Spring @Autowired 注解原理
1.@Autowired 使用
@ComponentScan("org.example.bean")
public class AnnoContextDemo {
@Autowired
private User user;
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AnnoContextDemo.class);
User user1 = context.getBean(AnnoContextDemo.class).user;
System.out.println("user1 = " + user1);
}
}
被扫描的组件配置类
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
@Bean
public User user(){
return new User(21,"张三");
}
}
输出结果
user1 = User{age=21, name='张三'}
2.依赖自动注入原理
定位@Autowired所在包 org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired
找到同包下 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 的类继承图如下
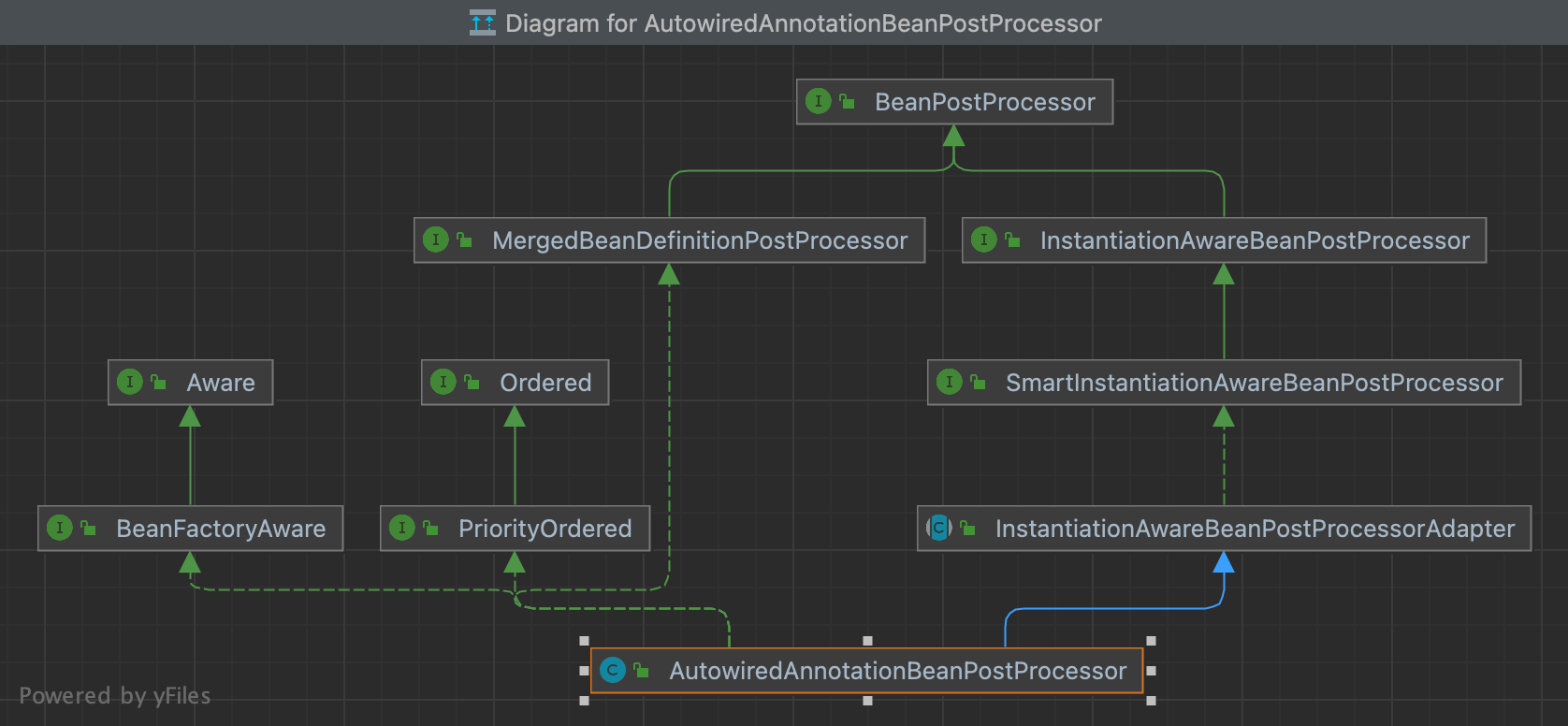
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor与
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor两个BeanPostProcessor后置处理器接口
-
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 此接口主要有两个方法 抽象方法 postProcessMergedBeanDefinition 默认方法 resetBeanDefinition
-
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 此接口 抽象方法 postProcessBeforeInstantiation ,postProcessAfterInstantiation ,默认方法 postProcessProperties ,默认过时方法 postProcessPropertyValues
想搞清楚@Autowried注入原理,先得知道这些接口对应方法执行的先后顺序 跟踪ApplicationContext.refresh方法,调用链路如下
ApplicationContext.refresh() -> AbstractApplicationContext.finishBeanFactoryInitialization() -> ConfigurableListableBeanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons() - > AbstractBeanFactory.getBean() -> AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean() -> AbstractBeanFactory.getSingleton() -> AbstractBeanFactory.createBean()
实例化前
-> resolveBeforeInstantiation() 执行 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInstantiation()前置方法 如果返回不为null,将执行 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization()后置方法。
创建bean实例阶段
-> doCreateBean() -> createBeanInstance 反射创建bean实例
-> applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors() 执行 MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor.MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor方法 合并bean定义信息
属性注入阶段
-> populateBean() -> 执行 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInstantiation 后置处理方法 -> 执行InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessProperties -> InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessPropertyValues -> applyPropertyValues 执行属性注入
初始化阶段
-> initializeBean() -> BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization() 执行前置方法 -> invokeInitMethods() 反射调用初始化方法 -> BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization 执行后置方法
收尾注册bean
->registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary() 注册bean
通过上面追踪refresh()方法我们可知,spring容器将先调用 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition方法,然后执行 postProcessProperties 方法
3. postProcessMergedBeanDefinition 查找需要自动注入的字段或方法
public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, beanType, null);
metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition);
}
进入findAutowiringMetadata方法
private InjectionMetadata findAutowiringMetadata(String beanName, Class<?> clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {
// Fall back to class name as cache key, for backwards compatibility with custom callers.
String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
if (metadata != null) {
metadata.clear(pvs);
}
//查找类的字段,方法,是否有需要自动注入对象的元素,封装InjectionMetadata
metadata = buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz);
//放入缓存中,供后面调用取出
this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
}
}
}
return metadata;
}
进入 buildAutowiringMetadata 方法
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(Class<?> clazz) {
//判断当前类是否有使用autowiredAnnotationTypes容器中的注解
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, this.autowiredAnnotationTypes)) {
return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;
}
List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
final List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements = new ArrayList<>();
//反射遍历类中所有字段
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
//字段上是否有标注自动装配相关的注解
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
if (ann != null) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);
}
return;
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
//封装InjectionMetadata
currElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
}
});
//反射遍历类中所有方法
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
return;
}
//方法上是否有标注自动装配相关的注解
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);
if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static methods: " + method);
}
return;
}
if (method.getParameterCount() == 0) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation should only be used on methods with parameters: " +
method);
}
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
//封装InjectionMetadata
currElements.add(new AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));
}
});
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
return InjectionMetadata.forElements(elements, clazz);
}
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes 为set集合,容器内为需要自动注入的注解类
private final Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> autowiredAnnotationTypes = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
public AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() {
## 1.@Autowired
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add(Autowired.class);
## 2.@Value
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add(Value.class);
try {
## 3.@javax.inject.Inject JSR-330规范中定义的一个注解
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add((Class<? extends Annotation>)
ClassUtils.forName("javax.inject.Inject", AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class.getClassLoader()));
logger.trace("JSR-330 'javax.inject.Inject' annotation found and supported for autowiring");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// JSR-330 API not available - simply skip.
}
}
4.postProcessProperties 需要自动注入的元素从容器中获取bean后注入
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
//首先从缓存中取出需要自动注入的元素(包括字段,方法)
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
//进行注入
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
进入 metadata.inject() 方法
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Collection<InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate =
(checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
//遍历需要注入的元素
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
//不同类型调用各自inject方法
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}
字段处理逻辑
通过 resolveFieldValue 方法,找到需要依赖的bean(单个或集合),通过 Filed.set方法注入
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Field field = (Field) this.member;
Object value;
if (this.cached) {
try {
value = resolvedCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Unexpected removal of target bean for cached argument -> re-resolve
value = resolveFieldValue(field, bean, beanName);
}
}
else {
//查找依赖的bean
value = resolveFieldValue(field, bean, beanName);
}
if (value != null) {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
//反射设置值
field.set(bean, value);
}
}
public Object doResolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {
InjectionPoint previousInjectionPoint = ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(descriptor);
try {
Object shortcut = descriptor.resolveShortcut(this);
if (shortcut != null) {
return shortcut;
}
Class<?> type = descriptor.getDependencyType();
Object value = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getSuggestedValue(descriptor);
if (value != null) {
if (value instanceof String) {
String strVal = resolveEmbeddedValue((String) value);
BeanDefinition bd = (beanName != null && containsBean(beanName) ?
getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName) : null);
value = evaluateBeanDefinitionString(strVal, bd);
}
TypeConverter converter = (typeConverter != null ? typeConverter : getTypeConverter());
try {
return converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getTypeDescriptor());
}
catch (UnsupportedOperationException ex) {
// A custom TypeConverter which does not support TypeDescriptor resolution...
return (descriptor.getField() != null ?
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getField()) :
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getMethodParameter()));
}
}
Object multipleBeans = resolveMultipleBeans(descriptor, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
if (multipleBeans != null) {
return multipleBeans;
}
//字段非集合类型时bean时查找方法
Map<String, Object> matchingBeans = findAutowireCandidates(beanName, type, descriptor);
if (matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
if (isRequired(descriptor)) {
raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);
}
return null;
}
String autowiredBeanName;
Object instanceCandidate;
if (matchingBeans.size() > 1) {
autowiredBeanName = determineAutowireCandidate(matchingBeans, descriptor);
if (autowiredBeanName == null) {
if (isRequired(descriptor) || !indicatesMultipleBeans(type)) {
return descriptor.resolveNotUnique(descriptor.getResolvableType(), matchingBeans);
}
else {
// In case of an optional Collection/Map, silently ignore a non-unique case:
// possibly it was meant to be an empty collection of multiple regular beans
// (before 4.3 in particular when we didn't even look for collection beans).
return null;
}
}
instanceCandidate = matchingBeans.get(autowiredBeanName);
}
else {
// We have exactly one match.
Map.Entry<String, Object> entry = matchingBeans.entrySet().iterator().next();
autowiredBeanName = entry.getKey();
instanceCandidate = entry.getValue();
}
if (autowiredBeanNames != null) {
autowiredBeanNames.add(autowiredBeanName);
}
if (instanceCandidate instanceof Class) {
instanceCandidate = descriptor.resolveCandidate(autowiredBeanName, type, this);
}
Object result = instanceCandidate;
if (result instanceof NullBean) {
if (isRequired(descriptor)) {
raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);
}
result = null;
}
if (!ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(type, result)) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(autowiredBeanName, type, instanceCandidate.getClass());
}
return result;
}
finally {
ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(previousInjectionPoint);
}
}
findAutowireCandidates() 会调用 BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors
底层通过类似双亲委派模型,找出所有的bean
public static String[] beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
ListableBeanFactory lbf, Class<?> type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit) {
Assert.notNull(lbf, "ListableBeanFactory must not be null");
String[] result = lbf.getBeanNamesForType(type, includeNonSingletons, allowEagerInit);
if (lbf instanceof HierarchicalBeanFactory) {
HierarchicalBeanFactory hbf = (HierarchicalBeanFactory) lbf;
if (hbf.getParentBeanFactory() instanceof ListableBeanFactory) {
String[] parentResult = beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
(ListableBeanFactory) hbf.getParentBeanFactory(), type, includeNonSingletons, allowEagerInit);
result = mergeNamesWithParent(result, parentResult, hbf);
}
}
return result;
}

![[JVM] 5. 运行时数据区(2)-- 程序计数器(Program Counter Register)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/b78d59aa6414cac49c11b50f86666f8f.png#pic_center)