目录
💥1 概述
📚2 运行结果
🎉3 参考文献
👨💻4 Matlab代码
💥1 概述
当机器人手指与障碍物接触时,呈现出2阶机械阻抗特性。在阻抗控制算法中,不需直接计算加速度,从而避免了因大加速度误差给控制带来的不利因素。结合期望轨迹和实际位置及速度,产生一个参考轨迹,手指跟踪此参考轨迹即可自动获得期望阻抗特性.。
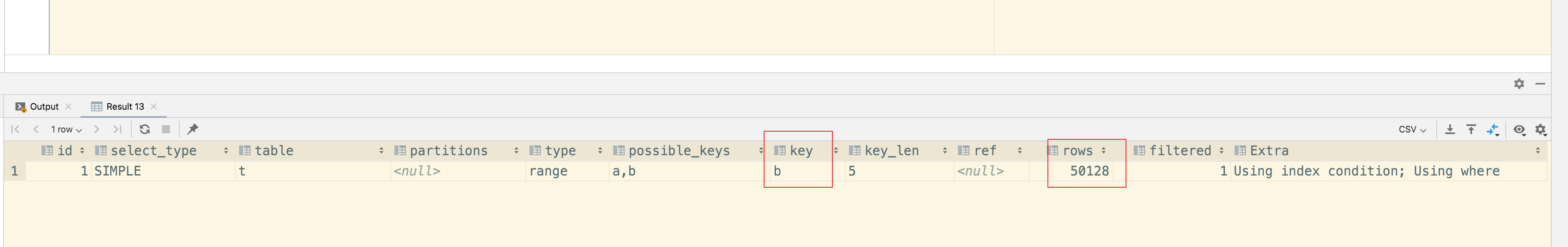
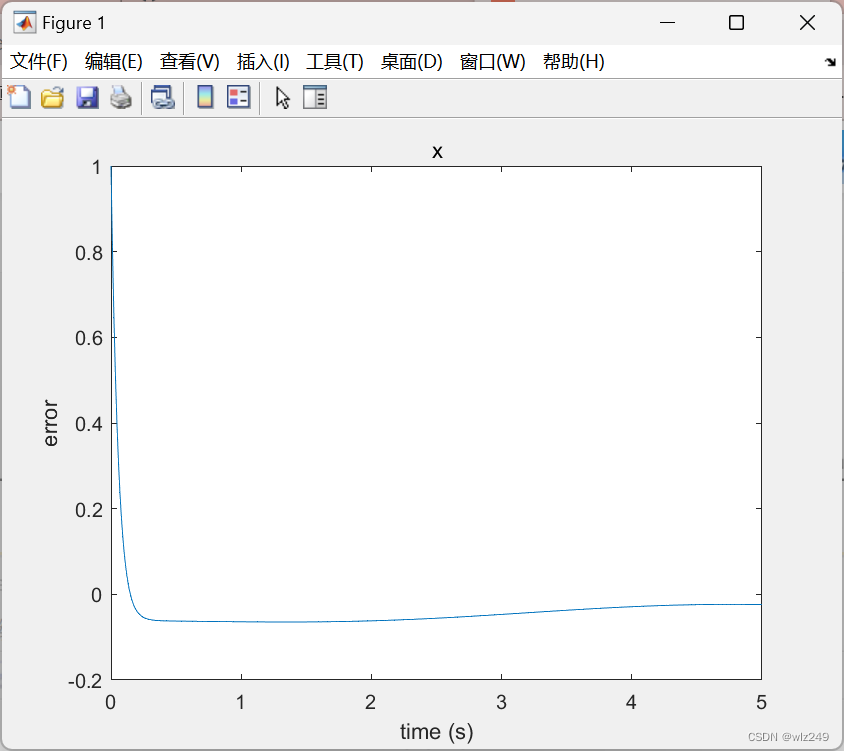
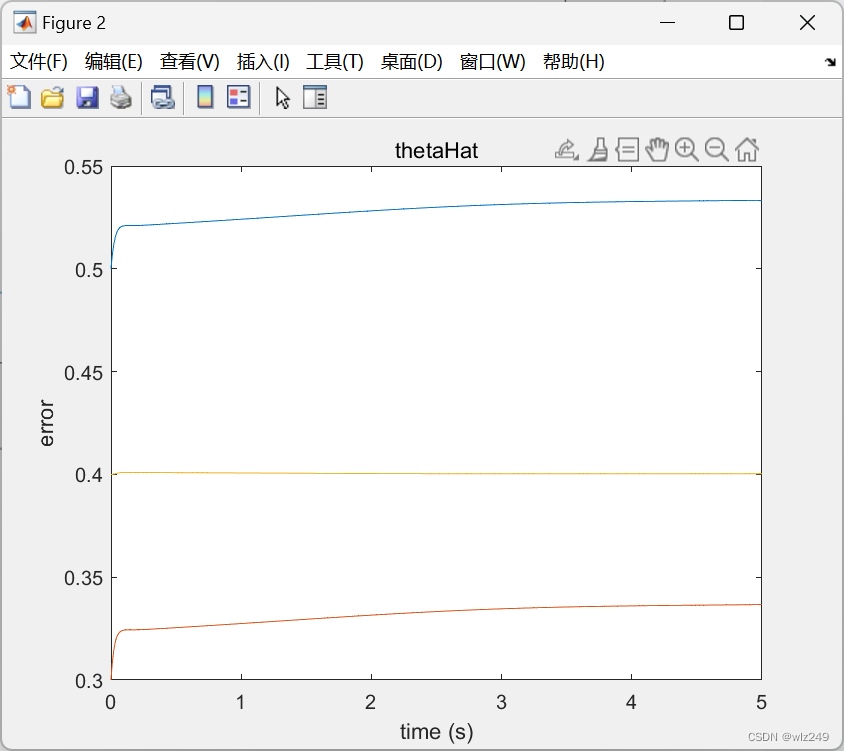
📚2 运行结果

🎉3 参考文献
[1]董晓星,李戈,刘刚峰,赵杰.冗余空间机械臂的运动学和笛卡尔阻抗控制方法[J].中国机械工程,2014,25(01):36-41.
👨💻4 Matlab代码
主函数部分代码:
clear all; close all; clc;
xinit = [0;0;0;0;0;0;0;pi/2;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0];
% tspan = linspace(t1,t2,n);
tspan = 0:.1:100;
% options = odeset('RelTol',1e-5,'Stats','on','OutputFcn',@odeplot);
[t,xt] = ode45('Dyn1',tspan,xinit);
% x_des = [0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0]';
x_telta1 = abs(xt(:,1));
x_telta2 = abs(xt(:,2));
[a,b] = size(xt);
x_telta3 = abs(4*ones(1,b)-xt(:,3));
% plot(t,x_telta1,t,x_telta2,t,x_telta3)
subplot(2,2,1)
plot(t,abs(xt(:,1)),'b');
xlabel('t');
ylabel('m');
title('x position')
subplot(2,2,2)
plot(t,abs(xt(:,2)),'b');
xlabel('t');
ylabel('m');
title('y-position')
subplot(2,2,3)
p = plot(t,x_telta3,'b');
p(1).LineWidth = 1;
xlabel('t');
ylabel('m');
title('z-position');
subplot(2,2,4)
plot(t,abs(xt(:,4)),'b');
xlabel('t');
ylabel('rad');
title('yaw');