编程导航算法通关村第 1关 | 白银挑战
剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点
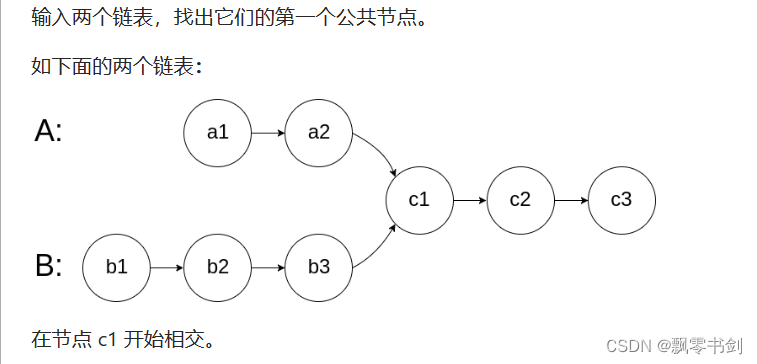
集合/map
- 将headA中的链表,放在一个set集合中, 依次遍历headB, headB中第一个包含在set集合中的节点就是第一个公共子节点
ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
// 将headA压入集合中
Set<ListNode> statckA = new HashSet<>();
ListNode temp = headA;
while (temp != null) {
statckA.add(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
ListNode tempB = headB;
while (tempB != null) {
if (statckA.contains(tempB)) {
return tempB;
}
tempB = tempB.next;
}
return null;
}
栈
- 将两个链表的节点分别压入栈中,然后同时出栈,当两个栈出栈的元素相等是,说明这个节点是公共子节点,当最后一个相等的元素出栈时,就是第一个公共子节点
/**
* 方法二:将两个链表的节点分别压入栈中,然后同时出栈,
* 当两个栈出栈的元素相等是,
* 说明这个节点是公共子节点,当最后一个相等的元素出栈时,就是第一个公共子节点
*/
ListNode getIntersectionNodeByStack(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
// 同时压入两个栈中
ListNode tempA = headA;
ListNode tempB = headB;
Stack<ListNode> stackA = new Stack<>();
Stack<ListNode> stackB = new Stack<>();
while (tempA != null) {
stackA.push(tempA);
tempA = tempA.next;
}
while (tempB != null) {
stackB.push(tempB);
tempB = tempB.next;
}
ListNode result = null;
while (stackA.size() != 0 && stackB.size() != 0) {
ListNode popA = stackA.pop();
ListNode popB = stackB.pop();
if (popA == popB) {
result = popA;
} else {
break;
}
}
return result;
}
拼接两个字符串

/**
* 分别遍历两个链表
* headA+headB;
* headB+headA
* 找到的第一个相等的点,就是两个的第一个公共子节点
*/
ListNode getIntersectionNodeByString(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode tempA = headA;
ListNode tempB = headB;
// 考虑链表为空的情况
if (headA == null) {
return null;
}
if (headB == null) {
return null;
}
while (tempA != tempB) {
tempA = tempA.next;
tempB = tempB.next;
if (tempA != tempB) {
if (tempA == null) {
tempA = headB;
}
if (tempB == null) {
tempB = headA;
}
}
}
return tempA;
}
差和双指针
- 先各自统计链表的长度
- 计算长度的差值
- 较长的链表移动差值距离
- 同时向后移动,第一个相等节点便是第一个公共子节点
ListNode getIntersectionNodeBysubA(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode tempA = headA;
ListNode tempB = headB;
// 考虑链表为空的情况
if (headA == null) {
return null;
}
if (headB == null) {
return null;
}
// 计算长度
int lengthA = 0;
int lengthB = 0;
while (tempA != null) {
tempA = tempA.next;
lengthA++;
}
while (tempB != null) {
tempB = tempB.next;
lengthB++;
}
// 计算差值
int sub = Math.abs(lengthA - lengthB);
tempA = headA;
tempB = headB;
if (lengthA > lengthB) {
int i = 0;
while (i < sub) {
tempA = tempA.next;
i++;
}
} else if (lengthB > lengthA) {
int i = 0;
while (i < sub) {
tempB = tempB.next;
i++;
}
}
// 同时向后移动
while (tempA != null && tempB != null) {
if (tempA == tempB) {
return tempA;
}
tempA = tempA.next;
tempB = tempB.next;
}
return null;
}
判断是否是回文序列
使用栈
- 将链表中的元素全部压入栈中,遍历链表,与栈中弹出的元素是否相等,如何全部相等,则为回文序列
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
Stack<ListNode> listNodes = new Stack<>();
ListNode temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
listNodes.push(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
//
temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
ListNode pop = listNodes.pop();
if (temp.val != pop.val) {
return false;
}
temp=temp.next;
}
return true;
}
优化:只遍历一半,将前一半与后一半进行对比
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
Stack<ListNode> listNodes = new Stack<>();
ListNode temp = head;
int length = 0;
while (temp != null) {
listNodes.push(temp);
temp = temp.next;
length++;
}
//
// 计算一半的值
int cout = length / 2;
temp = head;
int i = 0;
while (temp != null && i < cout) {
ListNode pop = listNodes.pop();
if (temp.val != pop.val) {
return false;
}
temp = temp.next;
i++;
}
return true;
}
快慢指针+一半反转法
-
首先,如果链表为空或者只有一个节点,那么它肯定是回文的,所以直接返回true。
-
创建两个指针slow和fast,都指向链表的头部。slow指针每次移动一步,fast指针每次移动两步。这样,当fast指针到达链表的末尾时,slow指针就会在链表的中间。
-
同时,我们还创建了pre和prepre两个指针,用于反转链表的前半部分。pre指针始终指向slow指针的前一个节点,prepre指针始终指向pre指针的前一个节点。在每次循环中,我们都将pre指针的next指向prepre,然后将prepre和pre分别更新为pre和slow,这样就可以反转链表的前半部分。
-
如果链表的长度是奇数,那么fast指针会停在最后一个节点上,此时slow指针指向的是链表的中间节点,我们需要将slow指针向后移动一步,跳过中间节点。
-
最后,我们同时遍历反转后的前半部分链表(从pre指针开始)和后半部分链表(从slow指针开始),如果发现有节点的值不相等,那么就返回false。如果所有节点的值都相等,那么就返回true。
-
这个函数的时间复杂度是O(n),空间复杂度是O(1),其中n是链表的长度。
public static boolean isPalindromeByFastAndSlow(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
// 当fast到达末尾时,slow正好到达中间
ListNode pre = null;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
ListNode next = slow;
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
// 进行翻转
next.next = pre;
pre = next;
// next = slow;
}
System.out.println(pre.val);
System.out.println(slow.val);
if (fast != null) {
slow = slow.next;
}
// 此时pre就是翻转后链表的头结点,
// slow是后半部分的头结点
while (pre != null && slow != null) {
if (pre.val != slow.val) {
return false;
}
pre = pre.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return true;
//
}
删除倒数第N个元素
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
输出:[1,2,3,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [1], n = 1
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1,2], n = 1
输出:[1]
提示:
链表中结点的数目为 sz
1 <= sz <= 30
0 <= Node.val <= 100
1 <= n <= sz
进阶:你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
Related Topics 链表 双指针 👍 2586 👎 0
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode listNode = new ListNode(0);
listNode.next = head;
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
// if ( head.next == null && n == 1 ) {
// return null;
// }
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = listNode;
//
int i = 0;
while (i < n) {
fast = fast.next;
i++;
}
while (fast != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
// slow.ne
// 删除slow 下一个节点的位置
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return listNode.next;
}
删除重复元素
- 设置虚拟头结点,防止出现删除head节点的情况
- 保留重复的值,直接删除
/**
*
* 删除重复元素
* */
public ListNode deleteDuplicatesNo(ListNode head) {
ListNode doumoNode = new ListNode(0);
doumoNode.next = head;
ListNode temp = doumoNode;
while (temp != null && temp.next != null && temp.next.next != null) {
if (temp.next.val == temp.next.next.val) {
int x = temp.next.val;
while (temp.next != null && temp.next.val == x) {
temp.next = temp.next.next;
}
} else {
temp = temp.next;
}
}
return doumoNode.next;
}