AutoSAR总体架构
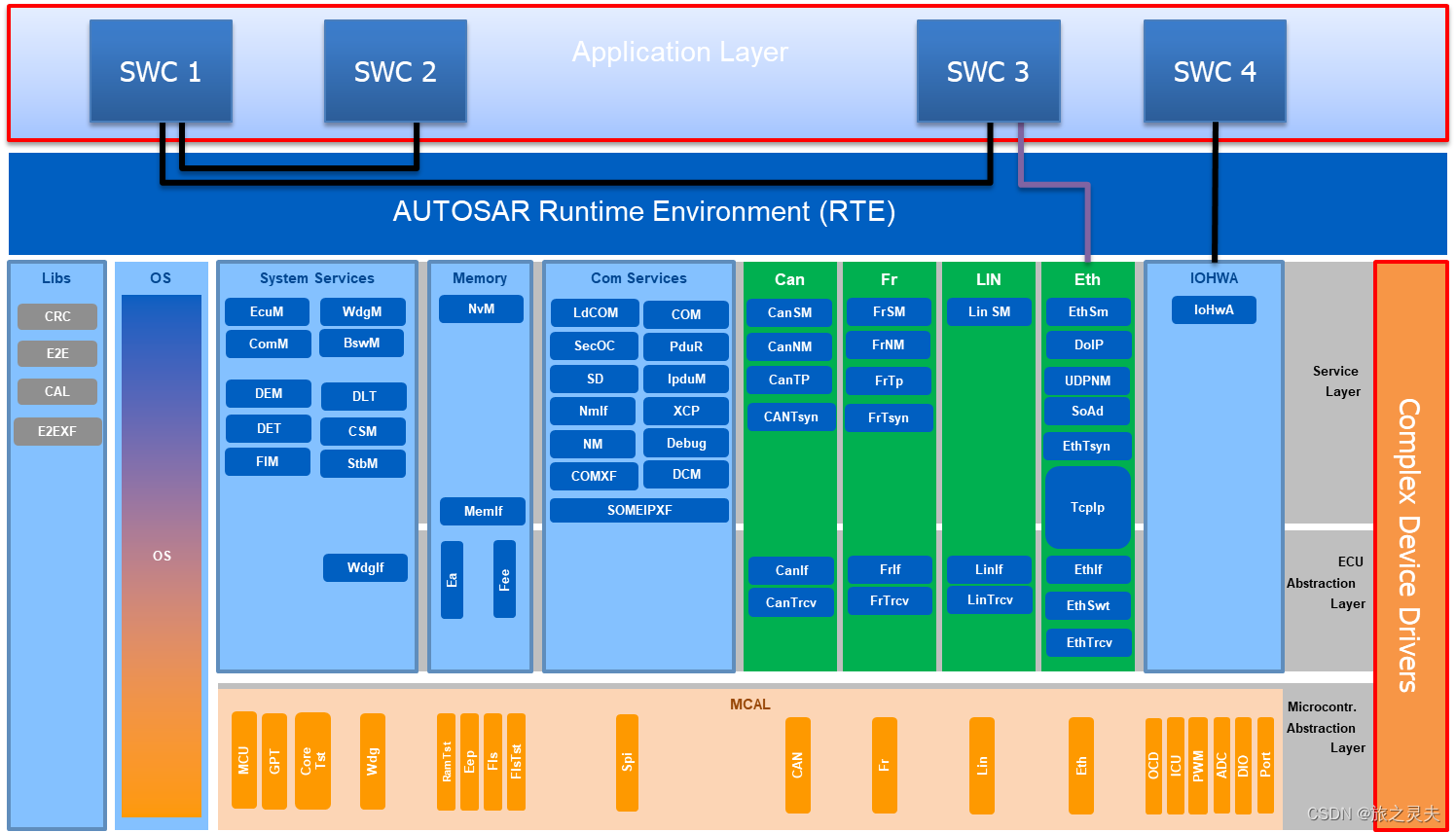
![]() 是本文讲解内容。
是本文讲解内容。
接口类型
AUTOSAR接口
- –SWCs和/或BSW模块交换的信息
- –独立于实施/网络/硬件
- –端口+接口
标准化AUTOSAR接口
- –AUTOSAR接口
- –标准化的语法和语义
- –标准化端口+接口
标准化接口
- –标准化API
- –通常为特定编程语言(“C”)定义
- –通常由同一ECU上的S/W模块使用

设计元素

设计流程

AutoSar数据类型设计
已经定义了三个级别的数据类型
- –应用程序数据类型
- –实现数据类型
- –基本数据类型


过程
Process Flow “DataType Creation”

应用程序数据类型
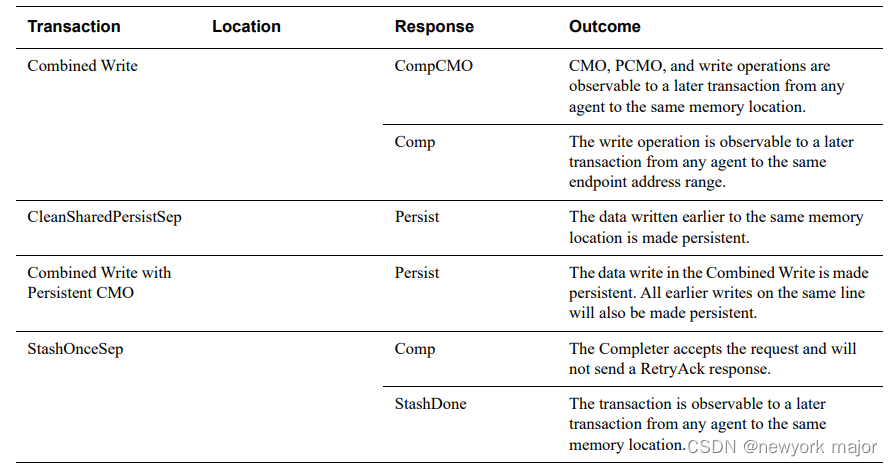
| Type | Scene | Sample |
| Boolean | compu method、 data constraints | - |
| Value | a unit, compu method and data constraints | - |
| String | compu method and to define the text properties of the string type. The text properties include the selection of the string’s base type, the definition of a fixed or variable size, and a filling character | - |
| Array | data type | - |
| Record | record elements | - |
| Axis | describes one of the input values of a characteristic table | - |
| Characteristic Table | define a number of input values (axis) and an output value (as Application Values Type). | - |
实施数据类型:
| Type | Scene | Sample |
| Value | Define a datatype of base type, can add compu method 、data constraint、invalid value | typedef unsigned long uint32; |
| Type Reference | A type reference expresses a redirection to another data type,not need to choose base type | typedef MySimpleType MyTypeRef; |
| Data Reference | A data reference expresses a pointer type as defined by the C code statement | typedef MySimpleType * MyDataRef; or typedef void * MyDataRef;. |
| Union | Only one of the union elements might hold data at a given time | typedef union{ uint32 UnionElement0; } MyUnitCode; |
| Array | The element type of the can be Value, Type Reference, Array or Record and a fixed or variable size | typedef uint64 MyArrayCode[5]; |
| Record | define a struct type | typedef struct{ uint16 RecordElement; CounterType RecordElement_1; } MyRecordCode; |
基本类型:
•使用本机声明定义基类型,例如uint8
–复用
•独立于平台
–无终止或对齐
•描述类型编码
–例如,"2C"
•描述本机声明
–例如:“typedef unsigned char“
平台类型是具有预定义缩写的实现数据类型。
它不必引用基本数据类型。
它们的原生声明来自Platform_types.h(BSW传递)。

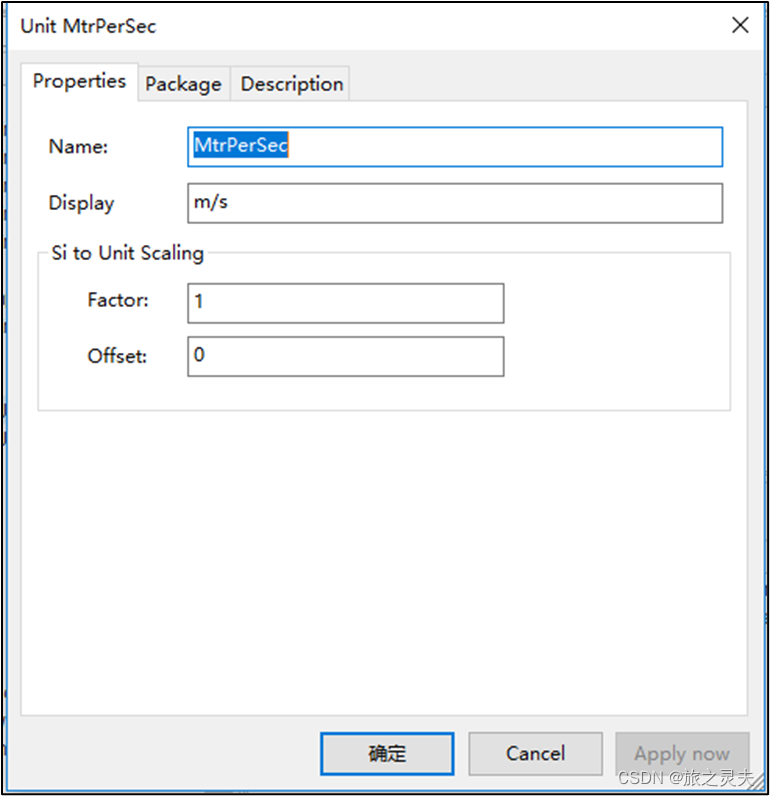
Unit:
In the New Unit dialog you may define the display name and the factor and offset.
计算方法:
计算方法(比例)定义内在价值和物理价值之间的转换规则
可以分配给数据类型、数据元素和操作参数
允许提供变量a
- –物理(测试和测量)含义
- –内部(校准)含义
也用于定义枚举
反向函数可由RTE导出

Compu Methods Category:
| Type | Scene | Sample |
| Identical | Only the unit is relevant, no compu scales can be defined | - |
| Linear | Exacty one compu scale expressing a linear conversion can be defined | - |
| Scale-Linear | Any number of compu scales expressing a linear conversion can be defined. The ranges must not overlap. | - |
| TextTable | Enumeration: Any number of compu scales expressing a constant value can be defined. | - |
| Scale-LinearAndTextTable | Any number of compu scales expressing a linear conversion can be defined. The ranges must not overlap. | - |
| BitfieldTextTable | Bitfield: Only compu scales of type Int to Phys can be defined. | - |
Compu Methods Compu Contents:

Int To Phys: computing the physical value out of the internal value.
Phys To Int: compu scales used for reversely computing the internal values out of the physical value.
Compu Methods Sample: defining enumerations

Data Constraints:

Scene:
define a minimum and maximum range.
define a range related to the internal value and/or to the physical value.
AutoSAR Interface Design --Summary
Interfaces are assigned to SWC Ports.
Interfaces define the communication-mechanism
between SWC-Ports
Sender/Receiver Interface
E.g. Data exchange between Application SWCs
Client/Server Interface
E.g. Data exchange between Application SWCs and BSW
Calibration Interface
Calibration
Additional Interfaces introduced with AUTOSAR 4.0
NvDataInterface (NvRAM)
ModeSwitchInterface (Mode Switch)
TriggerInterface (external triggering, e.g. from ComplexDevicerDriver)
Client Server Interface: The operations that are implemented by the server and invoked by the client are defined.
· Sender Receiver Interface: Defines the data elements that are exchanged.
· Parameter Interface: Constant, fixed or calibration data is accessed via the parameter interfaces.
· Non Volatile Data Interface: Provide access to the data at the element level.
· Trigger Interface: A signal of triggered event is passed to the component via the trigger interface.
· Mode Switch Interface: The information about the current mode is passed to the component via mode switch interface.
AutoSAR Interface Design --Flow
Process Flow “Interface Creation”

AutoSAR Interface Design --Relationship
Port/Interface Relationship:

AutoSAR Interface Design –-S/R Interface
Sender/Receiver Communication
- 1..m Multiplicity (Multicast)
- n..1 Multiplicity
- Transfer of Data element
- of a certain Data type (e.g. Uint8)
- Data Elements are Variables:Base Type、record

AutoSAR Interface Design –-S/R Sample
S/R Interface Sample:

AutoSAR Interface Design -- C/S Interface
Client/Server Communication
- n..1 Multiplicity
- Sync or async
- Transfer of Arguments to/from an Operation
- Arguments are Variables
- Arguments have a direction “in, out, inout”
- Return of ErrorCodes possible using “ApplicationError”
AutoSAR Interface Design –-C/S Sample
C/S Interface Sample:

AutoSAR Interface Design –-Trigger Interface
Trigger Interface Sample:
AutoSAR Interface Design –-Calibration Interface
Calibration Interface :
Type of calibration support can be defined in the ‘Calibration’ column for the dataelements of the different interfaces
This information can be used by the RTE generator to be able to support McSupportData generation (that maps symbol with the dataelement)
McSupportData is the bridge from Autosar to the A2L generation
Affects: ModeSwitch, ClientServer and SenderReceiver communication
AutoSAR Interface Design -- Service Interface
Service Interface :
Communication between SWC and BSW
IsService = true
Can be Client/Server, Sender/Receiver, etc...

AutoSAR SWC Design –-SWC Component Type
Component Type :

AutoSAR SWC Design -- Atomic Component
Define Atomic Component Sample :

AutoSAR SWC Design -- Composition
Define Composition Component Sample:
 1.Application component should be assigned to Composition component.
1.Application component should be assigned to Composition component.
2.Application component instance will be added automatic after sync in Davinci Configurator.
3.In this project, DIMswarch will be used to export ECUExtract.
AutoSAR SWC Design -- Ports

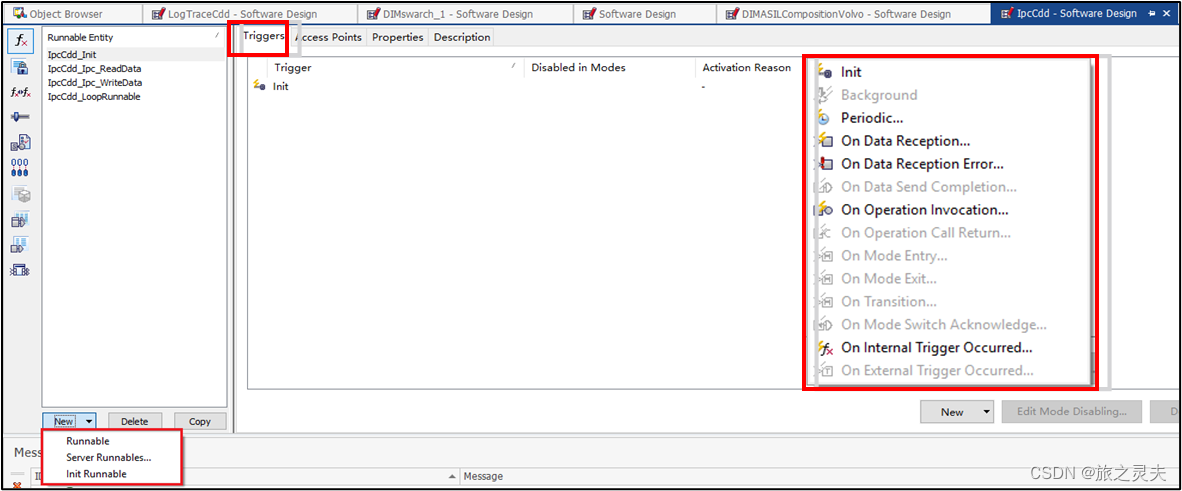
AutoSAR Runnable Design --Triggers
Triggers
Init
The runnable entity is triggered exactly once on start up of the component.
Runnables with init triggers are not allowed to have other triggers.
Periodic
The runnable entity is periodically triggered.
On Data Reception
The runnable entity is triggered upon an incoming data element.
Can select data elements of all receiver port of the component type.
Used for unqueued communication.
On Data Reception Error
The runnable entity is triggered upon an incoming data element.
Can select data elements of all receiver port of the component type.
On Data Send Completion
The runnable entity is triggered upon completion of sending an output data element (Tx Acknowledge).
Can select data elements of all sender port of the component type.
AutoSAR Runnable Design -- Access points
Access Points
Receive Data
The runnable entity may receive data from a receiver port prototype.
This kind of port access is only available for queued data element prototypes.
Read Data
The runnable entity may read data from a receiver port prototype.
This kind of port access is only available for unqueued data element prototypes
Send Data
The runnable entity may send data to a sender port prototype.
This kind of port access is only available for queued data element prototypes.
Write Data
The runnable entity may write data to a sender port prototype.
This kind of port access is only available for unqueued data element prototypes
Invoke Operations
The runnable entity may invoke operations of a client port prototype

AutoSAR Runnable Design -- Exclusive Area List
The runnable entity does not access the exclusive area.
The runnable entity runs in the exclusive area during the complete execution.
The runnable entity can enter the exclusive area during its execution.

1.Solve the issue of the swc runnables run in different task.
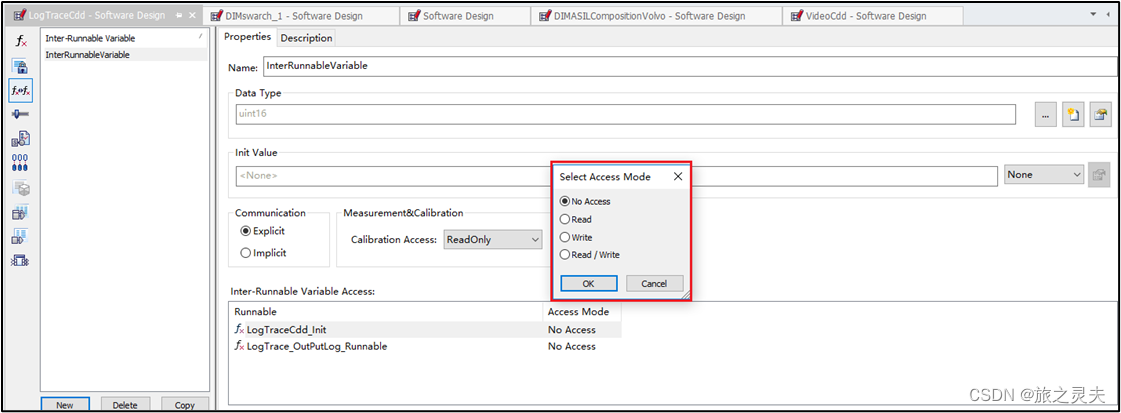
AutoSAR Runnable Design --InterRunnableVariable
The runnable entity does not access the inter-runnable variable .
The runnable entity only reads the inter-runnable variable .
The runnable entity only writes the inter-runnable variable .
The runnable entity reads and writes the inter-runnable variable.