我们平时做 AOP 开发的时候,基本上都是增强某一个方法,在某一个方法执行之前或者执行之后做一些事情,这种叫做 PointcutAdvisor,实际上,Spring 中的 Advisor 大致可以分为两种类型,除了 PointcutAdvisor 之外,还有另外一种 Advisor 叫做 IntroductionAdvisor,因为最近想和小伙伴们聊一聊 Spring AOP 的源码,看源码有一个前提就是得先掌握 Spring 的各种用法,这样看源码的时候往往就有一种醍醐灌顶的感觉,否则看源码的时候就容易懵!
1. 实践
不同于 PointcutAdvisor,IntroductionAdvisor 这种增强主要是针对一个类来增强。
接下来松哥写一个简单的案例,小伙伴们来看下 IntroductionAdvisor 到底做了什么工作。
假设我有一个 Animal 接口,如下:
public interface Animal {
void eat();
}
这个动物具备吃的能力。
现在我还有一个 Dog,如下:
public interface Dog {
void run();
}
public class DogImpl implements Dog{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Dog run");
}
}
Dog 具备跑的能力,注意,Dog 和 Animal 之间并无继承/实现的关系。
现在,我们通过 Spring 中的 IntroductionAdvisor,就能让 Dog 具备 Animal 的能力,我们来看下具体怎么做。
首先,我们先来开发一个 Advice,这个 Advice 同时也是 Animal 接口的实现类,如下:
public class AnimalIntroductionInterceptor implements IntroductionInterceptor, Animal {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
if (implementsInterface(invocation.getMethod().getDeclaringClass())) {
return invocation.getMethod().invoke(this, invocation.getArguments());
}
return invocation.proceed();
}
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("Animal eat");
}
@Override
public boolean implementsInterface(Class<?> intf) {
return intf.isAssignableFrom(this.getClass());
}
}
跟普通 AOP 一样,当目标方法被拦截下来的时候,这里的 invoke 方法会被触发,在 invoke 方法中我们需要先调用 implementsInterface 方法进行判断,如果被拦截下来的方法所属的类是 Animal 的话,即 implementsInterface 方法返回 true 的情况(this 其实就是 Animal),那么就直接获取到 method 对象然后通过反射去调用就行了,这样会就会导致这里的 eat 方法被触发;否则,说明是被拦截下来的方法本身,那么就调用 invocation.proceed(); 让拦截器链继续往下执行即可。
接下来我们来定义 Advisor:
@Component
public class DogIntroductionAdvisor implements IntroductionAdvisor {
@Override
public ClassFilter getClassFilter() {
return new ClassFilter() {
@Override
public boolean matches(Class<?> clazz) {
return Dog.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz);
}
};
}
@Override
public void validateInterfaces() throws IllegalArgumentException {
}
@Override
public Advice getAdvice() {
return new AnimalIntroductionInterceptor();
}
@Override
public boolean isPerInstance() {
return true;
}
@Override
public Class<?>[] getInterfaces() {
return new Class[]{Animal.class};
}
}
这里有几个方法需要实现:
- getClassFilter:哪些类需要拦截在这里配置,ClassFilter 松哥在上篇文章中已经讲过了,这里只需要返回被拦截的类就行了,不需要具体到哪个方法被拦截。
- getAdvice:这个就是返回拦截下来后执行的通知,我们就返回前面定义的通知即可,这里有一个要求,就是 这个 Advice 需要实现 Animal 接口。
- getInterfaces:这个方法还比较重要,生成代理对象的时候,代理对象需要实现哪些接口,就是从这个地方定义的,这里返回 Animal,所以将来我拿到手的代理对象就实现了 Animal 接口,就能调用 Animal 中的方法了。
- isPerInstance:这个方法暂时没有实现,返回 true 就行了。
- validateInterfaces:这个方法是做接口校验的,我这里就不校验了。
好啦,我的代码现在就写好了,我们来测试看下:
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("introduction.xml");
Dog dog = ctx.getBean(Dog.class);
dog.run();
System.out.println("Animal.class.isAssignableFrom(dog.getClass()) = " + Animal.class.isAssignableFrom(dog.getClass()));
Animal animal = (Animal) dog;
animal.eat();
执行结果如下:

我们拿到手的 dog 对象其实也是一个 Animal。
这就是 Spring AOP 中的 IntroductionAdvisor,当一个类需要具备另一个类的能力的时候,可以使用 IntroductionAdvisor。
2. 源码分析
那么这一切是怎么实现的呢?
因为这篇文章我主要是想和小伙伴们分享 IntroductionAdvisor 的知识点,所以关于 AOP 完整的创建流程我先不说,在后续的文章中我会和大家做一个详细介绍,我今天就来和大家聊一聊在 Spring AOP 执行的过程中,究竟是如何处理 IntroductionAdvisor 的。
Spring AOP 中创建代理对象,一般是通过后置处理器来完成,从 AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessAfterInitialization 方法开始,大致时序图如下:
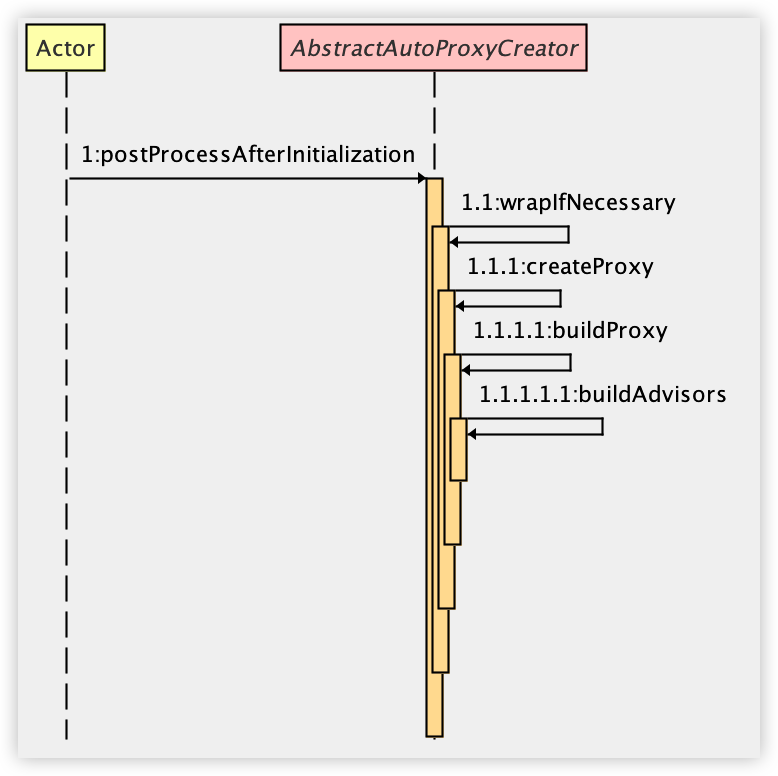
我们就从 buildProxy 方法开始看起吧,这个方法看名字就知道是用来构建代理对象的。
AbstractAutoProxyCreator#buildProxy:
private Object buildProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource, boolean classOnly) {
//...
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
//...
return (classOnly ? proxyFactory.getProxyClass(classLoader) : proxyFactory.getProxy(classLoader));
}
这里有一个 buildAdvisors 方法,这个方法是用来处理 Advisor 的,我们自定义的 DogIntroductionAdvisor 将在这里被读取进来,然后将之添加到 proxyFactory 对象中,在添加的过程中,会进行一些额外的处理,proxyFactory#addAdvisors 最终会来到 AdvisedSupport#addAdvisors 方法中:
public void addAdvisors(Collection<Advisor> advisors) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(advisors)) {
for (Advisor advisor : advisors) {
if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor introductionAdvisor) {
validateIntroductionAdvisor(introductionAdvisor);
}
this.advisors.add(advisor);
}
adviceChanged();
}
}
在这里会遍历所有的 Advisor,判断类型是不是 IntroductionAdvisor 类型的,我们自定义的 DogIntroductionAdvisor 恰好就是 IntroductionAdvisor 类型的,所以会进一步调用 validateIntroductionAdvisor 方法,如下:
private void validateIntroductionAdvisor(IntroductionAdvisor advisor) {
advisor.validateInterfaces();
Class<?>[] ifcs = advisor.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> ifc : ifcs) {
addInterface(ifc);
}
}
public void addInterface(Class<?> intf) {
if (!this.interfaces.contains(intf)) {
this.interfaces.add(intf);
adviceChanged();
}
}
小伙伴们看一下,advisor.getInterfaces(); 实际上就调用到我们自定义的 DogIntroductionAdvisor 中的 getInterfaces 方法了,所以这里会返回 Animal 接口,然后这里会把 Animal 接口存入到 interfaces 这个变量中,将来在生成 AOP 对象的时候会用到。
好啦,现在回到 buildProxy 方法中,该方法最终会执行到 proxyFactory.getProxy 方法,该方法最终执行的时候,要么是 JDK 动态代理,要么是 CGLIB 动态代理,我们分别来说一下。
2.1 JDK 动态代理
先说如果是 JDK 动态代理,那么 proxyFactory.getProxy 方法就需要构建一个 JdkDynamicAopProxy 出来,如下:
public JdkDynamicAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
this.advised = config;
this.proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised, true);
findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(this.proxiedInterfaces);
}
参数 config 中就包含了我们前面说的要实现的接口,所以这里 proxiedInterfaces 变量中保存的就是代理对象将来要实现的接口,以我们前面的代码为例,这里 proxiedInterfaces 的值如下:
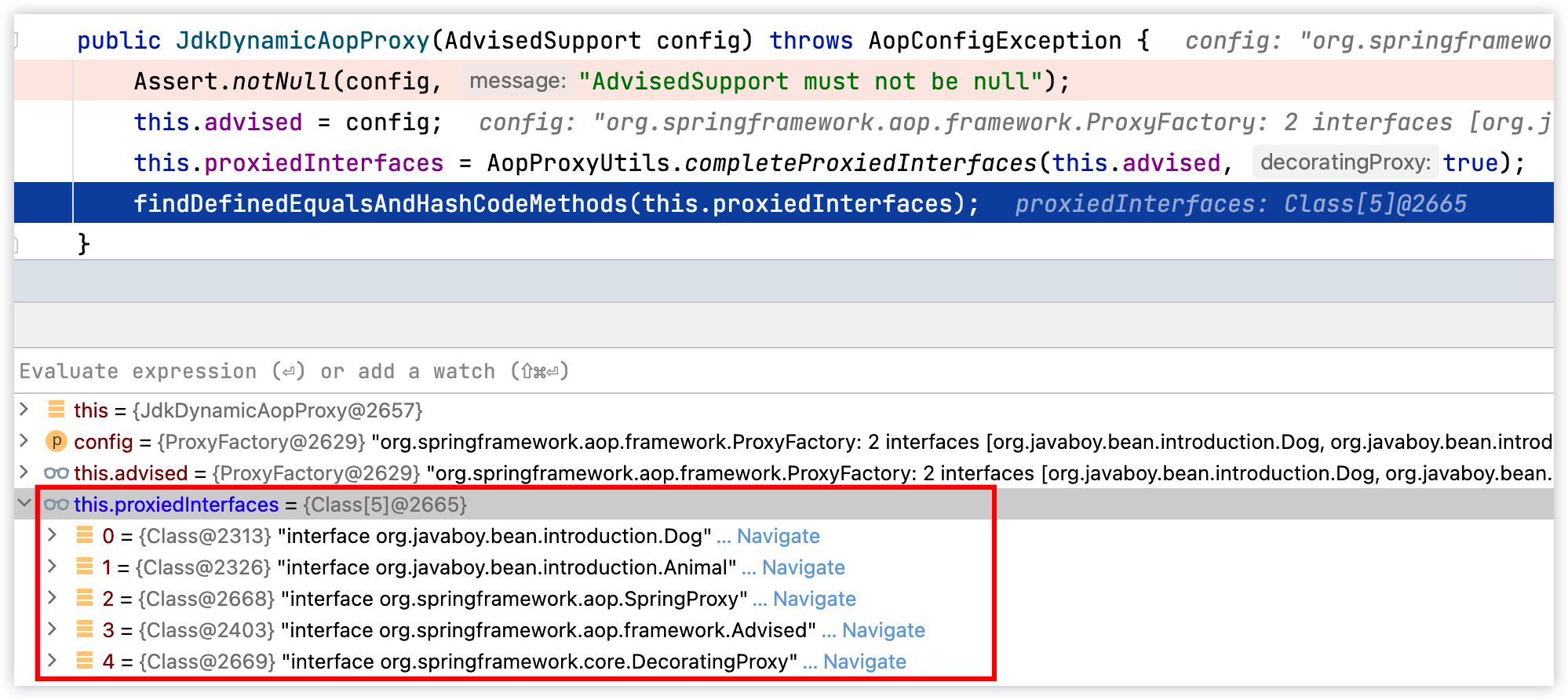
可以看到,就包含了 Animal 接口。
最后,调用 JdkDynamicAopProxy#getProxy 方法生成代理对象,如下:
@Override
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, this.proxiedInterfaces, this);
}
这就是大家比较熟悉的 JDK 动态代理了,可以看到,生成的代理对象有五个接口,生成的代理对象不仅仅是 Dog、Animal 的实例,也是 SpringProxy 等的实例。现在大家就明白了为什么我们拿到手的 dog 对象还能强转成 Animal 了。
2.2 CGLIB 动态代理
再来看 CGLIB 动态代理的实现逻辑,其实也差不多:
public CglibAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
this.advised = config;
this.advisedDispatcher = new AdvisedDispatcher(this.advised);
}
@Override
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
return buildProxy(classLoader, false);
}
private Object buildProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader, boolean classOnly) {
//...
enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);
enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));
//...
// Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance.
return (classOnly ? createProxyClass(enhancer) : createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks));
}
可以看到,其实跟 JDK 里边的思路差不多,也是从 advised 中提取出来接口设置进去,advised 也是在 CglibAopProxy 对象构建的时候传入进来的。
3. 小结
好了,现在小伙伴们应该明白了什么是 IntroductionAdvisor 了吧?说白了,就是在生成代理对象的时候,把我们在 Advisor 中设置好的接口也考虑进去,这样生成的代理对象同时也是该接口的实现类,当然,在我们提供的 Advice 中,必须也要实现该接口,否则代理对象执行接口中的方法,找不到具体实现的时候就会报错了。
感兴趣的小伙伴赶紧体验一把吧~