buddy bitmap
根据《Ext4文件系统介绍 - 理论篇_nginux的博客-CSDN博客》我们知道磁盘上有1block 大小(默认4K)data block bitmap,每bit位代表一个block的使用情况,1代表占用,0代表空闲。data block bitmap 可以表示4 * 1024 * 8 = 32768个block,32768 * 4K = 128M正好是1个block group大小。为了加速data block bitmap访问内存中同样会有一份缓存。
磁盘block管理为了尽量避免碎片化问题,跟内存管理模块一样同样采用了buddy算法,同时内存构建一个buddy的bitmap,即bitmap buddy。
cat /proc/fs/ext4/xxx/mb_groups
代码在:fs/ext4/mballoc. :
static int ext4_mb_seq_groups_show(struct seq_file *seq, void *v)
#group: free frags first [ 2^0 2^1 2^2 2^3 2^4 2^5 2^6 2^7 2^8 2^9 2^10 2^11 2^12 2^13 ]
#0 : 18017 2 4262 [ 1 2 1 1 1 2 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 2 ]
#1 : 26581 5 2125 [ 3 3 1 1 2 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 3 ]
#2 : 32713 2 27 [ 3 1 3 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 ]
#3 : 32639 1 129 [ 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 3 ]
#4 : 24576 1 8192 [ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 ]
#5 : 32634 3 130 [ 2 4 2 3 1 2 2 1 2 0 1 1 1 3 ]
#6 : 32749 1 19 [ 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 ]
#7 : 32639 1 129 [ 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 3 ]
free:代表group所有空闲block总数,该值来自于ext4_group_info.bb_free
frags :代表group连续的空闲空间段数目,该值来自于ext4_group_info.bb_fragments
first : 第一个空闲的physical block number,该值来自于ext4_group_info.bb_first_free
ext4_mb_seq_groups_show:
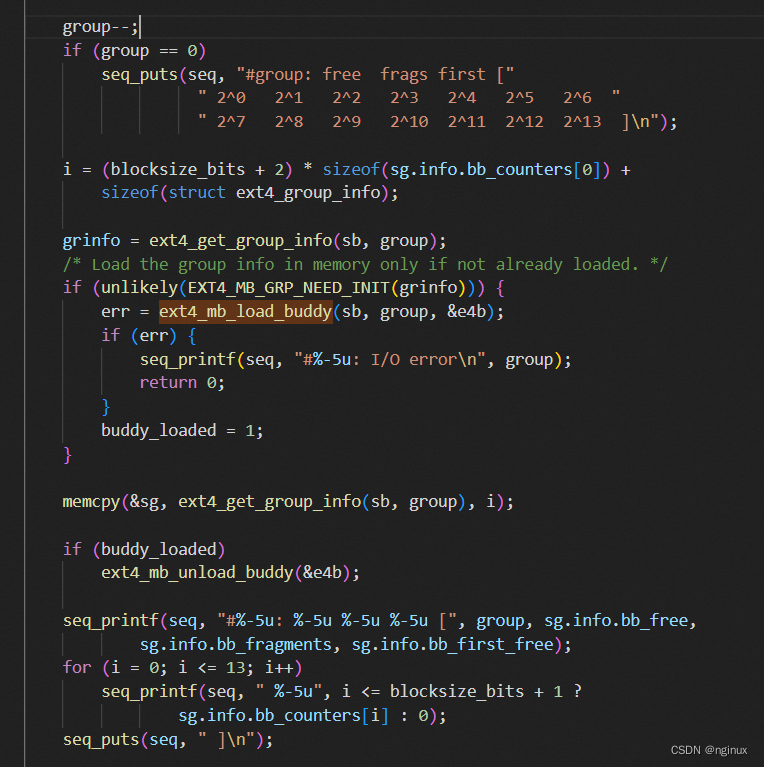
结合代码和上面分析我们知道打印数值来自于ext4_group_info,即通过ext4_get_group_info来获取的: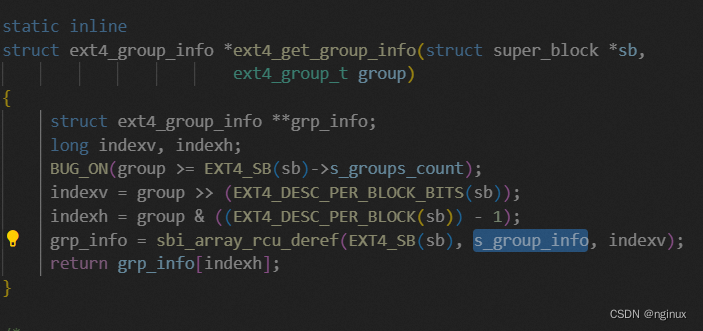
最终ext4_group_info来自于EXT4_SB(sb) ext4_sb_info中的成员s_group_info[group],所以s_group_info成员初始化来自哪里?ext4_mb_init_cache,而是ext4_mb_load_buddy就会调用ext4_mb_init_cache,这里init cache就是指保存磁盘data block bitmap的pagecache和buddy bitmap。
ext4_mb_load_buddy->ext4_mb_init_cache->ext4_mb_generate_buddy。
根据ext4_mb_init_cache的代码注释我们知道磁盘data block bitmap和只是内存中构建的(磁盘上无对应数据,unmount时会删除)的buddy bitmap,他们各占用1个block。

buddy bitmap格式

注意:
- 上面每个竖线代表二分
- 二分表示,每个区间都可以完整表示一个128M block group所有的block的使用情况,1表示占用,0表示空闲。
- 内核通过sbi->s_mb_offsets[]和sbi->s_mb_maxs[]两个数据记录每个区域的offset和最大的bit数量。
fs/ext4/mballoc.c : ext4_mb_init构建相应数组:

sbi->s_mb_offset[0] = 0,sbi->s_mb_maxs[1] = 32768
sbi->s_mb_offset[1] = 0,sbi->s_mb_maxs[1] = 16384
sbi->s_mb_offset[2] = 16384 sbi->s_mb_maxs[2] = 8192
...ext4_buddy数据结构
struct ext4_buddy {
//buddy_bitmap的page
struct page *bd_buddy_page;
//buddy bitmap的内存区域
void *bd_buddy;
//data block bitmap的内存缓存的page
struct page *bd_bitmap_page;
void *bd_bitmap;
struct ext4_group_info *bd_info;
struct super_block *bd_sb;
__u16 bd_blkbits;
ext4_group_t bd_group;
};ext4_mb_load_buddy函数核心就是初始化ext4_buddy数据结构和bd_sb对应的ext4_sb_info中的s_group_info成员。注意每一个group对应一个ext4_buddy结构体。
buddy bitmap构建过程
ext4_mb_init_group和ext4_mb_load_buddy都会调用ext4_mb_init_cache,我们就以ext4_mb_init_group调用为启动分析。
static noinline_for_stack
int ext4_mb_init_group(struct super_block *sb, ext4_group_t group, gfp_t gfp)
{
struct ext4_group_info *this_grp;
struct ext4_buddy e4b;
struct page *page;
int ret = 0;
might_sleep();
mb_debug(sb, "init group %u\n", group);
this_grp = ext4_get_group_info(sb, group);
...
ret = ext4_mb_get_buddy_page_lock(sb, group, &e4b, gfp);
...
page = e4b.bd_bitmap_page;
ret = ext4_mb_init_cache(page, NULL, gfp);
...
/* init buddy cache */
page = e4b.bd_buddy_page;
//传入的参数incore是e4b.bd_bitmap是磁盘中读取data block bitmap,通过这个构建buddy bitmap
ret = ext4_mb_init_cache(page, e4b.bd_bitmap, gfp);
...
return ret;
}
1.ext4_mb_get_buddy_page_lock获取group对应的data block bitmap和buddy bitmap对应的pagecache。然后page会挂在inode的高速缓存address space,这里是哪个inode?linux采用了特殊inode = 2。
2.分别调用两次ext4_mb_init_cache初始化刚才创建的page缓存,第一次是data block bitmap,第二次是buddy bitmap。
ext4_mb_get_buddy_page_lock
/*
* Lock the buddy and bitmap pages. This make sure other parallel init_group
* on the same buddy page doesn't happen whild holding the buddy page lock.
* Return locked buddy and bitmap pages on e4b struct. If buddy and bitmap
* are on the same page e4b->bd_buddy_page is NULL and return value is 0.
*/
static int ext4_mb_get_buddy_page_lock(struct super_block *sb,
ext4_group_t group, struct ext4_buddy *e4b, gfp_t gfp)
{
struct inode *inode = EXT4_SB(sb)->s_buddy_cache;
int block, pnum, poff;
int blocks_per_page;
struct page *page;
e4b->bd_buddy_page = NULL;
e4b->bd_bitmap_page = NULL;
blocks_per_page = PAGE_SIZE / sb->s_blocksize;
/*
* the buddy cache inode stores the block bitmap
* and buddy information in consecutive blocks.
* So for each group we need two blocks.
*/
block = group * 2;
pnum = block / blocks_per_page;
poff = block % blocks_per_page;
page = find_or_create_page(inode->i_mapping, pnum, gfp);
if (!page)
return -ENOMEM;
BUG_ON(page->mapping != inode->i_mapping);
e4b->bd_bitmap_page = page;
e4b->bd_bitmap = page_address(page) + (poff * sb->s_blocksize);
if (blocks_per_page >= 2) {
/* buddy and bitmap are on the same page */
return 0;
}
block++;
pnum = block / blocks_per_page;
page = find_or_create_page(inode->i_mapping, pnum, gfp);
if (!page)
return -ENOMEM;
BUG_ON(page->mapping != inode->i_mapping);
e4b->bd_buddy_page = page;
return 0;
}上面函数要注意pnum就是page->index,比如group =0,那么其data block bitmap对应page->index = 0, buddy bitmap对应page->index = 1。find_or_create_page如果已经存在缓存则返回,否则创建。
ext4_mb_init_cache
static int ext4_mb_init_cache(struct page *page, char *incore, gfp_t gfp)
{
ext4_group_t ngroups;
int blocksize;
int blocks_per_page;
int groups_per_page;
int err = 0;
int i;
ext4_group_t first_group, group;
int first_block;
struct super_block *sb;
struct buffer_head *bhs;
struct buffer_head **bh = NULL;
struct inode *inode;
char *data;
char *bitmap;
struct ext4_group_info *grinfo;
inode = page->mapping->host;
sb = inode->i_sb;
ngroups = ext4_get_groups_count(sb);
blocksize = i_blocksize(inode);
blocks_per_page = PAGE_SIZE / blocksize;
mb_debug(sb, "init page %lu\n", page->index);
groups_per_page = blocks_per_page >> 1;
if (groups_per_page == 0)
groups_per_page = 1;
/* allocate buffer_heads to read bitmaps */
if (groups_per_page > 1) {
i = sizeof(struct buffer_head *) * groups_per_page;
bh = kzalloc(i, gfp);
if (bh == NULL) {
err = -ENOMEM;
goto out;
}
} else
bh = &bhs;
first_group = page->index * blocks_per_page / 2;
/* read all groups the page covers into the cache */
for (i = 0, group = first_group; i < groups_per_page; i++, group++) {
if (group >= ngroups)
break;
grinfo = ext4_get_group_info(sb, group);
/*
* If page is uptodate then we came here after online resize
* which added some new uninitialized group info structs, so
* we must skip all initialized uptodate buddies on the page,
* which may be currently in use by an allocating task.
*/
if (PageUptodate(page) && !EXT4_MB_GRP_NEED_INIT(grinfo)) {
bh[i] = NULL;
continue;
}
bh[i] = ext4_read_block_bitmap_nowait(sb, group, false);
if (IS_ERR(bh[i])) {
err = PTR_ERR(bh[i]);
bh[i] = NULL;
goto out;
}
mb_debug(sb, "read bitmap for group %u\n", group);
}
/* wait for I/O completion */
for (i = 0, group = first_group; i < groups_per_page; i++, group++) {
int err2;
if (!bh[i])
continue;
err2 = ext4_wait_block_bitmap(sb, group, bh[i]);
if (!err)
err = err2;
}
first_block = page->index * blocks_per_page;
for (i = 0; i < blocks_per_page; i++) {
group = (first_block + i) >> 1;
if (group >= ngroups)
break;
if (!bh[group - first_group])
/* skip initialized uptodate buddy */
continue;
if (!buffer_verified(bh[group - first_group]))
/* Skip faulty bitmaps */
continue;
err = 0;
/*
* data carry information regarding this
* particular group in the format specified
* above
*
*/
data = page_address(page) + (i * blocksize);
bitmap = bh[group - first_group]->b_data;
/*
* We place the buddy block and bitmap block
* close together
*/
if ((first_block + i) & 1) {
/* this is block of buddy */
BUG_ON(incore == NULL);
mb_debug(sb, "put buddy for group %u in page %lu/%x\n",
group, page->index, i * blocksize);
trace_ext4_mb_buddy_bitmap_load(sb, group);
grinfo = ext4_get_group_info(sb, group);
grinfo->bb_fragments = 0;
memset(grinfo->bb_counters, 0,
sizeof(*grinfo->bb_counters) *
(sb->s_blocksize_bits+2));
/*
* incore got set to the group block bitmap below
*/
ext4_lock_group(sb, group);
/* init the buddy */
memset(data, 0xff, blocksize);
ext4_mb_generate_buddy(sb, data, incore, group);
ext4_unlock_group(sb, group);
incore = NULL;
} else {
/* this is block of bitmap */
BUG_ON(incore != NULL);
mb_debug(sb, "put bitmap for group %u in page %lu/%x\n",
group, page->index, i * blocksize);
trace_ext4_mb_bitmap_load(sb, group);
/* see comments in ext4_mb_put_pa() */
ext4_lock_group(sb, group);
memcpy(data, bitmap, blocksize);
/* mark all preallocated blks used in in-core bitmap */
ext4_mb_generate_from_pa(sb, data, group);
ext4_mb_generate_from_freelist(sb, data, group);
ext4_unlock_group(sb, group);
/* set incore so that the buddy information can be
* generated using this
*/
incore = data;
}
}
SetPageUptodate(page);
out:
if (bh) {
for (i = 0; i < groups_per_page; i++)
brelse(bh[i]);
if (bh != &bhs)
kfree(bh);
}
return err;
}读取磁盘中的data block bitmap,初始化刚刚创建的page cache,这个逻辑比较简单,只是将磁盘中的bitmap赋值给page cache。复杂的时候初始化只在内存中的buddy bitmap,这是通过ext4_mb_generate_buddy,这个地方要注意buddy bitmap开始默认都初始化为1,代表占用状态,ext4_mb_generate_buddy通过bd_bitmap构建出来buddy bitmap

max:group最大的cluster数量(如果block size = cluster size就是block数量)
i = mb_find_next_zero_bit(bitmap, max, 0);根据data block bitmap找到第一个空闲的位置返回给i。
mb_find_next_bit(bitmap, max, i)找到下一给1的bit,那么len = i - first就是一段连续空闲的长度。
ext4_mb_mark_free_simple将这段连续的空闲区域记录到buddy bitmap中。
假设有个block group从129 block之后全部是空闲,ext4_mb_mark_free_simple的执行流程:
32639 chunk = 1
first = 129
第一轮:first = 129 len = 32639
bb_counters[0]++
第二轮: = 130 len = 32638
max = ffs(130) - 1 = 1
min = fls(32638) - 1 = 14
min = 1; chunk = 1 << min = 2
bb_counters[1]++;
第三轮:first = 132 len = 32636
max = ffs(132) - 1= 2
min = fls(32636) - 1= 14
min = 2; chunk = 1 << min = 4
bb_counters[2]++;
4: first = 136 len = 32632
max = ffs(136) -1 = 3
min = fls(32632) - 1= 14
min = 3 chunk = 1 << 3 = 8
bb_counters[3]++;
5: first = 144 len = 32624
max = ffs(144) - 1 = 4
min = fls(32624) - 1= 14
min = 4 chunk = 16
bb_counter[4]++
6: first = 160 len = 32608
max = ffs(160) -1 = 5
min = fls(32608) - 1 = 14
min = min (max, min) = 5
chunk = 1 << min = 1 << 5 = 32
bb_counter[5]++
7: fisrt = 192 len = 32576
max = ffs(192) - 1 = 6
min = fls(32576) -1 = 14
min = min(max, min) =6
chunk = 1 << min = 64
bb_counters[6]++
8: first = 256 len = 32512
max = ffs(256) - 1 = 8
min = fls(32512) - 1= 14
min = min(max, min) = 8
chunk = 1 << 8 = 256
bb_counters[8]++
9: first = 512 len = 32256
max = ffs(512) -1 = 9
min = fls(32256) - 1 = 14
min = min(max, min) = 9
chunk = 1 << 9 = 512
bb_counters[9]++
10: first = 1024 len = 31744
max = ffs(1024) - 1 = 10
min = fls(31744) - 1 = 14
min = min(max, min) = 10
chunk = 1 << 10 = 1024
bb_counters[10]++
11: first = 2048 len = 30720
max = ffs(2048) -1 = 11
min = fls(30720)-1 = 14
min = min(max, min) = 11
chunk = 1 << 11= 2048
bb_counters[11]++;
12: first = 4096 len = 26624
max = ffs(4096) - 1 = 12
min = fls(26624) - 1 = 14
min = min(max,min) = 12
chunk = 1 << 12 = 4096
bb_counters[12]++
13: first = 8192 len = 24576
max = ffs(8192) -1 = 13
min = fls(24576) -1 = 14
min = min(max,min) = 13
chunk = 1 << 13 = 8192
bb_counters[13]++
14: first = 16384 len = 16384
max = ffs(16384|border) -1 = 13
min = fls(16384) - 1= 14
min = min(max, min) = 13
chunk = 1 << 13 = 8192
bb_counter[13]++
14: first = 24576 len = 8192
max = ffs(24576|border) -1 = 13
min = fls(8192) -1 = 13
min = min(max ,min) = 13
chunk = 1 << 13 = 8192
bb_counters[13]++
15: first = 32768 len = 0最终引用google的一个PPT中图示 :
参考文章:
关于ext4 buddy bitmap构建分析_ext4 ext4_buddy_五年一剑的博客-CSDN博客
https://www.cnblogs.com/kanie/p/15359346.html