需求:用SpringBoot+Redis+RabbitMQ技术,PostMan发送一个请求,存储到Redis中,并且在控制台获取打印该信息。用PostMan发送一个请求将信息存储到RabbitMQ,并且在监听该队列打印出信息。
练习1:SpringBoot+Redis
PostMan发送一个请求,存储到Redis中,并且在控制台获取打印该信息。
1.创建一个SpringBoot项目,添加Spring Data Redis的依赖。(省略)
2.创建一个Controller类,编写Pos请求的接口方法,用于接收Postman发送的请求数据并存储到Redis中。示例代码如下:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class RedisController {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String,String> redisTemplate;
@PostMapping("/storeData")
public String storeData(@RequestBody String data){
// 将请求数据存储到Redis中,可以使用任意自定义的键名
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("requestData",data);
return "Data stored successfully in Redis";
}
3.在创建的Controller类,添加一个GET请求的接口方法,用于从Redis中获取数据并在控制台打印该信息。示例代码如下:
package com.example.redisdemo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class RedisController {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String,String> redisTemplate;
@GetMapping("/getData")
public String getData() {
// 从Redis中获取数据
String data = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("requestData");
System.out.println("Data from Redis: " + data);
return "Data from Redis: " + data;
}
}
4.在应用的配置文件(例如application.properties)中添加端口信息和Redis的配置信息。示例代码如下:
server.port=8888
spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1
spring.redis.port=6379
spring.redis.password=123456
spring.redis.database=0
以上示例中,配置了Redis的主机地址、端口和数据库信息。如果 Redis 没有设置密码,spring.redis.password 可以为空。
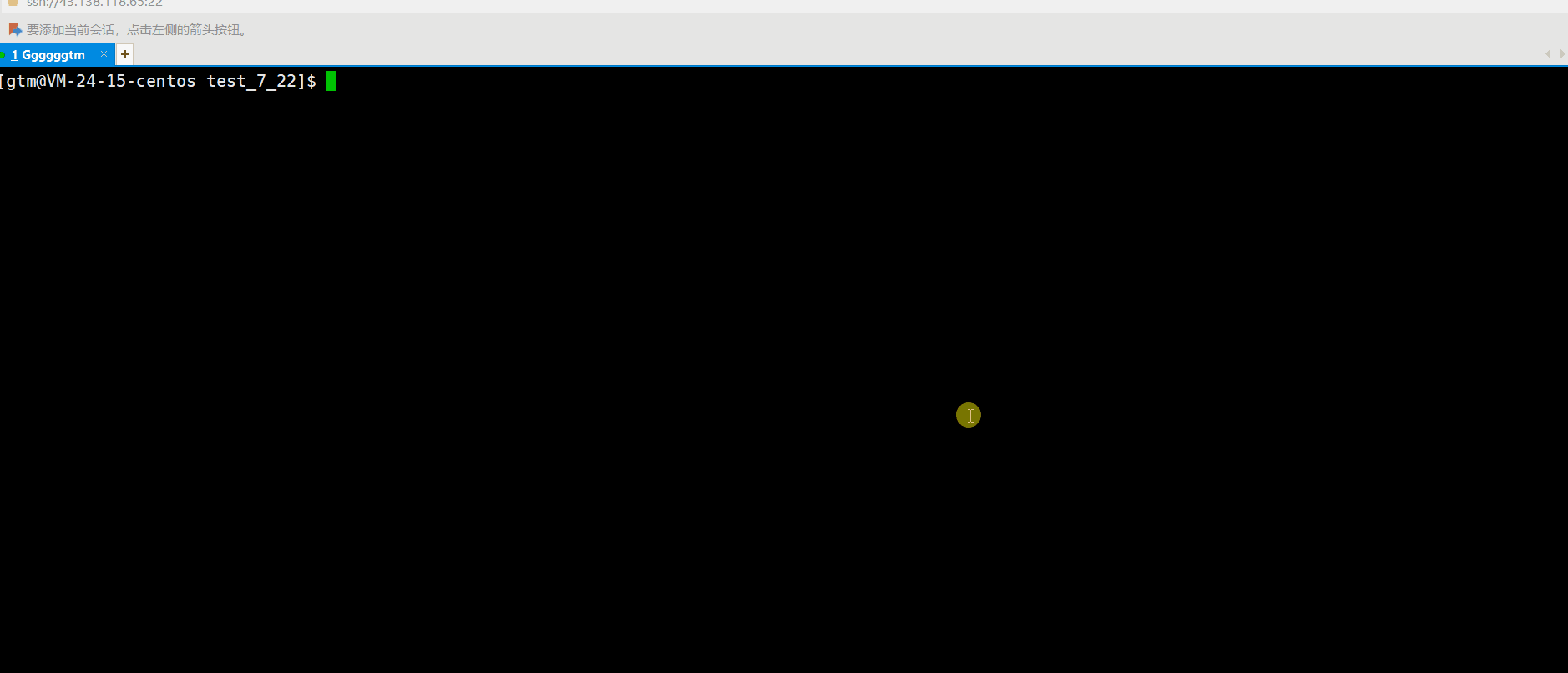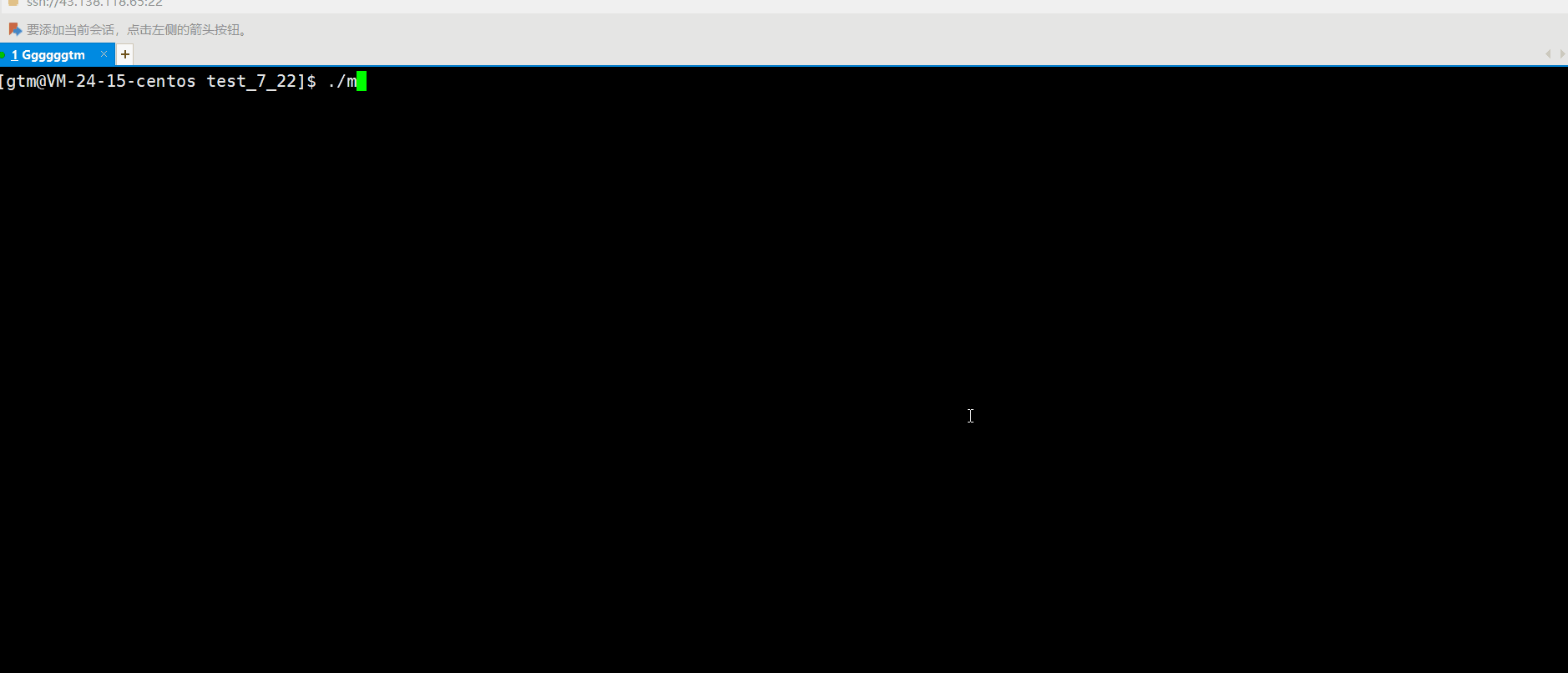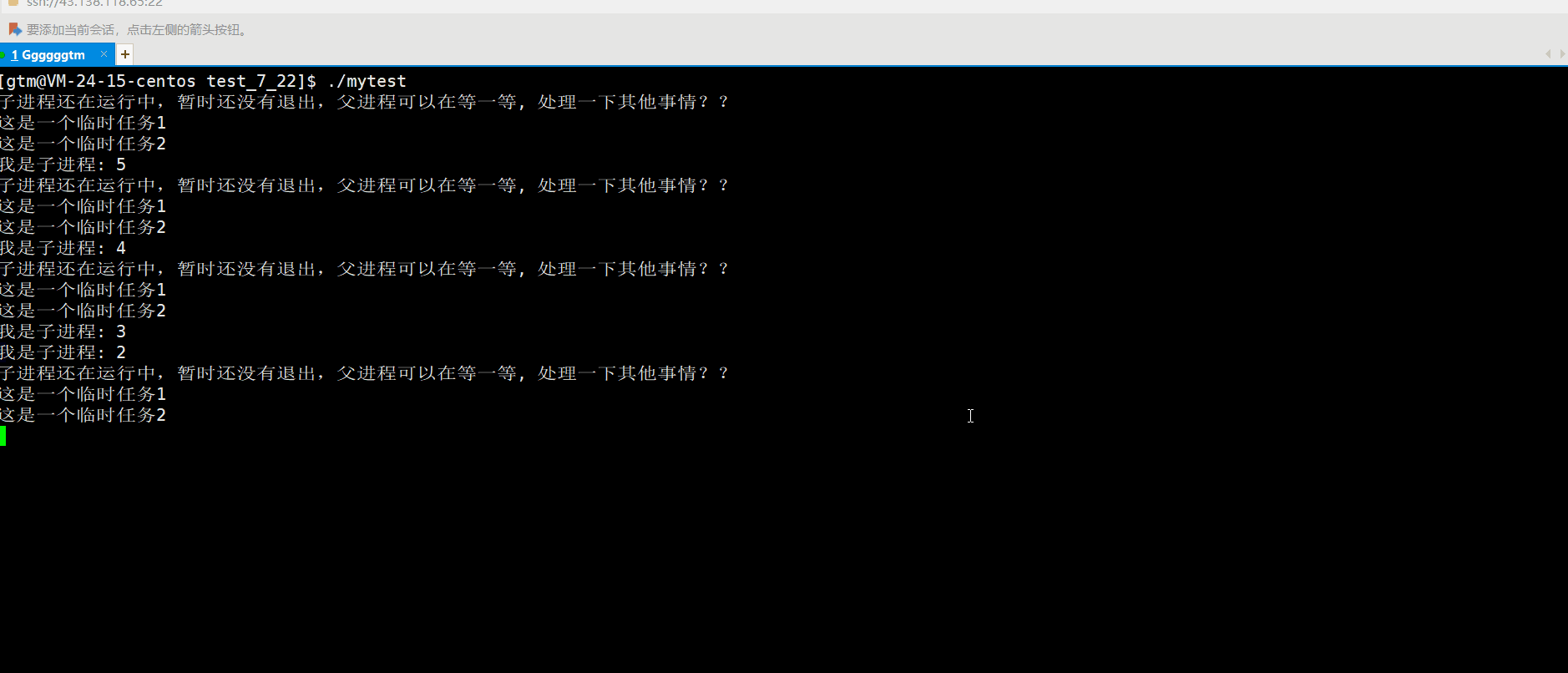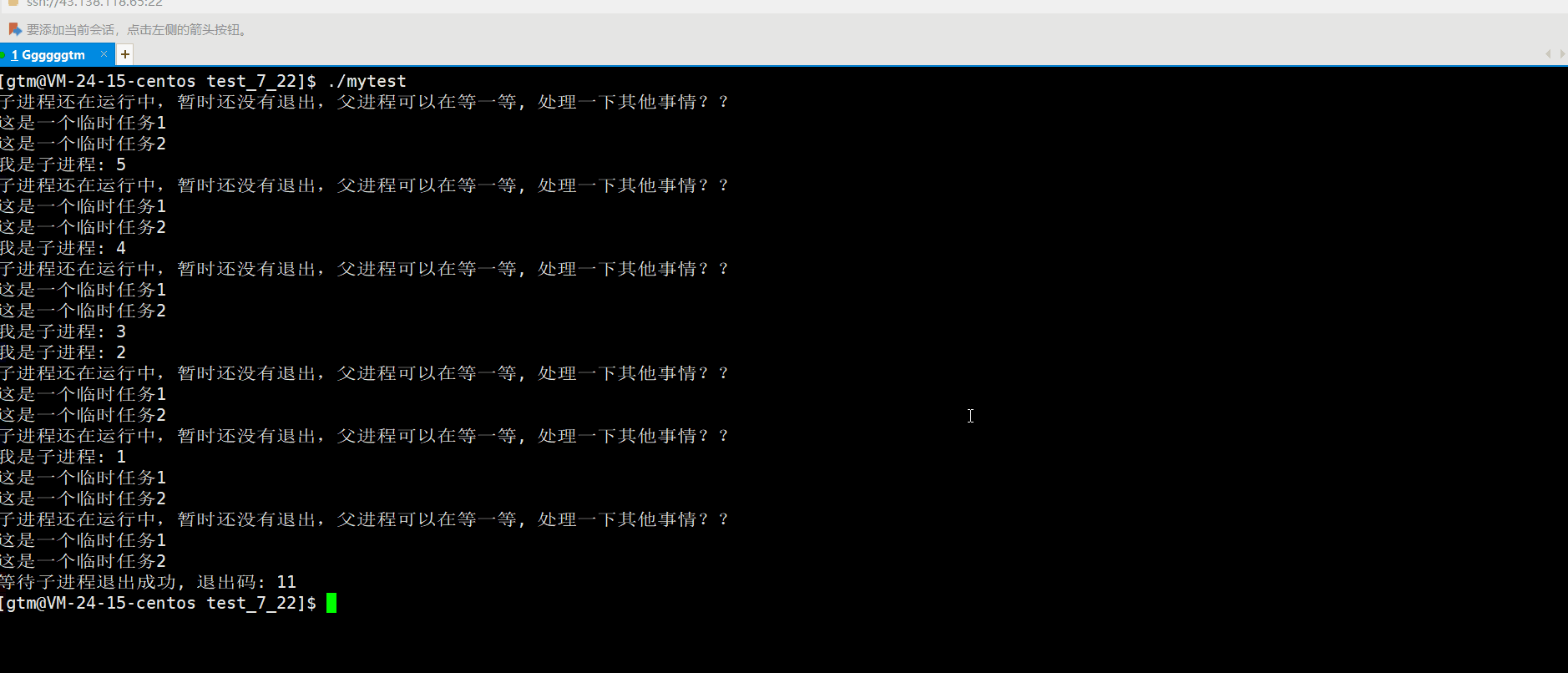
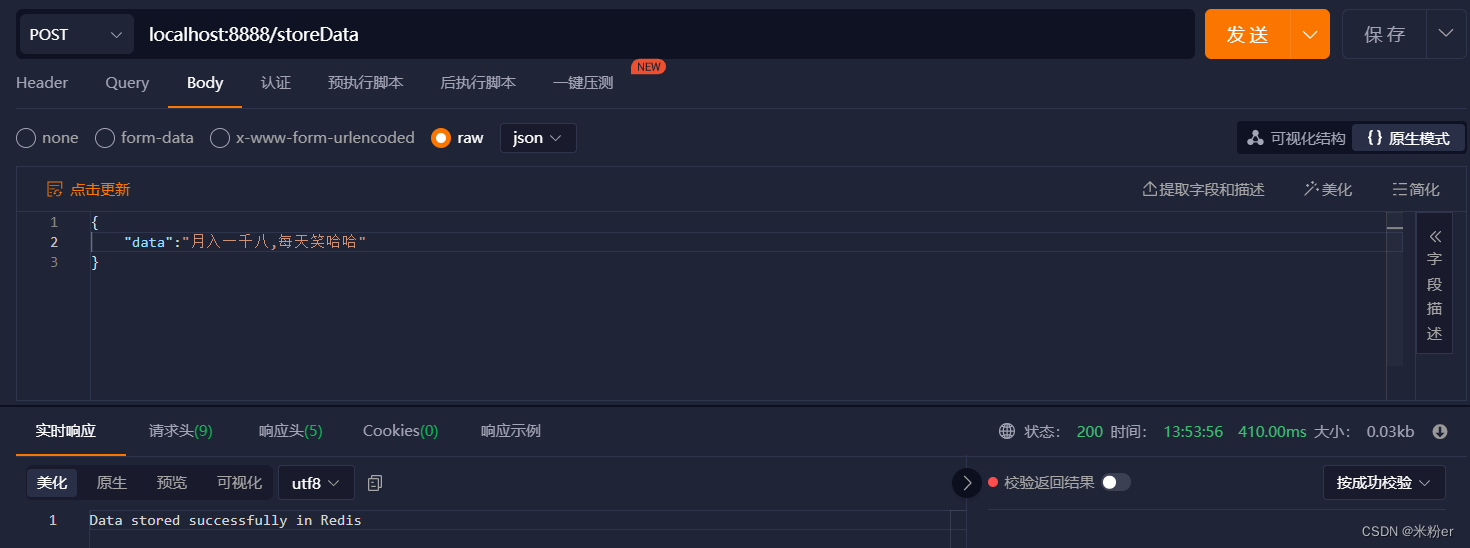
5.启动应用,然后使用Postman发送一个POST请求,请求的URL为http://localhost:8888/storeData,请求体中包含要存储到Redis的数据。
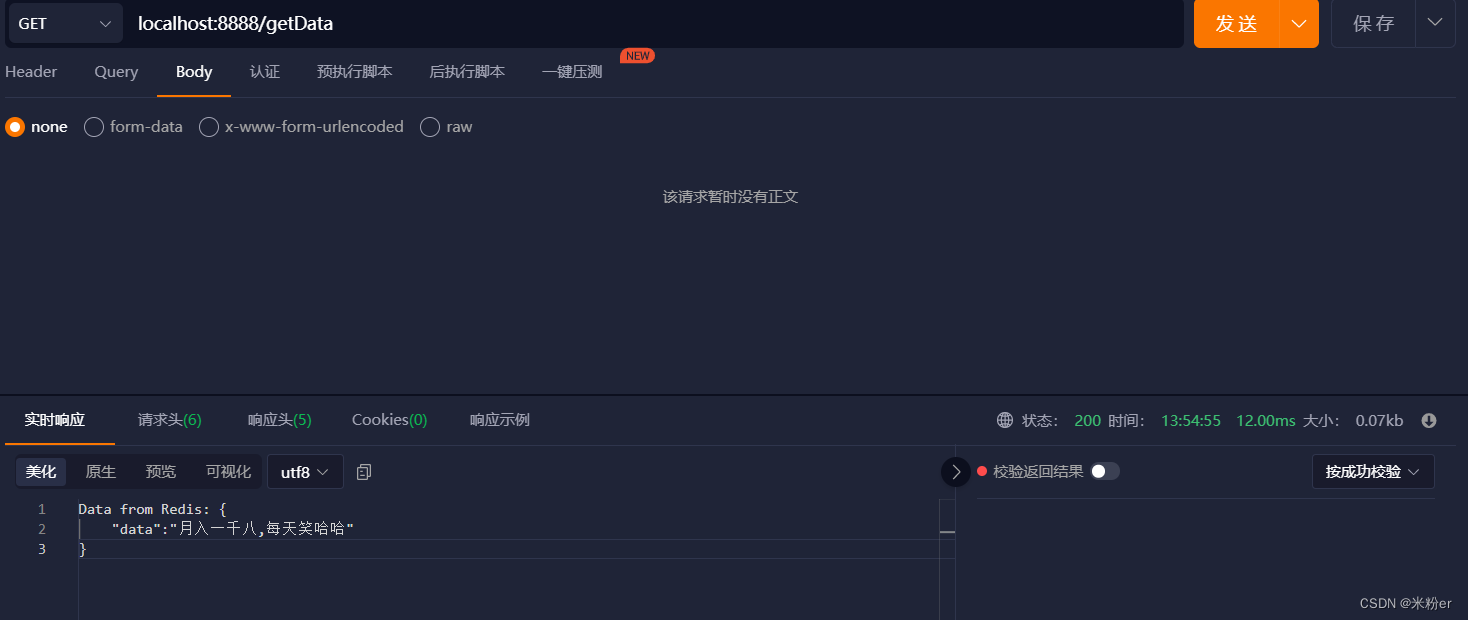
6.再使用Postman发送一个GET请求,请求的URL为http://localhost:8888/getData,你将在控制台中看到打印出存储在Redis中的信息。
练习2:SpringBoot+RabbitMQ
PostMan发送一个请求,存储到RabbitMQ中,并且在监听该队列打印出信息。
1.配置RabbitMQ连接:在Spring Boot的配置文件(application.properties或application.yml)中添加以下配置信息:
server.port=8888
spring.rabbitmq.host=127.0.0.1
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
spring.rabbitmq.username=guest
spring.rabbitmq.password=guest
2.创建消息发送者:创建一个发送消息的类,比如MessageSender,使用RabbitTemplate发送消息到RabbitMQ队列,同时在该类中添加一个方法用于发送消息,例如:
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class MessageSender {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Bean
public Queue queue() {
return new Queue("ccc", false);
}
public void sendMessage(String message) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("ccc", message);
}
}
3.创建消息监听者:创建一个消息监听的类,比如MessageListener,使用@RabbitListener注解监听队列中的消息,并在方法中将消息打印到控制台,例如:
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MessageListener {
@RabbitListener(queues = "ccc")
public void receiveMessage(String message) {
System.out.println("Message received: " + message);
}
}
4.启动应用程序:在Spring Boot的入口类上添加 @EnableRabbit 注解,以启用RabbitMQ的相关功能,例如:
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.EnableRabbit;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableRabbit
public class RabbitmqdemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RabbitmqdemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
5.发送和监听消息:在需要发送和监听消息的地方使用 @Autowired注入MessageSender,并调用 sendMessage 方法发送消息。监听者将自动侦听指定队列的消息并将其打印到控制台。例如:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private MessageSender messageSender;
@PostMapping("/send")
@ResponseBody
public String sendMessage(@RequestParam("message") String message) {
messageSender.sendMessage(message);
return "Message sent successfully.";
}
}