目录
1.字符串的驻留机制编辑
2.字符串查找
2.1字符串查询操作方法
3.字符串大小写转换
3.1字符串的大小写转换方法
4.字符串内容对齐
4.1字符串内容对齐操作方法
5.字符串的劈分
5.1字符串劈分操作的方法编辑
6.字符串判断
6.1判断字符串操作的方法编辑
6.2字符串替换和合并编辑
1.字符串的驻留机制
a='Python'
b='Python'
c='Python'
print('a:',a,id(a))
print('b:',b,id(b))
print('c:',c,id(c))
# a: Python 2834106576176
# b: Python 2834106576176
# c: Python 2834106576176

2.字符串查找
2.1字符串查询操作方法
| 方法名称 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| index() | 查找子串substr第一次出现的位置,如果查找的子串不存在时,则抛出ValueError |
| rindex() | 查找子串substr最后一次出现的位置,如果查找的子串不存在时,则抛出ValueError |
| find() | 查找子串substr第一次出现的位置,如果查找的子串不存在时,则返回-1 |
| rfind() | 查找子串substr最后一次出现的位置,如果查找的子串不存在时,则返回-1 |
s='hello,hello'
print(s.index('lo'))#3
print(s.rindex('lo'))#9
print(s.find('lo'))#3
print(s.rfind('lo'))#9
#print(s.index('k'))ValueError: substring not found
print(s.find('k')) #-1
3.字符串大小写转换
3.1字符串的大小写转换方法
| 方法名称 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| upper() | 把字符串中所有字符都转换成大写字母 |
| lower() | 把字符串中所有字符都转换成小写字母 |
| swapcase() | 把字符串中所有大写字母都转换成小写字母,把所有小写字母都转换成大写字母 |
| capitalize() | 把第一个字符转换成大写,把其余字符转换为小写 |
| title() | 把每个单词的第一个字符转换为大写,把每个单词的剩余字符转换成小写 |
转换之后,会产生一个新的字符串对象
s='hello,python'
print(s,id(s))
print(s.upper(),id(s.upper()))
# hello,python 2564162926064
# HELLO,PYTHON 2564162925936
a='HELLO,PYTHON'
print(a,id(a))
print(a.lower(),id(a.lower()))
# HELLO,PYTHON 2564162926448
# hello,python 2564162926512
print(a==s.upper())
print(a is s.upper())
# True
# False
#内容相同,地址不同
s1='asfJSEOFH'
print(s1.swapcase())
print(s1.capitalize())
s2='sdjf ddjo EJOSD CNDDScjd'
print(s2.title())
# ASFjseofh
# Asfjseofh
# Sdjf Ddjo Ejosd Cnddscjd
4.字符串内容对齐
4.1字符串内容对齐操作方法
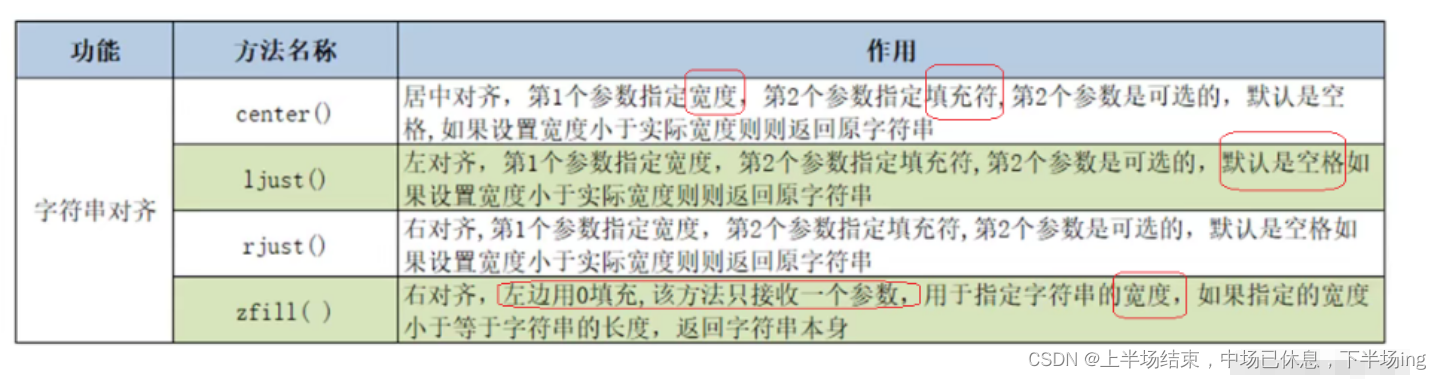
宽度,指定填充符
s='hello,Python'
print(s.center(20,'*'))
# ****hello,Python****
print(s.ljust(20,'*'))
print(s.ljust(10,'*'))
print(s.ljust(20))
# hello,Python********
# hello,Python
# hello,Python
print(s.rjust(20,'*'))
print(s.rjust(20))
print(s.rjust(10))
# ********hello,Python
# hello,Python
# hello,Python
print(s.zfill(20))
print('-9010'.zfill(8))
# 00000000hello,Python
# -0009010
5.字符串的劈分
5.1字符串劈分操作的方法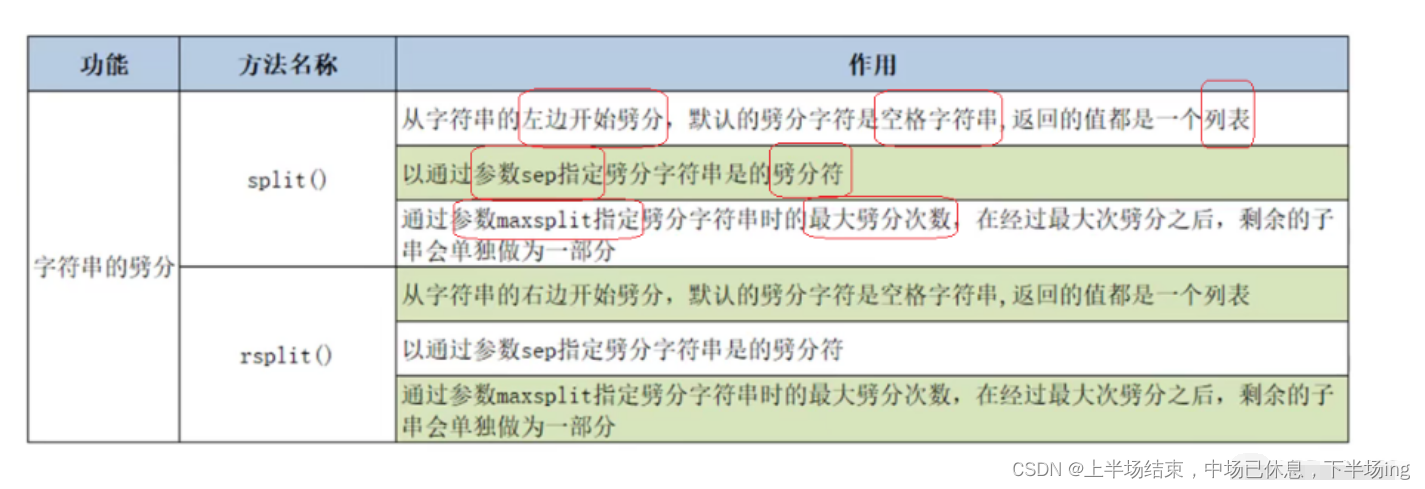
s='hello world python'
lst=s.split()
print(lst)
s1='hello|world|python'
print(s1.split())
print(s1.split(sep='|'))#让分隔符为竖线
print(s1.split(sep='|',maxsplit=1))#只分一次
# ['hello', 'world', 'python']
# ['hello|world|python']
# ['hello', 'world', 'python']
# ['hello', 'world|python']
s='hello world python'
lst=s.rsplit()
print(lst)
s1='hello|world|python'
print(s1.rsplit())
print(s1.rsplit(sep='|'))#让分隔符为竖线
print(s1.rsplit(sep='|',maxsplit=1)) #从右侧开始劈分,只分一次
# ['hello', 'world', 'python']
# ['hello|world|python']
# ['hello', 'world', 'python']
# ['hello|world', 'python']
6.字符串判断
6.1判断字符串操作的方法
s='hello,python'
print(s.isidentifier())
s='hello2341_python'#字母数字下划线
print(s.isidentifier())
# False
# True
s=' \n \t'
print(s.isspace())
# True
s='dsjfSDLFJ'
print(s.isalpha())
s='dsf3'
print(s.isalpha())
# True
# False
s='238509'
print(s.isdecimal())
s='九02347'
print(s.isdecimal())
# True
# False
s='32840四五十四'
print(s.isnumeric())
# True
s='sdjf324'
print(s.isalnum())
# True
6.2字符串替换和合并
s='hello,python,python,python'
print(s.replace('python','c++'))
s='hello,python,python,python'
print(s.replace('python','c++',2))
# hello,c++,c++,c++
# hello,c++,c++,python
lst=['hello','java','python']
print('|'.join(lst))
print(''.join(lst))
# hello|java|python
# hellojavapython
t=('hello','java','python')
print('|'.join(t))
print(''.join(t))
# hello|java|python
# hellojavapython
print('*'.join('Python'))
# P*y*t*h*o*n