Kubernetes ~ k8s 从入门到入坑。
文章目录
- Kubernetes ~ k8s 从入门到入坑。
- 1. Kubernetes 介绍。
- 1.1 应用部署方式演变。
- 1.2 kubernetes 简介。
- 1.3 kubernetes 组件。
- 1.4 kubernetes 概念。
- 2. kubernetes 集群环境搭建。
- 2.1 前置知识点。
- 2.2 kubeadm 部署方式介绍。
- 2.3 安装要求。
- 2.4 最终目标。
- 2.5 准备环境。
- 2.6 环境初始化。
- 2.6.1 检查操作系统的版本。
- 2.6.2 主机名解析。
- 2.6.3 时间同步。
- 2.6.4 禁用 iptables 和 firewalld 服务。
- 2.6.5 禁用 selinux。
- 2.6.6 禁用 swap 分区。
- 2.6.7 修改 linux 的内核参数。
- 2.6.8 配置 ipvs 功能。
- 2.6.9 安装 docker。
- 2.6.10 安装 Kubernetes 组件。
- 2.6.11 准备集群镜像。
- 2.6.12 集群初始化。
- 2.6.13 安装网络插件,只在 master 节点操作即可。
- 2.6.14 使用 kubeadm reset 重置集群。
- 2.6.15 重启 kubelet 和 docker。
- 2.6.16 kubeadm 中的命令。
- 2.7 集群测试。
- 2.7.1 创建一个 nginx 服务。
- 2.7.2 暴露端口。
- 2.7.3 查看服务。
- 2.7.4 查看 pod。
- 3. 资源管理。
- 3.1 资源管理介绍。
- 3.2 YAML 语言介绍。
- 3.3 资源管理方式。
- 3.3.1 命令式对象管理。
- 3.3.2 命令式对象配置。
- 3.3.3 声明式对象配置。
- 4. 实战入门。
- 4.1 Namespace。
- 4.1.1 查看。
- 4.1.2 创建。
- 4.1.3 删除。
- 4.1.4 配置方式。
- 4.2 Pod。
- 4.2.1 创建并运行。
- 4.2.2 查看 pod 信息。
- 4.2.3 访问 Pod。
- 4.2.4 删除指定 Pod。
- 4.2.5 配置操作。
- 4.3 Label。
- 4.3.1 命令方式。
- 4.3.2 配置方式。
- 4.4 Deployment。
- 4.4.1 命令操作。
- 4.4.2 配置操作。
- 4.5 Service。
- 4.5.1 创建集群内部可访问的 Service。
- 4.5.2 创建集群外部也可访问的 Service。
- 4.5.3 删除 Service。
- 4.5.4 配置方式。
- 5. Pod 详解。
- 5.1 Pod 介绍。
- 5.1.1 Pod 结构。
- 5.1.2 Pod 定义。
- 5.2 Pod 配置。
- 5.2.1 基本配置。
- 5.2.2 镜像拉取。
- 5.2.3 启动命令。
- 5.2.4 环境变量。
- 5.2.5 端口设置。
- 5.2.6 资源配额。
- 5.3 Pod 生命周期。
- 5.3.1 创建和终止。
- 5.3.2 初始化容器。
- 5.3.3 钩子函数。
- 5.3.4 容器探测。
- 5.3.5 重启策略。
- 5.4 Pod 调度。
- 5.4.1 定向调度。
- - **NodeName**。
- - **NodeSelector**。
- 5.4.2 亲和性调度。
- - **NodeAffinity**。
- - **PodAffinity**。
- - **PodAntiAffinity**。
- 5.4.3 污点和容忍。
- - **污点(Taints)**。
- - **容忍(Toleration)**。
- 6. Pod 控制器详解。
- 6.1 Pod 控制器介绍。
- 6.2 ReplicaSet(RS)。
- **扩缩容**。
- **镜像升级**。
- 6.3 Deployment(Deploy)。
- 6.3.1 创建 deployment。
- 6.3.2 扩缩容。
- **镜像更新**。
- - 重建更新。
- - 滚动更新。
- 6.3.3 版本回退。
- 6.3.4 金丝雀发布。
- 6.4 Horizontal Pod Autoscaler(HPA)。
- 6.4.1 安装 metrics-server。
- 6.4.2 准备 deployment 和 service。
- 6.4.3 部署 HPA。
- 6.4.4 测试。
- 6.5 DaemonSet(DS)。
- 6.6 Job。
- 6.7 CronJob(CJ)。
- StatefulSet。
- 7. Service 详解。
- 7.1 Service 介绍。
- 7.1.1 userspace 模式。
- 7.1.2 iptables 模式。
- 7.1.3 ipvs 模式。
- 7.2 Service 类型。
- 7.3 Service 使用。
- 7.3.1 实验环境准备。
- 7.3.2 ClusterIP 类型的 Service。
- 7.3.3 Endpoint。
- 7.3.4 HeadLiness 类型的 Service。
- 7.3.5 NodePort 类型的 Service。
- 7.3.6 LoadBalancer 类型的 Service。
- 7.3.7 ExternalName 类型的 Service。
- 7.4 Ingress 介绍。
- 7.5 Ingress 使用。
- 7.5.1 环境准备 ~ 搭建 ingress 环境。
- 7.5.2 准备 service 和 pod。
- 7.5.2 Http 代理。
- 7.5.3 Https 代理。
- 8. 数据存储。
- 9. 安全认证。
- 10. dashboard。
1. Kubernetes 介绍。
1.1 应用部署方式演变。
在部署应用程序的方式上,主要经历了三个时代。
- 传统部署:互联网早期,会直接将应用程序部署在物理机上。
优点:简单,不需要其它技术的参与。
缺点:不能为应用程序定义资源使用边界,很难合理地分配计算资源,而且程序之间容易产生影响。
- 虚拟化部署:可以在一台物理机上运行多个虚拟机,每个虚拟机都是独立的一个环境。
优点:程序环境不会相互产生影响,提供了一定程度的安全性。
缺点:增加了操作系统,浪费了部分资源。
- 容器化部署:与虚拟化类似,但是共享了操作系统。
优点。
可以保证每个容器拥有自己的文件系统、CPU、内存、进程空间等。
运行应用程序所需要的资源都被容器包装,并和底层基础架构解耦。
容器化的应用程序可以跨云服务商、跨 Linux 操作系统发行版进行部署。

容器化部署方式给带来很多的便利,但是也会出现一些问题,比如说。
- 一个容器故障停机了,怎么样让另外一个容器立刻启动去替补停机的容器。
- 当并发访问量变大的时候,怎么样做到横向扩展容器数量。
这些容器管理的问题统称为容器编排问题,为了解决这些容器编排问题,就产生了一些容器编排的软件。
- Swarm:Docker 自己的容器编排工具。
- Mesos:Apache 的一个资源统一管控的工具,需要和 Marathon 结合使用。
- Kubernetes:Google 开源的的容器编排工具。
1.2 kubernetes 简介。

kubernetes,是一个全新的基于容器技术的分布式架构领先方案,是谷歌严格保密十几年的秘密武器 —— Borg 系统的一个开源版本,于 2014 年 9 月发布第一个版本,2015 年 7 月发布第一个正式版本。
kubernetes 的本质是一组服务器集群,它可以在集群的每个节点上运行特定的程序,来对节点中的容器进行管理。目的是实现资源管理的自动化,主要提供了如下的主要功能:
- 自我修复:一旦某一个容器崩溃,能够在 1 秒中左右迅速启动新的容器。
- 弹性伸缩:可以根据需要,自动对集群中正在运行的容器数量进行调整。
- 服务发现:服务可以通过自动发现的形式找到它所依赖的服务。
- 负载均衡:如果一个服务起动了多个容器,能够自动实现请求的负载均衡。
- 版本回退:如果发现新发布的程序版本有问题,可以立即回退到原来的版本。
- 存储编排:可以根据容器自身的需求自动创建存储卷。
1.3 kubernetes 组件。
一个 kubernetes 集群主要是由控制节点(master)、工作节点(node)构成,每个节点上都会安装不同的组件。
master:集群的控制平面,负责集群的决策(管理)。
ApiServer:资源操作的唯一入口,接收用户输入的命令,提供认证、授权、API 注册和发现等机制。
Scheduler:负责集群资源调度,按照预定的调度策略将 Pod 调度到相应的 node 节点上。
ControllerManager:负责维护集群的状态,比如程序部署安排、故障检测、自动扩展、滚动更新等。
Etcd:负责存储集群中各种资源对象的信息。
node:集群的数据平面,负责为容器提供运行环境(干活)。
Kubelet:负责维护容器的生命周期,即通过控制 docker,来创建、更新、销毁容器。
KubeProxy:负责提供集群内部的服务发现和负载均衡。
Docker:负责节点上容器的各种操作。
下面,以部署一个 Nginx 服务来说明 kubernetes 系统各个组件调用关系。
-
首先要明确,一旦 kubernetes 环境启动之后,master 和 node 都会将自身的信息存储到 etcd 数据库中。
-
一个 Nginx 服务的安装请求会首先被发送到 master 节点的 apiServer 组件。
-
apiServer 组件会调用 scheduler 组件来决定到底应该把这个服务安装到哪个 node 节点上。
在此时,它会从 etcd 中读取各个 node 节点的信息,然后按照一定的算法进行选择,并将结果告知 apiServer。 -
apiServer 调用 controller-manager 去调度 node 节点安装 Nginx 服务。
-
kubelet 接收到指令后,会通知 docker,然后由 docker 来启动一个 Nginx 的 pod。
pod 是 kubernetes 的最小操作单元,容器必须跑在 pod 中。 -
至此,一个 Nginx 服务就运行了,如果需要访问 Nginx,就需要通过 kube-proxy 来对 pod 产生访问的代理。
这样,外界用户就可以访问集群中的 Nginx 服务了。
1.4 kubernetes 概念。
Master:集群控制节点,每个集群需要至少一个 master 节点负责集群的管控。
Node:工作负载节点,由 master 分配容器到这些 node 工作节点上,然后 node 节点上的 docker 负责容器的运行。
Pod:kubernetes 的最小控制单元,容器都是运行在 pod 中的,一个 pod 中可以有 1 个或者多个容器。
Controller:控制器,通过它来实现对 pod 的管理,比如启动 pod、停止 pod、伸缩 pod 的数量等等。
Service:pod 对外服务的统一入口,下面可以维护者同一类的多个 pod。
Label:标签,用于对 pod 进行分类,同一类 pod 会拥有相同的标签。(app:tom、app:tomcat)
NameSpace:命名空间,用来隔离 pod 的运行环境。(虚线)。

2. kubernetes 集群环境搭建。
https://www.yuque.com/fairy-era/yg511q/hg3u04

2.1 前置知识点。
目前生产部署 Kubernetes 集群主要有:
-
minikube:用于快速搭建单节点 kubernetes 的工具。
-
kubeadm。
Kubeadm 是一个 K8s 部署工具,提供 kubeadm init 和 kubeadm join,用于快速部署 Kubernetes 集群。
官方地址:https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/setup-tools/kubeadm/kubeadm/。
- 二进制包。
从 github 下载发行版的二进制包,手动部署每个组件,组成 Kubernetes 集群。
Kubeadm 降低部署门槛,但屏蔽了很多细节,遇到问题很难排查。如果想更容易可控,推荐使用二进制包部署 Kubernetes 集群,虽然手动部署麻烦点,期间可以学习很多工作原理,也利于后期维护。
2.2 kubeadm 部署方式介绍。
kubeadm 是官方社区推出的一个用于快速部署 kubernetes 集群的工具,这个工具能通过两条指令完成一个 kubernetes 集群的部署:
- 创建一个 Master 节点 kubeadm init。
- 将 Node 节点加入到当前集群中$ kubeadm join <Master 节点的 IP 和端口>。
2.3 安装要求。
在开始之前,部署 Kubernetes 集群机器需要满足以下几个条件:
- 一台或多台机器,操作系统 CentOS7.x-86_x64。
- 硬件配置:2GB 或更多 RAM,2 个 CPU 或更多 CPU,硬盘 30GB 或更多。
- 集群中所有机器之间网络互通。
- 可以访问外网,需要拉取镜像。
- 禁止 swap 分区。
2.4 最终目标。
- 在所有节点上安装 Docker 和 kubeadm。
- 部署 Kubernetes Master。
- 部署容器网络插件。
- 部署 Kubernetes Node,将节点加入 Kubernetes 集群中。
- 部署 Dashboard Web 页面,可视化查看 Kubernetes 资源。
2.5 准备环境。
| 角色 | IP 地址 | 组件 |
|---|---|---|
| master01 | 192.168.142.150 | docker,kubectl,kubeadm,kubelet |
| node01 | 192.168.142.151 | docker,kubectl,kubeadm,kubelet |
| node02 | 192.168.142.152 | docker,kubectl,kubeadm,kubelet |
2.6 环境初始化。
2.6.1 检查操作系统的版本。
http://mirrors.163.com/.help/centos.html
# 此方式下安装 kubernetes 集群要求 Centos 版本要在 7.5 或之上。
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release
CentOS Linux release 7.9.2009 (Core)
2.6.2 主机名解析。
为了方便集群节点间的直接调用,在这个配置一下主机名解析,企业中推荐使用内部 DNS 服务器。
vim /etc/hosts
# 主机名成解析 编辑三台服务器的 /etc/hosts 文件,添加下面内容。
192.168.142.150 localhost.localdomain.k8s.master
192.168.142.151 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1
192.168.142.152 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2
2.6.3 时间同步。
kubernetes 要求集群中的节点时间必须精确一直,这里使用 chronyd 服务从网络同步时间。
企业中建议配置内部的会见同步服务器。
# 启动 chronyd 服务。
[root@master ~]# systemctl start chronyd
[root@master ~]# systemctl enable chronyd
[root@master ~]# date
2.6.4 禁用 iptables 和 firewalld 服务。
kubernetes 和 docker 在运行的中会产生大量的 iptables 规则,为了不让系统规则跟它们混淆,直接关闭系统的规则。
# 关闭 firewalld 服务。
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop firewalld
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl disable firewalld
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/firewalld.service.
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service.
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop iptables
Failed to stop iptables.service: Unit iptables.service not loaded.
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl disable iptables
Failed to execute operation: No such file or directory
2.6.5 禁用 selinux。
selinux 是 linux 系统下的一个安全服务,如果不关闭它,在安装集群中会产生各种各样的奇葩问题。
[root@localhost ~]# getenforce
Enforcing
vim /etc/selinux/config
# 编辑 /etc/selinux/config 文件,修改 SELINUX 的值为 disable。
# 注意修改完毕之后需要重启 linux 服务。
SELINUX=disabled
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
# SELINUX=enforcing
SELINUX=disabled
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of three values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected.
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
2.6.6 禁用 swap 分区。
swap 分区指的是虚拟内存分区,它的作用是物理内存使用完,之后将磁盘空间虚拟成内存来使用,启用 swap 设备会对系统的性能产生非常负面的影响,因此 kubernetes 要求每个节点都要禁用 swap 设备,但是如果因为某些原因确实不能关闭 swap 分区,就需要在集群安装过程中通过明确的参数进行配置说明。
# 编辑分区配置文件 /etc/fstab,注释掉 swap 分区一行。
# 注意修改完毕之后需要重启 linux 服务。
vim /etc/fstab
# 注释掉 /dev/mapper/centos-swap swap。
# /dev/mapper/centos-swap swap
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/fstab
#
#
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Thu Dec 1 01:25:13 2022
#
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Thu Dec 1 01:25:13 2022
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
#
/dev/mapper/centos_localhost-root / xfs defaults 0 0
UUID=c393aaa9-2e37-4fa2-8b32-e8b88af1e576 /boot xfs defaults 0 0
/dev/mapper/centos_localhost-home /home xfs defaults 0 0
# /dev/mapper/centos_localhost-swap swap swap defaults 0 0
2.6.7 修改 linux 的内核参数。
vim /etc/sysctl.d/kubernetes.comf
# 修改 linux 的内核参数,添加网桥过滤和地址转发功能。
# 编辑 /etc/sysctl.d/kubernetes.conf 文件,添加如下配置:
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
# 重新加载配置。
[root@master ~]# sysctl -p
# 加载网桥过滤模块。
[root@master ~]# modprobe br_netfilter
# 查看网桥过滤模块是否加载成功。
[root@localhost ~]# lsmod | grep br_netfilter
br_netfilter 22256 0
bridge 151336 1 br_netfilter
2.6.8 配置 ipvs 功能。
在 Kubernetes 中 Service 有两种带来模型,一种是基于 iptables 的,一种是基于 ipvs 的两者比较的话,ipvs 的性能明显要高一些,但是如果要使用它,需要手动载入 ipvs 模块。
# 安装 ipset 和 ipvsadm。
[root@master ~]# yum install ipset ipvsadm -y
# 添加需要加载的模块写入脚本文件。
[root@master ~]# cat <<EOF> /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules
#!/bin/bash
modprobe -- ip_vs
modprobe -- ip_vs_rr
modprobe -- ip_vs_wrr
modprobe -- ip_vs_sh
modprobe -- nf_conntrack_ipv4
EOF
# 为脚本添加执行权限。
[root@master ~]# chmod +x /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules
# 执行脚本文件。
[root@master ~]# /bin/bash /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules
# 查看对应的模块是否加载成功。
[root@localhost ~]# lsmod | grep -e ip_vs -e nf_conntrack_ipv4
nf_conntrack_ipv4 15053 0
nf_defrag_ipv4 12729 1 nf_conntrack_ipv4
ip_vs_sh 12688 0
ip_vs_wrr 12697 0
ip_vs_rr 12600 0
ip_vs 145458 6 ip_vs_rr,ip_vs_sh,ip_vs_wrr
nf_conntrack 139264 2 ip_vs,nf_conntrack_ipv4
libcrc32c 12644 3 xfs,ip_vs,nf_conntrack
重启。
[root@localhost ~]# getenforce
Disabled
[root@localhost ~]# free -m
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 1819 193 1451 9 174 1476
Swap: 0 0 0
[root@localhost ~]#
2.6.9 安装 docker。
https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/centos/
sudo yum install docker-ce-<VERSION_STRING> docker-ce-cli-<VERSION_STRING> containerd.io docker-compose-plugin
18.06.3.ce-3.el7
sudo yum install docker-ce-18.06.3.ce-3.el7 docker-ce-cli-18.06.3.ce-3.el7 containerd.io docker-compose-plugin
yum clean all
yum makecache
# 切换镜像源。
[root@master ~]# wget https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo -O /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo
# 查看当前镜像源中支持的 docker 版本。
[root@master ~]# yum list docker-ce --showduplicates
# 安装特定版本的 docker-ce。
# 必须指定 --setopt=obsoletes=0,否则 yum 会自动安装更高版本。
[root@master ~]# yum install --setopt=obsoletes=0 docker-ce-18.06.3.ce-3.el7 -y
# 4、添加一个配置文件。
# Docker 在默认情况下使用 Vgroup Driver 为 cgroupfs,而 Kubernetes 推荐使用 systemd 来替代 cgroupfs。
[root@master ~]# mkdir /etc/docker
[root@master ~]# cat <<EOF> /etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"],
"registry-mirrors": ["https://4utvh5ib.mirror.aliyuncs.com"]
}
EOF
# 启动 dokcer。
[root@master ~]# systemctl restart docker
[root@master ~]# systemctl enable docker
[root@localhost ~]# sudo systemctl enable docker
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/docker.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service.
sudo mkdir -p /etc/docker
sudo tee /etc/docker/daemon.json <<-'EOF'
{
"exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"],
"registry-mirrors": ["https://4utvh5ib.mirror.aliyuncs.com"]
}
EOF
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl restart docker
sudo systemctl enable docker
[root@localhost ~]# sudo systemctl enable docker
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/docker.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service.
sudo yum install --setopt=obsoletes=0 docker-ce-18.06.3.ce-3.el7 docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-plugin
2.6.10 安装 Kubernetes 组件。
https://developer.aliyun.com/mirror/kubernetes
cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
repo_gpgcheck=0
gpgkey=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
EOF
setenforce 0
# yum install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl
# systemctl enable kubelet && systemctl start kubelet
# 由于 kubernetes 的镜像在国外,速度比较慢,这里切换成国内的镜像源。
# 编辑/etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo,添加下面的配置。
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64
enabled=1
gpgchech=0
repo_gpgcheck=0
gpgkey=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg
http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
# 安装 kubeadm、kubelet 和 kubectl。
[root@master ~]# yum install --setopt=obsoletes=0 kubeadm-1.17.4-0 kubelet-1.17.4-0 kubectl-1.17.4-0 -y
# 配置 kubelet 的 cgroup。
vim /etc/sysconfig/kubelet
# 编辑 /etc/sysconfig/kubelet, 添加下面的配置。
KUBELET_CGROUP_ARGS="--cgroup-driver=systemd"
KUBE_PROXY_MODE="ipvs"
# 5、设置 kubelet 开机自启。
[root@master ~]# systemctl enable kubelet
2.6.11 准备集群镜像。
# 在安装 kubernetes 集群之前,必须要提前准备好集群需要的镜像,所需镜像可以通过下面命令查看。
[root@localhost ~]# kubeadm config images list
W1201 23:46:05.541002 55376 version.go:101] could not fetch a Kubernetes version from the internet: unable to get URL "https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable-1.txt": Get https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable-1.txt: net/http: request canceled while waiting for connection (Client.Timeout exceeded while awaiting headers)
W1201 23:46:05.541156 55376 version.go:102] falling back to the local client version: v1.17.4
W1201 23:46:05.541308 55376 validation.go:28] Cannot validate kube-proxy config - no validator is available
W1201 23:46:05.541316 55376 validation.go:28] Cannot validate kubelet config - no validator is available
k8s.gcr.io/kube-apiserver:v1.17.4
k8s.gcr.io/kube-controller-manager:v1.17.4
k8s.gcr.io/kube-scheduler:v1.17.4
k8s.gcr.io/kube-proxy:v1.17.4
k8s.gcr.io/pause:3.1
k8s.gcr.io/etcd:3.4.3-0
k8s.gcr.io/coredns:1.6.5
[root@localhost ~]#
# 下载镜像。
# 此镜像 kubernetes 的仓库中,由于网络原因,无法连接,下面提供了一种替换方案。
images=(
kube-apiserver:v1.17.4
kube-controller-manager:v1.17.4
kube-scheduler:v1.17.4
kube-proxy:v1.17.4
pause:3.1
etcd:3.4.3-0
coredns:1.6.5
)
for imageName in ${images[@]};do
docker pull registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/$imageName
docker tag registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/$imageName k8s.gcr.io/$imageName
docker rmi registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/$imageName
done
[root@localhost ~]# docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
k8s.gcr.io/kube-proxy v1.17.4 6dec7cfde1e5 2 years ago 116MB
k8s.gcr.io/kube-apiserver v1.17.4 2e1ba57fe95a 2 years ago 171MB
k8s.gcr.io/kube-controller-manager v1.17.4 7f997fcf3e94 2 years ago 161MB
k8s.gcr.io/kube-scheduler v1.17.4 5db16c1c7aff 2 years ago 94.4MB
k8s.gcr.io/coredns 1.6.5 70f311871ae1 3 years ago 41.6MB
k8s.gcr.io/etcd 3.4.3-0 303ce5db0e90 3 years ago 288MB
k8s.gcr.io/pause 3.1 da86e6ba6ca1 4 years ago 742kB
2.6.12 集群初始化。
下面的操作只需要在 master 节点上执行即可。
https://kubernetes.io/zh-cn/docs/reference/setup-tools/kubeadm/kubeadm-init/
# 创建集群。
[root@master ~]# kubeadm init \
--apiserver-advertise-address=192.168.142.150 \
--image-repository=registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers \
--kubernetes-version=v1.17.4 \
--pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16 \
--service-cidr=10.96.0.0/12
# To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
[root@master ~]# mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
[root@master ~]# sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
[root@master ~]# sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
[root@localhost ~]# kubeadm init \
> --apiserver-advertise-address=192.168.142.150 \
> --image-repository=registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers \
> --kubernetes-version=v1.17.4 \
> --pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16 \
> --service-cidr=10.96.0.0/12
W1202 00:11:31.437970 57290 validation.go:28] Cannot validate kubelet config - no validator is available
W1202 00:11:31.438028 57290 validation.go:28] Cannot validate kube-proxy config - no validator is available
[init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.17.4
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster
[preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection
[preflight] You can also perform this action in beforehand using 'kubeadm config images pull'
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet
[certs] Using certificateDir folder "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[certs] Generating "ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver" certificate and key
[certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [localhost.localdomain.k8s.master kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local] and IPs [10.96.0.1 192.168.142.150]
[certs] Generating "apiserver-kubelet-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/server" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [localhost.localdomain.k8s.master localhost] and IPs [192.168.142.150 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/peer" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [localhost.localdomain.k8s.master localhost] and IPs [192.168.142.150 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/healthcheck-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver-etcd-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "sa" key and public key
[kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder "/etc/kubernetes"
[kubeconfig] Writing "admin.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "kubelet.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "controller-manager.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "scheduler.conf" kubeconfig file
[control-plane] Using manifest folder "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-apiserver"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-controller-manager"
W1202 00:19:51.720839 57290 manifests.go:214] the default kube-apiserver authorization-mode is "Node,RBAC"; using "Node,RBAC"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-scheduler"
W1202 00:19:51.721669 57290 manifests.go:214] the default kube-apiserver authorization-mode is "Node,RBAC"; using "Node,RBAC"
[etcd] Creating static Pod manifest for local etcd in "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[wait-control-plane] Waiting for the kubelet to boot up the control plane as static Pods from directory "/etc/kubernetes/manifests". This can take up to 4m0s
[apiclient] All control plane components are healthy after 23.003244 seconds
[upload-config] Storing the configuration used in ConfigMap "kubeadm-config" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[kubelet] Creating a ConfigMap "kubelet-config-1.17" in namespace kube-system with the configuration for the kubelets in the cluster
[upload-certs] Skipping phase. Please see --upload-certs
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node localhost.localdomain.k8s.master as control-plane by adding the label "node-role.kubernetes.io/master=''"
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node localhost.localdomain.k8s.master as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule]
[bootstrap-token] Using token: xs70mz.1j3eaj8unj3g11cp
[bootstrap-token] Configuring bootstrap tokens, cluster-info ConfigMap, RBAC Roles
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to post CSRs in order for nodes to get long term certificate credentials
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow the csrapprover controller automatically approve CSRs from a Node Bootstrap Token
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow certificate rotation for all node client certificates in the cluster
[bootstrap-token] Creating the "cluster-info" ConfigMap in the "kube-public" namespace
[kubelet-finalize] Updating "/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf" to point to a rotatable kubelet client certificate and key
[addons] Applied essential addon: CoreDNS
[addons] Applied essential addon: kube-proxy
Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully!
To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster.
Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/
Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root:
kubeadm join 192.168.142.150:6443 --token xs70mz.1j3eaj8unj3g11cp \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:8cb8adbc0147bc1c15fc689f98ab49e8442d16d28e85062d2db9b8f47225c6cc
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
localhost.localdomain.k8s.master NotReady master 4m11s v1.17.4
下面的操作只需要在 node 节点上执行即可。
[root@localhost ~]# kubeadm join 192.168.142.150:6443 --token xs70mz.1j3eaj8unj3g11cp \
> --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:8cb8adbc0147bc1c15fc689f98ab49e8442d16d28e85062d2db9b8f47225c6cc
W1202 00:25:46.290777 86902 join.go:346] [preflight] WARNING: JoinControlPane.controlPlane settings will be ignored when control-plane flag is not set.
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[preflight] Reading configuration from the cluster...
[preflight] FYI: You can look at this config file with 'kubectl -n kube-system get cm kubeadm-config -oyaml'
[kubelet-start] Downloading configuration for the kubelet from the "kubelet-config-1.17" ConfigMap in the kube-system namespace
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet
[kubelet-start] Waiting for the kubelet to perform the TLS Bootstrap...
This node has joined the cluster:
* Certificate signing request was sent to apiserver and a response was received.
* The Kubelet was informed of the new secure connection details.
Run 'kubectl get nodes' on the control-plane to see this node join the cluster.
在 master 上查看节点信息。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
localhost.localdomain.k8s.master NotReady master 6m31s v1.17.4
localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 NotReady <none> 56s v1.17.4
localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 NotReady <none> 52s v1.17.4
NotReady
↓ ↓ ↓
2.6.13 安装网络插件,只在 master 节点操作即可。
kubernetes 支持多种网络插件。eg. flannel、calico、canal 等。任选一种使用即可。本次选择 flannel。
下面操作依旧只在 master 节点执行即可,插件使用的是 DaemonSet 的控制器,ta 会在每个节点上都运行。
- 获取 fannel 的配置文件。
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
由于外网不好访问,如果出现无法访问的情况,可以直接用下面的记得文件名是 kube-flannel.yml,位置:/root/kube-flannel.yml 内容。
https://github.com/flannel-io/flannel/tree/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
修改文件中的 quay.io 仓库为 quay-mirror.qiniu.com。
- 使用配置文件启动 fannel。
kubectl apply -f kube-flannel.yml
稍等片刻。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl apply -f kube-flannel.yml
namespace/kube-flannel created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/flannel created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/flannel created
serviceaccount/flannel created
configmap/kube-flannel-cfg created
daemonset.apps/kube-flannel-ds created
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
localhost.localdomain.k8s.master Ready master 62m v1.17.4
localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 Ready <none> 57m v1.17.4
localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Ready <none> 57m v1.17.4
也可手动拉取指定版本。
# 拉取 flannel 网络,三台主机。
docker pull quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.14.0
# 查看仓库是否拉去下来。
docker images
若是集群状态一直是 notready,用下面语句查看原因。
journalctl -f -u kubelet.service
若原因是: cni.go:237] Unable to update cni config: no networks found in /etc/cni/net.d
mkdir -p /etc/cni/net.d
vim /etc/cni/net.d/10-flannel.conf
{
"name":"cbr0",
"cniVersion":"0.3.1",
"type":"flannel",
"deledate":{
"hairpinMode":true,
"isDefaultGateway":true
}
}
2.6.14 使用 kubeadm reset 重置集群。
# 在 master 节点之外的节点进行操作。
kubeadm reset
systemctl stop kubelet
systemctl stop docker
rm -rf /var/lib/cni/
rm -rf /var/lib/kubelet/*
rm -rf /etc/cni/
ifconfig cni0 down
ifconfig flannel.1 down
ifconfig docker0 down
ip link delete cni0
ip link delete flannel.1
# 重启 kubelet。
systemctl restart kubelet
# 重启 docker。
systemctl restart docker
2.6.15 重启 kubelet 和 docker。
# 重启 kubelet
systemctl restart kubelet
# 重启 docker
systemctl restart docker
使用配置文件启动 fannel。
kubectl apply -f kube-flannel.yml
等待它安装完毕,发现集群的状态已经是 Ready。
2.6.16 kubeadm 中的命令。
# 生成新的 token。
[root@master ~]# kubeadm token create --print-join-command
2.7 集群测试。
2.7.1 创建一个 nginx 服务。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create deployment nginx --image=nginx:1.14-alpine
deployment.apps/nginx created
2.7.2 暴露端口。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl expose deploy nginx --port=80 --target-port=80 --type=NodePort
service/nginx exposed
2.7.3 查看服务。
2.7.4 查看 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-6867cdf567-5p8k4 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 83s
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-6867cdf567-5p8k4 1/1 Running 0 2m47s
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 71m
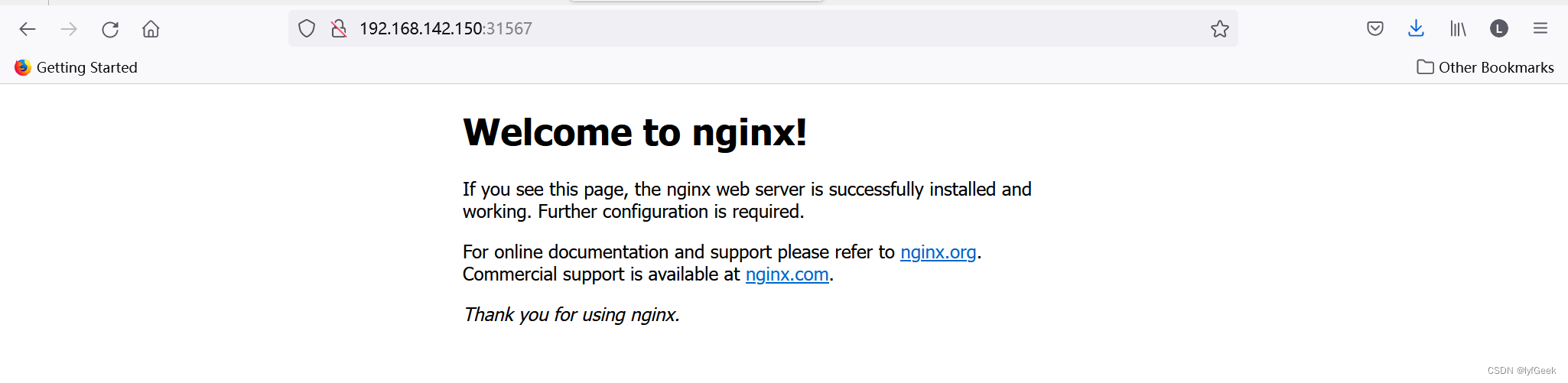
nginx NodePort 10.107.6.137 <none> 80:31567/TCP 67s
3. 资源管理。
3.1 资源管理介绍。
在 kubernetes 中,所有的内容都抽象为资源,用户需要通过操作资源来管理 kubernetes。
kubernetes 的本质上就是一个集群系统,用户可以在集群中部署各种服务,所谓的部署服务,其实就是在 kubernetes 集群中运行一个个的容器,并将指定的程序跑在容器中。
kubernetes 的最小管理单元是 pod 而不是容器,所以只能将容器放在Pod中,而 kubernetes 一般也不会直接管理 Pod,而是通过Pod 控制器来管理 Pod 的。
Pod 可以提供服务之后,就要考虑如何访问 Pod 中服务,kubernetes 提供了Service资源实现这个功能。
当然,如果 Pod 中程序的数据需要持久化,kubernetes 还提供了各种存储系统。

学习 kubernetes 的核心,就是学习如何对集群上的
Pod、Pod 控制器、Service、存储等各种资源进行操作。
3.2 YAML 语言介绍。
YAML 是一个类似 XML、JSON 的标记性语言。它强调以数据为中心,并不是以标识语言为重点。因而 YAML 本身的定义比较简单,号称"一种人性化的数据格式语言"。
<geek>
<age>15</age>
<address>Beijing</address>
</geek>
geek:
age: 15
address: Beijing
YAML 的语法比较简单,主要有下面几个:
- 大小写敏感。
- 使用缩进表示层级关系。
- 缩进不允许使用 tab,只允许空格(低版本限制)。
- 缩进的空格数不重要,只要相同层级的元素左对齐即可。
#表示注释。
YAML 支持以下几种数据类型:
- 纯量:单个的、不可再分的值。
- 对象:键值对的集合,又称为映射(mapping)/哈希(hash)/字典(dictionary)。
- 数组:一组按次序排列的值,又称为序列(sequence)/列表(list)。
# 纯量, 就是指的一个简单的值,字符串、布尔值、整数、浮点数、Null、时间、日期。
# 布尔类型。
eg. true (或者 True)
# 整型。
eg. 234
# 浮点型。
eg. 3.14
# null 类型。
eg. ~ # 使用 ~ 表示 null。
# 日期类型。
eg. 2018-02-17 # 日期必须使用 ISO 8601 格式,即 yyyy-MM-dd。
# 时间类型。
eg. 2018-02-17T15:02:31+08:00 # 时间使用 ISO 8601 格式,时间和日期之间使用 T 连接,最后使用 + 代表时区。
# 字符串类型。
eg. geek # 简单写法,直接写值,如果字符串中间有特殊字符,必须使用双引号或者单引号包裹。
eg. line1
line2 # 字符串过多的情况可以拆成多行,每一行会被转化成一个空格。
# 对象。
# 形式一(推荐)。
geek:
age: 15
address: Beijing
# 形式二(了解)。
geek: {age: 15, address: Beijing}
# 数组。
# 形式一(推荐)。
address:
- 顺义
- 昌平
# 形式二(了解)。
address: [顺义, 昌平]
tips
书写 yaml 切记
:后面要加一个空格。如果需要将多段 yaml 配置放在一个文件中,中间要使用
---分隔。下面是一个 yaml 转 json 的网站,可以通过它验证 yaml 是否书写正确。
https://www.json2yaml.com/convert-yaml-to-json。
3.3 资源管理方式。
- 命令式对象管理:直接使用命令去操作 kubernetes 资源。
kubectl run nginx-pod --image=nginx:1.17.1 --port=80
- 命令式对象配置:通过命令配置和配置文件去操作 kubernetes 资源。
kubectl create/patch -f nginx-pod.yaml
- 声明式对象配置:通过 apply 命令和配置文件去操作 kubernetes 资源。
kubectl apply -f nginx-pod.yaml
# 创建 or 更新。
| 类型 | 操作对象 | 适用环境 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 命令式对象管理 | 对象 | 测试 | 简单 | 只能操作活动对象,无法审计、跟踪 |
| 命令式对象配置 | 文件 | 开发 | 可以审计、跟踪 | 项目大时,配置文件多,操作麻烦 |
| 声明式对象配置 | 目录 | 开发 | 支持目录操作 | 意外情况下难以调试 |
3.3.1 命令式对象管理。
kubectl 命令。
kubectl 是 kubernetes 集群的命令行工具,通过它能够对集群本身进行管理,并能够在集群上进行容器化应用的安装部署。
- kubectl 命令的语法。
kubectl [command] [type] [name] [flags]
command:指定要对资源执行的操作,例如 create、get、delete。
type:指定资源类型,比如 deployment、pod、service。
name:指定资源的名称,名称大小写敏感。
flags:指定额外的可选参数。
# 查看所有 pod。
kubectl get pod
# 查看某个 pod。
kubectl get pod pod_name
# 查看某个 pod,以 yaml / json 格式展示结果。
kubectl get pod pod_name -o yaml
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl version
Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"17", GitVersion:"v1.17.4", GitCommit:"8d8aa39598534325ad77120c120a22b3a990b5ea", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2020-03-12T21:03:42Z", GoVersion:"go1.13.8", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
Server Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"17", GitVersion:"v1.17.4", GitCommit:"8d8aa39598534325ad77120c120a22b3a990b5ea", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2020-03-12T20:55:23Z", GoVersion:"go1.13.8", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl cluster-info
Kubernetes master is running at https://192.168.142.150:6443
KubeDNS is running at https://192.168.142.150:6443/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns:dns/proxy
To further debug and diagnose cluster problems, use 'kubectl cluster-info dump'.
资源类型。
kubernetes 中所有的内容都抽象为资源,可以通过下面的命令进行查看。
kubectl api-resources
经常使用的资源有下面这些。
| 资源分类 | 资源名称 | 缩写 | 资源作用 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 集群级别资源 | nodes | no | 集群组成部分 |
| namespaces | ns | 隔离 Pod | |
| pod 资源 | pods | po | 装载容器 |
| pod 资源控制器 | replicationcontrollers | rc | 控制 pod 资源 |
| replicasets | rs | 控制 pod 资源 | |
| deployments | deploy | 控制 pod 资源 | |
| daemonsets | ds | 控制 pod 资源 | |
| jobs | 控制 pod 资源 | ||
| cronjobs | cj | 控制 pod 资源 | |
| horizontalpodautoscalers | hpa | 控制 pod 资源 | |
| statefulsets | sts | 控制 pod 资源 | |
| 服务发现资源 | services | svc | 统一 pod 对外接口 |
| ingress | ing | 统一 pod 对外接口 | |
| 存储资源 | volumeattachments | 存储 | |
| persistentvolumes | pv | 存储 | |
| persistentvolumeclaims | pvc | 存储 | |
| 配置资源 | configmaps | cm | 配置 |
| secrets | 配置 |
操作。
kubernetes 允许对资源进行多种操作,可以通过–help 查看详细的操作命令。
kubectl --help
经常使用的操作有下面这些。
| 命令分类 | 命令 | 翻译 | 命令作用 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 基本命令 | create | 创建 | 创建一个资源 |
| edit | 编辑 | 编辑一个资源 | |
| get | 获取 | 获取一个资源 | |
| patch | 更新 | 更新一个资源 | |
| delete | 删除 | 删除一个资源 | |
| explain | 解释 | 展示资源文档 | |
| 运行和调试 | run | 运行 | 在集群中运行一个指定的镜像 |
| expose | 暴露 | 暴露资源为 Service | |
| describe | 描述 | 显示资源内部信息 | |
| logs | 日志输出容器在 pod 中的日志 | 输出容器在 pod 中的日志 | |
| attach | 缠绕进入运行中的容器 | 进入运行中的容器 | |
| exec | 执行容器中的一个命令 | 执行容器中的一个命令 | |
| cp | 复制 | 在 Pod 内外复制文件 | |
| rollout | 首次展示 | 管理资源的发布 | |
| scale | 规模 | 扩(缩)容 Pod 的数量 | |
| autoscale | 自动调整 | 自动调整 Pod 的数量 | |
| 高级命令 | apply | rc | 通过文件对资源进行配置 |
| label | 标签 | 更新资源上的标签 | |
| 其他命令 | cluster-info | 集群信息 | 显示集群 |
| version | 版本 | 显示当前 Server 和 Client 的版本 |
下面以一个 namespace / pod 的创建和删除简单演示下命令的使用。
# 创建一个 namespace。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl create namespace dev
namespace/dev created
# 获取 namespace。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get ns
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 13h
dev Active 17s
kube-flannel Active 12h
kube-node-lease Active 13h
kube-public Active 13h
kube-system Active 13h
# 在此 namespace 下创建并运行一个 nginx 的 Pod。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl run pod --image=nginx:1.17.1 -n dev
kubectl run --generator=deployment/apps.v1 is DEPRECATED and will be removed in a future version. Use kubectl run --generator=run-pod/v1 or kubectl create instead.
deployment.apps/pod created
# 查看新创建的 pod。不加 -n dev 默认查 default。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get pod -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod-644584df94-5gx6f 1/1 Running 0 3m33s
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-6867cdf567-tlmw5 1/1 Running 0 25m
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get pod -n default
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-6867cdf567-tlmw5 1/1 Running 0 26m
# 删除指定的 pod。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl delete pods pod-644584df94-5gx6f -n dev
pod "pod-644584df94-5gx6f" deleted
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get pod -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod-644584df94-wzzcv 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 40s
# 删除后又生成了一个。控制器,后面讲解。
# 删除指定的 namespace。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl delete ns dev
namespace "dev" deleted
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get ns
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 13h
kube-flannel Active 12h
kube-node-lease Active 13h
kube-public Active 13h
kube-system Active 13h
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get pod -n dev
No resources found in dev namespace.
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get pod -n dev
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl describe pods pod-644584df94-5gx6f -n dev
Name: pod-644584df94-5gx6f
Namespace: dev
Priority: 0
Node: localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2/192.168.142.152
Start Time: Fri, 02 Dec 2022 13:35:27 +0800
Labels: pod-template-hash=644584df94
run=pod
Annotations: <none>
Status: Running
IP: 10.244.2.3
IPs:
IP: 10.244.2.3
Controlled By: ReplicaSet/pod-644584df94
Containers:
pod:
Container ID: docker://26a71073d6b9f116bd7411aacdf862f77c1d1f485844e33a55aa2590edeb8614
Image: nginx:1.17.1
Image ID: docker-pullable://nginx@sha256:0d17b565c37bcbd895e9d92315a05c1c3c9a29f762b011a10c54a66cd53c9b31
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
State: Running
Started: Fri, 02 Dec 2022 13:36:34 +0800
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-khzf8 (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready True
ContainersReady True
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
default-token-khzf8:
Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret)
SecretName: default-token-khzf8
Optional: false
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 5m24s default-scheduler Successfully assigned dev/pod-644584df94-5gx6f to localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2
Normal Pulling 5m23s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Pulling image "nginx:1.17.1"
Normal Pulled 4m19s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Successfully pulled image "nginx:1.17.1"
Normal Created 4m18s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Created container pod
Normal Started 4m17s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Started container pod
3.3.2 命令式对象配置。
命令式对象配置就是使用命令配合配置文件一起来操作 kubernetes 资源。
1) 创建一个 nginxpod.yaml,内容如下。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: dev
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginxpod
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-containers
image: nginx:1.17.1
2)执行 create 命令,创建资源。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f nginxpod.yaml
namespace/dev created
pod/nginxpod created
此时发现创建了两个资源对象,分别是 namespace 和 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get ns dev
NAME STATUS AGE
dev Active 37s
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pod -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginxpod 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 43s
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginxpod 1/1 Running 0 90s
3)执行 get 命令,查看资源。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get -f nginxpod.yaml
NAME STATUS AGE
namespace/dev Active 2m15s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/nginxpod 1/1 Running 0 2m14s
这样就显示了两个资源对象的信息。
4)执行 delete 命令,删除资源:
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl delete -f nginxpod.yaml
namespace "dev" deleted
pod "nginxpod" deleted
此时发现两个资源对象被删除了。
- 总结。
命令式对象配置的方式操作资源,可以简单的认为:命令 + yaml 配置文件(里面是命令需要的各种参数)。
3.3.3 声明式对象配置。
声明式对象配置跟命令式对象配置很相似,但是它只有一个命令 apply。
# 首先执行一次 kubectl apply -f yaml 文件,发现创建了资源。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl apply -f nginxpod.yaml
namespace/dev created
pod/nginxpod created
# 再次执行一次 kubectl apply -f yaml 文件,发现说资源没有变动。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl apply -f nginxpod.yaml
namespace/dev unchanged
pod/nginxpod unchanged
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl apply -f nginxpod.yaml
namespace/dev unchanged
pod/nginxpod unchanged
[root@localhost k8s]# !vim
vim nginxpod.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl apply -f nginxpod.yaml
namespace/dev unchanged
pod/nginxpod configured
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl describe pods nginxpod -n dev
Name: nginxpod
Namespace: dev
Priority: 0
Node: localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2/192.168.142.152
Start Time: Fri, 02 Dec 2022 13:52:33 +0800
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration:
{"apiVersion":"v1","kind":"Pod","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"nginxpod","namespace":"dev"},"spec":{"containers":[{"image":"nginx:1....
Status: Running
IP: 10.244.2.6
IPs:
IP: 10.244.2.6
Containers:
nginx-containers:
Container ID: docker://37a117c2d9d75053ce590c9d1fc306d5c90053960258891fff5bf0c046840089
Image: nginx:1.17.1
Image ID: docker-pullable://nginx@sha256:0d17b565c37bcbd895e9d92315a05c1c3c9a29f762b011a10c54a66cd53c9b31
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
State: Running
Started: Fri, 02 Dec 2022 13:53:30 +0800
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-5ksc8 (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready True
ContainersReady True
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
default-token-5ksc8:
Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret)
SecretName: default-token-5ksc8
Optional: false
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 3m default-scheduler Successfully assigned dev/nginxpod to localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2
Normal Pulling 2m59s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Pulling image "nginx:1.17.1"
Normal Pulled 2m3s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Successfully pulled image "nginx:1.17.1"
Normal Created 2m3s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Created container nginx-containers
Normal Started 2m3s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Started container nginx-containers
Normal Killing 52s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Container nginx-containers definition changed, will be restarted
Normal Pulling 52s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Pulling image "nginx:1.17.1"
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f nginxpod.yaml
Error from server (AlreadyExists): error when creating "nginxpod.yaml": namespaces "dev" already exists
Error from server (AlreadyExists): error when creating "nginxpod.yaml": pods "nginxpod" already exists
- 总结。
其实声明式对象配置就是使用 apply 描述一个资源最终的状态(在 yaml 中定义状态)。
使用 apply 操作资源。
如果资源不存在,就创建,相当于 kubectl create。
如果资源已存在,就更新,相当于 kubectl patch。
扩展:kubectl 可以在 node 节点上运行吗?
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get nodes
The connection to the server localhost:8080 was refused - did you specify the right host or port?
kubectl 的运行是需要进行配置的,它的配置文件是 $HOME/.kube,如果想要在 node 节点运行此命令,需要将 master 上的 .kube 文件复制到 node 节点上,即在 master 节点上执行下面操作:
scp -r $HOME/.kube localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1:$HOME/
[root@localhost ~]# ls .kube/
cache config http-cache
使用推荐: 三种方式应该怎么用?
创建/更新资源 使用声明式对象配置 kubectl apply -f XXX.yaml。
删除资源 使用命令式对象配置 kubectl delete -f XXX.yaml。
查询资源 使用命令式对象管理 kubectl get(describe) 资源名称。
4. 实战入门。
本章节将介绍如何在 kubernetes 集群中部署一个 Nginx 服务,并且能够对其进行访问。
4.1 Namespace。
Namespace 是 kubernetes 系统中的一种非常重要资源,它的主要作用是用来实现多套环境的资源隔离或者多租户的资源隔离。
默认情况下,kubernetes 集群中的所有的 Pod 都是可以相互访问的。但是在实际中,可能不想让两个 Pod 之间进行互相的访问,那此时就可以将两个 Pod 划分到不同的 namespace 下。kubernetes 通过将集群内部的资源分配到不同的 Namespace 中,可以形成逻辑上的"组",以方便不同的组的资源进行隔离使用和管理。
可以通过 kubernetes 的授权机制,将不同的 namespace 交给不同租户进行管理,这样就实现了多租户的资源隔离。此时还能结合 kubernetes 的资源配额机制,限定不同租户能占用的资源,例如 CPU 使用量、内存使用量等等,来实现租户可用资源的管理。

kubernetes 在集群启动之后,会默认创建几个 namespace。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get ns
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 13h # 所有未指定 Namespace 的对象都会被分配在 default 命名空间。
#dev Active 17m
#kube-flannel Active 12h
kube-node-lease Active 13h # 集群节点之间的心跳维护,v1.13 开始引入。
kube-public Active 13h # 此命名空间下的资源可以被所有人访问(包括未认证用户)。
kube-system Active 13h # 所有由 Kubernetes 系统创建的资源都处于这个命名空间。
下面来看 namespace 资源的具体操作。
4.1.1 查看。
# 查看所有的 ns。命令:kubectl get ns
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get ns
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 13h
dev Active 23m
kube-flannel Active 12h
kube-node-lease Active 13h
kube-public Active 13h
kube-system Active 13h
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get pods -n kube-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
coredns-9d85f5447-5959v 1/1 Running 0 13h
coredns-9d85f5447-gvqxh 1/1 Running 0 13h
etcd-localhost.localdomain.k8s.master 1/1 Running 0 13h
kube-apiserver-localhost.localdomain.k8s.master 1/1 Running 0 13h
kube-controller-manager-localhost.localdomain.k8s.master 1/1 Running 0 13h
kube-proxy-7dc95 1/1 Running 1 13h
kube-proxy-7hss2 1/1 Running 0 13h
kube-proxy-rpnvx 1/1 Running 0 13h
kube-scheduler-localhost.localdomain.k8s.master 1/1 Running 0 13h
# 查看指定的 ns。命令:kubectl get ns ns 名称
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get ns default
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 13h
# 指定输出格式。命令:kubectl get ns ns 名称 -o 格式参数
# kubernetes 支持的格式有很多,比较常见的是 wide、json、yaml
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get ns default -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2022-12-01T16:20:14Z"
name: default
resourceVersion: "146"
selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/default
uid: 11fb6c7d-f67f-4d9e-8e2b-66621c0d5d08
spec:
finalizers:
- kubernetes
status:
phase: Active
# 查看 ns 详情。命令:kubectl describe ns ns 名称
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl describe ns default
Name: default
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Status: Active
No resource quota.
No LimitRange resource.
# status
# Active 命名空间正在使用中 Terminating 正在删除命名空间。
# ResourceQuota 针对 namespace 做的资源限制。
# LimitRange 针对 namespace 中的每个组件做的资源限制。
4.1.2 创建。
# 创建 namespace。
[root@master ~]# kubectl create ns dev
namespace/dev created
4.1.3 删除。
# 删除 namespace。
[root@master ~]# kubectl delete ns dev
namespace "dev" deleted
4.1.4 配置方式。
首先准备一个 yaml 文件:ns-dev.yaml。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: dev
然后就可以执行对应的创建和删除命令了:
创建:kubectl create -f ns-dev.yaml。
删除:kubectl delete -f ns-dev.yaml。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim ns-dev.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f ns-dev.yaml
Error from server (AlreadyExists): error when creating "ns-dev.yaml": namespaces "dev" already exists
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl delete -f ns-dev.yaml
namespace "dev" deleted
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f ns-dev.yaml
namespace/dev created
4.2 Pod。
Pod 是 kubernetes 集群进行管理的最小单元,程序要运行必须部署在容器中,而容器必须存在于 Pod 中。
Pod 可以认为是容器的封装,一个 Pod 中可以存在一个或者多个容器。

kubernetes 在集群启动之后,集群中的各个组件也都是以 Pod 方式运行的。可以通过下面命令查看。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pod -n kube-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
coredns-9d85f5447-5959v 1/1 Running 0 14h
coredns-9d85f5447-gvqxh 1/1 Running 0 14h
etcd-localhost.localdomain.k8s.master 1/1 Running 0 14h
kube-apiserver-localhost.localdomain.k8s.master 1/1 Running 0 14h
kube-controller-manager-localhost.localdomain.k8s.master 1/1 Running 0 14h
kube-proxy-7dc95 1/1 Running 1 14h
kube-proxy-7hss2 1/1 Running 0 14h
kube-proxy-rpnvx 1/1 Running 0 14h
kube-scheduler-localhost.localdomain.k8s.master 1/1 Running 0 14h
4.2.1 创建并运行。
kubernetes 没有提供单独运行 Pod 的命令,都是通过 Pod 控制器来实现的。
# 命令格式:kubectl run (pod 控制器名称) [参数]
# --image 指定 Pod 的镜像。
# --port 指定端口。
# --namespace 指定 namespace。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl run nginx --image=nginx:1.17.1 --port=80 --namespace dev
kubectl run --generator=deployment/apps.v1 is DEPRECATED and will be removed in a future version. Use kubectl run --generator=run-pod/v1 or kubectl create instead.
deployment.apps/nginx created
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pod -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-64777cd554-kwbhk 1/1 Running 0 2m8s
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pod -n dev -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
nginx-64777cd554-kwbhk 1/1 Running 0 2m13s 10.244.2.7 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 <none> <none>
# READY ~ pod 中容器数量。
4.2.2 查看 pod 信息。
# 查看 Pod 基本信息。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-64777cd554-kwbhk 1/1 Running 0 4m26s
# 查看 Pod 的详细信息。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl describe pod nginx -n dev
Name: nginx-64777cd554-kwbhk
Namespace: dev
Priority: 0
Node: localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2/192.168.142.152
Start Time: Fri, 02 Dec 2022 14:41:15 +0800
Labels: pod-template-hash=64777cd554
run=nginx
Annotations: <none>
Status: Running
IP: 10.244.2.7
IPs:
IP: 10.244.2.7
Controlled By: ReplicaSet/nginx-64777cd554
Containers:
nginx:
Container ID: docker://f96e2bc540280474d7e6f7942ae42c08b485b86e18c090152d0bcdf6ea6fed21
Image: nginx:1.17.1
Image ID: docker-pullable://nginx@sha256:b4b9b3eee194703fc2fa8afa5b7510c77ae70cfba567af1376a573a967c03dbb
Port: 80/TCP
Host Port: 0/TCP
State: Running
Started: Fri, 02 Dec 2022 14:41:17 +0800
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-z9vht (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready True
ContainersReady True
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
default-token-z9vht:
Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret)
SecretName: default-token-z9vht
Optional: false
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 4m37s default-scheduler Successfully assigned dev/nginx-64777cd554-kwbhk to localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2
Normal Pulled 4m36s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Container image "nginx:1.17.1" already present on machine
Normal Created 4m36s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Created container nginx
Normal Started 4m35s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Started container nginx
4.2.3 访问 Pod。
# 获取 pod IP。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
nginx-64777cd554-kwbhk 1/1 Running 0 8m32s 10.244.2.7 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 <none> <none>
# 访问 POD。
[root@localhost k8s]# curl http://10.244.2.7:80
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
body {
width: 35em;
margin: 0 auto;
font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
<p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
working. Further configuration is required.</p>
<p>For online documentation and support please refer to
<a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/>
Commercial support is available at
<a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p>
<p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p>
</body>
</html>
4.2.4 删除指定 Pod。
# 删除指定 Pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pod -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-64777cd554-kwbhk 1/1 Running 0 11m
# 此时,显示删除 Pod 成功,但是再查询,发现又新产生了一个。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pod -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-64777cd554-xwknq 1/1 Running 0 26s
# kubectl run (pod 控制器名称) [参数]
# 这是因为当前 Pod 是由 Pod 控制器创建的,控制器会监控 Pod 状况,一旦发现 Pod 死亡,会立即重建。
# 此时要想删除 Pod,必须删除 Pod 控制器。
# 先来查询一下当前 namespace 下的 Pod 控制器。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get deploy -n dev
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
nginx 1/1 1 1 12m
# 接下来,删除此 Pod 控制器。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl delete deploy nginx -n dev
deployment.apps "nginx" deleted
# 稍等片刻,再查询 Pod,发现 Pod 被删除了。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev
No resources found in dev namespace.
4.2.5 配置操作。
创建一个 pod-nginx.yaml,内容如下。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx:1.17.1
name: pod
ports:
- name: nginx-port
containerPort: 80
protocol: TCP
然后就可以执行对应的创建和删除命令了。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim pod-nginx.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pod-nginx.yaml
pod/nginx created
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl delete -f pod-nginx.yaml
pod "nginx" deleted
4.3 Label。
Label 是 kubernetes 系统中的一个重要概念。它的作用就是在资源上添加标识,用来对它们进行区分和选择。
Label 的特点。
- 一个 Label 会以 key/value 键值对的形式附加到各种对象上,如 Node、Pod、Service 等等。
- 一个资源对象可以定义任意数量的 Label,同一个 Label 也可以被添加到任意数量的资源对象上去。
- Label 通常在资源对象定义时确定,当然也可以在对象创建后动态添加或者删除。
可以通过 Label 实现资源的多维度分组,以便灵活、方便地进行资源分配、调度、配置、部署等管理工作。
一些常用的 Label 示例如下:
- 版本标签:“version”:“release”, “version”:“stable”…
- 环境标签:“environment”:“dev”,“environment”:“test”,“environment”:“pro”
- 架构标签:“tier”:“frontend”,“tier”:“backend”。
标签定义完毕之后,还要考虑到标签的选择,这就要使用到 Label Selector,即:
Label 用于给某个资源对象定义标识。
Label Selector 用于查询和筛选拥有某些标签的资源对象。
当前有两种 Label Selector。
- 基于等式的 Label Selector。
name = slave: 选择所有包含 Label 中 key=“name” 且 value=“slave” 的对象。
env != production: 选择所有包括 Label 中的 key=“env” 且 value 不等于 “production” 的对象。
- 基于集合的 Label Selector。
name in (master, slave): 选择所有包含 Label 中的 key=“name” 且 value=“master” 或 “slave” 的对象。
name not in (frontend): 选择所有包含 Label 中的 key=“name” 且 value 不等于 “frontend” 的对象。
标签的选择条件可以使用多个,此时将多个 Label Selector 进行组合,使用逗号","进行分隔即可。例如:
name=slave,env!=production
name not in (frontend),env!=production
4.3.1 命令方式。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pod-nginx.yaml
pod/nginx created
# 查看标签。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pod -n dev --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS
nginx 1/1 Running 0 69s <none>
# 为 pod 资源打标签。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl label pod nginx version=1.0 -n dev
pod/nginx labeled
# 查看标签。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pod -n dev --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS
nginx 1/1 Running 0 2m19s version=1.0
# 追加打标签。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl label pod nginx tier=back -n dev
pod/nginx labeled
# 查看标签。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pod -n dev --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS
nginx 1/1 Running 0 3m4s tier=back,version=1.0
# 为 pod 资源更新标签。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl label pod nginx version=2.0 -n dev
error: 'version' already has a value (1.0), and --overwrite is false
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl label pod nginx version=2.0 -n dev --overwrite
pod/nginx labeled
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pod -n dev --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS
# 筛选标签。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx1
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx:1.17.1
name: pod
ports:
- name: nginx-port
containerPort: 80
protocol: TCP
[root@localhost k8s]# vim pod-nginx1.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pod-nginx1.yaml
pod/nginx1 created
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl label pod nginx1 version=1.0 -n dev --overwrite
pod/nginx1 labeled
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS
nginx 1/1 Running 0 10m tier=back,version=2.0
nginx1 1/1 Running 0 48s version=1.0
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pod -n dev -l version=2.0 --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS
nginx 1/1 Running 0 11m tier=back,version=2.0
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pod -n dev -l version!=2.0 --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS
nginx1 1/1 Running 0 117s version=1.0
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pod -n dev -l version=3.0 --show-labels
No resources found in dev namespace.
# 删除标签。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl label pod nginx tier- -n dev
pod/nginx labeled
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS
nginx 1/1 Running 0 14m version=2.0
nginx1 1/1 Running 0 4m32s version=1.0
4.3.2 配置方式。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx
namespace: dev
labels:
version: "3.0"
env: "test"
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx:1.17.1
name: pod
ports:
- name: nginx-port
containerPort: 80
protocol: TCP
然后就可以执行对应的更新命令了:kubectl apply -f pod-nginx.yaml。
4.4 Deployment。
在 kubernetes 中,Pod 是最小的控制单元,但是 kubernetes 很少直接控制 Pod,一般都是通过 Pod 控制器来完成的。Pod 控制器用于 pod 的管理,确保 pod 资源符合预期的状态,当 pod 的资源出现故障时,会尝试进行重启或重建 pod。
在 kubernetes 中 Pod 控制器的种类有很多,本章节只介绍一种:Deployment。

4.4.1 命令操作。
kubectl run。。。
底层使用了 pod 控制器。
# 命令格式: kubectl create deployment 名称 [参数]
# --image 指定 pod 的镜像。
# --port 指定端口。
# --replicas 指定创建 pod 数量。
# --namespace 指定 namespace。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl delete ns dev
namespace "dev" deleted
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl create ns dev
namespace/dev created
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get deployment, pods -n dev
error: arguments in resource/name form must have a single resource and name
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get deployment,pods -n dev
No resources found in dev namespace.
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl run nginx --image=nginx:1.17.1 --port=80 --replicas=3 -n dev
kubectl run --generator=deployment/apps.v1 is DEPRECATED and will be removed in a future version. Use kubectl run --generator=run-pod/v1 or kubectl create instead.
deployment.apps/nginx created
# 查看创建的 Pod。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get deployment,pods -n dev
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/nginx 2/3 3 2 44s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/nginx-64777cd554-64kzc 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 44s
pod/nginx-64777cd554-6zmhj 1/1 Running 0 44s
pod/nginx-64777cd554-tdrjw 1/1 Running 0 44s
# 查看 deployment 的信息。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get deploy -n dev
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
nginx 3/3 3 3 4m16s
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get pods -n dev --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS
nginx-64777cd554-64kzc 1/1 Running 0 3m38s pod-template-hash=64777cd554,run=nginx
nginx-64777cd554-6zmhj 1/1 Running 0 3m38s pod-template-hash=64777cd554,run=nginx
nginx-64777cd554-tdrjw 1/1 Running 0 3m38s pod-template-hash=64777cd554,run=nginx
# UP-TO-DATE:成功升级的副本数量
# AVAILABLE:可用副本的数量
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get deploy -n dev -o wide
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR
nginx 3/3 3 3 6m7s nginx nginx:1.17.1 run=nginx
# 查看 deployment 的详细信息。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl describe deploy nginx -n dev
Name: nginx
Namespace: dev
CreationTimestamp: Fri, 02 Dec 2022 23:28:04 +0800
Labels: run=nginx
Annotations: deployment.kubernetes.io/revision: 1
Selector: run=nginx
Replicas: 3 desired | 3 updated | 3 total | 3 available | 0 unavailable
StrategyType: RollingUpdate
MinReadySeconds: 0
RollingUpdateStrategy: 25% max unavailable, 25% max surge
Pod Template:
Labels: run=nginx
Containers:
nginx:
Image: nginx:1.17.1
Port: 80/TCP
Host Port: 0/TCP
Environment: <none>
Mounts: <none>
Volumes: <none>
Conditions:
Type Status Reason
---- ------ ------
Available True MinimumReplicasAvailable
Progressing True NewReplicaSetAvailable
OldReplicaSets: <none>
NewReplicaSet: nginx-64777cd554 (3/3 replicas created)
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal ScalingReplicaSet 6m33s deployment-controller Scaled up replica set nginx-64777cd554 to 3
# 删除。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl delete deploy nginx -n dev
deployment.apps "nginx" deleted
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get pods -n dev
No resources found in dev namespace.
4.4.2 配置操作。
创建一个 deploy-nginx.yaml,内容如下。
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx
namespace: dev
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
run: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
run: nginx
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx:1.17.1
name: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
protocol: TCP
然后就可以执行对应的创建和删除命令了:
创建:kubectl create -f deploy-nginx.yaml。
删除:kubectl delete -f deploy-nginx.yaml。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim deploy-nginx.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f deploy-nginx.yaml
deployment.apps/nginx created
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get deployment,pods -n dev
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/nginx 3/3 3 3 33s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/nginx-64777cd554-25w54 1/1 Running 0 32s
pod/nginx-64777cd554-p862l 1/1 Running 0 32s
pod/nginx-64777cd554-ppsbl 1/1 Running 0 33s
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl delete -f deploy-nginx.yaml
deployment.apps "nginx" deleted
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get deployment,pods -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/nginx-64777cd554-25w54 0/1 Terminating 0 59s
pod/nginx-64777cd554-p862l 0/1 Terminating 0 59s
pod/nginx-64777cd554-ppsbl 0/1 Terminating 0 60s
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get deployment,pods -n dev
No resources found in dev namespace.
[root@localhost k8s]#
4.5 Service。
通过上节课的学习,已经能够利用 Deployment 来创建一组 Pod 来提供具有高可用性的服务。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f deploy-nginx.yaml
deployment.apps/nginx created
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
nginx-64777cd554-8d26x 1/1 Running 0 19s 10.244.1.5 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 <none> <none>
nginx-64777cd554-dtm27 1/1 Running 0 19s 10.244.2.17 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 <none> <none>
nginx-64777cd554-t9x4n 1/1 Running 0 19s 10.244.2.16 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 <none> <none>
[root@localhost k8s]# curl 10.244.1.5
curl: (7) Failed connect to 10.244.1.5:80; Connection refused
# 删除后,会重新创建一个新 pod,ip 会变。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl delete pod nginx-64777cd554-t9x4n -n dev
pod "nginx-64777cd554-t9x4n" deleted
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
nginx-64777cd554-8d26x 1/1 Running 0 4m50s 10.244.1.5 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 <none> <none>
nginx-64777cd554-ck66j 1/1 Running 0 10s 10.244.2.18 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 <none> <none>
nginx-64777cd554-dtm27 1/1 Running 0 4m50s 10.244.2.17 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 <none> <none>
虽然每个 Pod 都会分配一个单独的 Pod IP,然而却存在如下两问题:
- Pod IP 会随着 Pod 的重建产生变化。
- Pod IP 仅仅是集群内可见的虚拟 IP,外部无法访问。
这样对于访问这个服务带来了难度。因此,kubernetes 设计了 Service 来解决这个问题。
Service 可以看作是一组同类 Pod 对外的访问接口。借助 Service,应用可以方便地实现服务发现和负载均衡。

4.5.1 创建集群内部可访问的 Service。
# 暴露 Service。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl expose deploy nginx --name=svc-nginx1 --type=ClusterIP --port=80 --target-port=80 -n dev
service/svc-nginx1 exposed
# 查看 service。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get service -n dev
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
svc-nginx1 ClusterIP 10.104.13.248 <none> 80/TCP 17s
# 这里产生了一个 CLUSTER-IP,这就是 service 的 IP,在 Service 的生命周期中,这个地址是不会变动的。
# 可以通过这个 IP 访问当前 service 对应的 POD。
[root@master ~]# curl 10.104.13.248:80
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
.......
</body>
</html>
4.5.2 创建集群外部也可访问的 Service。
# 上面创建的 Service 的 type 类型为 ClusterIP,这个 ip 地址只用集群内部可访问。
# 如果需要创建外部也可以访问的 Service,需要修改 type 为 NodePort。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl expose deploy nginx --name=svc-nginx2 --type=NodePort --port=80 --target-port=80 -n dev
service/svc-nginx2 exposed
# 此时查看,会发现出现了 NodePort 类型的 Service,而且有一对 Port(80:31928/TC)。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get svc -n dev
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
svc-nginx1 ClusterIP 10.104.13.248 <none> 80/TCP 22m
svc-nginx2 NodePort 10.97.109.91 <none> 80:30228/TCP 2m17s
# 接下来就可以通过集群外的主机访问节点 IP:30228 访问服务了。
# 例如在的电脑主机上通过浏览器访问下面的地址。
http://192.168.142.150:30228
4.5.3 删除 Service。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl delete service svc-nginx1 -n dev
service "svc-nginx1" deleted
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl delete svc svc-nginx2 -n dev
service "svc-nginx2" deleted
4.5.4 配置方式。
创建一个 svc-nginx.yaml,内容如下。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: svc-nginx
namespace: dev
spec:
clusterIP: 10.109.179.231 # 固定 svc 的内网 ip。
ports:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
run: nginx
type: ClusterIP
然后就可以执行对应的创建和删除命令了:
创建:kubectl create -f svc-nginx.yaml。
删除:kubectl delete -f svc-nginx.yaml。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim svc-nginx.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f svc-nginx.yaml
service/svc-nginx created
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get service -n dev
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
svc-nginx ClusterIP 10.109.179.231 <none> 80/TCP 13s
[root@localhost k8s]# curl 10.109.179.231:80
curl: (7) Failed connect to 10.109.179.231:80; Connection refused
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl delete -f svc-nginx.yaml
service "svc-nginx" deleted
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get service -n dev
No resources found in dev namespace.
- 小结。
至此,已经掌握了 Namespace、Pod、Deployment、Service 资源的基本操作,有了这些操作,就可以在 kubernetes 集群中实现一个服务的简单部署和访问了,但是如果想要更好的使用 kubernetes,就需要深入学习这几种资源的细节和原理。
5. Pod 详解。
5.1 Pod 介绍。
5.1.1 Pod 结构。

每个 Pod 中都可以包含一个或者多个容器,这些容器可以分为两类:
-
用户程序所在的容器,数量可多可少。
-
Pause 容器,这是每个 Pod 都会有的一个根容器,它的作用有两个:
- 可以以它为依据,评估整个 Pod 的健康状态。
- 可以在根容器上设置 Ip 地址,其它容器都此 Ip(Pod IP),以实现 Pod 内部的网路通信。
这里是 Pod 内部的通讯,Pod 的之间的通讯采用虚拟二层网络技术来实现,我们当前环境用的是 Flannel。
5.1.2 Pod 定义。
下面是 Pod 的资源清单。
apiVersion: v1 # 必选,版本号,例如 v1。
kind: Pod # 必选,资源类型,例如 Pod。
metadata: # 必选,元数据。
name: string # 必选,Pod 名称。
namespace: string # Pod 所属的命名空间,默认为 "default"。
labels: # 自定义标签列表。
- name: string
spec: # 必选,Pod 中容器的详细定义。
containers: # 必选,Pod 中容器列表。
- name: string # 必选,容器名称。
image: string # 必选,容器的镜像名称。
imagePullPolicy: [ Always|Never|IfNotPresent ] # 获取镜像的策略。
command: [ string ] # 容器的启动命令列表,如不指定,使用打包时使用的启动命令。
args: [ string ] # 容器的启动命令参数列表。
workingDir: string # 容器的工作目录。
volumeMounts: # 挂载到容器内部的存储卷配置。
- name: string # 引用 pod 定义的共享存储卷的名称,需用 volumes[] 部分定义的的卷名。
mountPath: string # 存储卷在容器内 mount 的绝对路径,应少于 512 字符。
readOnly: boolean # 是否为只读模式。
ports: # 需要暴露的端口库号列表。
- name: string # 端口的名称。
containerPort: int # 容器需要监听的端口号。
hostPort: int # 容器所在主机需要监听的端口号,默认与 Container 相同。
protocol: string # 端口协议,支持 TCP 和 UDP,默认 TCP。
env: # 容器运行前需设置的环境变量列表。
- name: string # 环境变量名称。
value: string # 环境变量的值。
resources: # 资源限制和请求的设置。
limits: # 资源限制的设置。
cpu: string # cpu 的限制,单位为 core 数,将用于 docker run --cpu-shares 参数。
memory: string # 内存限制,单位可以为 Mib/Gib,将用于 docker run --memory 参数。
requests: # 资源请求的设置。
cpu: string # cpu 请求,容器启动的初始可用数量。
memory: string # 内存请求,容器启动的初始可用数量。
lifecycle: # 生命周期钩子。
postStart: # 容器启动后立即执行此钩子,如果执行失败,会根据重启策略进行重启。
preStop: # 容器终止前执行此钩子,无论结果如何,容器都会终止。
livenessProbe: # 对 Pod 内各容器健康检查的设置,当探测无响应几次后将自动重启该容器。
exec: # 对 Pod 容器内检查方式设置为 exec 方式。
command: [ string ] # exec 方式需要制定的命令或脚本。
httpGet: # 对 Pod 内个容器健康检查方法设置为 HttpGet,需要制定 Path、port。
path: string
port: number
host: string
scheme: string
HttpHeaders:
- name: string
value: string
tcpSocket: # 对 Pod 内个容器健康检查方式设置为 tcpSocket 方式。
port: number
initialDelaySeconds: 0 # 容器启动完成后首次探测的时间,单位为秒。
timeoutSeconds: 0 # 对容器健康检查探测等待响应的超时时间,单位秒,默认 1 秒。
periodSeconds: 0 # 对容器监控检查的定期探测时间设置,单位秒,默认 10 秒一次。
successThreshold: 0
failureThreshold: 0
securityContext:
privileged: false
restartPolicy: [ Always | Never | OnFailure ] # Pod 的重启策略。
nodeName: <string> # 设置 NodeName 表示将该 Pod 调度到指定到名称的 node 节点上。
nodeSelector: object # 设置 NodeSelector 表示将该 Pod 调度到包含这个 label 的 node 上。
imagePullSecrets: # Pull 镜像时使用的 secret 名称,以 key:secretKey 格式指定。
- name: string
hostNetwork: false # 是否使用主机网络模式,默认为 false,如果设置为 true,表示使用宿主机网络。
volumes: # 在该 pod 上定义共享存储卷列表。
- name: string # 共享存储卷名称 (volumes 类型有很多种)。
emptyDir: { } # 类型为 emptyDir 的存储卷,与 Pod 同生命周期的一个临时目录。为空值。
hostPath: string # 类型为 hostPath 的存储卷,表示挂载 Pod 所在宿主机的目录。
path: string # Pod 所在宿主机的目录,将被用于同期中 mount 的目录。
secret: # 类型为 secret 的存储卷,挂载集群与定义的 secret 对象到容器内部。
secretname: string
items:
- key: string
path: string
configMap: # 类型为 configMap 的存储卷,挂载预定义的 configMap 对象到容器内部。
name: string
items:
- key: string
path: string
# 小提示:
# 在这里,可通过一个命令来查看每种资源的可配置项。
# kubectl explain 资源类型 查看某种资源可以配置的一级属性。
# kubectl explain 资源类型.属性 查看属性的子属性。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl explain pod
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1
DESCRIPTION:
Pod is a collection of containers that can run on a host. This resource is
created by clients and scheduled onto hosts.
FIELDS:
apiVersion <string>
APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation of an
object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest internal
value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources
kind <string>
Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this object
represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client submits
requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds
metadata <Object>
Standard object's metadata. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata
spec <Object>
Specification of the desired behavior of the pod. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status
status <Object>
Most recently observed status of the pod. This data may not be up to date.
Populated by the system. Read-only. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl explain pod.metadata
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1
RESOURCE: metadata <Object>
DESCRIPTION:
Standard object's metadata. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata
ObjectMeta is metadata that all persisted resources must have, which
includes all objects users must create.
FIELDS:
annotations <map[string]string>
Annotations is an unstructured key value map stored with a resource that
may be set by external tools to store and retrieve arbitrary metadata. They
are not queryable and should be preserved when modifying objects. More
info: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/annotations
clusterName <string>
The name of the cluster which the object belongs to. This is used to
distinguish resources with same name and namespace in different clusters.
This field is not set anywhere right now and apiserver is going to ignore
it if set in create or update request.
creationTimestamp <string>
CreationTimestamp is a timestamp representing the server time when this
object was created. It is not guaranteed to be set in happens-before order
across separate operations. Clients may not set this value. It is
represented in RFC3339 form and is in UTC. Populated by the system.
Read-only. Null for lists. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata
deletionGracePeriodSeconds <integer>
Number of seconds allowed for this object to gracefully terminate before it
will be removed from the system. Only set when deletionTimestamp is also
set. May only be shortened. Read-only.
deletionTimestamp <string>
DeletionTimestamp is RFC 3339 date and time at which this resource will be
deleted. This field is set by the server when a graceful deletion is
requested by the user, and is not directly settable by a client. The
resource is expected to be deleted (no longer visible from resource lists,
and not reachable by name) after the time in this field, once the
finalizers list is empty. As long as the finalizers list contains items,
deletion is blocked. Once the deletionTimestamp is set, this value may not
be unset or be set further into the future, although it may be shortened or
the resource may be deleted prior to this time. For example, a user may
request that a pod is deleted in 30 seconds. The Kubelet will react by
sending a graceful termination signal to the containers in the pod. After
that 30 seconds, the Kubelet will send a hard termination signal (SIGKILL)
to the container and after cleanup, remove the pod from the API. In the
presence of network partitions, this object may still exist after this
timestamp, until an administrator or automated process can determine the
resource is fully terminated. If not set, graceful deletion of the object
has not been requested. Populated by the system when a graceful deletion is
requested. Read-only. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata
finalizers <[]string>
Must be empty before the object is deleted from the registry. Each entry is
an identifier for the responsible component that will remove the entry from
the list. If the deletionTimestamp of the object is non-nil, entries in
this list can only be removed. Finalizers may be processed and removed in
any order. Order is NOT enforced because it introduces significant risk of
stuck finalizers. finalizers is a shared field, any actor with permission
can reorder it. If the finalizer list is processed in order, then this can
lead to a situation in which the component responsible for the first
finalizer in the list is waiting for a signal (field value, external
system, or other) produced by a component responsible for a finalizer later
in the list, resulting in a deadlock. Without enforced ordering finalizers
are free to order amongst themselves and are not vulnerable to ordering
changes in the list.
generateName <string>
GenerateName is an optional prefix, used by the server, to generate a
unique name ONLY IF the Name field has not been provided. If this field is
used, the name returned to the client will be different than the name
passed. This value will also be combined with a unique suffix. The provided
value has the same validation rules as the Name field, and may be truncated
by the length of the suffix required to make the value unique on the
server. If this field is specified and the generated name exists, the
server will NOT return a 409 - instead, it will either return 201 Created
or 500 with Reason ServerTimeout indicating a unique name could not be
found in the time allotted, and the client should retry (optionally after
the time indicated in the Retry-After header). Applied only if Name is not
specified. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#idempotency
generation <integer>
A sequence number representing a specific generation of the desired state.
Populated by the system. Read-only.
labels <map[string]string>
Map of string keys and values that can be used to organize and categorize
(scope and select) objects. May match selectors of replication controllers
and services. More info: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/labels
managedFields <[]Object>
ManagedFields maps workflow-id and version to the set of fields that are
managed by that workflow. This is mostly for internal housekeeping, and
users typically shouldn't need to set or understand this field. A workflow
can be the user's name, a controller's name, or the name of a specific
apply path like "ci-cd". The set of fields is always in the version that
the workflow used when modifying the object.
name <string>
Name must be unique within a namespace. Is required when creating
resources, although some resources may allow a client to request the
generation of an appropriate name automatically. Name is primarily intended
for creation idempotence and configuration definition. Cannot be updated.
More info: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/identifiers#names
namespace <string>
Namespace defines the space within each name must be unique. An empty
namespace is equivalent to the "default" namespace, but "default" is the
canonical representation. Not all objects are required to be scoped to a
namespace - the value of this field for those objects will be empty. Must
be a DNS_LABEL. Cannot be updated. More info:
http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/namespaces
ownerReferences <[]Object>
List of objects depended by this object. If ALL objects in the list have
been deleted, this object will be garbage collected. If this object is
managed by a controller, then an entry in this list will point to this
controller, with the controller field set to true. There cannot be more
than one managing controller.
resourceVersion <string>
An opaque value that represents the internal version of this object that
can be used by clients to determine when objects have changed. May be used
for optimistic concurrency, change detection, and the watch operation on a
resource or set of resources. Clients must treat these values as opaque and
passed unmodified back to the server. They may only be valid for a
particular resource or set of resources. Populated by the system.
Read-only. Value must be treated as opaque by clients and . More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#concurrency-control-and-consistency
selfLink <string>
SelfLink is a URL representing this object. Populated by the system.
Read-only. DEPRECATED Kubernetes will stop propagating this field in 1.20
release and the field is planned to be removed in 1.21 release.
uid <string>
UID is the unique in time and space value for this object. It is typically
generated by the server on successful creation of a resource and is not
allowed to change on PUT operations. Populated by the system. Read-only.
More info: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/identifiers#uids
在 kubernetes 中基本所有资源的一级属性都是一样的,主要包含 5 部分。
-
apiVersion
<string>。
版本,由 kubernetes 内部定义,版本号必须可以用 kubectl api-versions 查询到。 -
kind
<string>。
类型,由 kubernetes 内部定义,版本号必须可以用 kubectl api-resources 查询到。 -
metadata
<Object>。
元数据,主要是资源标识和说明,常用的有 name、namespace、labels 等。 -
spec
<Object>。
描述,这是配置中最重要的一部分,里面是对各种资源配置的详细描述。 -
status
<Object>。
状态信息,里面的内容不需要定义,由 kubernetes 自动生成。
在上面的属性中,spec 是接下来研究的重点,继续看下 ta 的常见子属性。
-
containers
<[]Object>。
容器列表,用于定义容器的详细信息。 -
nodeName
<String>。
根据 nodeName 的值将 pod 调度到指定的 Node 节点上。 -
nodeSelector
<map[]>。
根据 nodeSelector 中定义的信息选择将该 Pod 调度到包含这些 label 的 Node 上。 -
hostNetwork
<boolean>。
是否使用主机网络模式,默认为 false,如果设置为 true,表示使用宿主机网络。 -
volumes
<[]Object>。
存储卷,用于定义 Pod 上面挂在的存储信息。 -
restartPolicy
<string>。
重启策略,表示 Pod 在遇到故障的时候的处理策略。
5.2 Pod 配置。
本小节主要来研究pod.spec.containers属性,这也是 pod 配置中最为关键的一项配置。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl explain pod.spec.containers
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1
RESOURCE: containers <[]Object> # 数组,代表可以有多个容器。
FIELDS:
name <string> # 容器名称。
image <string> # 容器需要的镜像地址。
imagePullPolicy <string> # 镜像拉取策略。
command <[]string> # 容器的启动命令列表,如不指定,使用打包时使用的启动命令。
args <[]string> # 容器的启动命令需要的参数列表。
env <[]Object> # 容器环境变量的配置。
ports <[]Object> # 容器需要暴露的端口号列表。
resources <Object> # 资源限制和资源请求的设置。
5.2.1 基本配置。
创建 pod-base.yaml 文件,内容如下。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-base
namespace: dev
labels:
user: geek
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
- name: busybox
image: busybox:1.35
上面定义了一个比较简单 Pod 的配置,里面有两个容器。
- nginx:用 1.17.1 版本的 nginx 镜像创建,(nginx 是一个轻量级 web 容器)
- busybox:用 1.35 版本的 busybox 镜像创建,(busybox 是一个小巧的 linux 命令集合)。
# 创建 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim pod-base.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl apply -f pod-base.yaml
pod/pod-base created
# 查看 Pod 状况。
# READY 1/2 : 表示当前 Pod 中有 2 个容器,其中 1 个准备就绪,1 个未就绪。
# RESTARTS : 重启次数,因为有 1 个容器故障了,Pod 一直在重启试图恢复它。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pod -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod-base 1/2 Running 3 113s
# 可以通过 describe 查看内部的详情。
# 此时已经运行起来了一个基本的 Pod,虽然它暂时有问题。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl describe pod pod-base -n dev
Name: pod-base
Namespace: dev
Priority: 0
Node: localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1/192.168.142.151
Start Time: Sat, 03 Dec 2022 00:57:16 +0800
Labels: user=geek
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration:
{"apiVersion":"v1","kind":"Pod","metadata":{"annotations":{},"labels":{"user":"geek"},"name":"pod-base","namespace":"dev"},"spec":{"contai...
Status: Running
IP: 10.244.1.6
IPs:
IP: 10.244.1.6
Containers:
nginx:
Container ID: docker://f424dc1d77faf39f022d2f30a581983cf3992a335e782333e20264a1ce424e6c
Image: nginx:1.17.1
Image ID: docker-pullable://nginx@sha256:b4b9b3eee194703fc2fa8afa5b7510c77ae70cfba567af1376a573a967c03dbb
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
State: Running
Started: Sat, 03 Dec 2022 00:57:20 +0800
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-2kklx (ro)
busybox:
Container ID: docker://79853ae3be8dba72637301356383866c18e9a62124d985085531d9e6f5043a5c
Image: busybox:1.35
Image ID: docker-pullable://busybox@sha256:130df6999605f982ec67e5bee29d3a52614a075e949490f0a41702ee1dd98f3f
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
State: Waiting
Reason: CrashLoopBackOff
Last State: Terminated
Reason: Completed
Exit Code: 0
Started: Sat, 03 Dec 2022 00:59:09 +0800
Finished: Sat, 03 Dec 2022 00:59:09 +0800
Ready: False
Restart Count: 3
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-2kklx (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready False
ContainersReady False
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
default-token-2kklx:
Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret)
SecretName: default-token-2kklx
Optional: false
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 2m27s default-scheduler Successfully assigned dev/pod-base to localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1
Normal Pulled 2m23s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 Container image "nginx:1.17.1" already present on machine
Normal Created 2m23s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 Created container nginx
Normal Started 2m23s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 Started container nginx
Normal Pulling 2m23s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 Pulling image "busybox:1.35"
Normal Pulled 76s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 Successfully pulled image "busybox:1.35"
Normal Created 35s (x4 over 76s) kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 Created container busybox
Normal Pulled 35s (x3 over 76s) kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 Container image "busybox:1.35" already present on machine
Normal Started 34s (x4 over 76s) kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 Started container busybox
Warning BackOff 5s (x7 over 75s) kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 Back-off restarting failed container
5.2.2 镜像拉取。
创建 pod-imagepullpolicy.yaml 文件,内容如下。
metadata.name 不允许大写。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-imagepullpolicy
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
imagePullPolicy: Never # 用于设置镜像拉取策略。
- name: busybox
image: busybox:1.30
imagePullPolicy,用于设置镜像拉取策略,kubernetes 支持配置三种拉取策略:
- Always ~ 总是从远程仓库拉取镜像(一直远程下载)。
- IfNotPresent ~ 本地有则使用本地镜像,本地没有则从远程仓库拉取镜像(本地有就本地 本地没远程下载)。
- Never ~ 只使用本地镜像,从不去远程仓库拉取,本地没有就报错 (一直使用本地)。
默认值说明。
如果镜像 tag 为具体版本号, 默认策略是:IfNotPresent。
如果镜像 tag 为:latest(最终版本),默认策略是 always。
# 创建 pod。
[root@k8s-master01 pod]# kubectl create -f pod-imagepullpolicy.yaml
pod/pod-imagepullpolicy created
# 查看 Pod 详情。
# 此时明显可以看到 nginx 镜像有一步 Pulling image "nginx:1.17.1" 的过程。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl apply -f pod-imagepullpolicy.yaml
pod/pod-imagepullpolicy created
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get pod -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-64777cd554-8d26x 1/1 Running 0 13h
nginx-64777cd554-ck66j 1/1 Running 0 13h
nginx-64777cd554-dtm27 1/1 Running 0 13h
pod-base 1/2 Running 7 12h
pod-imagepullpolicy 0/2 ContainerCreating 0 13s
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl describe pod pod-imagepullpolicy -n dev
Name: pod-imagepullpolicy
Namespace: dev
Priority: 0
Node: localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2/192.168.142.152
Start Time: Sat, 03 Dec 2022 13:06:31 +0800
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration:
{"apiVersion":"v1","kind":"Pod","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"pod-imagepullpolicy","namespace":"dev"},"spec":{"containers":[{"image...
Status: Pending
IP: 10.244.2.19
IPs:
IP: 10.244.2.19
Containers:
nginx:
Container ID:
Image: nginx:1.17.2
Image ID:
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
State: Waiting
Reason: ErrImageNeverPull
Ready: False
Restart Count: 0
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-2kklx (ro)
busybox:
Container ID: docker://3e65f9a0e53f9277cf1347c0f00624d7c857d4b7981a749397263826b8f58d3a
Image: busybox:1.30
Image ID: docker-pullable://busybox@sha256:4b6ad3a68d34da29bf7c8ccb5d355ba8b4babcad1f99798204e7abb43e54ee3d
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
State: Terminated
Reason: Completed
Exit Code: 0
Started: Sat, 03 Dec 2022 13:07:55 +0800
Finished: Sat, 03 Dec 2022 13:07:55 +0800
Last State: Terminated
Reason: Completed
Exit Code: 0
Started: Sat, 03 Dec 2022 13:07:40 +0800
Finished: Sat, 03 Dec 2022 13:07:40 +0800
Ready: False
Restart Count: 2
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-2kklx (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready False
ContainersReady False
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
default-token-2kklx:
Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret)
SecretName: default-token-2kklx
Optional: false
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 90s default-scheduler Successfully assigned dev/pod-imagepullpolicy to localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2
Normal Pulling 89s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Pulling image "busybox:1.30"
Normal Pulled 23s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Successfully pulled image "busybox:1.30"
Normal Pulled 6s (x2 over 21s) kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Container image "busybox:1.30" already present on machine
Normal Created 6s (x3 over 23s) kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Created container busybox
Normal Started 6s (x3 over 22s) kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Started container busybox
Warning Failed 5s (x6 over 89s) kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Error: ErrImageNeverPull
Warning ErrImageNeverPull 5s (x6 over 89s) kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Container image "nginx:1.17.2" is not present with pull policy of Never
Warning BackOff 5s (x3 over 20s) kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Back-off restarting failed container
5.2.3 启动命令。
在前面的案例中,一直有一个问题没有解决,就是的 busybox 容器一直没有成功运行,那么到底是什么原因导致这个容器的故障呢?
原来 busybox 并不是一个程序,而是类似于一个工具类的集合,kubernetes 集群启动管理后,它会自动关闭。解决方法就是让其一直在运行,这就用到了 command 配置。
创建 pod-command.yaml 文件,内容如下。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-command
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
- name: busybox
image: busybox:1.30
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "touch /tmp/hello.txt; while true; do /bin/echo $(date +%T) >> /tmp/hello.txt; sleep 3; done;"]
command,用于在 pod 中的容器初始化完毕之后运行一个命令。
稍微解释下上面命令的意思:
“/bin/sh”,“-c”; 使用 sh 执行命令。
touch /tmp/hello.txt; 创建一个 /tmp/hello.txt 文件。
while true; do /bin/echo $(date +%T) >> /tmp/hello.txt; sleep 3; done; 每隔 3 秒向文件中写入当前时间。
# 创建 pod。
[root@localhost ~]# vim pod-command.yaml
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl create -f pod-command.yaml
pod/pod-command created
# 查看 Pod 状态。
# 此时发现两个 pod 都正常运行了。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get pods -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-64777cd554-8d26x 1/1 Running 0 13h
nginx-64777cd554-ck66j 1/1 Running 0 13h
nginx-64777cd554-dtm27 1/1 Running 0 13h
pod-base 1/2 CrashLoopBackOff 9 12h
pod-command 2/2 Running 0 11s
pod-imagepullpolicy 1/2 CrashLoopBackOff 6 8m3s
# 进入 pod 中的 busybox 容器,查看文件内容。
# 补充一个命令: kubectl exec pod 名称 -n 命名空间 -it -c 容器名称 /bin/sh 在容器内部执行命令。
# 使用这个命令就可以进入某个容器的内部,然后进行相关操作了。
# 比如,可以查看 txt 文件的内容。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl exec pod-command -n dev -it -c busybox /bin/sh
/ #
/ # tail -f /tmp/hello.txt
05:20:34
05:20:37
05:20:40
特别说明:
通过上面发现 command 已经可以完成启动命令和传递参数的功能,为什么这里还要提供一个 args 选项,用于传递参数呢?这其实跟 docker 有点关系,kubernetes 中的 command、args 两项其实是实现覆盖 Dockerfile 中 ENTRYPOINT 的功能。
- 如果 command 和 args 均没有写,那么用 Dockerfile 的配置。
- 如果 command 写了,但 args 没有写,那么 Dockerfile 默认的配置会被忽略,执行输入的 command。
- 如果 command 没写,但 args 写了,那么 Dockerfile 中配置的 ENTRYPOINT 的命令会被执行,使用当前 args 的参数。
- 如果 command 和 args 都写了,那么 Dockerfile 的配置被忽略,执行 command 并追加上 args 参数。
5.2.4 环境变量。
创建 pod-env.yaml 文件,内容如下。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-env
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- name: busybox
image: busybox:1.30
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "while true; do /bin/echo $(date +%T); sleep 60; done;"]
env: # 设置环境变量列表。
- name: "username"
value: "admin"
- name: "password"
value: "123456"
env,环境变量,用于在 pod 中的容器设置环境变量。
# 创建 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pod-env.yaml
pod/pod-env created
# 进入容器,输出环境变量。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl exec pod-env -n dev -c busybox -it /bin/sh
/ #
/ # echo $username
admin
/ # echo $password
123456
/ # echo $a
/ #
这种方式不是很推荐,推荐将这些配置单独存储在配置文件中,这种方式将在后面介绍。
5.2.5 端口设置。
本小节来介绍容器的端口设置,也就是 containers 的 ports 选项。
首先看下 ports 支持的子选项。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl explain pod.spec.containers.ports
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1
RESOURCE: ports <[]Object>
DESCRIPTION:
List of ports to expose from the container. Exposing a port here gives the
system additional information about the network connections a container
uses, but is primarily informational. Not specifying a port here DOES NOT
prevent that port from being exposed. Any port which is listening on the
default "0.0.0.0" address inside a container will be accessible from the
network. Cannot be updated.
ContainerPort represents a network port in a single container.
FIELDS:
# 容器要监听的端口(0 < x < 65536)。
containerPort <integer> -required-
Number of port to expose on the pod's IP address. This must be a valid port
number, 0 < x < 65536.
# 要将外部端口绑定到的主机 IP(一般省略)。
hostIP <string>
What host IP to bind the external port to.
# 容器要在主机上公开的端口,如果设置,主机上只能运行容器的一个副本(一般省略)。
hostPort <integer>
Number of port to expose on the host. If specified, this must be a valid
port number, 0 < x < 65536. If HostNetwork is specified, this must match
ContainerPort. Most containers do not need this.
# 端口名称,如果指定,必须保证 name 在 pod 中是唯一的。
name <string>
If specified, this must be an IANA_SVC_NAME and unique within the pod. Each
named port in a pod must have a unique name. Name for the port that can be
referred to by services.
# 端口协议。必须是 UDP、TCP 或 SCTP。默认为“TCP”。
protocol <string>
Protocol for port. Must be UDP, TCP, or SCTP. Defaults to "TCP".
接下来,编写一个测试案例,创建 pod-ports.yaml。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-ports
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
ports: # 设置容器暴露的端口列表。
- name: nginx-port
containerPort: 80
protocol: TCP
# 创建 pod。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl create -f pod-ports.yaml
pod/pod-ports created。
# 查看 pod。
# 在下面可以明显看到配置信息。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pod pod-ports -n dev -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2022-12-03T06:08:56Z"
name: pod-ports
namespace: dev
resourceVersion: "65413"
selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/dev/pods/pod-ports
uid: bc4257ef-5274-42cd-9e06-56b0f98aba80
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx:1.17.1
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: nginx-port
protocol: TCP
resources: {}
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount
name: default-token-2kklx
readOnly: true
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
enableServiceLinks: true
nodeName: localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1
priority: 0
restartPolicy: Always
schedulerName: default-scheduler
securityContext: {}
serviceAccount: default
serviceAccountName: default
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
tolerations:
- effect: NoExecute
key: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready
operator: Exists
tolerationSeconds: 300
- effect: NoExecute
key: node.kubernetes.io/unreachable
operator: Exists
tolerationSeconds: 300
volumes:
- name: default-token-2kklx
secret:
defaultMode: 420
secretName: default-token-2kklx
status:
conditions:
- lastProbeTime: null
lastTransitionTime: "2022-12-03T06:08:56Z"
status: "True"
type: Initialized
- lastProbeTime: null
lastTransitionTime: "2022-12-03T06:08:58Z"
status: "True"
type: Ready
- lastProbeTime: null
lastTransitionTime: "2022-12-03T06:08:58Z"
status: "True"
type: ContainersReady
- lastProbeTime: null
lastTransitionTime: "2022-12-03T06:08:56Z"
status: "True"
type: PodScheduled
containerStatuses:
- containerID: docker://889c267fd92e32a251bceb6eaf87f8f37b3d55772a63ca1e67886f119c3bfd43
image: nginx:1.17.1
imageID: docker-pullable://nginx@sha256:b4b9b3eee194703fc2fa8afa5b7510c77ae70cfba567af1376a573a967c03dbb
lastState: {}
name: nginx
ready: true
restartCount: 0
started: true
state:
running:
startedAt: "2022-12-03T06:08:57Z"
hostIP: 192.168.142.151
phase: Running
podIP: 10.244.1.9
podIPs:
- ip: 10.244.1.9
qosClass: BestEffort
startTime: "2022-12-03T06:08:56Z"
[root@localhost k8s]#
访问容器中的程序需要使用的是 Podip:containerPort。
5.2.6 资源配额。
容器中的程序要运行,肯定是要占用一定资源的,比如 cpu 和内存等,如果不对某个容器的资源做限制,那么它就可能吃掉大量资源,导致其它容器无法运行。针对这种情况,kubernetes 提供了对内存和 cpu 的资源进行配额的机制,这种机制主要通过 resources 选项实现,他有两个子选项。
- limits:用于限制运行时容器的最大占用资源,当容器占用资源超过 limits 时会被终止,并进行重启。
- requests:用于设置容器需要的最小资源,如果环境资源不够,容器将无法启动。
可以通过上面两个选项设置资源的上下限。
接下来,编写一个测试案例,创建 pod-resources.yaml。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-resources
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
resources: # 资源配额。
limits: # 限制资源(上限)。
cpu: "2" # CPU 限制,单位是 core 数。
memory: "10Gi" # 内存限制。
requests: # 请求资源(下限)。
cpu: "1" # CPU 限制,单位是 core 数。
memory: "10Mi" # 内存限制。
在这对 cpu 和 memory 的单位做一个说明。
- cpu:core 数,可以为整数或小数。
- memory: 内存大小,可以使用 Gi、Mi、G、M 等形式。
# 运行 Pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim pod-resources.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pod-resources.yaml
pod/pod-resources created
# 查看发现 pod 运行正常。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim pod-resources.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pod-resources.yaml
pod/pod-resources created
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod-resources 1/1 Running 0 8s
# 接下来,停止 Pod。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl delete -f pod-resources.yaml
pod "pod-resources" deleted。
# 编辑 pod,修改 resources.requests.memory 的值为 10Gi。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# vim pod-resources.yaml
# 再次启动 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pod-resources.yaml
pod/pod-resources created
# 查看 Pod 状态,发现 Pod 启动失败。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pod pod-resources -n dev -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
pod-resources 0/1 Pending 0 10s <none> <none> <none> <none>
# 查看 pod 详情会发现,如下提示。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl describe pod pod-resources -n dev
Name: pod-resources
Namespace: dev
Priority: 0
Node: <none>
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Status: Pending
IP:
IPs: <none>
Containers:
nginx:
Image: nginx:1.17.1
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
Limits:
cpu: 2
memory: 10Gi
Requests:
cpu: 1
memory: 10Gi
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-n8qxp (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
PodScheduled False
Volumes:
default-token-n8qxp:
Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret)
SecretName: default-token-n8qxp
Optional: false
QoS Class: Burstable
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Warning FailedScheduling 57s (x2 over 57s) default-scheduler 0/3 nodes are available: 3 Insufficient memory.
5.3 Pod 生命周期。
我们一般将 pod 对象从创建至终的这段时间范围称为 pod 的生命周期,它主要包含下面的过程。
- pod 创建过程。
- 运行 初始化容器(init container)过程。
- 运行 主容器(main container)。
- 容器启动后钩子(post start)、容器终止前钩子(pre stop)。
- 容器的存活性探测(liveness probe)、就绪性探测(readiness probe)。
- pod 终止过程。

在整个生命周期中,Pod 会出现 5 种状态(相位),分别如下。
- 挂起(Pending):apiserver 已经创建了 pod 资源对象,但 ta 尚未被调度完成或者仍处于下载镜像的过程中。
- 运行中(Running):pod 已经被调度至某节点,并且所有容器都已经被 kubelet 创建完成。
- 成功(Succeeded):pod 中的所有容器都已经成功终止并且不会被重启。
- 失败(Failed):所有容器都已经终止,但至少有一个容器终止失败,即容器返回了非 0 值的退出状态。
- 未知(Unknown):apiserver 无法正常获取到 pod 对象的状态信息,通常由网络通信失败所导致。
5.3.1 创建和终止。
pod 的创建过程。
-
用户通过 kubectl 或其他 api 客户端提交需要创建的 pod 信息给 apiServer。
-
apiServer 开始生成 pod 对象的信息,并将信息存入 etcd,然后返回确认信息至客户端。
-
apiServer 开始反映 etcd 中的 pod 对象的变化,其它组件使用 watch 机制(etcd 提供)来跟踪检查 apiServer 上的变动。
-
scheduler 发现有新的 pod 对象要创建,开始为 Pod 分配主机并将结果信息更新至 apiServer。
-
node 节点上的 kubelet 发现有 pod 调度过来,尝试调用 docker 启动容器,并将结果回送至 apiServer。
-
apiServer 将接收到的 pod 状态信息存入 etcd 中。

pod 的终止过程。
- 用户向 apiServer 发送删除 pod 对象的命令。
- apiServcer 中的 pod 对象信息会随着时间的推移而更新,在宽限期内(默认30s),pod 被视为 dead。
- 将 pod 标记为 terminating 状态。
- kubelet 在监控到 pod 对象转为 terminating 状态的同时启动 pod 关闭过程。
- 端点控制器监控到 pod 对象的关闭行为时将其从所有匹配到此端点的 service 资源的端点列表中移除。
- 如果当前 pod 对象定义了 preStop 钩子处理器,则在其标记为 terminating 后即会以同步的方式启动执行。
- pod 对象中的容器进程收到停止信号。
- 宽限期结束后,若 pod 中还存在仍在运行的进程,那么 pod 对象会收到立即终止的信号。
- kubelet 请求 apiServer 将此 pod 资源的宽限期设置为 0 从而完成删除操作,此时 pod 对于用户已不可见。
5.3.2 初始化容器。
初始化容器是在 pod 的主容器启动之前要运行的容器,主要是做一些主容器的前置工作,ta 具有两大特征。
- 初始化容器必须运行完成直至结束,若某初始化容器运行失败,那么 kubernetes 需要重启它直到成功完成。
- 初始化容器必须按照定义的顺序执行,当且仅当前一个成功之后,后面的一个才能运行。
初始化容器有很多的应用场景,下面列出的是最常见的几个。
- 提供主容器镜像中不具备的工具程序或自定义代码。
- 初始化容器要先于应用容器串行启动并运行完成,因此可用于延后应用容器的启动直至其依赖的条件得到满足。
接下来做一个案例,模拟下面这个需求。
假设要以主容器来运行 nginx,但是要求在运行 nginx 之前先要能够连接上 mysql 和 redis 所在服务器。
为了简化测试,事先规定好 mysql(192.168.90.14)和 redis(192.168.90.15)服务器的地址。
创建 pod-initcontainer.yaml,内容如下。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-initcontainer
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- name: main-container
image: nginx:1.17.1
ports:
- name: nginx-port
containerPort: 80
initContainers:
- name: test-mysql
image: busybox:1.30
command: ['sh', '-c', 'until ping 192.168.142.9 -c 1; do echo waiting for mysql...; sleep 2; done;']
- name: test-redis
image: busybox:1.30
command: ['sh', '-c', 'until ping 192.168.142.10 -c 1; do echo waiting for reids...; sleep 2; done;']
# 创建 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pod-initcontainer.yaml
pod/pod-initcontainer created
# 查看 pod 状态。
# 发现 pod 卡在启动第一个初始化容器过程中,后面的容器不会运行。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl describe pod pod-initcontainer -n dev
Name: pod-initcontainer
Namespace: dev
Priority: 0
Node: localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2/192.168.142.152
Start Time: Sat, 03 Dec 2022 15:01:41 +0800
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Status: Pending
IP: 10.244.2.23
IPs:
IP: 10.244.2.23
Init Containers:
test-mysql:
Container ID: docker://1f138691a56326f1ee619c2afb9a158ba576504f4edb1b154d1deaf386afda3c
Image: busybox:1.30
Image ID: docker-pullable://busybox@sha256:4b6ad3a68d34da29bf7c8ccb5d355ba8b4babcad1f99798204e7abb43e54ee3d
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
Command:
sh
-c
until ping 192.168.142.9 -c 1; do echo waiting for mysql...; sleep 2; done;
State: Running
Started: Sat, 03 Dec 2022 15:01:42 +0800
Ready: False
Restart Count: 0
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-n8qxp (ro)
test-redis:
Container ID:
Image: busybox:1.30
Image ID:
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
Command:
sh
-c
until ping 192.168.142.10 -c 1; do echo waiting for reids...; sleep 2; done;
State: Waiting
Reason: PodInitializing
Ready: False
Restart Count: 0
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-n8qxp (ro)
Containers:
main-container:
Container ID:
Image: nginx:1.17.1
Image ID:
Port: 80/TCP
Host Port: 0/TCP
State: Waiting
Reason: PodInitializing
Ready: False
Restart Count: 0
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-n8qxp (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized False
Ready False
ContainersReady False
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
default-token-n8qxp:
Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret)
SecretName: default-token-n8qxp
Optional: false
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 26s default-scheduler Successfully assigned dev/pod-initcontainer to localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2
Normal Pulled 26s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Container image "busybox:1.30" already present on machine
Normal Created 26s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Created container test-mysql
Normal Started 25s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Started container test-mysql
# 动态查看 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods pod-initcontainer -n dev -w
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod-initcontainer 0/1 Init:0/2 0 72s
# 接下来新开一个 shell,为当前服务器新增两个 ip,观察 pod 的变化。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# ifconfig ens33:1 192.168.142.10 netmask 255.255.255.0 up
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# ifconfig ens33:2 192.168.142.9 netmask 255.255.255.0 up
5.3.3 钩子函数。
钩子函数能够感知自身生命周期中的事件,并在相应的时刻到来时运行用户指定的程序代码。
kubernetes 在主容器的启动之后和停止之前提供了两个钩子函数。
- post start:容器创建之后执行,如果失败了会重启容器。
- pre stop :容器终止之前执行,执行完成之后容器将成功终止,在其完成之前会阻塞删除容器的操作。
钩子处理器支持使用下面三种方式定义动作。
- Exec 命令:在容器内执行一次命令。
。。。
lifecycle:
postStart:
exec:
command:
- cat
- /tmp/healthy
。。。
- TCPSocket:在当前容器尝试访问指定的 socket。
。。。
lifecycle:
postStart:
tcpSocket:
port: 8080
。。。
- HTTPGet:在当前容器中向某 url 发起 http 请求。
。。。
lifecycle:
postStart:
httpGet:
path: / # URI 地址。
port: 80 # 端口号。
host: 192.168.5.3 # 主机地址。
scheme: HTTP # 支持的协议,http 或者 https。
。。。
接下来,以 exec 方式为例,演示下钩子函数的使用,创建 pod-hook-exec.yaml 文件,内容如下。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-hook-exec
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- name: main-container
image: nginx:1.17.1
ports:
- name: nginx-port
containerPort: 80
lifecycle:
postStart:
exec: # 在容器启动的时候执行一个命令,修改掉 nginx 的默认首页内容。
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "echo postStart... > /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html"]
preStop:
exec: # 在容器停止之前停止 nginx 服务。
command: ["/usr/sbin/nginx", "-s", "quit"]
# 创建 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim pod-hook-exec.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pod-hook-exec.yaml
pod/pod-hook-exec created
# 查看 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods pod-hook-exec -n dev -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
pod-hook-exec 1/1 Running 0 30s 10.244.2.24 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 <none> <none>
# 访问 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# curl 10.244.2.24
curl: (7) Failed connect to 10.244.2.24:80; Connection refused
[root@localhost k8s]# curl 10.244.2.24:80
5.3.4 容器探测。
容器探测用于检测容器中的应用实例是否正常工作,是保障业务可用性的一种传统机制。如果经过探测,实例的状态不符合预期,那么 kubernetes 就会把该问题实例"摘除",不承担业务流量。kubernetes 提供了两种探针来实现容器探测,分别是:
- liveness probes:存活性探针,用于检测应用实例当前是否处于正常运行状态,如果不是,k8s 会重启容器。
- readiness probes:就绪性探针,用于检测应用实例当前是否可以接收请求,如果不能,k8s 不会转发流量。
livenessProbe 决定是否重启容器,readinessProbe 决定是否将请求转发给容器。
上面两种探针目前均支持三种探测方式:
- Exec 命令:在容器内执行一次命令,如果命令执行的退出码为 0,则认为程序正常,否则不正常。
。。。
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- cat
- /tmp/healthy
。。。
- TCPSocket:将会尝试访问一个用户容器的端口,如果能够建立这条连接,则认为程序正常,否则不正常。
。。。
livenessProbe:
tcpSocket:
port: 8080
。。。
- HTTPGet:调用容器内 Web 应用的 URL,如果返回的状态码在 200 和 399 之间,则认为程序正常,否则不正常。
。。。
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: / # URI 地址。
port: 80 # 端口号。
host: 127.0.0.1 # 主机地址。
scheme: HTTP # 支持的协议,http 或者 https。
。。。
下面以 liveness probes 为例,做几个演示。
方式一:Exec。
创建 pod-liveness-exec.yaml。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-liveness-exec
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
ports:
- name: nginx-port
containerPort: 80
livenessProbe:
exec:
command: ["/bin/cat", "/tmp/hello.txt"] # 执行一个查看文件的命令。
创建 pod,观察效果。
# 创建 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim pod-liveness-exec.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pod-liveness-exec.yaml
pod/pod-liveness-exec created
# 查看 Pod 详情。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl describe pods pod-liveness-exec -n dev
Name: pod-liveness-exec
Namespace: dev
Priority: 0
Node: localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2/192.168.142.152
Start Time: Sat, 03 Dec 2022 15:33:19 +0800
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Status: Running
IP: 10.244.2.25
IPs:
IP: 10.244.2.25
Containers:
nginx:
Container ID: docker://d793bc844ad1ae63a2c318a42d95cafcfa5d46951ee7988c308afd659b4924ad
Image: nginx:1.17.1
Image ID: docker-pullable://nginx@sha256:b4b9b3eee194703fc2fa8afa5b7510c77ae70cfba567af1376a573a967c03dbb
Port: 80/TCP
Host Port: 0/TCP
State: Running
Started: Sat, 03 Dec 2022 15:33:21 +0800
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Liveness: exec [/bin/cat /tmp/hello.txt] delay=0s timeout=1s period=10s #success=1 #failure=3
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-n8qxp (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready True
ContainersReady True
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
default-token-n8qxp:
Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret)
SecretName: default-token-n8qxp
Optional: false
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 24s default-scheduler Successfully assigned dev/pod-liveness-exec to localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2
Normal Pulled 23s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Container image "nginx:1.17.1" already present on machine
Normal Created 23s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Created container nginx
Normal Started 22s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Started container nginx
Warning Unhealthy 8s (x2 over 18s) kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Liveness probe failed: /bin/cat: /tmp/hello.txt: No such file or directory
# 观察上面的信息就会发现 nginx 容器启动之后就进行了健康检查。
# 检查失败之后,容器被 kill 掉,然后尝试进行重启(这是重启策略的作用,后面讲解)。
# 稍等一会之后,再观察 pod 信息,就可以看到 RESTARTS 不再是 0,而是一直增长。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods pod-liveness-exec -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod-liveness-exec 1/1 Running 2 75s
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods pod-liveness-exec -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod-liveness-exec 0/1 CrashLoopBackOff 4 2m30s
# 当然接下来,可以修改成一个存在的文件,比如 ls /tmp,再试,结果就正常了。
方式二:TCPSocket。
创建 pod-liveness-tcpsocket.yaml。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-liveness-tcpsocket
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
ports:
- name: nginx-port
containerPort: 80
livenessProbe:
tcpSocket:
port: 8080 # 尝试访问 8080 端口。
创建 pod,观察效果。
# 创建 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim pod-liveness-tcpsocket.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl delete -f pod-liveness-tcpsocket.yaml
Error from server (NotFound): error when deleting "pod-liveness-tcpsocket.yaml": pods "pod-liveness-tcpsocket" not found
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pod-liveness-tcpsocket.yaml
pod/pod-liveness-tcpsocket created
# 查看 Pod 详情
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods pod-liveness-tcpsocket -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod-liveness-tcpsocket 1/1 Running 1 32s
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl describe pods pod-liveness-tcpsocket -n dev
Name: pod-liveness-tcpsocket
Namespace: dev
Priority: 0
Node: localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2/192.168.142.152
Start Time: Sat, 03 Dec 2022 15:39:33 +0800
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Status: Running
IP: 10.244.2.27
IPs:
IP: 10.244.2.27
Containers:
nginx:
Container ID: docker://cc5286f2e45ebd642aad55b098a7f5cd292649649e0abce54e8d250f0ddf87a2
Image: nginx:1.17.1
Image ID: docker-pullable://nginx@sha256:b4b9b3eee194703fc2fa8afa5b7510c77ae70cfba567af1376a573a967c03dbb
Port: 80/TCP
Host Port: 0/TCP
State: Running
Started: Sat, 03 Dec 2022 15:39:59 +0800
Last State: Terminated
Reason: Completed
Exit Code: 0
Started: Sat, 03 Dec 2022 15:39:35 +0800
Finished: Sat, 03 Dec 2022 15:39:58 +0800
Ready: True
Restart Count: 1
Liveness: tcp-socket :8080 delay=0s timeout=1s period=10s #success=1 #failure=3
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-n8qxp (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready True
ContainersReady True
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
default-token-n8qxp:
Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret)
SecretName: default-token-n8qxp
Optional: false
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 49s default-scheduler Successfully assigned dev/pod-liveness-tcpsocket to localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2
Normal Pulled 24s (x2 over 48s) kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Container image "nginx:1.17.1" already present on machine
Normal Created 24s (x2 over 48s) kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Created container nginx
Normal Killing 24s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Container nginx failed liveness probe, will be restarted
Normal Started 23s (x2 over 47s) kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Started container nginx
Warning Unhealthy 4s (x5 over 44s) kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Liveness probe failed: dial tcp 10.244.2.27:8080: connect: connection refused
# 观察上面的信息,发现尝试访问 8080 端口,但是失败了。
# 稍等一会之后,再观察 pod 信息,就可以看到 RESTARTS 不再是 0,而是一直增长。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods pod-liveness-tcpsocket -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod-liveness-tcpsocket 1/1 Running 4 2m7s
# 当然接下来,可以修改成一个可以访问的端口,比如 80,再试,结果就正常了......
方式三:HTTPGet。
创建 pod-liveness-httpget.yaml。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-liveness-httpget
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
ports:
- name: nginx-port
containerPort: 80
livenessProbe:
httpGet: # 其实就是访问 http://127.0.0.1:80/hello
scheme: HTTP # 支持的协议,http 或者 https。
port: 80 # 端口号。
path: /hello # URI 地址。
创建 pod,观察效果。
# 创建 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim pod-liveness-httpget.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pod-liveness-httpget.yaml
pod/pod-liveness-httpget created
# 查看 Pod 详情。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl describe pod pod-liveness-httpget -n dev
Name: pod-liveness-httpget
Namespace: dev
Priority: 0
Node: localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2/192.168.142.152
Start Time: Sat, 03 Dec 2022 15:43:59 +0800
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Status: Running
IP: 10.244.2.28
IPs:
IP: 10.244.2.28
Containers:
nginx:
Container ID: docker://4013170e9f8d37db6b3bc6bb59eac50d93b4b42b4ba76f55ace2862a34ad4570
Image: nginx:1.17.1
Image ID: docker-pullable://nginx@sha256:b4b9b3eee194703fc2fa8afa5b7510c77ae70cfba567af1376a573a967c03dbb
Port: 80/TCP
Host Port: 0/TCP
State: Running
Started: Sat, 03 Dec 2022 15:44:00 +0800
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Liveness: http-get http://:80/hello delay=0s timeout=1s period=10s #success=1 #failure=3
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-n8qxp (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready True
ContainersReady True
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
default-token-n8qxp:
Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret)
SecretName: default-token-n8qxp
Optional: false
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 13s default-scheduler Successfully assigned dev/pod-liveness-httpget to localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2
Normal Pulled 12s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Container image "nginx:1.17.1" already present on machine
Normal Created 12s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Created container nginx
Normal Started 12s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Started container nginx
Warning Unhealthy 7s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Liveness probe failed: HTTP probe failed with statuscode: 404
# 观察上面信息,尝试访问路径,但是未找到,出现 404 错误。
# 稍等一会之后,再观察 pod 信息,就可以看到 RESTARTS 不再是 0,而是一直增长。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pod pod-liveness-httpget -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod-liveness-httpget 1/1 Running 2 68s
# 当然接下来,可以修改成一个可以访问的路径 path,比如 /,再试,结果就正常了。
至此,已经使用 liveness Probe 演示了三种探测方式,但是查看 livenessProbe 的子属性,会发现除了这三种方式,还有一些其他的配置,在这里一并解释下。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl explain pod.spec.containers.livenessProbe
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1
RESOURCE: livenessProbe <Object>
DESCRIPTION:
Periodic probe of container liveness. Container will be restarted if the
probe fails. Cannot be updated. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-lifecycle#container-probes
Probe describes a health check to be performed against a container to
determine whether it is alive or ready to receive traffic.
FIELDS:
exec <Object>
One and only one of the following should be specified. Exec specifies the
action to take.
# 连续探测失败多少次才被认定为失败。默认是 3。最小值是 1。
failureThreshold <integer>
Minimum consecutive failures for the probe to be considered failed after
having succeeded. Defaults to 3. Minimum value is 1.
httpGet <Object>
HTTPGet specifies the http request to perform.
# 容器启动后等待多少秒执行第一次探测。
initialDelaySeconds <integer>
Number of seconds after the container has started before liveness probes
are initiated. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-lifecycle#container-probes
# 执行探测的频率。默认是 10 秒,最小 1 秒。
periodSeconds <integer>
How often (in seconds) to perform the probe. Default to 10 seconds. Minimum
value is 1.
# 连续探测成功多少次才被认定为成功。默认是 1。
successThreshold <integer>
Minimum consecutive successes for the probe to be considered successful
after having failed. Defaults to 1. Must be 1 for liveness and startup.
Minimum value is 1.
tcpSocket <Object>
TCPSocket specifies an action involving a TCP port. TCP hooks not yet
supported
# 探测超时时间。默认 1 秒,最小 1 秒。
timeoutSeconds <integer>
Number of seconds after which the probe times out. Defaults to 1 second.
Minimum value is 1. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-lifecycle#container-probes
下面稍微配置两个,演示下效果即可:
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# more pod-liveness-httpget.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-liveness-httpget
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
ports:
- name: nginx-port
containerPort: 80
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
scheme: HTTP
port: 80
path: /
initialDelaySeconds: 30 # 容器启动后 30s 开始探测。
timeoutSeconds: 5 # 探测超时时间为 5s。
5.3.5 重启策略。
在上一节中,一旦容器探测出现了问题,kubernetes 就会对容器所在的 Pod 进行重启,其实这是由 pod 的重启策略决定的,pod 的重启策略有 3 种,分别如下。
- Always :容器失效时,自动重启该容器,这也是默认值。
- OnFailure : 容器终止运行且退出码不为 0 时重启。
- Never : 不论状态为何,都不重启该容器。
重启策略适用于 pod 对象中的所有容器,首次需要重启的容器,将在其需要时立即进行重启,随后再次需要重启的操作将由 kubelet 延迟一段时间后进行,且反复的重启操作的延迟时长以此为10s、20s、40s、80s、160s 和 300s,300s 是最大延迟时长。
创建 pod-restartpolicy.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-restartpolicy
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
ports:
- name: nginx-port
containerPort: 80
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
scheme: HTTP
port: 80
path: /hello
restartPolicy: Never # 设置重启策略为 Never。
运行 Pod 测试。
# 创建 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim pod-restartpolicy.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pod-restartpolicy.yaml
pod/pod-restartpolicy created
# 查看 Pod 详情,发现 nginx 容器失败。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl describe pods pod-restartpolicy -n dev
Name: pod-restartpolicy
Namespace: dev
Priority: 0
Node: localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2/192.168.142.152
Start Time: Sat, 03 Dec 2022 15:50:00 +0800
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Status: Running
IP: 10.244.2.29
IPs:
IP: 10.244.2.29
Containers:
nginx:
Container ID: docker://5e3a86bc04bf5eff2a861c0db69fb2c87ae730fe680b633def25d7a18c08ed05
Image: nginx:1.17.1
Image ID: docker-pullable://nginx@sha256:b4b9b3eee194703fc2fa8afa5b7510c77ae70cfba567af1376a573a967c03dbb
Port: 80/TCP
Host Port: 0/TCP
State: Running
Started: Sat, 03 Dec 2022 15:50:01 +0800
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Liveness: http-get http://:80/hello delay=0s timeout=1s period=10s #success=1 #failure=3
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-n8qxp (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready True
ContainersReady True
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
default-token-n8qxp:
Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret)
SecretName: default-token-n8qxp
Optional: false
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 17s default-scheduler Successfully assigned dev/pod-restartpolicy to localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2
Normal Pulled 16s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Container image "nginx:1.17.1" already present on machine
Normal Created 16s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Created container nginx
Normal Started 16s kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Started container nginx
Warning Unhealthy 3s (x2 over 13s) kubelet, localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Liveness probe failed: HTTP probe failed with statuscode: 404
# 多等一会,再观察 pod 的重启次数,发现一直是 0,并未重启。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods pod-restartpolicy -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod-restartpolicy 0/1 Completed 0 78s
5.4 Pod 调度。
在默认情况下,一个 Pod 在哪个 Node 节点上运行,是由 Scheduler 组件采用相应的算法计算出来的,这个过程是不受人工控制的。但是在实际使用中,这并不满足的需求,因为很多情况下,我们想控制某些 Pod 到达某些节点上,那么应该怎么做呢?这就要求了解 kubernetes 对 Pod 的调度规则,kubernetes 提供了四大类调度方式。
- 自动调度:运行在哪个节点上完全由 Scheduler 经过一系列的算法计算得出。
- 定向调度:NodeName、NodeSelector。
- 亲和性调度:NodeAffinity、PodAffinity、PodAntiAffinity。
- 污点(容忍)调度:Taints、Toleration。
5.4.1 定向调度。
定向调度,指的是利用在 pod 上声明 nodeName 或者 nodeSelector,以此将 Pod 调度到期望的 node 节点上。注意,这里的调度是强制的,这就意味着即使要调度的目标 Node 不存在,也会向上面进行调度,只不过 pod 运行失败而已。
- NodeName。
NodeName 用于强制约束将 Pod 调度到指定的 Name 的 Node 节点上。这种方式,其实是直接跳过 Scheduler 的调度逻辑,直接将 Pod 调度到指定名称的节点。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
localhost.localdomain.k8s.master Ready master 39h v1.17.4
localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 Ready <none> 39h v1.17.4
localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Ready <none> 39h v1.17.4
接下来,实验一下:创建一个 pod-nodename.yaml 文件。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-nodename
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
nodeName: localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 # 指定调度到 node2 节点上。
# 创建 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim pod-nodename.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pod-nodename.yaml
pod/pod-nodename created
# 查看 Pod 调度到 NODE 属性,确实是调度到了 node1 节点上。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods pod-nodename -n dev -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
pod-nodename 1/1 Running 0 31s 10.244.2.30 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 <none> <none>
# 接下来,删除 pod,修改 nodeName 的值为 node3(并没有 node3 节点)。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim pod-nodename.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl delete -f pod-nodename.yaml
pod "pod-nodename" deleted
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pod-nodename.yaml
pod/pod-nodename created
# 再次查看,发现已经向 Node3节点调度,但是由于不存在 node3 节点,所以 pod 无法正常运行。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods pod-nodename -n dev -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
pod-nodename 0/1 Pending 0 27s <none> localhost.localdomain.k8s.node3 <none> <none>
- NodeSelector。
NodeSelector 用于将 pod 调度到添加了指定标签的 node 节点上。它是通过 kubernetes 的 label-selector 机制实现的,也就是说,在 pod 创建之前,会由 scheduler 使用 MatchNodeSelector 调度策略进行 label 匹配,找出目标 node,然后将 pod 调度到目标节点,该匹配规则是强制约束。
接下来,实验一下。
1 首先分别为 node 节点添加标签。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl label nodes localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 nodeenv=prod
node/localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 labeled
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl label nodes localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 nodeenv=dev
node/localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 labeled
2 创建一个 pod-nodeselector.yaml 文件,并使用它创建 Pod。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-nodeselector
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
nodeSelector:
nodeenv: prod # 指定调度到具有 nodeenv=pro 标签的节点上。
# 创建 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim pod-nodeselector.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pod-nodeselector.yaml
pod/pod-nodeselector created
# 查看 Pod 调度到 NODE 属性,确实是调度到了 node1 节点上。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods pod-nodeselector -n dev -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
pod-nodeselector 1/1 Running 0 8s 10.244.1.12 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 <none> <none>
# 接下来,删除 pod,修改 nodeSelector 的值为 nodeenv: xxxx(不存在打有此标签的节点)。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl delete -f pod-nodeselector.yaml
pod "pod-nodeselector" deleted
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# vim pod-nodeselector.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl create -f pod-nodeselector.yaml
pod/pod-nodeselector created。
# 再次查看,发现 pod 无法正常运行,Node 的值为 none。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods pod-nodeselector -n dev -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
pod-nodeselector 0/1 Pending 0 21s <none> <none> <none> <none>
# 查看详情,发现 node selector 匹配失败的提示
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl describe pods pod-nodeselector -n dev
Name: pod-nodeselector
Namespace: dev
Priority: 0
Node: <none>
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Status: Pending
IP:
IPs: <none>
Containers:
nginx:
Image: nginx:1.17.1
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-n8qxp (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
PodScheduled False
Volumes:
default-token-n8qxp:
Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret)
SecretName: default-token-n8qxp
Optional: false
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: nodeenv=pro
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Warning FailedScheduling 5s default-scheduler 0/3 nodes are available: 3 node(s) didn't match node selector.
5.4.2 亲和性调度。
上一节,介绍了两种定向调度的方式,使用起来非常方便,但是也有一定的问题,那就是如果没有满足条件的 Node,那么 Pod 将不会被运行,即使在集群中还有可用 Node 列表也不行,这就限制了它的使用场景。
基于上面的问题,kubernetes 还提供了一种亲和性调度(Affinity)。它在 NodeSelector 的基础之上的进行了扩展,可以通过配置的形式,实现优先选择满足条件的 Node 进行调度,如果没有,也可以调度到不满足条件的节点上,使调度更加灵活。
Affinity 主要分为三类。
- nodeAffinity(node 亲和性):以 node 为目标,解决 pod 可以调度到哪些 node 的问题。
- podAffinity(pod 亲和性):以 pod 为目标,解决 pod 可以和哪些已存在的 pod 部署在同一个拓扑域中的问题。
- podAntiAffinity(pod 反亲和性):以 pod 为目标,解决 pod 不能和哪些已存在 pod 部署在同一个拓扑域中的问题。
关于亲和性(反亲和性)使用场景的说明。
亲和性:如果两个应用频繁交互,那就有必要利用亲和性让两个应用的尽可能的靠近,这样可以减少因网络通信而带来的性能损耗。
反亲和性:当应用的采用多副本部署时,有必要采用反亲和性让各个应用实例打散分布在各个 node 上,这样可以提高服务的高可用性。
affinity
n. 密切关系; 喜好; 喜爱; 密切的关系; 类同;
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl explain pod.spec.affinity
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1
RESOURCE: affinity <Object>
DESCRIPTION:
If specified, the pod's scheduling constraints
Affinity is a group of affinity scheduling rules.
FIELDS:
nodeAffinity <Object>
Describes node affinity scheduling rules for the pod.
podAffinity <Object>
Describes pod affinity scheduling rules (e.g. co-locate this pod in the
same node, zone, etc. as some other pod(s)).
podAntiAffinity <Object>
Describes pod anti-affinity scheduling rules (e.g. avoid putting this pod
in the same node, zone, etc. as some other pod(s)).
- NodeAffinity。
首先来看一下 NodeAffinity 的可配置项。
pod.spec.affinity.nodeAffinity
- requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution <Object> ~ Node 节点必须满足指定的所有规则才可以,相当于硬限制。
- - nodeSelectorTerms 节点选择列表。
matchFields 按节点字段列出的节点选择器要求列表。
matchExpressions 按节点标签列出的节点选择器要求列表(推荐)。
key 键
values 值
operator 关系符 支持 Exists, DoesNotExist, In, NotIn, Gt, Lt
- - preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution <[]Object> 优先调度到满足指定的规则的 Node,相当于软限制(倾向)。
preference 一个节点选择器项,与相应的权重相关联。
matchFields 按节点字段列出的节点选择器要求列表。
matchExpressions 按节点标签列出的节点选择器要求列表(推荐)。
key 键
values 值
operator 关系符 支持 In, NotIn, Exists, DoesNotExist, Gt, Lt
weight 倾向权重,在范围 1-100。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl explain pod.spec.affinity.nodeAffinity
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1
RESOURCE: nodeAffinity <Object>
DESCRIPTION:
Describes node affinity scheduling rules for the pod.
Node affinity is a group of node affinity scheduling rules.
FIELDS:
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution <[]Object>
The scheduler will prefer to schedule pods to nodes that satisfy the
affinity expressions specified by this field, but it may choose a node that
violates one or more of the expressions. The node that is most preferred is
the one with the greatest sum of weights, i.e. for each node that meets all
of the scheduling requirements (resource request, requiredDuringScheduling
affinity expressions, etc.), compute a sum by iterating through the
elements of this field and adding "weight" to the sum if the node matches
the corresponding matchExpressions; the node(s) with the highest sum are
the most preferred.
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution <Object>
If the affinity requirements specified by this field are not met at
scheduling time, the pod will not be scheduled onto the node. If the
affinity requirements specified by this field cease to be met at some point
during pod execution (e.g. due to an update), the system may or may not try
to eventually evict the pod from its node.
关系符的使用说明。
- matchExpressions:
- key: nodeenv # 匹配存在标签的 key 为 nodeenv 的节点。
operator: Exists
- key: nodeenv # 匹配标签的 key 为 nodeenv,且 value 是 "xxx" 或 "yyy" 的节点。
operator: In
values: ["xxx","yyy"]
- key: nodeenv # 匹配标签的 key 为 nodeenv,且 value 大于 "xxx" 的节点。
operator: Gt
values: "xxx"
接下来首先演示一下 requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution。
创建 pod-nodeaffinity-required.yaml。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-nodeaffinity-required
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
affinity: # 亲和性设置。
nodeAffinity: # 设置 node 亲和性。
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: # 硬限制。
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions: # 匹配 env 的值在["xxx", "yyy"]中的标签。
- key: nodeenv
operator: In
values: ["xxx", "yyy"]
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get nodes --show-labels
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION LABELS
localhost.localdomain.k8s.master Ready master 2d23h v1.17.4 beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=localhost.localdomain.k8s.master,kubernetes.io/os=linux,node-role.kubernetes.io/master=
localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 Ready <none> 2d23h v1.17.4 beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1,kubernetes.io/os=linux,nodeenv=prod
localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 Ready <none> 2d23h v1.17.4 beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2,kubernetes.io/os=linux,nodeenv=dev
# 创建 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim pod-nodeaffinity-required.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pod-nodeaffinity-required.yaml
pod/pod-nodeaffinity-required created
# 查看 pod 状态(运行失败)。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods pod-nodeaffinity-required -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod-nodeaffinity-required 0/1 Pending 0 16s
# 查看 Pod 的详情。
# 发现调度失败,提示 node 选择失败。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl describe pods pod-nodeaffinity-required -n dev
Name: pod-nodeaffinity-required
Namespace: dev
Priority: 0
Node: <none>
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Status: Pending
IP:
IPs: <none>
Containers:
nginx:
Image: nginx:1.17.1
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-n8qxp (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
PodScheduled False
Volumes:
default-token-n8qxp:
Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret)
SecretName: default-token-n8qxp
Optional: false
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Warning FailedScheduling 28s (x2 over 28s) default-scheduler 0/3 nodes are available: 3 node(s) didn't match node selector.
# 接下来,停止 pod。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl delete -f pod-nodeaffinity-required.yaml
pod "pod-nodeaffinity-required" deleted
# 修改文件,将 values: ["xxx","yyy"] --> ["prod","yyy"]。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# vim pod-nodeaffinity-required.yaml
# 再次启动。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pod-nodeaffinity-required.yaml
pod/pod-nodeaffinity-required created
# 此时查看,发现调度成功,已经将 pod 调度到了 node1 上。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods pod-nodeaffinity-required -n dev -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
pod-nodeaffinity-required 1/1 Running 0 12s 10.244.1.14 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 <none> <none>
接下来再演示一下requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution。
创建 pod-nodeaffinity-preferred.yaml。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-nodeaffinity-preferred
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
affinity: # 亲和性设置。
nodeAffinity: # 设置 node 亲和性。
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: # 软限制。
- weight: 1
preference:
matchExpressions: # 匹配 env 的值在 ["xxx", "yyy"] 中的标签(当前环境没有)。
- key: nodeenv
operator: In
values: ["xxx", "yyy"]
# 创建 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim pod-nodeaffinity-preferred.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pod-nodeaffinity-preferred.yaml
pod/pod-nodeaffinity-preferred created
# 查看 pod 状态 (运行成功)。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pod pod-nodeaffinity-preferred -n dev -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
pod-nodeaffinity-preferred 1/1 Running 0 21s 10.244.2.33 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 <none> <none>
NodeAffinity 规则设置的注意事项。
-
如果同时定义了 nodeSelector 和 nodeAffinity,那么必须两个条件都得到满足,Pod 才能运行在指定的 Node 上。
-
如果 nodeAffinity 指定了多个 nodeSelectorTerms,那么只需要其中一个能够匹配成功即可。
-
如果一个 nodeSelectorTerms 中有多个 matchExpressions,则一个节点必须满足所有的才能匹配成功。
-
如果一个 pod 所在的 Node 在 Pod 运行期间其标签发生了改变,不再符合该 Pod 的节点亲和性需求,则系统将忽略此变化。
- PodAffinity。
PodAffinity 主要实现以运行的 Pod 为参照,实现让新创建的 Pod 跟参照 pod 在一个区域的功能。
首先来看一下 PodAffinity 的可配置项。
pod.spec.affinity.podAffinity
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution 硬限制。
namespaces 指定参照 pod 的 namespace。
topologyKey 指定调度作用域。
labelSelector 标签选择器。
matchExpressions 按节点标签列出的节点选择器要求列表(推荐)。
key 键。
values 值。
operator 关系符 支持 In, NotIn, Exists, DoesNotExist.
matchLabels 指多个 matchExpressions 映射的内容。
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution 软限制。
podAffinityTerm 选项。
namespaces
topologyKey
labelSelector
matchExpressions
key 键。
values 值。
operator
matchLabels
weight 倾向权重,在范围 1-100。
topologyKey 用于指定调度时作用域,例如:
如果指定为 kubernetes.io/hostname,那就是以 Node 节点为区分范围。
如果指定为 beta.kubernetes.io/os,则以 Node 节点的操作系统类型来区分。
接下来,演示下requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution。
1)首先创建一个参照 Pod,pod-podaffinity-target.yaml。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-podaffinity-target
namespace: dev
labels:
podenv: prod # 设置标签。
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
nodeName: localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 # 将目标 pod 名确指定到 node1 上。
# 启动目标 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pod-podaffinity-target.yaml
pod/pod-podaffinity-target created
# 查看 pod 状况。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods pod-podaffinity-target -n dev --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS
pod-podaffinity-target 1/1 Running 0 8s podenv=prod
2)创建 pod-podaffinity-required.yaml,内容如下。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-podaffinity-required
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
affinity: # 亲和性设置。
podAffinity: # 设置 pod 亲和性。
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: # 硬限制。
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions: # 匹配 env 的值在 ["xxx", "yyy"] 中的标签。
- key: podenv
operator: In
values: ["xxx", "yyy"]
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
上面配置表达的意思是:新 Pod 必须要与拥有标签 nodeenv=xxx 或者 nodeenv=yyy 的 pod 在同一 Node 上,显然现在没有这样 pod,接下来,运行测试一下。
# 启动 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pod-podaffinity-required.yaml
pod/pod-podaffinity-required created
# 查看 pod 状态,发现未运行。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods pod-podaffinity-required -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod-podaffinity-required 0/1 Pending 0 19s
# 查看详细信息。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl describe pods pod-podaffinity-required -n dev
Name: pod-podaffinity-required
Namespace: dev
Priority: 0
Node: <none>
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Status: Pending
IP:
IPs: <none>
Containers:
nginx:
Image: nginx:1.17.1
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-n8qxp (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
PodScheduled False
Volumes:
default-token-n8qxp:
Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret)
SecretName: default-token-n8qxp
Optional: false
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Warning FailedScheduling 49s default-scheduler 0/3 nodes are available: 1 node(s) had taints that the pod didn't tolerate, 2 node(s) didn't match pod affinity rules.
# 接下来修改 values: ["xxx", "yyy"] —> values: ["prod", "yyy"]。
# 意思是:新 Pod 必须要与拥有标签 nodeenv=xxx 或者 nodeenv=yyy 的 pod 在同一 Node 上。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# vim pod-podaffinity-required.yaml
# 然后重新创建 pod,查看效果。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl delete -f pod-podaffinity-required.yaml
pod "pod-podaffinity-required" deleted
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pod-podaffinity-required.yaml
pod/pod-podaffinity-required created
# 发现此时 Pod 运行正常。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods pod-podaffinity-required -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod-podaffinity-required 1/1 Running 0 32s
关于PodAffinity的 preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution,这里不再演示。
- PodAntiAffinity。
PodAntiAffinity 主要实现以运行的 Pod 为参照,让新创建的 Pod 跟参照 pod 不在一个区域中的功能。
它的配置方式和选项跟 PodAffinty 是一样的,这里不再做详细解释,直接做一个测试案例。
1)继续使用上个案例中目标 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev -o wide --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES LABELS
pod-podaffinity-required 1/1 Running 0 92s 10.244.1.17 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 <none> <none> <none>
pod-podaffinity-target 1/1 Running 0 5m30s 10.244.1.16 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 <none> <none> podenv=prod
2)创建 pod-podantiaffinity-required.yaml,内容如下。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-podantiaffinity-required
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
affinity: # 亲和性设置。
podAntiAffinity: # 设置 pod 亲和性。
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: # 硬限制。
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions: # 匹配 podenv 的值在 ["prod"] 中的标签。
- key: podenv
operator: In
values: ["prod"]
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
上面配置表达的意思是:新 Pod 必须要与拥有标签 nodeenv=pro 的 pod 不在同一 Node 上,运行测试一下。
# 创建 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pod-podantiaffinity-required.yaml
pod/pod-podantiaffinity-required created
# 查看 pod。
# 发现调度到了 node2 上。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods pod-podantiaffinity-required -n dev -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
pod-podantiaffinity-required 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 2s <none> localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 <none> <none>
5.4.3 污点和容忍。
- 污点(Taints)。
前面的调度方式都是站在 Pod 的角度上,通过在 Pod 上添加属性,来确定 Pod 是否要调度到指定的 Node 上,其实我们也可以站在 Node 的角度上,通过在 Node 上添加污点属性,来决定是否允许 Pod 调度过来。
Node 被设置上污点之后就和 Pod 之间存在了一种相斥的关系,进而拒绝 Pod 调度进来,甚至可以将已经存在的 Pod 驱逐出去。
污点的格式为:key=value:effect, key 和 value 是污点的标签;effect 描述污点的作用,支持如下三个选项。
- PreferNoSchedule:kubernetes 将尽量避免把 Pod 调度到具有该污点的 Node 上,除非没有其他节点可调度
- NoSchedule:kubernetes 将不会把 Pod 调度到具有该污点的 Node 上,但不会影响当前 Node 上已存在的 Pod
- NoExecute:kubernetes 将不会把 Pod 调度到具有该污点的 Node 上,同时也会将 Node 上已存在的 Pod 驱离。

使用 kubectl 设置和去除污点的命令示例如下。
# 设置污点。
kubectl taint nodes node1 key=value:effect
# 去除污点。
kubectl taint nodes node1 key:effect-
# 去除所有污点。
kubectl taint nodes node1 key-
接下来,演示下污点的效果。
- 准备节点 node1(为了演示效果更加明显,暂时停止 node2 节点)。
- 为 node1 节点设置一个污点:
tag=geek:PreferNoSchedule;然后创建 pod1(pod1 可以)。 - 修改为 node1 节点设置一个污点:
tag=geek:NoSchedule;然后创建 pod2(pod1 正常 pod2 失败)。 - 修改为 node1 节点设置一个污点:
tag=geek:NoExecute;然后创建 pod3(3 个 pod 都失败)。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
localhost.localdomain.k8s.master Ready master 3d v1.17.4
localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 Ready <none> 2d23h v1.17.4
localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 NotReady <none> 2d23h v1.17.4
# 为 node1 设置污点(PreferNoSchedule)。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# [root@localhost ~]# kubectl taint nodes localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 tag=geek:PreferNoSchedule
node/localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 tainted
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl describe nodes localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1
Name: localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1
Roles: <none>
Labels: beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64
beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux
kubernetes.io/arch=amd64
kubernetes.io/hostname=localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1
kubernetes.io/os=linux
nodeenv=prod
Annotations: flannel.alpha.coreos.com/backend-data: {"VNI":1,"VtepMAC":"66:a6:00:57:7a:a6"}
flannel.alpha.coreos.com/backend-type: vxlan
flannel.alpha.coreos.com/kube-subnet-manager: true
flannel.alpha.coreos.com/public-ip: 192.168.142.151
kubeadm.alpha.kubernetes.io/cri-socket: /var/run/dockershim.sock
node.alpha.kubernetes.io/ttl: 0
volumes.kubernetes.io/controller-managed-attach-detach: true
CreationTimestamp: Fri, 02 Dec 2022 00:25:48 +0800
Taints: tag=geek:PreferNoSchedule
Unschedulable: false
Lease:
HolderIdentity: localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1
AcquireTime: <unset>
RenewTime: Mon, 05 Dec 2022 13:56:18 +0800
Conditions:
Type Status LastHeartbeatTime LastTransitionTime Reason Message
---- ------ ----------------- ------------------ ------ -------
NetworkUnavailable False Sun, 04 Dec 2022 23:30:00 +0800 Sun, 04 Dec 2022 23:30:00 +0800 FlannelIsUp Flannel is running on this node
MemoryPressure False Mon, 05 Dec 2022 13:52:28 +0800 Fri, 02 Dec 2022 00:25:48 +0800 KubeletHasSufficientMemory kubelet has sufficient memory available
DiskPressure False Mon, 05 Dec 2022 13:52:28 +0800 Fri, 02 Dec 2022 00:25:48 +0800 KubeletHasNoDiskPressure kubelet has no disk pressure
PIDPressure False Mon, 05 Dec 2022 13:52:28 +0800 Fri, 02 Dec 2022 00:25:48 +0800 KubeletHasSufficientPID kubelet has sufficient PID available
Ready True Mon, 05 Dec 2022 13:52:28 +0800 Sun, 04 Dec 2022 23:30:02 +0800 KubeletReady kubelet is posting ready status
Addresses:
InternalIP: 192.168.142.151
Hostname: localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1
Capacity:
cpu: 4
ephemeral-storage: 47179256Ki
hugepages-1Gi: 0
hugepages-2Mi: 0
memory: 1862820Ki
pods: 110
Allocatable:
cpu: 4
ephemeral-storage: 43480402258
hugepages-1Gi: 0
hugepages-2Mi: 0
memory: 1760420Ki
pods: 110
System Info:
Machine ID: b0218335ca0f416b8fb63b6ee93ddc0e
System UUID: B57D4D56-529A-F125-26C4-7C12D02ABD9E
Boot ID: 42ee3a4d-08fa-41b4-a591-bee319cabf5e
Kernel Version: 3.10.0-1160.80.1.el7.x86_64
OS Image: CentOS Linux 7 (Core)
Operating System: linux
Architecture: amd64
Container Runtime Version: docker://18.6.3
Kubelet Version: v1.17.4
Kube-Proxy Version: v1.17.4
PodCIDR: 10.244.1.0/24
PodCIDRs: 10.244.1.0/24
Non-terminated Pods: (5 in total)
Namespace Name CPU Requests CPU Limits Memory Requests Memory Limits AGE
--------- ---- ------------ ---------- --------------- ------------- ---
default nginx-6867cdf567-tlmw5 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 3d
dev pod-podaffinity-required 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 13h
dev pod-podaffinity-target 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 13h
kube-flannel kube-flannel-ds-jgfg2 100m (2%) 100m (2%) 50Mi (2%) 50Mi (2%) 3d12h
kube-system kube-proxy-7hss2 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 3d13h
Allocated resources:
(Total limits may be over 100 percent, i.e., overcommitted.)
Resource Requests Limits
-------- -------- ------
cpu 100m (2%) 100m (2%)
memory 50Mi (2%) 50Mi (2%)
ephemeral-storage 0 (0%) 0 (0%)
Events: <none>
# 创建 pod1。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl run taint1 --image=nginx:1.17.1 -n dev
kubectl run --generator=deployment/apps.v1 is DEPRECATED and will be removed in a future version. Use kubectl run --generator=run-pod/v1 or kubectl create instead.
deployment.apps/taint1 created
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get pods -n dev -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
taint1-766c47bf55-h44gv 1/1 Running 0 18s 10.244.1.18 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 <none> <none>
# 为 node1 设置污点(取消 PreferNoSchedule,设置 NoSchedule)。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl taint nodes localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 tag:PreferNoSchedule-
node/localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 untainted
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl taint nodes localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 tag=geek:NoSchedule
node/localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 tainted
# 创建 pod2。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl run taint2 --image=nginx:1.17.1 -n dev
kubectl run --generator=deployment/apps.v1 is DEPRECATED and will be removed in a future version. Use kubectl run --generator=run-pod/v1 or kubectl create instead.
deployment.apps/taint2 created
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get pods taint2-84946958cf-d4498 -n dev -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
taint2-84946958cf-d4498 0/1 Pending 0 2m48s <none> <none> <none> <none>
<none>
# 为 node1设置污点(取消 NoSchedule,设置 NoExecute)。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl taint nodes localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 tag:NoSchedule-
node/localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 untainted
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl taint nodes localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 tag=geek:NoExecute
node/localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 tainted
# 创建 pod3。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl run taint3 --image=nginx:1.17.1 -n dev
kubectl run --generator=deployment/apps.v1 is DEPRECATED and will be removed in a future version. Use kubectl run --generator=run-pod/v1 or kubectl create instead.
deployment.apps/taint3 created
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get pods -n dev -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
taint1-766c47bf55-8f67k 0/1 Pending 0 48s <none> <none> <none> <none>
taint2-84946958cf-kwgnz 0/1 Pending 0 48s <none> <none> <none> <none>
taint3-57d45f9d4c-xr6m5 0/1 Pending 0 21s <none> <none> <none> <none>
小提示。
使用 kubeadm 搭建的集群,默认就会给 master 节点添加一个污点标记,所以 pod 就不会调度到 master 节点上。
Taints: node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl describe node localhost.localdomain.k8s.master
Name: localhost.localdomain.k8s.master
Roles: master
Labels: beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64
beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux
kubernetes.io/arch=amd64
kubernetes.io/hostname=localhost.localdomain.k8s.master
kubernetes.io/os=linux
node-role.kubernetes.io/master=
Annotations: flannel.alpha.coreos.com/backend-data: {"VNI":1,"VtepMAC":"96:44:60:1c:0b:7c"}
flannel.alpha.coreos.com/backend-type: vxlan
flannel.alpha.coreos.com/kube-subnet-manager: true
flannel.alpha.coreos.com/public-ip: 192.168.142.150
kubeadm.alpha.kubernetes.io/cri-socket: /var/run/dockershim.sock
node.alpha.kubernetes.io/ttl: 0
volumes.kubernetes.io/controller-managed-attach-detach: true
CreationTimestamp: Fri, 02 Dec 2022 00:20:13 +0800
Taints: node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule
Unschedulable: false
Lease:
HolderIdentity: localhost.localdomain.k8s.master
AcquireTime: <unset>
RenewTime: Mon, 05 Dec 2022 14:19:01 +0800
Conditions:
Type Status LastHeartbeatTime LastTransitionTime Reason Message
---- ------ ----------------- ------------------ ------ -------
NetworkUnavailable False Sun, 04 Dec 2022 23:30:04 +0800 Sun, 04 Dec 2022 23:30:04 +0800 FlannelIsUp Flannel is running on this node
MemoryPressure False Mon, 05 Dec 2022 14:17:22 +0800 Fri, 02 Dec 2022 00:20:09 +0800 KubeletHasSufficientMemory kubelet has sufficient memory available
DiskPressure False Mon, 05 Dec 2022 14:17:22 +0800 Fri, 02 Dec 2022 00:20:09 +0800 KubeletHasNoDiskPressure kubelet has no disk pressure
PIDPressure False Mon, 05 Dec 2022 14:17:22 +0800 Fri, 02 Dec 2022 00:20:09 +0800 KubeletHasSufficientPID kubelet has sufficient PID available
Ready True Mon, 05 Dec 2022 14:17:22 +0800 Fri, 02 Dec 2022 01:22:30 +0800 KubeletReady kubelet is posting ready status
Addresses:
InternalIP: 192.168.142.150
Hostname: localhost.localdomain.k8s.master
Capacity:
cpu: 4
ephemeral-storage: 47179256Ki
hugepages-1Gi: 0
hugepages-2Mi: 0
memory: 1862820Ki
pods: 110
Allocatable:
cpu: 4
ephemeral-storage: 43480402258
hugepages-1Gi: 0
hugepages-2Mi: 0
memory: 1760420Ki
pods: 110
System Info:
Machine ID: 9734395072ce48a9b565195bdbf0982d
System UUID: 9B324D56-75BB-F217-45D6-EF53F6928B12
Boot ID: b37848c2-96d0-4e60-928a-91e17849dc23
Kernel Version: 3.10.0-1160.80.1.el7.x86_64
OS Image: CentOS Linux 7 (Core)
Operating System: linux
Architecture: amd64
Container Runtime Version: docker://18.6.3
Kubelet Version: v1.17.4
Kube-Proxy Version: v1.17.4
PodCIDR: 10.244.0.0/24
PodCIDRs: 10.244.0.0/24
Non-terminated Pods: (8 in total)
Namespace Name CPU Requests CPU Limits Memory Requests Memory Limits AGE
--------- ---- ------------ ---------- --------------- ------------- ---
kube-flannel kube-flannel-ds-mtnd8 100m (2%) 100m (2%) 50Mi (2%) 50Mi (2%) 3d13h
kube-system coredns-9d85f5447-5959v 100m (2%) 0 (0%) 70Mi (4%) 170Mi (9%) 3d13h
kube-system coredns-9d85f5447-gvqxh 100m (2%) 0 (0%) 70Mi (4%) 170Mi (9%) 3d13h
kube-system etcd-localhost.localdomain.k8s.master 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 3d13h
kube-system kube-apiserver-localhost.localdomain.k8s.master 250m (6%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 3d13h
kube-system kube-controller-manager-localhost.localdomain.k8s.master 200m (5%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 3d13h
kube-system kube-proxy-rpnvx 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 3d13h
kube-system kube-scheduler-localhost.localdomain.k8s.master 100m (2%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 3d13h
Allocated resources:
(Total limits may be over 100 percent, i.e., overcommitted.)
Resource Requests Limits
-------- -------- ------
cpu 850m (21%) 100m (2%)
memory 190Mi (11%) 390Mi (22%)
ephemeral-storage 0 (0%) 0 (0%)
Events: <none>
- 容忍(Toleration)。
上面介绍了污点的作用,我们可以在 node 上添加污点用于拒绝 pod 调度上来,但是如果就是想将一个 pod 调度到一个有污点的 node 上去,这时候应该怎么做呢?这就要使用到容忍。

污点就是拒绝,容忍就是忽略,Node 通过污点拒绝 pod 调度上去,Pod 通过容忍忽略拒绝。
下面先通过一个案例看下效果:
- 上一小节,已经在 node1 节点上打上了
NoExecute的污点,此时 pod 是调度不上去的。 - 本小节,可以通过给 pod 添加容忍,然后将其调度上去。
创建 pod-toleration.yaml,内容如下。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-toleration
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
tolerations: # 容忍。
- key: "tag" # 要容忍的污点的 key。
operator: "Equal" # 操作符。
value: "geek" # 容忍的污点的 value。
effect: "NoExecute" # 添加容忍的规则,这里必须和标记的污点规则相同。
# 添加容忍之前的 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod-toleration 0/1 Pending 0 9s
taint1-766c47bf55-8f67k 0/1 Pending 0 25m
taint2-84946958cf-kwgnz 0/1 Pending 0 25m
taint3-57d45f9d4c-xr6m5 0/1 Pending 0 24m
# 添加容忍之后的 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
pod-toleration 1/1 Running 0 22s 10.244.1.22 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 <none> <none>
下面看一下容忍的详细配置。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl explain pod.spec.tolerations
......
FIELDS:
key # 对应着要容忍的污点的键,空意味着匹配所有的键。
value # 对应着要容忍的污点的值。
operator # key-value 的运算符,支持 Equal 和 Exists(默认)。
effect # 对应污点的 effect,空意味着匹配所有影响。
tolerationSeconds # 容忍时间, 当 effect 为 NoExecute 时生效,表示 pod 在 Node 上的停留时间。
6. Pod 控制器详解。
6.1 Pod 控制器介绍。
Pod 是 kubernetes 的最小管理单元,在 kubernetes 中,按照 pod 的创建方式可以将其分为两类。
- 自主式 pod:kubernetes 直接创建出来的 Pod,这种 pod 删除后就没有了,也不会重建。
- 控制器创建的 pod:kubernetes 通过控制器创建的 pod,这种 pod 删除了之后还会自动重建。
什么是 Pod 控制器。Pod 控制器是管理 pod 的中间层,使用 Pod 控制器之后,只需要告诉 Pod 控制器,想要多少个什么样的 Pod 就可以了,它会创建出满足条件的 Pod 并确保每一个 Pod 资源处于用户期望的目标状态。如果 Pod 资源在运行中出现故障,它会基于指定策略重新编排 Pod。
在 kubernetes 中,有很多类型的 pod 控制器,每种都有自己的适合的场景,常见的有下面这些:
- ReplicationController:比较原始的 pod 控制器,已经被废弃,由 ReplicaSet 替代。
- ReplicaSet:保证副本数量一直维持在期望值,并支持 pod 数量扩缩容,镜像版本升级。
- Deployment:通过控制 ReplicaSet 来控制 Pod,并支持滚动升级、回退版本。
- Horizontal Pod Autoscaler:可以根据集群负载自动水平调整 Pod 的数量,实现削峰填谷。
- DaemonSet:在集群中的指定 Node 上运行且仅运行一个副本,一般用于守护进程类的任务。
- Job:它创建出来的 pod 只要完成任务就立即退出,不需要重启或重建,用于执行一次性任务。
- Cronjob:它创建的 Pod 负责周期性任务控制,不需要持续后台运行。
- StatefulSet:管理有状态应用。
6.2 ReplicaSet(RS)。
ReplicaSet 的主要作用是保证一定数量的 pod 正常运行,它会持续监听这些 Pod 的运行状态,一旦 Pod 发生故障,就会重启或重建。同时它还支持对 pod 数量的扩缩容和镜像版本的升降级。

ReplicaSet 的资源清单文件。
apiVersion: apps/v1 # 版本号。
kind: ReplicaSet # 类型。
metadata: # 元数据。
name: # rs 名称。
namespace: # 所属命名空间。
labels: # 标签。
controller: rs
spec: # 详情描述。
replicas: 3 # 副本数量。
selector: # 选择器,通过它指定该控制器管理哪些 pod。
matchLabels: # Labels 匹配规则。
app: nginx-pod
matchExpressions: # Expressions 匹配规则。
- {key: app, operator: In, values: [nginx-pod]}
template: # 模板,当副本数量不足时,会根据下面的模板创建 pod 副本。
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
ports:
- containerPort: 80
在这里面,需要新了解的配置项就是 spec 下面几个选项。
-
replicas:指定副本数量,其实就是当前 rs 创建出来的 pod 的数量,默认为 1。
-
selector:选择器,它的作用是建立 pod 控制器和 pod 之间的关联关系,采用的 Label Selector 机制。
在 pod 模板上定义 label,在控制器上定义选择器,就可以表明当前控制器能管理哪些 pod 了。
- template:模板,就是当前控制器创建 pod 所使用的模板板,里面其实就是前一章学过的 pod 的定义。
创建 ReplicaSet。
创建 pc-replicaset.yaml 文件,内容如下。
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: ReplicaSet
metadata:
name: pc-replicaset
namespace: dev
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx-pod
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
# 创建 rs。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim pc-replicaset.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pc-replicaset.yaml
replicaset.apps/pc-replicaset created
# 查看 rs。
# DESIRED ~ 期望副本数量。
# CURRENT ~ 当前副本数量。
# READY ~ 已经准备好提供服务的副本数量。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get rs pc-replicaset -n dev -o wide
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR
pc-replicaset 3 3 0 49s nginx nginx:1.17.1 app=nginx-pod
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl describe rs pc-replicaset -n dev
Name: pc-replicaset
Namespace: dev
Selector: app=nginx-pod
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Replicas: 3 current / 3 desired
Pods Status: 0 Running / 3 Waiting / 0 Succeeded / 0 Failed
Pod Template:
Labels: app=nginx-pod
Containers:
nginx:
Image: nginx:1.17.1
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
Environment: <none>
Mounts: <none>
Volumes: <none>
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal SuccessfulCreate 78s replicaset-controller Created pod: pc-replicaset-64z8n
Normal SuccessfulCreate 78s replicaset-controller Created pod: pc-replicaset-74msh
Normal SuccessfulCreate 78s replicaset-controller Created pod: pc-replicaset-m5rsv
# 查看当前控制器创建出来的 pod。
# 这里发现控制器创建出来的 pod 的名称是在控制器名称后面拼接了-xxxxx 随机码。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl get pod -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pc-replicaset-6vmvt 1/1 Running 0 54s
pc-replicaset-fmb8f 1/1 Running 0 54s
pc-replicaset-snrk2 1/1 Running 0 54s
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl taint nodes localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 tag=geek:NoExecute-
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get rs pc-replicaset -n dev -o wide
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR
pc-replicaset 3 3 3 5m58s nginx nginx:1.17.1 app=nginx-pod
扩缩容。
# 编辑 rs 的副本数量,修改 spec:replicas: 6 即可。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl edit rs pc-replicaset -n dev
replicaset.apps/pc-replicaset edited
# 查看 pod。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get rs pc-replicaset -n dev -o wide
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR
pc-replicaset 6 6 6 23m nginx nginx:1.17.1 app=nginx-pod
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get pod -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pc-replicaset-5x5tx 1/1 Running 0 25s
pc-replicaset-64z8n 1/1 Running 0 23m
pc-replicaset-74msh 1/1 Running 0 23m
pc-replicaset-8fxqq 1/1 Running 0 25s
pc-replicaset-bbtj8 1/1 Running 0 25s
pc-replicaset-m5rsv 1/1 Running 0 23m
# 当然也可以直接使用命令实现。
# 使用 scale 命令实现扩缩容,后面 --replicas=n 直接指定目标数量即可。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl scale rs pc-replicaset --replicas=2 -n dev
replicaset.apps/pc-replicaset scaled
# 命令运行完毕,立即查看,发现已经有 4 个开始准备退出了。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get pods -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pc-replicaset-64z8n 1/1 Running 0 25m
pc-replicaset-74msh 1/1 Running 0 25m
pc-replicaset-ddzk9 1/1 Terminating 0 9s
pc-replicaset-gvsbq 0/1 Terminating 0 9s
pc-replicaset-m8q76 0/1 Terminating 0 9s
pc-replicaset-zn5xk 0/1 Terminating 0 9s
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pc-replicaset-64z8n 1/1 Running 0 26m
pc-replicaset-74msh 1/1 Running 0 26m
镜像升级。
# 编辑 rs 的容器镜像 - image: nginx:1.17.2
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl edit rs pc-replicaset -n dev
replicaset.apps/pc-replicaset edited
# 再次查看,发现镜像版本已经变更了。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get rs pc-replicaset -n dev -o wide
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR
pc-replicaset 2 2 2 28m nginx nginx:1.17.2 app=nginx-pod
# 同样的道理,也可以使用命令完成这个工作。
# kubectl set image rs rs 名称 容器=镜像版本 -n namespace
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl set image rs pc-replicaset nginx=nginx:1.17.1 -n dev
replicaset.apps/pc-replicaset image updated
# 再次查看,发现镜像版本已经变更了。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get rs -n dev -o wide
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR
pc-replicaset 2 2 2 29m nginx nginx:1.17.1 app=nginx-pod
删除 ReplicaSet。
# 使用 kubectl delete 命令会删除此 RS 以及它管理的 Pod。
# 在 kubernetes 删除 RS 前,会将 RS 的 replicasclear 调整为0,等待所有的 Pod 被删除后,在执行 RS 对象的删除。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl delete rs pc-replicaset -n dev
replicaset.apps "pc-replicaset" deleted
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl get pod -n dev -o wide
No resources found in dev namespace.。
# 如果希望仅仅删除 RS 对象(保留 Pod),可以使用 kubectl delete 命令时添加--cascade=false 选项(不推荐)。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl delete rs pc-replicaset -n dev --cascade=false
replicaset.apps "pc-replicaset" deleted
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl get pods -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pc-replicaset-cl82j 1/1 Running 0 75s
pc-replicaset-dslhb 1/1 Running 0 75s。
# 也可以使用 yaml 直接删除(推荐)。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get rs -n dev
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
pc-replicaset 2 2 2 33m
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl delete -f pc-replicaset.yaml
replicaset.apps "pc-replicaset" deleted
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get rs -n dev
No resources found in dev namespace.
6.3 Deployment(Deploy)。
为了更好的解决服务编排的问题,kubernetes 在 V1.2 版本开始,引入了 Deployment 控制器。值得一提的是,这种控制器并不直接管理 pod,而是通过管理 ReplicaSet 来简介管理 Pod,即:Deployment 管理 ReplicaSet,ReplicaSet 管理 Pod。所以 Deployment 比 ReplicaSet 功能更加强大。

Deployment 主要功能有下面几个。
- 支持 ReplicaSet 的所有功能。
- 支持发布的停止、继续。
- 支持滚动升级更新和回滚版本。
Deployment 的资源清单文件。
apiVersion: apps/v1 # 版本号。
kind: Deployment # 类型。
metadata: # 元数据。
name: # rs 名称。
namespace: # 所属命名空间。
labels: # 标签。
controller: deploy
spec: # 详情描述。
replicas: 3 # 副本数量。
revisionHistoryLimit: 3 # 保留历史版本。默认是 10。
paused: false # 暂停部署,默认是 false。
progressDeadlineSeconds: 600 # 部署超时时间(s),默认是 600。
strategy: # 策略。
type: RollingUpdate # 滚动更新策略。
rollingUpdate: # 滚动更新。
max 违规词汇: 30% # 最大额外可以存在的副本数,可以为百分比,也可以为整数。
maxUnavailable: 30% # 最大不可用状态的 Pod 的最大值,可以为百分比,也可以为整数。
selector: # 选择器,通过它指定该控制器管理哪些 pod。
matchLabels: # Labels 匹配规则。
app: nginx-pod
matchExpressions: # Expressions 匹配规则。
- {key: app, operator: In, values: [nginx-pod]}
template: # 模板,当副本数量不足时,会根据下面的模板创建 pod 副本。
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
ports:
- containerPort: 80
6.3.1 创建 deployment。
创建 pc-deployment.yaml,内容如下。
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: pc-deployment
namespace: dev
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx-pod
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
# 创建 deployment。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pc-deployment.yaml
deployment.apps/pc-deployment created
# 查看 deployment。
# UP-TO-DATE 最新版本的 pod 的数量。
# AVAILABLE 当前可用的 pod 的数量。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pc-deployment.yaml
deployment.apps/pc-deployment created
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get deploy pc-deployment -n dev
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
pc-deployment 3/3 3 3 8s
# 查看 rs。
# 发现 rs 的名称是在原来 deployment 的名字后面添加了一个 10 位数的随机串。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get rs -n dev
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9 3 3 3 90s
# 查看 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-29p82 1/1 Running 0 112s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-dhnhn 1/1 Running 0 112s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-hh4s4 1/1 Running 0 112s
6.3.2 扩缩容。
# 变更副本数量为 5 个。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl scale deploy pc-deployment --replicas=5 -n dev
deployment.apps/pc-deployment scaled
# 查看 deployment。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get rs -n dev
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9 5 5 5 8m21s
# 查看 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-25xdq 1/1 Running 0 6s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-29p82 1/1 Running 0 6m47s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-dhnhn 1/1 Running 0 6m47s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-hh4s4 1/1 Running 0 6m47s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-jkxsj 1/1 Running 0 6s
# 编辑 deployment 的副本数量,修改 spec:replicas: 3 即可。
# 查看 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl edit deploy pc-deployment -n dev
deployment.apps/pc-deployment edited
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-29p82 1/1 Running 0 9m14s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-dhnhn 1/1 Running 0 9m14s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-jkxsj 1/1 Running 0 2m33s
镜像更新。
deployment 支持两种更新策略:重建更新和滚动更新(默认),可以通过 strategy 指定策略类型,支持两个属性。
strategy:指定新的 Pod 替换旧的 Pod 的策略,支持两个属性。
type:指定策略类型,支持两种策略。
Recreate:在创建出新的 Pod 之前会先杀掉所有已存在的 Pod。
RollingUpdate:滚动更新,就是杀死一部分,就启动一部分,在更新过程中,存在两个版本 Pod。
rollingUpdate:当 type 为 RollingUpdate 时生效,用于为 RollingUpdate 设置参数,支持两个属性。
maxUnavailable:用来指定在升级过程中不可用 Pod 的最大数量,默认为 25%。
max 违规词汇: 用来指定在升级过程中可以超过期望的 Pod 的最大数量,默认为 25%。
- 重建更新。
- 编辑 pc-deployment.yaml,在 spec 节点下添加更新策略。
spec:
strategy: # 策略。
type: Recreate # 重建更新。
- 创建 deploy 进行验证。
# 变更镜像。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim pc-deployment.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl apply -f pc-deployment.yaml
Warning: kubectl apply should be used on resource created by either kubectl create --save-config or kubectl apply
deployment.apps/pc-deployment configured
# 观察升级过程。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev -w
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-29p82 1/1 Running 0 31m
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-dhnhn 1/1 Running 0 31m
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-jkxsj 1/1 Running 0 24m
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl set image deploy pc-deployment nginx=nginx:1.17.2 -n dev
deployment.apps/pc-deployment image updated
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev -w
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-29p82 1/1 Running 0 31m
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-dhnhn 1/1 Running 0 31m
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-jkxsj 1/1 Running 0 24m
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-dhnhn 1/1 Terminating 0 33m
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-29p82 1/1 Terminating 0 33m
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-jkxsj 1/1 Terminating 0 26m
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-dhnhn 0/1 Terminating 0 33m
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-jkxsj 0/1 Terminating 0 26m
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-29p82 0/1 Terminating 0 33m
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-29p82 0/1 Terminating 0 33m
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-29p82 0/1 Terminating 0 33m
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-jkxsj 0/1 Terminating 0 26m
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-jkxsj 0/1 Terminating 0 26m
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-dhnhn 0/1 Terminating 0 33m
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-dhnhn 0/1 Terminating 0 33m
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-s4x84 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-s4x84 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-nl952 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-2l4qg 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-2l4qg 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-nl952 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-s4x84 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-2l4qg 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-nl952 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-nl952 1/1 Running 0 2s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-s4x84 1/1 Running 0 81s
- 滚动更新。
- 编辑 pc-deployment.yaml,在 spec 节点下添加更新策略。
spec:
strategy: # 策略。
type: RollingUpdate # 滚动更新策略。
rollingUpdate:
maxSurge: 25%
maxUnavailable: 25%
- 创建 deploy 进行验证。
# 变更镜像。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl set image deploy pc-deployment nginx=nginx:1.17.1 -n dev
deployment.apps/pc-deployment image updated
# 观察升级过程。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev -w
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-2l4qg 1/1 Running 0 4m23s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-nl952 1/1 Running 0 4m23s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-s4x84 1/1 Running 0 4m23s
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev -w
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-drkkh 1/1 Running 0 2m
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-wrtfd 1/1 Running 0 2m
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-zc6h4 1/1 Running 0 2m
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-rqnts 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-rqnts 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-rqnts 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-rqnts 1/1 Running 0 1s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-zc6h4 1/1 Terminating 0 5m3s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-qpj84 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-qpj84 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-qpj84 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-zc6h4 0/1 Terminating 0 5m4s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-qpj84 1/1 Running 0 2s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-wrtfd 1/1 Terminating 0 5m5s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-4qdl9 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-4qdl9 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-4qdl9 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 1s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-wrtfd 0/1 Terminating 0 5m6s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-4qdl9 1/1 Running 0 2s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-drkkh 1/1 Terminating 0 5m7s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-drkkh 0/1 Terminating 0 5m8s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-wrtfd 0/1 Terminating 0 5m16s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-wrtfd 0/1 Terminating 0 5m16s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-zc6h4 0/1 Terminating 0 5m16s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-zc6h4 0/1 Terminating 0 5m16s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-drkkh 0/1 Terminating 0 5m20s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-drkkh 0/1 Terminating 0 5m20s
# 至此,新版本的 pod 创建完毕,就版本的 pod 销毁完毕。
# 中间过程是滚动进行的,也就是边销毁边创建。
滚动更新的过程。
镜像更新中 rs 的变化。
# 查看 rs,发现原来的 rs 的依旧存在,只是 pod 数量变为了 0,而后又新产生了一个 rs,pod 数量为 4。
# 其实这就是 deployment 能够进行版本回退的奥妙所在,后面会详细解释。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pc-deployment.yaml --record
deployment.apps/pc-deployment created
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get deploy,rs,pod -n dev
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/pc-deployment 3/3 3 3 21s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9 3 3 3 21s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-bdjdp 1/1 Running 0 21s
pod/pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-ntb5t 1/1 Running 0 21s
pod/pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-v6wtg 1/1 Running 0 21s
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pod -n dev -w
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-c6sbq 1/1 Running 0 27s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-jvfgf 1/1 Running 0 25s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-lds2k 1/1 Running 0 30s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-rw46s 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-rw46s 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-rw46s 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-rw46s 1/1 Running 0 1s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-jvfgf 1/1 Terminating 0 35s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-5drv2 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-5drv2 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-5drv2 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-jvfgf 0/1 Terminating 0 36s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-5drv2 1/1 Running 0 2s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-c6sbq 1/1 Terminating 0 39s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-9jzpr 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-9jzpr 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-9jzpr 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-c6sbq 0/1 Terminating 0 40s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-9jzpr 1/1 Running 0 2s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-lds2k 1/1 Terminating 0 44s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-lds2k 0/1 Terminating 0 45s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-c6sbq 0/1 Terminating 0 48s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-c6sbq 0/1 Terminating 0 48s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-jvfgf 0/1 Terminating 0 46s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-jvfgf 0/1 Terminating 0 46s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-lds2k 0/1 Terminating 0 55s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-lds2k 0/1 Terminating 0 55s
# rs -pod
# 会新创建 rs。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get rs -n dev
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9 3 3 3 6m31s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b 0 0 0 2m44s
# pc-deployment-675d469f8b 留着用于版本回退。
6.3.3 版本回退。
deployment 支持版本升级过程中的暂停、继续功能以及版本回退等诸多功能,下面具体来看。
kubectl rollout:版本升级相关功能,支持下面的选项。
- status 显示当前升级状态。
- history 显示升级历史记录。
- pause 暂停版本升级过程。
- resume 继续已经暂停的版本升级过程。
- restart 重启版本升级过程。
- undo 回滚到上一级版本(可以使用 --to-revision 回滚到指定版本)。
# 查看当前升级版本的状态。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl rollout status deploy pc-deployment -n dev
deployment "pc-deployment" successfully rolled out
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl set image deploy pc-deployment nginx=nginx:1.17.1 -n dev
deployment.apps/pc-deployment image updated
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl rollout status deploy pc-deployment -n dev
Waiting for deployment "pc-deployment" rollout to finish: 1 out of 3 new replicas have been updated...
Waiting for deployment "pc-deployment" rollout to finish: 1 out of 3 new replicas have been updated...
Waiting for deployment "pc-deployment" rollout to finish: 1 out of 3 new replicas have been updated...
Waiting for deployment "pc-deployment" rollout to finish: 2 out of 3 new replicas have been updated...
Waiting for deployment "pc-deployment" rollout to finish: 2 out of 3 new replicas have been updated...
Waiting for deployment "pc-deployment" rollout to finish: 2 old replicas are pending termination...
Waiting for deployment "pc-deployment" rollout to finish: 1 old replicas are pending termination...
Waiting for deployment "pc-deployment" rollout to finish: 1 old replicas are pending termination...
deployment "pc-deployment" successfully rolled out
# 查看升级历史记录。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl rollout history deploy pc-deployment -n dev
deployment.apps/pc-deployment
REVISION CHANGE-CAUSE
4 kubectl create --filename=pc-deployment.yaml --record=true
5 kubectl create --filename=pc-deployment.yaml --record=true
# 可以发现有 5 次版本记录,说明完成过 4 次升级。
# 版本回滚。
# 这里直接使用 --to-revision=1 回滚到了 1 版本,如果省略这个选项,就是回退到上个版本,就是 2 版本。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl rollout undo deployment pc-deployment --to-revision=1 -n dev
error: unable to find specified revision 1 in history
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl rollout undo deployment pc-deployment --to-revision=4 -n dev
deployment.apps/pc-deployment rolled back
# 查看发现,通过 nginx 镜像版本可以发现到了第一版。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get deploy -n dev -o wide
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR
pc-deployment 3/3 3 3 19m nginx nginx:1.17.2 app=nginx-pod
# 查看 rs,发现第一个 rs 中有 3 个 pod 运行,后面两个版本的 rs 中 pod 为运行。
# 其实 deployment 之所以可是实现版本的回滚,就是通过记录下历史 rs 来实现的,一旦想回滚到哪个版本,只需要将当前版本 pod 数量降为 0,然后将回滚版本的 pod 提升为目标数量就可以了。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get rs -n dev
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9 0 0 0 18m
pc-deployment-675d469f8b 3 3 3 14m
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl rollout history deploy pc-deployment -n dev
deployment.apps/pc-deployment
REVISION CHANGE-CAUSE
5 kubectl create --filename=pc-deployment.yaml --record=true
6 kubectl create --filename=pc-deployment.yaml --record=true
6.3.4 金丝雀发布。
Deployment 控制器支持控制更新过程中的控制,如“暂停(pause)”或“继续(resume)”更新操作。
比如有一批新的 Pod 资源创建完成后立即暂停更新过程,此时,仅存在一部分新版本的应用,主体部分还是旧的版本。然后,再筛选一小部分的用户请求路由到新版本的 Pod 应用,继续观察能否稳定地按期望的方式运行。确定没问题之后再继续完成余下的 Pod 资源滚动更新,否则立即回滚更新操作。这就是所谓的金丝雀发布。
# 更新 deployment 的版本,并配置暂停 deployment。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl set image deploy pc-deployment nginx=nginx:1.17.1 -n dev && kubectl rollout pause deployment pc-deployment -n dev
deployment.apps/pc-deployment image updated
deployment.apps/pc-deployment paused
# 观察更新状态。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl rollout status deploy pc-deployment -n dev
Waiting for deployment "pc-deployment" rollout to finish: 1 out of 3 new replicas have been updated...
# 监控更新的过程,可以看到已经新增了一个资源,但是并未按照预期的状态去删除一个旧的资源,就是因为使用了 pause 暂停命令。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get rs -n dev -o wide
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9 1 1 1 24m nginx nginx:1.17.1 app=nginx-pod,pod-template-hash=5d89bdfbf9
pc-deployment-675d469f8b 3 3 3 20m nginx nginx:1.17.2 app=nginx-pod,pod-template-hash=675d469f8b
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-qnnvk 1/1 Running 0 94s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-bk7zd 1/1 Running 0 8m10s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-jjwkr 1/1 Running 0 8m13s
pc-deployment-675d469f8b-prbfd 1/1 Running 0 8m9s
# 确保更新的 pod 没问题了,继续更新。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl rollout resume deploy pc-deployment -n dev
deployment.apps/pc-deployment resumed
# 查看最后的更新情况
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get rs -n dev -o wide
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9 3 3 3 26m nginx nginx:1.17.1 app=nginx-pod,pod-template-hash=5d89bdfbf9
pc-deployment-675d469f8b 0 0 0 22m nginx nginx:1.17.2 app=nginx-pod,pod-template-hash=675d469f8b
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-2vccz 1/1 Running 0 74s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-7j727 1/1 Running 0 73s
pc-deployment-5d89bdfbf9-qnnvk 1/1 Running 0 3m21s
删除 Deployment。
# 删除 deployment,其下的 rs 和 pod 也将被删除。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl delete -f pc-deployment.yaml
deployment.apps "pc-deployment" deleted
6.4 Horizontal Pod Autoscaler(HPA)。
在前面的课程中,我们已经可以实现通过手工执行 kubectl scale 命令实现 Pod 扩容或缩容,但是这显然不符合 Kubernetes 的定位目标–自动化、智能化。Kubernetes 期望可以实现通过监测 Pod 的使用情况,实现 pod 数量的自动调整,于是就产生了 Horizontal Pod Autoscaler(HPA)这种控制器。
HPA 可以获取每个 Pod 利用率,然后和 HPA 中定义的指标进行对比,同时计算出需要伸缩的具体值,最后实现 Pod 的数量的调整。其实 HPA 与之前的 Deployment 一样,也属于一种 Kubernetes 资源对象,它通过追踪分析 RC 控制的所有目标 Pod 的负载变化情况,来确定是否需要针对性地调整目标 Pod 的副本数,这是 HPA 的实现原理。

接下来,我们来做一个实验。
6.4.1 安装 metrics-server。
https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server/releases/download/v0.3.7/components.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server/releases/download/v0.3.6/components.yaml
metrics-server 可以用来收集集群中的资源使用情况。
# 安装 git
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# yum install git -y
# 获取 metrics-server,注意使用的版本。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# git clone -b v0.3.6 https://github.com/kubernetes-incubator/metrics-server
geek@LAPTOP-0GJSKR6T MINGW64 /d/lyfGeek。download。/metrics_server
$ git clone -b v0.3.6 https://github.com/kubernetes-incubator/metrics-server
Cloning into 'metrics-server'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 14982, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (92/92), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (59/59), done.
remote: Total 14982 (delta 35), reused 72 (delta 30), pack-reused 14890
Receiving objects: 100% (14982/14982), 13.45 MiB | 3.24 MiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (7951/7951), done.
Note: switching to 'd1f4f6fc09cd3134e8ea5ba4e0bd2db4e8002ed8'.
You are in 'detached HEAD' state. You can look around, make experimental
changes and commit them, and you can discard any commits you make in this
state without impacting any branches by switching back to a branch.
If you want to create a new branch to retain commits you create, you may
do so (now or later) by using -c with the switch command. Example:
git switch -c <new-branch-name>
Or undo this operation with:
git switch -
Turn off this advice by setting config variable advice.detachedHead to false
Updating files: 100% (2971/2971), done.
# 修改 deployment,注意修改的是镜像和初始化参数。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# cd /root/metrics-server/deploy/1.8+/
[root@k8s-master01 1.8+]# vim metrics-server-deployment.yaml
按图中添加下面选项
hostNetwork: true
image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/metrics-server-amd64:v0.3.6
args:
- --kubelet-insecure-tls
- --kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP,Hostname,InternalDNS,ExternalDNS,ExternalIP
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-5CRBNMZz-1666419286934)(Kubenetes.assets/image-20200608163326496.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6789da8708b94e4cb32bd7eb7fec86e2.png)
# 安装 metrics-server。
[root@localhost 1.8+]# cp metrics-server-deployment.yaml metrics-server-deployment.yaml.bak
[root@localhost 1.8+]# vim metrics-server-deployment.yaml
[root@localhost 1.8+]# kubectl apply -f ./
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/system:aggregated-metrics-reader created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/metrics-server:system:auth-delegator created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/metrics-server-auth-reader created
apiservice.apiregistration.k8s.io/v1beta1.metrics.k8s.io created
serviceaccount/metrics-server created
deployment.apps/metrics-server created
service/metrics-server created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/system:metrics-server created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/system:metrics-server created
# 查看 pod 运行情况。
[root@localhost 1.8+]# kubectl get pod -n kube-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
coredns-9d85f5447-5959v 0/1 Running 155 3d18h
coredns-9d85f5447-gvqxh 0/1 CrashLoopBackOff 155 3d18h
etcd-localhost.localdomain.k8s.master 1/1 Running 1 3d18h
kube-apiserver-localhost.localdomain.k8s.master 1/1 Running 9 3d18h
kube-controller-manager-localhost.localdomain.k8s.master 1/1 Running 2 3d18h
kube-proxy-7dc95 1/1 Running 2 3d17h
kube-proxy-7hss2 1/1 Running 1 3d17h
kube-proxy-rpnvx 1/1 Running 1 3d18h
kube-scheduler-localhost.localdomain.k8s.master 1/1 Running 2 3d18h
metrics-server-6b976979db-j5g6s 1/1 Running 0 74s
# 使用 kubectl top node 查看资源使用情况。
[root@localhost 1.8+]# kubectl top pod -n kube-system
NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
coredns-9d85f5447-gvqxh 0m 0Mi
etcd-localhost.localdomain.k8s.master 27m 83Mi
kube-apiserver-localhost.localdomain.k8s.master 71m 352Mi
kube-controller-manager-localhost.localdomain.k8s.master 39m 53Mi
kube-proxy-7dc95 1m 16Mi
kube-proxy-7hss2 2m 16Mi
kube-proxy-rpnvx 1m 20Mi
kube-scheduler-localhost.localdomain.k8s.master 11m 25Mi
metrics-server-6b976979db-j5g6s 2m 10Mi
# 至此,metrics-server 安装完成。
6.4.2 准备 deployment 和 service。
创建 pc-hpa-pod.yaml 文件,内容如下。
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx
namespace: dev
spec:
strategy: # 策略。
type: RollingUpdate # 滚动更新策略。
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx-pod
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
resources: # 资源配额。
limits: # 限制资源(上限)。
cpu: "1" # CPU 限制,单位是 core 数。
requests: # 请求资源(下限)。
cpu: "100m" # CPU 限制,单位是 core 数。
为了操作简单,直接使用命令。
# 创建 deployment。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl run nginx --image=nginx:1.17.1 --requests=cpu=100m -n dev
kubectl run --generator=deployment/apps.v1 is DEPRECATED and will be removed in a future version. Use kubectl run --generator=run-pod/v1 or kubectl create instead.
deployment.apps/nginx created
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get deploy,pod -n dev
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/nginx 1/1 1 1 4s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/nginx-778cb5fb7b-dgntb 1/1 Running 0 4s
# 创建 service。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl expose deployment nginx --type=NodePort --port=80 -n dev
service/nginx exposed
# 查看。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get deploy,pods,services -n dev
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/nginx 1/1 1 1 2m3s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/nginx-778cb5fb7b-dgntb 1/1 Running 0 2m3s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/nginx NodePort 10.107.80.13 <none> 80:30994/TCP 73s
6.4.3 部署 HPA。
创建 pc-hpa.yaml 文件,内容如下。
apiVersion: autoscaling/v1
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: pc-hpa
namespace: dev
spec:
minReplicas: 1 # 最小 pod 数量。
maxReplicas: 10 # 最大 pod 数量。
targetCPUUtilizationPercentage: 3 # CPU 使用率指标。
scaleTargetRef: # 指定要控制的 nginx 信息。
apiVersion: /v1
kind: Deployment
name: nginx
name: nginx 指
pod/nginx-778cb5fb7b-dgntb
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get deploy,pods,services -n dev
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/nginx 1/1 1 1 8m24s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/nginx-778cb5fb7b-c4fv5 1/1 Running 0 8m24s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/nginx NodePort 10.97.197.88 <none> 80:32496/TCP 7m52s
# 创建 hpa。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pc-hpa.yaml
horizontalpodautoscaler.autoscaling/pc-hpa created
# 查看 hpa。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get hpa -n dev
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
pc-hpa Deployment/nginx <unknown>/3% 1 10 0 24s
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get deploy -n dev -w
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
nginx 1/1 1 1 9m56s
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get hpa -n dev -w
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
pc-hpa Deployment/nginx <unknown>/3% 1 10 0 3m15s
6.4.4 测试。
使用压测工具对 service 地址 192.168.5.4:31830 进行压测,然后通过控制台查看 hpa 和 pod 的变化。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get hpa -n dev -w
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
pc-hpa Deployment/nginx <unknown>/3% 1 10 0 2m37s
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get deployment -n dev -w
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
nginx 1/1 1 1 4m
nginx-deployment 3/3 3 3 145m
tomcat-deployment 3/3 3 3 145m
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev -w
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-778cb5fb7b-c4fv5 1/1 Running 0 4m25s
hpa 变化。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl get hpa -n dev -w
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
deployment 变化。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl get deployment -n dev -w
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
pod 变化。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl get pods -n dev -w
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
6.5 DaemonSet(DS)。
DaemonSet 类型的控制器可以保证在集群中的每一台(或指定)节点上都运行一个副本。一般适用于日志收集、节点监控等场景。也就是说,如果一个 Pod 提供的功能是节点级别的(每个节点都需要且只需要一个),那么这类 Pod 就适合使用 DaemonSet 类型的控制器创建。

DaemonSet 控制器的特点。
- 每当向集群中添加一个节点时,指定的 Pod 副本也将添加到该节点上。
- 当节点从集群中移除时,Pod 也就被垃圾回收了。
下面先来看下 DaemonSet 的资源清单文件。
apiVersion: apps/v1 # 版本号。
kind: DaemonSet # 类型。
metadata: # 元数据。
name: # rs 名称。
namespace: # 所属命名空间。
labels: # 标签。
controller: daemonset
spec: # 详情描述。
revisionHistoryLimit: 3 # 保留历史版本。
updateStrategy: # 更新策略。
type: RollingUpdate # 滚动更新策略。
rollingUpdate: # 滚动更新。
maxUnavailable: 1 # 最大不可用状态的 Pod 的最大值,可以为百分比,也可以为整数。
selector: # 选择器,通过它指定该控制器管理哪些 pod。
matchLabels: # Labels 匹配规则。
app: nginx-pod
matchExpressions: # Expressions 匹配规则。
- {key: app, operator: In, values: [nginx-pod]}
template: # 模板,当副本数量不足时,会根据下面的模板创建 pod 副本。
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
ports:
- containerPort: 80
创建 pc-daemonset.yaml,内容如下。
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: pc-daemonset
namespace: dev
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx-pod
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
# 创建 daemonset。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim pc-daemonset.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pc-daemonset.yaml
daemonset.apps/pc-daemonset created
# 查看 daemonset。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim pc-daemonset.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pc-daemonset.yaml
daemonset.apps/pc-daemonset created
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get ds pc-daemonset -n dev
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE
pc-daemonset 2 2 2 2 2 <none> 23s
# 查看 pod,发现在每个 Node 上都运行一个 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
nginx-778cb5fb7b-dgntb 1/1 Running 0 2d19h 10.244.2.57 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 <none> <none>
pc-daemonset-2fhlg 1/1 Running 0 41s 10.244.2.58 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 <none> <none>
pc-daemonset-9hvlw 1/1 Running 0 41s 10.244.1.49 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 <none> <none>
# 删除 daemonset。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl delete -f pc-daemonset.yaml
daemonset.apps "pc-daemonset" deleted
6.6 Job。
Job,主要用于负责**批量处理(一次要处理指定数量任务)短暂的一次性(每个任务仅运行一次就结束)**任务。Job 特点如下:
- 当 Job 创建的 pod 执行成功结束时,Job 将记录成功结束的 pod 数量。
- 当成功结束的 pod 达到指定的数量时,Job 将完成执行。

Job 的资源清单文件。
apiVersion: batch/v1 # 版本号。
kind: Job # 类型。
metadata: # 元数据。
name: # rs 名称。
namespace: # 所属命名空间 。
labels: # 标签。
controller: job
spec: # 详情描述。
completions: 1 # 指定 job 需要成功运行 Pods 的次数。默认值: 1。
parallelism: 1 # 指定 job 在任一时刻应该并发运行 Pods 的数量。默认值: 1。
activeDeadlineSeconds: 30 # 指定 job 可运行的时间期限,超过时间还未结束,系统将会尝试进行终止。
backoffLimit: 6 # 指定 job 失败后进行重试的次数。默认是 6。
manualSelector: true # 是否可以使用 selector 选择器选择 pod,默认是 false。
selector: # 选择器,通过它指定该控制器管理哪些 pod。
matchLabels: # Labels 匹配规则。
app: counter-pod
matchExpressions: # Expressions 匹配规则。
- {key: app, operator: In, values: [counter-pod]}。
template: # 模板,当副本数量不足时,会根据下面的模板创建 pod 副本。
metadata:
labels:
app: counter-pod
spec:
restartPolicy: Never # 重启策略只能设置为 Never 或者 OnFailure。
containers:
- name: counter
image: busybox:1.30
command: ["bin/sh", "-c", "for i in 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1; do echo $i; sleep 2; done"]
关于重启策略设置的说明。
如果指定为 OnFailure,则 job 会在 pod 出现故障时重启容器,而不是创建 pod,failed 次数不变。
如果指定为 Never,则 job 会在 pod 出现故障时创建新的 pod,并且故障 pod 不会消失,也不会重启,failed 次数加 1。
如果指定为 Always 的话,就意味着一直重启,意味着 job 任务会重复去执行了,当然不对,所以不能设置为 Always。
创建 pc-job.yaml,内容如下。
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: pc-job
namespace: dev
spec:
manualSelector: true
selector:
matchLabels:
app: counter-pod
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: counter-pod
spec:
restartPolicy: Never
containers:
- name: counter
image: busybox:1.30
command: ["bin/sh", "-c", "for i in 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1; do echo $i; sleep 3; done"]
# 创建 job。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim pc-job.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pc-job.yaml
job.batch/pc-job created
# 查看 job。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get job -n dev -w
NAME COMPLETIONS DURATION AGE
pc-job 0/1 0s
pc-job 0/1 0s 0s
pc-job 1/1 29s 29s
# 通过观察 pod 状态可以看到,pod 在运行完毕任务后,就会变成 Completed 状态。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev -w
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-778cb5fb7b-dgntb 1/1 Running 0 2d19h
pc-job-dl669 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-job-dl669 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-job-dl669 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
pc-job-dl669 1/1 Running 0 2s
pc-job-dl669 0/1 Completed 0 29s
# 接下来,调整下 pod 运行的总数量和并行数量 即:在 spec 下设置下面两个选项。
# completions: 6 # 指定 job 需要成功运行 Pods 的次数为 6。
# parallelism: 3 # 指定 job 并发运行 Pods 的数量为 3。
# 然后重新运行 job,观察效果,此时会发现,job 会每次运行 3 个 pod,总共执行了 6 个 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get job -n dev -w
NAME COMPLETIONS DURATION AGE
pc-job 0/6 0s
pc-job 0/6 0s 0s
pc-job 1/6 29s 29s
pc-job 2/6 30s 30s
pc-job 3/6 30s 30s
pc-job 4/6 59s 59s
pc-job 5/6 59s 59s
pc-job 6/6 59s 59s
pc-job 6/6 59s 115s
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev -w
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-778cb5fb7b-dgntb 1/1 Running 0 2d19h
pc-job-whj2h 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-job-whj2h 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-job-66jkk 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-job-rsv76 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-job-66jkk 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-job-rsv76 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-job-whj2h 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
pc-job-66jkk 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
pc-job-rsv76 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
pc-job-66jkk 1/1 Running 0 2s
pc-job-rsv76 1/1 Running 0 3s
pc-job-whj2h 1/1 Running 0 3s
pc-job-66jkk 0/1 Completed 0 29s
pc-job-62qwm 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-job-62qwm 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-job-62qwm 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
pc-job-rsv76 0/1 Completed 0 30s
pc-job-t2djt 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-job-t2djt 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-job-whj2h 0/1 Completed 0 30s
pc-job-sg4wm 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-job-sg4wm 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-job-t2djt 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
pc-job-sg4wm 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
pc-job-62qwm 1/1 Running 0 3s
pc-job-t2djt 1/1 Running 0 2s
pc-job-sg4wm 1/1 Running 0 2s
pc-job-62qwm 0/1 Completed 0 30s
pc-job-t2djt 0/1 Completed 0 29s
pc-job-sg4wm 0/1 Completed 0 29s
# 删除 job。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl delete -f pc-job.yaml
job.batch "pc-job" deleted
6.7 CronJob(CJ)。
CronJob 控制器以 Job 控制器资源为其管控对象,并借助它管理 pod 资源对象,Job 控制器定义的作业任务在其控制器资源创建之后便会立即执行,但 CronJob 可以以类似于 Linux 操作系统的周期性任务作业计划的方式控制其运行时间点及重复运行的方式。也就是说,CronJob 可以在特定的时间点(反复的)去运行 job 任务。

CronJob 的资源清单文件。
apiVersion: batch/v1beta1 # 版本号。
kind: CronJob # 类型。
metadata: # 元数据。
name: # rs 名称。
namespace: # 所属命名空间。
labels: # 标签。
controller: cronjob
spec: # 详情描述。
schedule: # cron 格式的作业调度运行时间点,用于控制任务在什么时间执行。
concurrencyPolicy: # 并发执行策略,用于定义前一次作业运行尚未完成时是否以及如何运行后一次的作业。
failedJobHistoryLimit: # 为失败的任务执行保留的历史记录数,默认为1。
successfulJobHistoryLimit: # 为成功的任务执行保留的历史记录数,默认为3。
startingDeadlineSeconds: # 启动作业错误的超时时长。
jobTemplate: # job 控制器模板,用于为 cronjob 控制器生成 job 对象;下面其实就是 job 的定义。
metadata:
spec:
completions: 1
parallelism: 1
activeDeadlineSeconds: 30
backoffLimit: 6
manualSelector: true
selector:
matchLabels:
app: counter-pod
matchExpressions: # 规则。
- {key: app, operator: In, values: [counter-pod]}
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: counter-pod
spec:
restartPolicy: Never
containers:
- name: counter
image: busybox:1.30
command: ["bin/sh", "-c", "for i in 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1; do echo $i; sleep 20; done"]
需要重点解释的几个选项。
schedule: cron 表达式,用于指定任务的执行时间。
*/1 * * * *
<分钟> <小时> <日> <月份> <星期>
分钟 值从 0 到 59。
小时 值从 0 到 23。
日 值从 1 到 31。
月 值从 1 到 12。
星期 值从 0 到 6, 0 代表星期日。
多个时间可以用逗号隔开;范围可以用连字符给出;* 可以作为通配符;/ 表示每 ...
concurrencyPolicy:
Allow: 允许 Jobs 并发运行(默认)。
Forbid: 禁止并发运行,如果上一次运行尚未完成,则跳过下一次运行。
Replace: 替换,取消当前正在运行的作业并用新作业替换它。
创建 pc-cronjob.yaml,内容如下。
apiVersion: batch/v1beta1
kind: CronJob
metadata:
name: pc-cronjob
namespace: dev
labels:
controller: cronjob
spec:
schedule: "*/1 * * * *"
jobTemplate:
metadata:
spec:
template:
spec:
restartPolicy: Never
containers:
- name: counter
image: busybox:1.30
command: ["bin/sh", "-c", "for i in 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1; do echo $i; sleep 3; done"]
# 创建 cronjob。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim pc-cronjob.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f pc-cronjob.yaml
cronjob.batch/pc-cronjob created
# 查看 cronjob。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get cj -n dev -w
NAME SCHEDULE SUSPEND ACTIVE LAST SCHEDULE AGE
pc-cronjob */1 * * * * False 0 <none> 0s
pc-cronjob */1 * * * * False 1 2s 56s
pc-cronjob */1 * * * * False 0 32s 86s
pc-cronjob */1 * * * * False 1 2s 116s
# 查看 job。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get job -n dev -w
NAME COMPLETIONS DURATION AGE
pc-cronjob-1670488080 0/1 0s
pc-cronjob-1670488080 0/1 0s 0s
pc-cronjob-1670488080 1/1 29s 29s
pc-cronjob-1670488140 0/1 0s
pc-cronjob-1670488140 0/1 0s 0s
pc-cronjob-1670488140 1/1 29s 29s
# 查看 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev -w
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-778cb5fb7b-dgntb 1/1 Running 0 2d20h
pc-cronjob-1670488080-pmxg7 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-cronjob-1670488080-pmxg7 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-cronjob-1670488080-pmxg7 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
pc-cronjob-1670488080-pmxg7 1/1 Running 0 2s
pc-cronjob-1670488080-pmxg7 0/1 Completed 0 29s
pc-cronjob-1670488140-l92vh 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-cronjob-1670488140-l92vh 0/1 Pending 0 0s
pc-cronjob-1670488140-l92vh 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
pc-cronjob-1670488140-l92vh 1/1 Running 0 1s
pc-cronjob-1670488140-l92vh 0/1 Completed 0 29s
# 删除 cronjob。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl delete -f pc-cronjob.yaml
cronjob.batch "pc-cronjob" deleted
StatefulSet。
7. Service 详解。
流量负载组件:Service & Ingress。
7.1 Service 介绍。
在 kubernetes 中,pod 是应用程序的载体,我们可以通过 pod 的 ip 来访问应用程序,但是 pod 的 ip 地址不是固定的,这也就意味着不方便直接采用 pod 的 ip 对服务进行访问。
为了解决这个问题,kubernetes 提供了 Service 资源,Service 会对提供同一个服务的多个 pod 进行聚合,并且提供一个统一的入口地址。通过访问 Service 的入口地址就能访问到后面的 pod 服务。

Service 在很多情况下只是一个概念,真正起作用的其实是 kube-proxy 服务进程,每个 Node 节点上都运行着一个 kube-proxy 服务进程。当创建 Service 的时候会通过 api-server 向 etcd 写入创建的 service 的信息,而 kube-proxy 会基于监听的机制发现这种 Service 的变动,然后 ta 会将最新的 Service 信息转换成对应的访问规则。

# 10.97.97.97:80 是 service 提供的访问入口。
# 当访问这个入口的时候,可以发现后面有三个 pod 的服务在等待调用,
# kube-proxy 会基于 rr(轮询)的策略,将请求分发到其中一个 pod 上去。
# 这个规则会同时在集群内的所有节点上都生成,所以在任何一个节点上,都可以访问。
[root@localhost k8s]# ipvsadm -Ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags
-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
# 没有对应规则,未开启。
-> 192.168.142.150:6443 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.96.0.10:53 rr
TCP 10.96.0.10:9153 rr
TCP 10.103.149.9:443 rr
kube-proxy 目前支持三种工作模式。
7.1.1 userspace 模式。
userspace 模式下,kube-proxy 会为每一个 Service 创建一个监听端口,发向 Cluster IP 的请求被 Iptables 规则重定向到 kube-proxy 监听的端口上,kube-proxy 根据 LB 算法选择一个提供服务的 Pod 并和其建立链接,以将请求转发到 Pod 上。该模式下,kube-proxy 充当了一个四层负责均衡器的角色。由于 kube-proxy 运行在 userspace 中,在进行转发处理时会增加内核和用户空间之间的数据拷贝,虽然比较稳定,但是效率比较低。
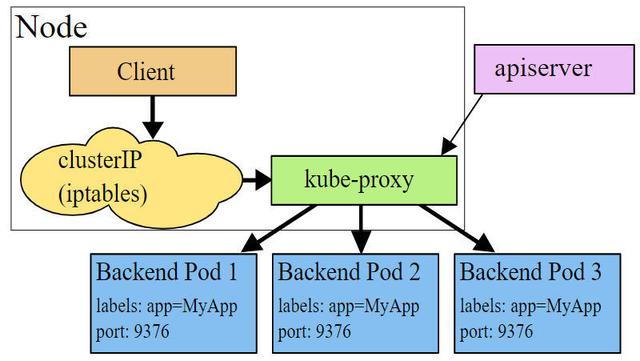
7.1.2 iptables 模式。
iptables 模式下,kube-proxy 为 service 后端的每个 Pod 创建对应的 iptables 规则,直接将发向 Cluster IP 的请求重定向到一个 Pod IP。该模式下 kube-proxy 不承担四层负责均衡器的角色,只负责创建 iptables 规则。该模式的优点是较 userspace 模式效率更高,但不能提供灵活的 LB 策略,当后端 Pod 不可用时也无法进行重试。

7.1.3 ipvs 模式。
ipvs 模式和 iptables 类似,kube-proxy 监控 Pod 的变化并创建相应的 ipvs 规则。ipvs 相对 iptables 转发效率更高。除此以外,ipvs 支持更多的 LB 算法。
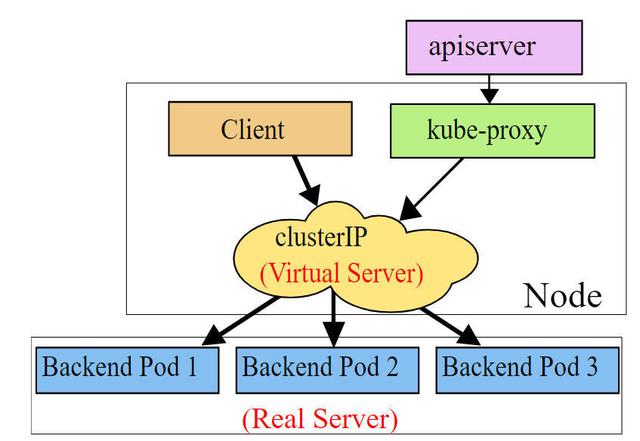
# 此模式必须安装 ipvs 内核模块,否则会降级为 iptables。
# 开启 ipvs。
# 修改 mode: "ipvs"
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl edit cm kube-proxy -n kube-system
configmap/kube-proxy edited
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl delete pod -l k8s-app=kube-proxy -n kube-system
pod "kube-proxy-bqd7w" deleted
pod "kube-proxy-nt48k" deleted
pod "kube-proxy-wpt6n" deleted
[root@localhost ~]# ipvsadm -Ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags
-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 192.168.142.150:30994 rr
-> 10.244.2.62:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 192.168.142.150:31567 rr
-> 10.244.2.63:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.96.0.1:443 rr
-> 192.168.142.150:6443 Masq 1 3 0
TCP 10.96.0.10:53 rr
-> 10.244.0.6:53 Masq 1 0 0
-> 10.244.0.7:53 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.96.0.10:9153 rr
-> 10.244.0.6:9153 Masq 1 0 0
-> 10.244.0.7:9153 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.97.97.97:80 rr persistent 10800
-> 10.244.1.62:80 Masq 1 0 0
-> 10.244.1.63:80 Masq 1 0 0
-> 10.244.2.64:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.103.149.9:443 rr
-> 192.168.142.151:443 Masq 1 2 0
TCP 10.107.6.137:80 rr
-> 10.244.2.63:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.107.80.13:80 rr
-> 10.244.2.62:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.244.0.0:30994 rr
-> 10.244.2.62:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.244.0.0:31567 rr
-> 10.244.2.63:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.244.0.1:30994 rr
-> 10.244.2.62:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.244.0.1:31567 rr
-> 10.244.2.63:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 127.0.0.1:30994 rr
-> 10.244.2.62:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 127.0.0.1:31567 rr
-> 10.244.2.63:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 172.17.0.1:30994 rr
-> 10.244.2.62:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 172.17.0.1:31567 rr
-> 10.244.2.63:80 Masq 1 0 0
UDP 10.96.0.10:53 rr
-> 10.244.0.6:53 Masq 1 0 0
-> 10.244.0.7:53 Masq 1 0 0
7.2 Service 类型。
Service 的资源清单文件。
kind: Service # 资源类型。
apiVersion: v1 # 资源版本。
metadata: # 元数据。
name: service # 资源名称。
namespace: dev # 命名空间。
spec: # 描述。
selector: # 标签选择器,用于确定当前 service 代理哪些 pod。
app: nginx
type: # Service 类型,指定 service 的访问方式。
clusterIP: # 虚拟服务的 ip 地址。
sessionAffinity: # session 亲和性,支持 ClientIP、None 两个选项。
ports: # 端口信息。
- protocol: TCP
port: 3017 # service 端口。
targetPort: 5003 # pod 端口。
nodePort: 31122 # 主机端口。
type
- ClusterIP:默认值,ta 是 Kubernetes 系统自动分配的虚拟 IP,只能在集群内部访问。
- NodePort:将 Service 通过指定的 Node 上的端口暴露给外部,通过此方法,就可以在集群外部访问服务。
- LoadBalancer:使用外接负载均衡器完成到服务的负载分发,注意此模式需要外部云环境支持。
- ExternalName:把集群外部的服务引入集群内部,直接使用。
7.3 Service 使用。
7.3.1 实验环境准备。
在使用 service 之前,首先利用 Deployment 创建出 3 个 pod,注意要为 pod 设置 app=nginx-pod 的标签。
创建 deployment.yaml,内容如下。
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: pc-deployment
namespace: dev
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx-pod
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
ports:
- containerPort: 80
[root@localhost k8s]# vim deployment.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f deployment.yaml
deployment.apps/pc-deployment created
# 查看 pod 详情。
# 为了方便后面的测试,修改下三台 nginx 的 index.html 页面(三台修改的 IP 地址不一致)。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get pods -n dev -o wide --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES LABELS
nginx-778cb5fb7b-dgntb 1/1 Running 1 2d22h 10.244.2.62 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 <none> <none> pod-template-hash=778cb5fb7b,run=nginx
pc-deployment-6696798b78-9s6pb 1/1 Running 1 55m 10.244.1.62 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 <none> <none> app=nginx-pod,pod-template-hash=6696798b78
pc-deployment-6696798b78-fz6xg 1/1 Running 1 55m 10.244.2.64 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node2 <none> <none> app=nginx-pod,pod-template-hash=6696798b78
pc-deployment-6696798b78-gp6fs 1/1 Running 1 55m 10.244.1.63 localhost.localdomain.k8s.node1 <none> <none> app=nginx-pod,pod-template-hash=6696798b78
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl exec -it pc-deployment-6696798b78-9s6pb -n dev /bin/sh
# cp /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html.bak
# echo "10.244.1.62" >> /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
# exit
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl exec -it pc-deployment-6696798b78-fz6xg -n dev /bin/sh
# cp /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html.bak
# echo "10.244.2.64" >> /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
# exit
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl exec -it pc-deployment-6696798b78-gp6fs -n dev /bin/sh
# cp /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html.bak
# echo "10.244.1.63" >> /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
# exit
# 修改完毕之后,访问测试。
[root@localhost ~]# curl 10.244.1.62
10.244.1.62
[root@localhost ~]# curl 10.244.2.64
10.244.2.64
[root@localhost ~]# curl 10.244.1.63
10.244.1.63
7.3.2 ClusterIP 类型的 Service。
创建 service-clusterip.yaml 文件。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: service-clusterip
namespace: dev
spec:
selector:
app: nginx-pod
clusterIP: 10.97.97.97 # service 的 ip 地址,如果不写,默认会生成一个。
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- port: 80 # Service 端口。
targetPort: 80 # pod 端口。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim service-clusterip.yaml
# 创建 service。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl create -f service-clusterip.yaml
service/service-clusterip created
# 查看 service。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get svc -n dev -o wide
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR
nginx NodePort 10.107.80.13 <none> 80:30994/TCP 2d22h run=nginx
service-clusterip ClusterIP 10.97.97.97 <none> 80/TCP 27s app=nginx-pod
# 查看 service 的详细信息。
# 在这里有一个 Endpoints 列表,里面就是当前 service 可以负载到的服务入口。
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl describe svc service-clusterip -n dev
Name: service-clusterip
Namespace: dev
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Selector: app=nginx-pod
Type: ClusterIP
IP: 10.97.97.97
Port: <unset> 80/TCP
TargetPort: 80/TCP
Endpoints: 10.244.1.62:80,10.244.1.63:80,10.244.2.64:80
Session Affinity: None
Events: <none>
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get endpoints -n dev
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
nginx 10.244.2.62:80 2d22h
service-clusterip 10.244.1.62:80,10.244.1.63:80,10.244.2.64:80 4m49s
# 查看 ipvs 的映射规则。(rr ~ 轮询)。
TCP 10.97.97.97:80 rr
-> 10.244.1.62:80 Masq 1 0 0
-> 10.244.1.63:80 Masq 1 0 0
-> 10.244.2.64:80 Masq 1 0 0
[root@localhost ~]# ipvsadm -Ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags
-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 192.168.142.150:30994 rr
-> 10.244.2.62:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 192.168.142.150:31567 rr
-> 10.244.2.63:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.96.0.1:443 rr
-> 192.168.142.150:6443 Masq 1 3 0
TCP 10.96.0.10:53 rr
-> 10.244.0.6:53 Masq 1 0 0
-> 10.244.0.7:53 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.96.0.10:9153 rr
-> 10.244.0.6:9153 Masq 1 0 0
-> 10.244.0.7:9153 Masq 1 0 0
-> 192.168.142.150:6443 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.96.0.10:53 rr
TCP 10.96.0.10:9153 rr
TCP 10.103.149.9:443 rr
TCP 10.103.149.9:443 rr
-> 192.168.142.151:443 Masq 1 2 0
TCP 10.107.6.137:80 rr
-> 10.244.2.63:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.107.80.13:80 rr
-> 10.244.2.62:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.244.0.0:30994 rr
-> 10.244.2.62:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.244.0.0:31567 rr
-> 10.244.2.63:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.244.0.1:30994 rr
-> 10.244.2.62:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.244.0.1:31567 rr
-> 10.244.2.63:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 127.0.0.1:30994 rr
-> 10.244.2.62:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 127.0.0.1:31567 rr
-> 10.244.2.63:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 172.17.0.1:30994 rr
-> 10.244.2.62:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 172.17.0.1:31567 rr
-> 10.244.2.63:80 Masq 1 0 0
UDP 10.96.0.10:53 rr
-> 10.244.0.6:53 Masq 1 0 0
# 访问 10.97.97.97:80 观察效果。(轮询)。
[root@localhost k8s]# while true; do curl 10.97.97.97:80; sleep 2; done;
[root@localhost k8s]# while true; do curl 10.97.97.97:80; sleep 2; done;
10.244.2.64
10.244.1.63
10.244.1.62
10.244.2.64
10.244.1.63
10.244.1.62
10.244.2.64
7.3.3 Endpoint。
Endpoint 是 kubernetes 中的一个资源对象,存储在 etcd 中,用来记录一个 service 对应的所有 pod 的访问地址,它是根据 service 配置文件中 selector 描述产生的。
一个 Service 由一组 Pod 组成,这些 Pod 通过 Endpoints 暴露出来,Endpoints 是实现实际服务的端点集合。换句话说,service 和 pod 之间的联系是通过 endpoints 实现的。

- 负载分发策略。
对 Service 的访问被分发到了后端的 Pod 上去,目前 kubernetes 提供了两种负载分发策略。
-
如果不定义,默认使用 kube-proxy 的策略,比如随机、轮询。
-
基于客户端地址的会话保持模式,即来自同一个客户端发起的所有请求都会转发到固定的一个 Pod 上。
此模式可以使在 spec 中添加sessionAffinity:ClientIP选项。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f service-clusterip.yaml
service/service-clusterip created
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl describe svc service-clusterip -n dev
Name: service-clusterip
Namespace: dev
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Selector: app=nginx-pod
Type: ClusterIP
IP: 10.97.97.97
Port: <unset> 80/TCP
TargetPort: 80/TCP
Endpoints: 10.244.1.62:80,10.244.1.63:80,10.244.2.64:80
Session Affinity: ClientIP
Events: <none>
# 查看 ipvs 的映射规则【rr 轮询】。
# persisrent ~ 持久化。(基于 session 保存)。
TCP 10.97.97.97:80 rr persistent 10800
-> 10.244.1.62:80 Masq 1 0 0
-> 10.244.1.63:80 Masq 1 0 0
-> 10.244.2.64:80 Masq 1 0 0
[root@localhost k8s]# ipvsadm -Ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags
-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 192.168.142.150:30994 rr
-> 10.244.2.62:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 192.168.142.150:31567 rr
-> 10.244.2.63:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.96.0.1:443 rr
-> 192.168.142.150:6443 Masq 1 3 0
TCP 10.96.0.10:53 rr
-> 10.244.0.6:53 Masq 1 0 0
-> 10.244.0.7:53 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.96.0.10:9153 rr
-> 10.244.0.6:9153 Masq 1 0 0
-> 10.244.0.7:9153 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.97.97.97:80 rr persistent 10800
-> 10.244.1.62:80 Masq 1 0 0
-> 10.244.1.63:80 Masq 1 0 0
-> 10.244.2.64:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.103.149.9:443 rr
-> 192.168.142.151:443 Masq 1 2 0
TCP 10.107.6.137:80 rr
-> 10.244.2.63:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.107.80.13:80 rr
-> 10.244.2.62:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.244.0.0:30994 rr
-> 10.244.2.62:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.244.0.0:31567 rr
-> 10.244.2.63:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.244.0.1:30994 rr
-> 10.244.2.62:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 10.244.0.1:31567 rr
-> 10.244.2.63:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 127.0.0.1:30994 rr
-> 10.244.2.62:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 127.0.0.1:31567 rr
-> 10.244.2.63:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 172.17.0.1:30994 rr
-> 10.244.2.62:80 Masq 1 0 0
TCP 172.17.0.1:31567 rr
-> 10.244.2.63:80 Masq 1 0 0
UDP 10.96.0.10:53 rr
-> 10.244.0.6:53 Masq 1 0 0
-> 10.244.0.7:53 Masq 1 0 0
#访问测试。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# while true; do curl 10.97.97.97:80; sleep 2; done;
10.244.2.64
10.244.2.64
10.244.2.64
10.244.2.64
# 修改分发策略---sessionAffinity:ClientIP。
# 查看 ipvs 规则【persistent 代表持久】。
# persisrent ~ 持久化。(基于 session 保存)。
# 删除 service。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl delete -f service-clusterip.yaml
service "service-clusterip" deleted
目前 10.97.97.97:80 只能在 k8s 集群内部访问。
7.3.4 HeadLiness 类型的 Service。
在某些场景中,开发人员可能不想使用 Service 提供的负载均衡功能,而希望自己来控制负载均衡策略,针对这种情况,kubernetes 提供了 HeadLiness Service,这类 Service 不会分配 Cluster IP,如果想要访问 service,只能通过 service 的域名进行查询。
创建 service-headliness.yaml。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: service-headliness
namespace: dev
spec:
selector:
app: nginx-pod
clusterIP: None # 将 clusterIP 设置为 None,即可创建 headliness Service。
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
# 创建 service。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim service-headliness.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f service-headliness.yaml
service/service-headliness created
# 获取 service,发现 CLUSTER-IP 未分配。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get svc service-headliness -n dev -o wide
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR
service-headliness ClusterIP None <none> 80/TCP 14s app=nginx-pod
# 查看 service 详情。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl describe svc service-headliness -n dev
Name: service-headliness
Namespace: dev
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Selector: app=nginx-pod
Type: ClusterIP
IP: None
Port: <unset> 80/TCP
TargetPort: 80/TCP
Endpoints: 10.244.1.62:80,10.244.1.63:80,10.244.2.64:80
Session Affinity: None
Events: <none>
# 查看域名的解析情况。进入其中一台 pod。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get pods -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-778cb5fb7b-dgntb 1/1 Running 1 3d4h
pc-deployment-6696798b78-9s6pb 1/1 Running 1 7h25m
pc-deployment-6696798b78-fz6xg 1/1 Running 1 7h25m
pc-deployment-6696798b78-gp6fs 1/1 Running 1 7h25m
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl exec -it pc-deployment-6696798b78-9s6pb -n dev /bin/bash
root@pc-deployment-6696798b78-9s6pb:/# cat /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver 10.96.0.10
search dev.svc.cluster.local svc.cluster.local cluster.local localdomain.k8s.node1
options ndots:5
# @nameserver(域名服务器) + 服务名称(service 名称 + namespace(dev)【dev.svc.cluster.local】)
[root@localhost k8s]# dig @10.96.0.10 service-headliness.dev.svc.cluster.local
; <<>> DiG 9.11.4-P2-RedHat-9.11.4-26.P2.el7_9.10 <<>> @10.96.0.10 service-headliness.dev.svc.cluster.local
; (1 server found)
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; WARNING: .local is reserved for Multicast DNS
;; You are currently testing what happens when an mDNS query is leaked to DNS
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 646
;; flags: qr aa rd; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 3, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1
;; WARNING: recursion requested but not available
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;service-headliness.dev.svc.cluster.local. IN A
;; ANSWER SECTION:
service-headliness.dev.svc.cluster.local. 30 IN A 10.244.1.63
service-headliness.dev.svc.cluster.local. 30 IN A 10.244.2.64
service-headliness.dev.svc.cluster.local. 30 IN A 10.244.1.62
;; Query time: 1 msec
;; SERVER: 10.96.0.10#53(10.96.0.10)
;; WHEN: Fri Dec 09 00:46:10 CST 2022
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 237
7.3.5 NodePort 类型的 Service。
在之前的样例中,创建的 Service 的 ip 地址只有集群内部才可以访问,如果希望将 Service 暴露给集群外部使用,那么就要使用到另外一种类型的 Service,称为 NodePort 类型。NodePort 的工作原理其实就是将 service 的端口映射到 Node 的一个端口上,然后就可以通过 NodeIp:NodePort 来访问 service 了。

创建 service-nodeport.yaml。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: service-nodeport
namespace: dev
spec:
selector:
app: nginx-pod
type: NodePort # service 类型。
ports:
- port: 80
nodePort: 30002 # 指定绑定的 node 的端口(默认的取值范围是:30000-32767),如果不指定,会默认分配。
targetPort: 80
# 创建 service。
[root@localhost k8s]# vim service-nodeport.yaml
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f service-nodeport.yaml
service/service-nodeport created
# 查看 service。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl get svc -n dev -o wide
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR
service-nodeport NodePort 10.110.23.187 <none> 80:30002/TCP 28s app=nginx-pod
# 接下来可以通过电脑主机的浏览器去访问集群中任意一个 nodeip 的 30002 端口,即可访问到 pod。
192.168.142.150:30002
7.3.6 LoadBalancer 类型的 Service。
LoadBalancer 和 NodePort 很相似,目的都是向外部暴露一个端口,区别在于 LoadBalancer 会在集群的外部再来做一个负载均衡设备,而这个设备需要外部环境支持的,外部服务发送到这个设备上的请求,会被设备负载之后转发到集群中。

7.3.7 ExternalName 类型的 Service。
ExternalName 类型的 Service 用于引入集群外部的服务,ta 通过 externalName 属性指定外部一个服务的地址,然后在集群内部访问此 service 就可以访问到外部的服务了。

apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: service-externalname
namespace: dev
spec:
type: ExternalName # service 类型。
externalName: www.baidu.com # 改成 ip 地址也可以。
# 创建 service。
[root@localhost k8s]# kubectl create -f service-externalname.yaml
service/service-externalname created
# 域名解析。
[root@localhost k8s]# dig @10.96.0.10 service-externalname.dev.svc.cluster.local
; <<>> DiG 9.11.4-P2-RedHat-9.11.4-26.P2.el7_9.10 <<>> @10.96.0.10 service-externalname.dev.svc.cluster.local
; (1 server found)
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; WARNING: .local is reserved for Multicast DNS
;; You are currently testing what happens when an mDNS query is leaked to DNS
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 16497
;; flags: qr aa rd; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 4, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1
;; WARNING: recursion requested but not available
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;service-externalname.dev.svc.cluster.local. IN A
;; ANSWER SECTION:
service-externalname.dev.svc.cluster.local. 5 IN CNAME www.baidu.com.
www.baidu.com. 5 IN CNAME www.a.shifen.com.
www.a.shifen.com. 5 IN A 112.80.248.75
www.a.shifen.com. 5 IN A 112.80.248.76
;; Query time: 10 msec
;; SERVER: 10.96.0.10#53(10.96.0.10)
;; WHEN: Fri Dec 09 14:34:23 CST 2022
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 247
7.4 Ingress 介绍。
在前面课程中已经提到,Service 对集群之外暴露服务的主要方式有两种:NotePort 和 LoadBalancer,但是这两种方式,都有一定的缺点:
- NodePort 方式的缺点是会占用很多集群机器的端口,那么当集群服务变多的时候,这个缺点就愈发明显
- LB 方式的缺点是每个 service 需要一个 LB,浪费、麻烦,并且需要 kubernetes 之外设备的支持。
基于这种现状,kubernetes 提供了 Ingress 资源对象,Ingress 只需要一个 NodePort 或者一个 LB 就可以满足暴露多个 Service 的需求。工作机制大致如下图表示。

实际上,Ingress 相当于一个 7 层的负载均衡器,是 kubernetes 对反向代理的一个抽象,ta 的工作原理类似于 Nginx,可以理解成在 Ingress 里建立诸多映射规则,Ingress Controller 通过监听这些配置规则并转化成 Nginx 的反向代理配置 , 然后对外部提供服务。在这里有两个核心概念:
- ingress:kubernetes 中的一个对象,作用是定义请求如何转发到 service 的规则。
- ingress controller:具体实现反向代理及负载均衡的程序,对 ingress 定义的规则进行解析,根据配置的规则来实现请求转发,实现方式有很多,比如 Nginx, Contour, Haproxy 等等。
Ingress(以 Nginx 为例)的工作原理如下:
- 用户编写 Ingress 规则,说明哪个域名对应 kubernetes 集群中的哪个 Service。
- Ingress 控制器动态感知 Ingress 服务规则的变化,然后生成一段对应的 Nginx 反向代理配置。
- Ingress 控制器会将生成的 Nginx 配置写入到一个运行着的 Nginx 服务中,并动态更新。
- 到此为止,其实真正在工作的就是一个 Nginx 了,内部配置了用户定义的请求转发规则。

7.5 Ingress 使用。
7.5.1 环境准备 ~ 搭建 ingress 环境。
https://github.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/releases/tag/nginx-0.30.0
# 创建文件夹。
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# mkdir ingress-controller
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# cd ingress-controller/
# 获取 ingress-nginx,本次案例使用的是 0.30 版本。
[root@k8s-master01 ingress-controller]# wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/nginx-0.30.0/deploy/static/mandatory.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 ingress-controller]# wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/nginx-0.30.0/deploy/static/provider/baremetal/service-nodeport.yaml。
# 修改 mandatory.yaml 文件中的仓库。
# 修改 quay.io/kubernetes-ingress-controller/nginx-ingress-controller:0.30.0
# 为 quay-mirror.qiniu.com/kubernetes-ingress-controller/nginx-ingress-controller:0.30.0
# (不用修改了)。
# 创建 ingress-nginx。
[root@localhost k8s]# mkdir ingress_controller
[root@localhost k8s]# cd ingress_controller/
[root@localhost ingress_controller]# ls
mandatory.yaml service-nodeport.yaml
[root@localhost ingress_controller]# kubectl apply -f ./
namespace/ingress-nginx created
configmap/nginx-configuration created
configmap/tcp-services created
configmap/udp-services created
serviceaccount/nginx-ingress-serviceaccount created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/nginx-ingress-clusterrole created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/nginx-ingress-role created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/nginx-ingress-role-nisa-binding created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/nginx-ingress-clusterrole-nisa-binding created
deployment.apps/nginx-ingress-controller created
limitrange/ingress-nginx created
service/ingress-nginx created
# 查看 ingress-nginx。
[root@localhost ingress_controller]# kubectl get pod -n ingress-nginx
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-ingress-controller-7f74f657bd-ng7fq 1/1 Running 0 50s
# 查看 service。
[root@localhost ingress_controller]# kubectl get svc -n ingress-nginx
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
ingress-nginx NodePort 10.105.121.237 <none> 80:31476/TCP,443:31813/TCP 76s
7.5.2 准备 service 和 pod。
为了后面的实验比较方便,创建如下图所示的模型。

创建 tomcat-nginx.yaml。
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
namespace: dev
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx-pod
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
ports:
- containerPort: 80
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: tomcat-deployment
namespace: dev
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: tomcat-pod
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: tomcat-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: tomcat
image: tomcat:8.5-jre10-slim
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
namespace: dev
spec:
selector:
app: nginx-pod
clusterIP: None
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: tomcat-service
namespace: dev
spec:
selector:
app: tomcat-pod
clusterIP: None
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- port: 8080
targetPort: 8080
# 创建。
[root@localhost ingress_controller]# kubectl create -f tomcat-nginx.yaml
deployment.apps/nginx-deployment created
deployment.apps/tomcat-deployment created
service/nginx-service created
service/tomcat-service created
# 查看。
[root@localhost ingress_controller]# kubectl get svc -n dev
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
nginx-service ClusterIP None <none> 80/TCP 28s
tomcat-service ClusterIP None <none> 8080/TCP 28s
[root@localhost ingress_controller]# kubectl get deployment -n dev
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
nginx-deployment 3/3 3 3 55s
tomcat-deployment 3/3 3 3 55s
7.5.2 Http 代理。
创建 ingress-http.yaml。
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress-http
namespace: dev
spec:
rules:
- host: nginx.geek.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: nginx-service
servicePort: 80
- host: tomcat.geek.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: tomcat-service
servicePort: 8080
# 创建。
[root@localhost ingress_controller]# vim ingress-http.yaml
[root@localhost ingress_controller]# kubectl create -f ingress-http.yaml
ingress.extensions/ingress-http created
# 查看。
[root@localhost ingress_controller]# kubectl get ing ingress-http -n dev
NAME HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
ingress-http nginx.geek.com,tomcat.geek.com 80 26s
# 查看详情。
[root@localhost ingress_controller]# kubectl describe ing ingress-http -n dev
Name: ingress-http
Namespace: dev
Address: 10.105.121.237
Default backend: default-http-backend:80 (<none>)
Rules:
Host Path Backends
---- ---- --------
nginx.geek.com
/ nginx-service:80 (10.244.1.72:80,10.244.1.73:80,10.244.2.75:80)
tomcat.geek.com
/ tomcat-service:8080 (10.244.1.71:8080,10.244.2.73:8080,10.244.2.74:8080)
Annotations:
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal CREATE 67s nginx-ingress-controller Ingress dev/ingress-http
Normal UPDATE 39s nginx-ingress-controller Ingress dev/ingress-http
# 接下来,在本地电脑上配置 host 文件,解析上面的两个域名到 192.168.142.150(master)上。
# 然后,就可以分别访问 tomcat.geek.com:31476 和 nginx.geek.com:31476 查看效果了。
7.5.3 Https 代理。
创建证书。
# 生成证书。
[root@localhost ingress_controller]# openssl req -x509 -sha256 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout tls.key -out tls.crt -subj "/C=CN/ST=BJ/L=BJ/O=nginx/CN=geek.com"
Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key
........................................................................+++
..........+++
writing new private key to 'tls.key'
-----
# 创建密钥。
[root@localhost ingress_controller]# ls
ingress-http.yaml mandatory.yaml service-nodeport.yaml tls.crt tls.key tomcat-nginx.yaml
[root@localhost ingress_controller]# kubectl create secret tls tls-secret --key tls.key --cert tls.crt
secret/tls-secret created
创建 ingress-https.yaml。
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress-https
namespace: dev
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
- nginx.geek.com
- tomcat.geek.com
secretName: tls-secret # 指定秘钥。
rules:
- host: nginx.geek.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: nginx-service
servicePort: 80
- host: tomcat.geek.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: tomcat-service
servicePort: 8080
# 创建。
[root@localhost ingress_controller]# kubectl create -f ingress-https.yaml
ingress.extensions/ingress-https created
# 查看。
[root@localhost ingress_controller]# kubectl get ing ingress-https -n dev
NAME HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
ingress-https nginx.geek.com,tomcat.geek.com 10.105.121.237 80, 443 24s
# 查看详情。
[root@localhost ingress_controller]# kubectl describe ing ingress-https -n dev
Name: ingress-https
Namespace: dev
Address: 10.105.121.237
Default backend: default-http-backend:80 (<none>)
TLS:
tls-secret terminates nginx.geek.com,tomcat.geek.com
Rules:
Host Path Backends
---- ---- --------
nginx.geek.com
/ nginx-service:80 (10.244.1.72:80,10.244.1.73:80,10.244.2.75:80)
tomcat.geek.com
/ tomcat-service:8080 (10.244.1.71:8080,10.244.2.73:8080,10.244.2.74:8080)
Annotations:
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal CREATE 47s nginx-ingress-controller Ingress dev/ingress-https
Normal UPDATE 32s nginx-ingress-controller Ingress dev/ingress-https
# 下面可以通过浏览器访问 https://nginx.geek.com:31813 和 https://tomcat.geek.com:31813 来查看了。
8. 数据存储。
《k8s ~ 数据存储。》
9. 安全认证。
《k8s ~ 安全认证。》
10. dashboard。
《k8s ~ dashboard。》