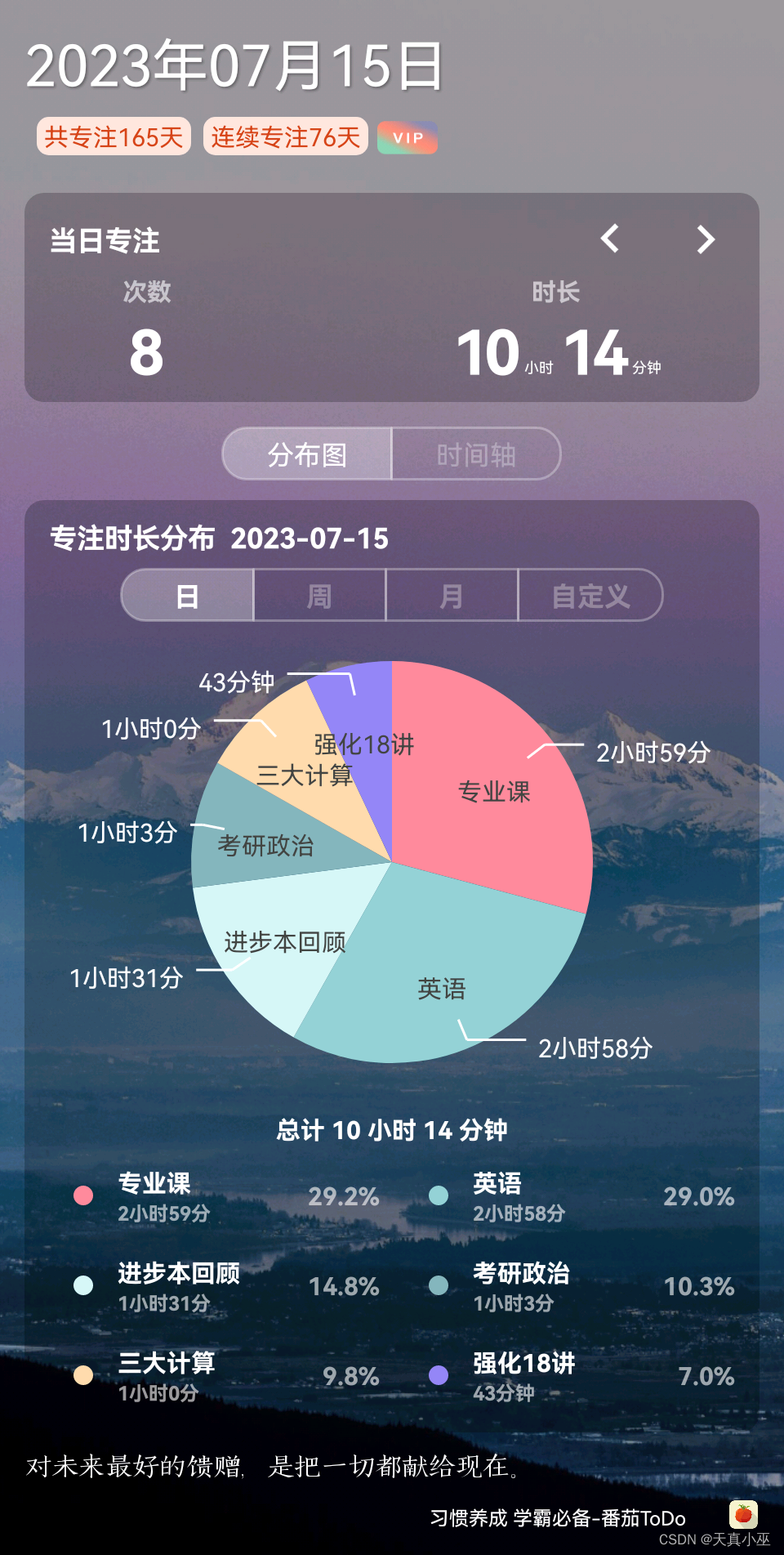
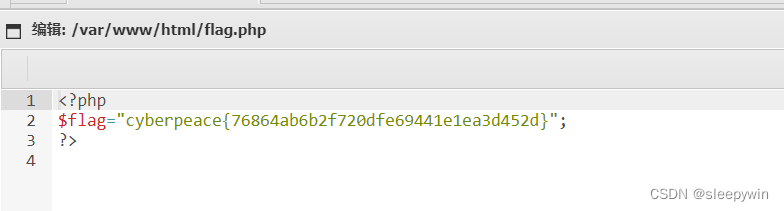
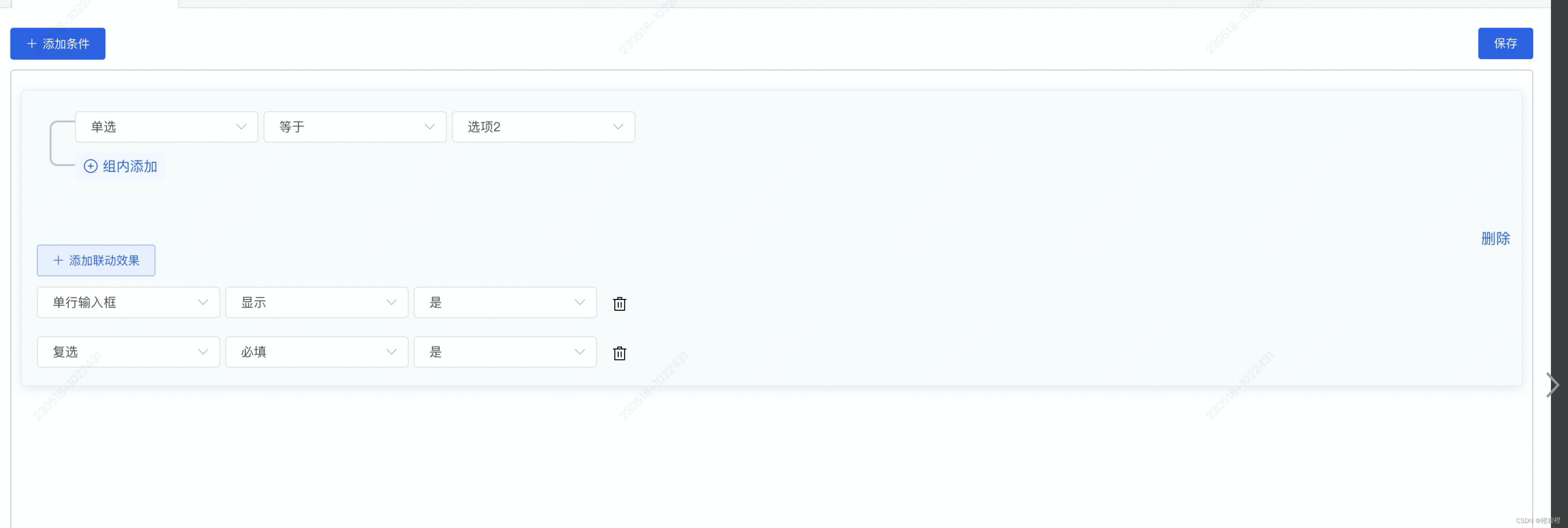
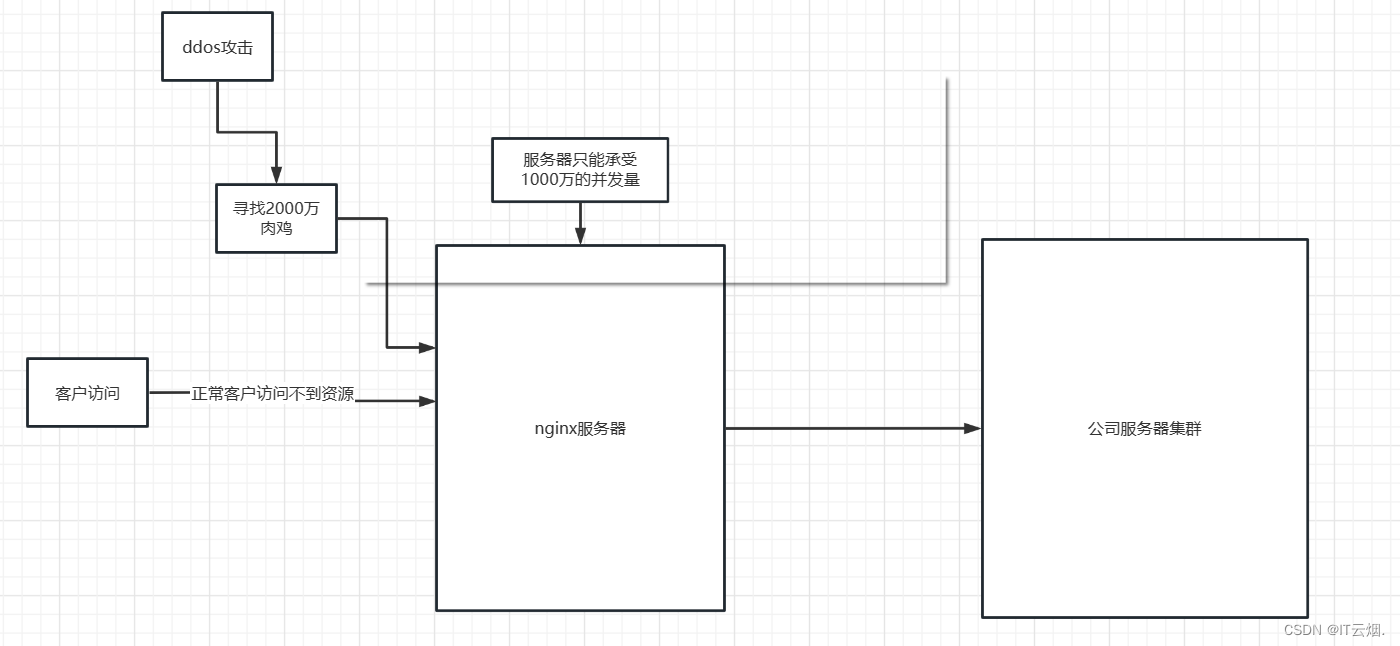
int dup(int oldfd);复制文件描述符
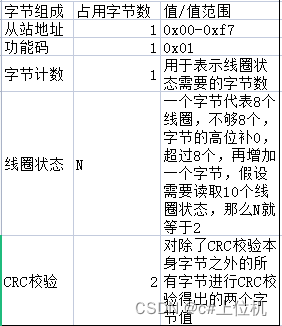
/*
#include <unistd.h>
int dup(int oldfd);
作用:复制一个新的文件描述符
fd=3, int fd1 = dup(fd),
fd指向的是a.txt, fd1也是指向a.txt
从空闲的文件描述符表中找一个最小的,作为新的拷贝的文件描述符
*/
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <string.h>
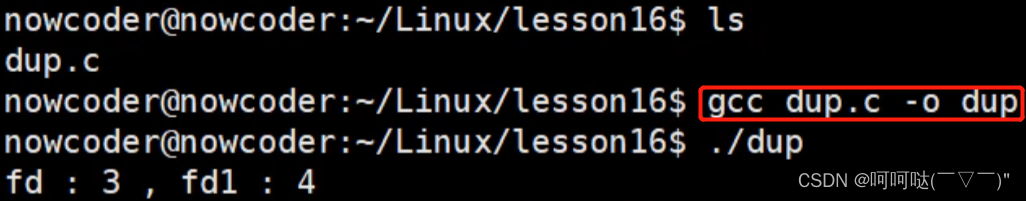
int main() {
int fd = open("a.txt", O_RDWR | O_CREAT, 0664);
int fd1 = dup(fd);
if(fd1 == -1) {
perror("dup");
return -1;
}
printf("fd : %d , fd1 : %d\n", fd, fd1);
close(fd);
char * str = "hello,world";
int ret = write(fd1, str, strlen(str));
if(ret == -1) {
perror("write");
return -1;
}
close(fd1);
return 0;
}

![]()

int dup2(int oldfd,int newfd);重定向文件描述符
#include <unistd.h>
int dup2(int oldfd, int newfd);
作用:重定向文件描述符
oldfd 指向 a.txt, newfd 指向 b.txt
调用函数成功后:newfd 和 b.txt 做close, newfd 指向了 a.txt
oldfd 必须是一个有效的文件描述符
oldfd和newfd值相同,相当于什么都没有做
/*
#include <unistd.h>
int dup2(int oldfd, int newfd);
作用:重定向文件描述符
oldfd 指向 a.txt, newfd 指向 b.txt
调用函数成功后:newfd 和 b.txt 做close, newfd 指向了 a.txt
oldfd 必须是一个有效的文件描述符
oldfd和newfd值相同,相当于什么都没有做
*/
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
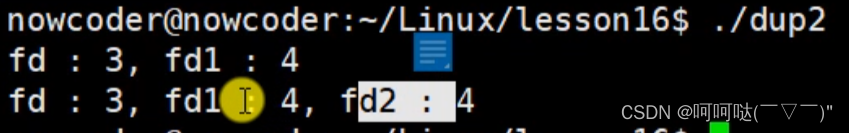
int main() {
int fd = open("1.txt", O_RDWR | O_CREAT, 0664);
if(fd == -1) {
perror("open");
return -1;
}
int fd1 = open("2.txt", O_RDWR | O_CREAT, 0664);
if(fd1 == -1) {
perror("open");
return -1;
}
printf("fd : %d, fd1 : %d\n", fd, fd1);
int fd2 = dup2(fd, fd1);
if(fd2 == -1) {
perror("dup2");
return -1;
}
// 通过fd1去写数据,实际操作的是1.txt,而不是2.txt
char * str = "hello, dup2";
int len = write(fd1, str, strlen(str));
if(len == -1) {
perror("write");
return -1;
}
printf("fd : %d, fd1 : %d, fd2 : %d\n", fd, fd1, fd2);
close(fd);
close(fd1);
return 0;
}
![]()