 |
| omp_get_num_threads | 返回并行区域中的线程数。 |
| omp_get_max_threads | 如果在代码中的该位置定义了没有 num_threads 的并行区域,则返回等于或大于可用线程数的整数。 |
| omp_get_thread_num | 返回在其线程组中执行的线程的线程编号。 |
| omp_get_num_procs | 返回调用函数时可用的处理器数。 |
| omp_in_parallel | 如果从并行区域内调用,则返回非零值。 |
| omp_set_nested | 启用或者禁用嵌套并行。 |
| omp_get_nested | 判断嵌套并行是否启用。 |
锁相关函数
| 函数名 | 函数功能说明 |
| omp_init_lock | 初始化锁 |
| omp_destroy_lock | 取消初始化锁 |
| omp_set_lock | 阻塞线程执行,直到锁可用 |
| omp_unset_lock | 释放锁 |
| omp_test_lock | 尝试设置锁但不阻塞线程执行 |
Open MP指令
| 函数名 | 函数功能说明 |
| omp_init_lock | 初始化锁 |
| omp_destroy_lock | 取消初始化锁 |
| omp_set_lock | 阻塞线程执行,直到锁可用 |
| omp_unset_lock | 释放锁 |
| omp_test_lock | 尝试设置锁但不阻塞线程执行 |
#include <iostream>
#include <omp.h>
using namespace std;
#include <windows.h>
void OMPTestAPI()
{
int max_threads = omp_get_max_threads();
int num_threads = omp_get_num_threads();
int num_procs = omp_get_num_procs();
printf("Max threads: %d\n", max_threads);
printf("Num threads: %d\n", num_threads);
printf("Num Procs:%d\n", num_procs);
omp_set_num_threads(6);
int nInparallel = omp_in_parallel();
printf("Inparallel:%d\n", nInparallel);
#pragma omp parallel
{
nInparallel = omp_in_parallel();
printf("Inparallel:%d\n", nInparallel);
num_threads = omp_get_num_threads();
int thread_id = omp_get_thread_num();
printf("Thread ID: %d, maxthread num:%d\n", thread_id, max_threads);
}
}
int nest_test() {
int nNest = omp_get_nested();
printf("Nest state:%d\n", nNest);
omp_set_nested(1); // 启用嵌套并行
#pragma omp parallel num_threads(2)
{
printf("Outer parallel region\n");
nNest = omp_get_nested();
printf("After SetNest Nest state:%d\n", nNest);
#pragma omp parallel num_threads(2)
{
printf("Inner parallel region\n");
}
}
}
void atomic_Cmd()
{
int count = 0;
#pragma omp parallel num_threads(10)
{
#pragma omp atomic
count++;
}
printf_s("Number of threads: %d\n", count);
}
void for_Cmd()
{
int count = 0;
omp_set_num_threads(2);
//并行for
#pragma omp parallel
#pragma omp for
//#pragma omp parallel for
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
++count;
printf_s("Thread num:%d, count:%d\r\n", omp_get_thread_num(), count);
}
//普通 for
count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
++count;
printf_s("ThreadID:%d, count:%d\r\n", GetCurrentThreadId(), count);
}
}
void master_Cmd()
{
DWORD dwThreadID = GetCurrentThreadId();
printf("main thread id is %d\r\n", dwThreadID);
#pragma omp parallel num_threads(3)
{
printf("Hello from thread %d\n", omp_get_thread_num());
#pragma omp master
{
printf("Hello from master thread %d, threadid:%d\n", omp_get_thread_num(), GetCurrentThreadId());
// 只有主线程执行下面的代码
// 执行一些仅需执行一次的工作
}
}
}
void barrier_Cmd()
{
#pragma omp parallel num_threads(4)
{
printf("Hello from thread %d\n", omp_get_thread_num());
//等待
#pragma omp barrier
printf("World from thread %d\n", omp_get_thread_num());
}
}
void critical_Cmd()
{
int shared_var = 0;
#pragma omp parallel num_threads(4)
{
int thread_num = omp_get_thread_num();
printf("Thread %d is executing before the critical section\n", thread_num);
#pragma omp critical
{
// 进入临界区代码块
printf("Thread %d is inside the critical section\n", thread_num);
shared_var++;
printf("Shared variable incremented by Thread %d: %d\n", thread_num, shared_var);
// 退出临界区代码块
}
printf("Thread %d is executing after the critical section\n", thread_num);
}
}
void flush_Cmd()
{
int shared_var = 0;
#pragma omp parallel num_threads(20)
{
#pragma omp critical
{
// 对共享变量进行修改
shared_var++;
printf("Thread %d: shared_var = %d\n", omp_get_thread_num(), shared_var);
}
// 执行 flush 操作以确保共享变量的修改对所有线程可见
//#pragma omp flush
// 访问共享变量
printf("Thread %d: shared_var = %d\n", omp_get_thread_num(), shared_var);
}
// int shared_var = 0;
//
//#pragma omp parallel num_threads(2)
// {
// int thread_num = omp_get_thread_num();
//
// if (thread_num == 0) {
// // 线程0写入共享变量(写入操作1)
// shared_var = 42;
#pragma omp flush(shared_var)
// // 写入操作1完成后,强制刷新到主存,使其对其他线程可见
// }
//
//#pragma omp barrier
//
// if (thread_num == 1) {
// // 线程1读取共享变量(读取操作1)
// // 在读取之前,需要使用 flush 指令确保对 shared_var 的最新写入全部对线程1可见
//#//pragma omp flush(shared_var)
//
// printf("Thread %d reads shared_var: %d\n", thread_num, shared_var);
// }
// }
}
void ordered_Cmd()
{
#pragma omp parallel num_threads(5)
{
int thread_num = omp_get_thread_num();
#pragma omp for ordered
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
#pragma omp ordered
{
printf("Thread %d is executing iteration %d\n", thread_num, i);
}
}
}
}
void section_Cmd()
{
#pragma omp parallel num_threads(4)
{
#pragma omp sections
{
#pragma omp section
{
printf("This is Section 1, executed by Thread %d\n", omp_get_thread_num());
}
#pragma omp section
{
printf("This is Section 2, executed by Thread %d\n", omp_get_thread_num());
}
#pragma omp section
{
printf("This is Section 3, executed by Thread %d\n", omp_get_thread_num());
}
}
}
//#pragma omp parallel sections num_threads(4)
// {
// printf_s("Hello from thread %d\n", omp_get_thread_num());
//#pragma omp section
// printf_s("Hello from thread %d\n", omp_get_thread_num());
// }
}
void single_Cmd()
{
#pragma omp parallel num_threads(4)
{
#pragma omp single
{
printf("This is executed by Thread %d\n", omp_get_thread_num());
}
}
}
int nx = 0; // 全局变量x
#pragma omp threadprivate(nx)
int g = 2;
#pragma omp threadprivate(g)
void threadprivate_Cmd()
{
/* Explicitly turn off dynamic threads */
//omp_set_dynamic(0);
DWORD dwID = GetCurrentThreadId();
printf("start g:%d, ThreadID:%d\r\n", g, dwID);
printf("Masterthread started\n\n");
#pragma omp parallel
{
dwID = GetCurrentThreadId();
g = omp_get_thread_num();
printf("tid: %d, Theadid:%d\n", g, dwID);
} // End of parallel region
printf("mid g:%d\r\n", g);
#pragma omp parallel
{
int temp = g * g+1;
printf("tid : %d, tid*tid: %d\n", g, temp);
} // End of parallel region
printf("Masterthread finished\n");
printf("end g:%d\r\n", g);
}
omp_lock_t simple_lock;
int Lock_test () {
omp_init_lock(&simple_lock);
#pragma omp parallel num_threads(4)
{
int tid = omp_get_thread_num();
while (!omp_test_lock(&simple_lock))
printf_s("Thread %d - failed to acquire simple_lock\n",
tid);
printf_s("Thread %d - acquired simple_lock\n", tid);
printf_s("Thread %d - released simple_lock\n", tid);
omp_unset_lock(&simple_lock);
}
omp_destroy_lock(&simple_lock);
}参考资料:
https://learn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/cpp/parallel/openmp/reference/openmp-environment-variables?view=msvc-170
https://blog.csdn.net/lovely_yoshino/article/details/127688670