thymeleaf是一个XML/XHTML/HTML5模板引擎,可用于Web与非Web环境中的应用开发
最开始网站开始发展时,使用HTML展示网页,随着技术的发展和需求变化,出现了前后端交互的页面,不需要使用多个页面去展示一个大同小异的页面。动态页面成为网页的新的方向。
95年,java语言出现,java使用servlet来实现页面,将其放在如Tomcat这样的servlet容器里面,来接受和响应数据,servlet会监听端口号,并将接受和响应的数据封装成request和response对象,并对底层网络通信做了抽象的封装,大大简化了web开发的难度。
后来,java开发了jsp,一种嵌在HTML的动态语言,使用模板生成动态的内容,jsp最终会被编译成servlet,所以无法在不运行的时候去查看页面的样式,也为开发增加了一点难度。
在之后,产生了新的用于前端开发的第三方脚本语言,Thymeleaf等许多标签语言,他们使用HTML模板语言,不适用web服务也可以查看页面。
Thymeleaf:
- 默认模板的位置是在resources/templates
- 模拟的静态文件css、js等实在 resources/static 下
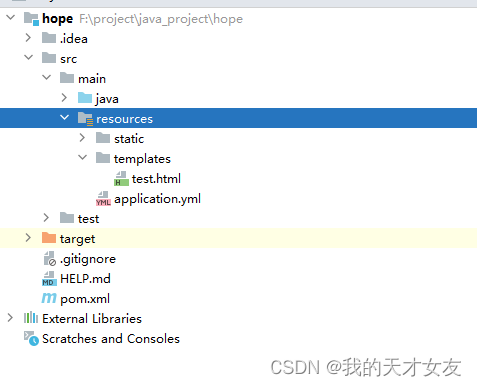
如上所以是一个Spring Boot新建的项目结构,在pom文件中引入thymeleaf包。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置
application.yml
添加一些配置便于开发
server:
port: 8080
spring:
thymeleaf:
cache: false
mode: HTML5
模板文件
在resouces下新建templates文件夹,新建test.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Thymeleaf的入门</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
<!--输出hello数据-->
<p th:utext="${message}"></p>
</body>
</html>
controller
然后在新建一个controller中指向此文件。
package com.zuiuxi.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
@Controller
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("test")
public String test(Model model){
model.addAttribute("message","<h1>hello world</h1>");
return "test";
}
}
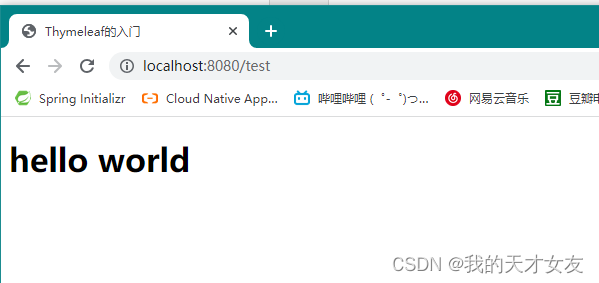
启动如下所示,thymeleaf模板启动成功了。
语法
th:text
用于显示文本内容
<p th:text="${message}"></p>
${message} 表示读取当前对象的属性。
*{} 对对象属性做一定的简化
#{} 表示读取属性文件中的值
@{} 用于拼接全路径
controller
@RequestMapping("test")
public String test(Model model){
model.addAttribute("message","<h1>hello world</h1>");
model.addAttribute("student",new Student("lvgui"));
return "test";
}
test.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Thymeleaf的入门</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
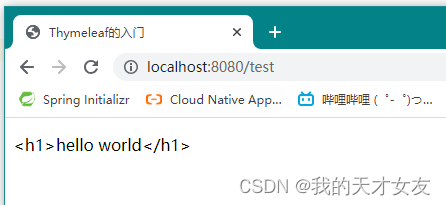
<!--输出hello数据-->
<p th:text="${message}"></p>
<a th:href="@{/index(userId=1)}">点击</a>
<div th:object="${student}">
<p th:text="*{name}"></p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
运行结果如下所示:
th:utext
用法和th:text相同,不过th:utext会解析对应的html语言
表达式
${ } 大括号中可以使用OGNL或SpEL表达式的引擎解析,常见的字符串拼接和比较语句都可以使用。
- 比较 < div th:text=“${student.age} > 20”></ div>
- 三目 < div th:text="${student.age} > 20? ‘大’:‘小’ "></ div>
选择分支
th:if 如果条件为真,填充数据到闭合标签内部
th:unless 条件为false, 填充数据到闭合标签内部
th:switch th:case 实现多重选择
<div th:object="${student}">
<p th:if="*{sex=='男'}" th:text="男性"></p>
</div>
循环
th:each 循环
controller
@RequestMapping("test")
public String test(Model model){
model.addAttribute("message","<h1>hello world</h1>");
List<Student> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
list1.add(new Student("寒冰","女"));
list1.add(new Student("蛮子","男"));
model.addAttribute("list1",list1);
return "test";
}
test.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Thymeleaf的入门</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
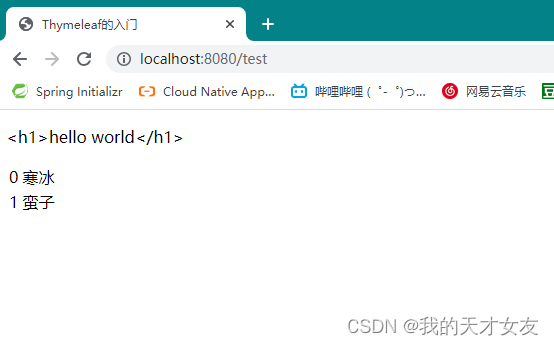
<!--输出hello数据-->
<p th:text="${message}"></p>
<table>
<tr th:each="stu,status:${list1}">
<td th:text="${status.index}"></td>
<td th:text="${stu.name}"></td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
循环中的增强特性
- index 从0开始的索引
- count 元素的个数,从1开始
- size 元素的总数
- current 当前遍历的元素
- even/odd 是否为奇偶,boolean的
- first/last 是否最后或者第一个
设置属性值
- th:attr
- th:value 绑定值
- th:checked 当前值是否会被选择
- th:selected 下来属性是否选择
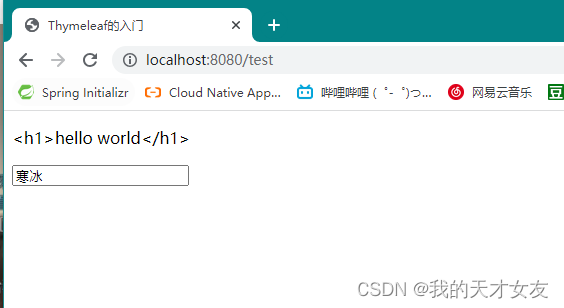
<input type="text" th:value="${student.name}">
css修饰
th:class
th:style
组合
th:block th:insert 来组合模板
<th:block th:insert="common"></th:block>
Thymeleaf高级特性
这些用于处理一些业务提供的公共类
- #dates
- #numbers
- #strings
- #arrays
- #lists
- #sets
- #request、#response
- #session、#servletContext
内联
th:inline 声明在内联的属性
[[]]去用于写入对应的变量