树的企业应用-哈夫曼编码树-有趣的数据压缩算法
哈夫曼编码 描述
张三去李四家里,但 李四是一个女生,所以张三找李四去上海迪尼斯玩 …
亚历山大.张三去伊丽莎白.李四家里,但 伊丽莎白.李四是一个女生,所以亚历山大.张三找伊丽莎白.李四去美国迪尼斯玩 …
我们发现 一个关键点 有些重复的也不多 无非就高亮的地方 所以简化一下
声明一下 在上方的引言里 凡是出现高亮的 统统替换为 “张三” and “李四”
张三去李四家里,但 李四是一个女生,所以张三找李四去上海迪尼斯玩 ………
张三去李四家里,但 李四是一个女生,所以张三找李四去美国迪尼斯玩 ………
哈夫曼编码:把字符出现的次数压缩成只有一个
这就是哈夫曼编码 基本描述
哈夫曼编码树原理
字符串为 **"yyds ndd yygq bbq jjz xdxl jj qq wx dy wb bz ww " **
进行压缩变成如下表格:
| 字符 | 该字符出现的次数 |
|---|---|
| ‘y’ | 5 |
| ‘d’ | 5 |
| ‘b’ | 4 |
| ‘g’ | 1 |
| ‘q’ | 4 |
| ‘z’ | 2 |
| ‘x’ | 3 |
| ‘j’ | 4 |
| ‘w’ | 4 |
| ’ ’ | 13 |
我们使用文本的方式储存这些 字符和出现的频率(注意:此博主比较懒输入,干脆整成一个文件)
input.txt:
y 5 d 5 g 1 q 4 z 2 x 3 j 4 w 4 13

那问题来了 哈夫曼编码树? 这些只是从文件读取到内存里整成了一个顺序表, 而已
我们使用C I/O的函数 来读取 文件 .
回过神来!
能看得出来这些是一体的 所以ndd(你懂的),我们应该定义 全新的数据类型 : Huffman_Code
哈夫曼编码树数据域定义
struct HuffmanCode{
char Val;//数据
int weight;//频率
}
定义完 先实现读取字符和频率
既然是顺序表 那还得用 统计 input.txt 文件的数据和频率多少个元素
const char* FileName = "input.txt";
const char* OpenMode = "r";
//读取的格式: 数据 空格 权值 空格
const char* readFormat = "%c %d ";
//统计文件中的数据和频率的个数并且通过参数修改
bool getSize(int& size) {
FILE* ReadStream = nullptr;
const errno_t openState = fopen_s(&ReadStream, FileName, OpenMode);
bool ret = openState == 0;
if (ret) {
int i = 0;
char ch = getc(ReadStream);
ret = ch != EOF;
if (ret) {
ungetc(ch, ReadStream);
HuffmanCodeValue value{};
int ReadNum = 0;
char read[alignof(HuffmanCodeValue) +2];
//&value.value, sizeof(value.value), &space, sizeof(space), &value.weight, sizeof(value.weight)
while (!feof(ReadStream)) {
ReadNum = fscanf_s(ReadStream, readFormat, &value.value, sizeof(value.value), &value.weight, sizeof(value.weight));
++i;
}
size = i;
}
else {
cerr << "错误:" << FileName << "里文件为空" << endl;
}
fclose(ReadStream);
ReadStream = nullptr;
}
else {
char error[1024]{};
strerror_s(error, errno);
cerr << "错误:" << error << endl;
}
return ret;
}
分配好内存 之后 读取文件中的数据
//获取文件 哈夫曼编码 以及编码的权值
void loadValue(HuffmanCodeValue* value, const int &size) {
if (size!=0){
FILE* ReadStream = nullptr;
const errno_t openState = fopen_s(&ReadStream, FileName, OpenMode);
bool ret = openState == 0;
if (ret) {
auto First = 0;
int ReadNum = 0;
char read[alignof(HuffmanCodeValue)+ 1];
while (First != size && !feof(ReadStream)) {
ReadNum = fscanf_s(ReadStream, readFormat, &value[First].value, sizeof(value[First].value), &value[First].weight, sizeof(value[First].weight));
++First;
}
fclose(ReadStream);
//free(ReadStream);
ReadStream = nullptr;
}
}
}
读取完毕后 ,是时候 该设计一些数据结构了(也是,最骚脑的时刻)
哈夫曼编码树的定义
//哈夫曼编码树节点
struct HuffmanCodeTreeNode{
HuffmanCode value;//数据
HuffmanCodeTreeNode* Parent;//父节点
HuffmanCodeTreeNode* LeftChild;//左子节点
HuffmanCodeTreeNode* RightChild;//右子节点
};
//哈夫曼编码树
struct HuffmanCodeTree {
HuffmanCodeTreeNode* root;//根节点
};
你以为到这里就结束了吗 …
那你就有点小瞧了哈夫曼编码树 还得按照优先级的频率来的
所以 还得吧写好的优先级队列搬出来
#ifndef __PriorityQueue_H__
#define __PriorityQueue_H__
#include"HuffmanTree.h"
using Element = HuffmanCodeTreeNode*;
using PriorityQueueNode = struct _PriorityQueueNode;
using PriorityCompare = bool (*)(const int &, const int &);
using PriorityQueueAuxiliary = struct _PriorityQueueAuxiliary;
using PriorityQueue = struct _PriorityQueue;
struct _PriorityQueueNode {
int Priority;
Element value;
PriorityQueueNode* next;
};
struct _PriorityQueueAuxiliary {
PriorityQueueNode* froot;
PriorityQueueNode* back;
};
struct _PriorityQueue {
PriorityCompare Compare;
size_t size;
PriorityQueueAuxiliary Auxiliary;
};
const size_t MaxSize = 1024;
void initPriorityQueue(PriorityQueue& priorityQueue, PriorityCompare c);
void PushPriorityQueue(PriorityQueue& priorityQueue,const Element& value);
bool fullPriorityQueue(const PriorityQueue& priorityQueue);
bool emptyPriorityQueue(const PriorityQueue& priorityQueue);
Element& PriorityQueueFroot(PriorityQueue& priorityQueue);// 禁止
//删除优先级队列 Element& value 设置到 value 里
void PopPriorityQueue(PriorityQueue& priorityQueue, Element& value);
void setCompare(PriorityQueue& priorityQueue, PriorityCompare Compare);
const size_t& PriorityQueueSize(PriorityQueue& priorityQueue);
void destroyPriorityQueue(PriorityQueue& priorityQueue);
#endif
PriorityQueue.cpp
#include"PriorityQueue.h"
#include<stdexcept>
using namespace std;
using Node = PriorityQueueNode;
const size_t zero = 0;
//创建优先级队列元素
Node* CreatePriorityQueueNode(const Element& value, Node* nullPtr = nullptr) {
Node* node = new Node{ value->value.weight,value,nullPtr };
return node;
}
void initPriorityQueue(PriorityQueue& priorityQueue, PriorityCompare c) {
priorityQueue.Auxiliary = { nullptr,nullptr };
priorityQueue.size = zero;
priorityQueue.Compare = c;
}
bool fullPriorityQueue(const PriorityQueue& priorityQueue) {
return priorityQueue.size == MaxSize;
}
bool emptyPriorityQueue(const PriorityQueue& priorityQueue) {
return priorityQueue.size == zero;
}
void GetPriorityNode(Node*&, PriorityCompare&);
Element& PriorityQueueFroot(PriorityQueue& priorityQueue)
{
if (emptyPriorityQueue(priorityQueue)) {
destroyPriorityQueue(priorityQueue);
terminate();
}
return priorityQueue.Auxiliary.froot->value;
}
void Link(Node*& node, Node* NewNode) {
if (node) {
node->next = NewNode;
}
node = NewNode;
}
const size_t& PriorityQueueSize(PriorityQueue& priorityQueue) {
return priorityQueue.size;
}
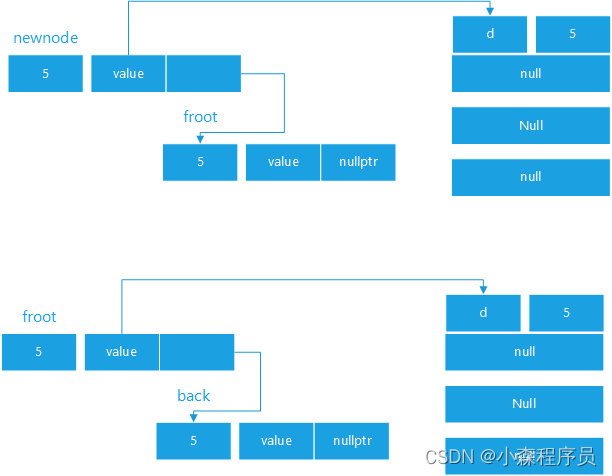
void PushPriorityQueue(PriorityQueue& priorityQueue, const Element& value) {
const bool iSfront = priorityQueue.size == zero;
if (fullPriorityQueue(priorityQueue)) {
destroyPriorityQueue(priorityQueue);
terminate();
}
auto&& newNode = CreatePriorityQueueNode(value);
auto& Froot = priorityQueue.Auxiliary.froot;
auto& back = priorityQueue.Auxiliary.back;
if (!iSfront) {
Link(newNode->next ,Froot);//小的 调整
Froot = newNode;
}else{
Link(back, newNode);
Froot = back;
}
++priorityQueue.size;
}
void GetPriorityNode(Node*& froot, PriorityCompare& Compare) {
Node** node = &froot;
Node* last = (froot);
if (last) {
Node* current = last->next;
while (current) {
if (Compare(current->Priority, (*node)->Priority)) {
node = &(last->next);
}
last = current;
current = current->next;
}
froot = *node;
}
}
void setCompare(PriorityQueue& priorityQueue, PriorityCompare Compare) {
priorityQueue.Compare = Compare;
}
void PopPriorityQueue(PriorityQueue& priorityQueue, Element& value) {
if (emptyPriorityQueue(priorityQueue)) {
destroyPriorityQueue(priorityQueue);
terminate();
}
size_t& size = priorityQueue.size;
Node** prev = NULL, * prev_node = NULL;
Node* last = NULL, * tmp = NULL;
prev = &(priorityQueue.Auxiliary.froot);
last = priorityQueue.Auxiliary.froot;
if (!last){
--size;
}
else {
tmp = last->next;
while (tmp) {
if (priorityQueue.Compare(tmp->Priority, (*prev)->Priority)) {
prev = &(last->next);
prev_node = last;
}
last = tmp;
tmp = tmp->next;
}
value = (*prev)->value;
auto DeleteNode = *prev;
*prev = (*prev)->next;
delete DeleteNode;
DeleteNode = nullptr;
--size;
}
if (size == zero) {
(priorityQueue.Auxiliary.back) = nullptr;
}
if (prev_node && prev_node->next == NULL) {
(priorityQueue.Auxiliary.back = prev_node);
}
}
void destroyPriorityQueue(PriorityQueue& priorityQueue) {
PriorityQueueAuxiliary& Auxiliary = priorityQueue.Auxiliary;
Node*& Firsh = Auxiliary.froot;
Node*& deleteNode = Firsh;
size_t& size = priorityQueue.size;
while (Firsh) {
Node* next = Firsh->next;
delete deleteNode;
deleteNode = next;
}
priorityQueue = {};
}
插入小调整
![=1670589638549)(assets/1670579952844.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6f348f55e02343e6a2f480a24848c607.png)
按照比较函数 经过比较函数来达到出队的目的
HuffmanTree.cpp
#include "HuffmanTree.h"
#include"PriorityQueue.h"
#include<iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
bool priorityCompare(const int& Left, const int& Right){
return Left < Right;
}
构建哈夫曼编码树
void build_HuffmanCodeTree(HuffmanCodeTree& tree, HuffmanCodeValue* value, size_t Size) {
PriorityQueue priorityQueue;
initPriorityQueue(priorityQueue, priorityCompare);
HuffmanCodeTreeNode* newNode = nullptr;
for (size_t i = 0; i < Size; i++) {
newNode = new HuffmanCodeTreeNode{};
newNode->value = value[i];
PushPriorityQueue(priorityQueue, newNode);
}
HuffmanCodeTreeNode* Node1 = nullptr;
HuffmanCodeTreeNode* Node2 = nullptr;
int i = 0;
do {
if (!emptyPriorityQueue(priorityQueue)) {
PopPriorityQueue(priorityQueue, Node1);
if (OutputISspace(Node1->value.value) == "空格") {
cout << "第"<<++i<<"次优先级队列 出队数据为:" << OutputISspace(Node1->value.value) << " 权值:" << Node1->value.weight << endl << endl;
}
else {
cout << "第" << ++i << "次优先级队列 出队数据为:" << (Node1->value.value) << " 权值:" << Node1->value.weight << endl << endl;
}
}
else {
break;
}
if (!emptyPriorityQueue(priorityQueue)) {
newNode = new HuffmanCodeTreeNode();
PopPriorityQueue(priorityQueue, Node2);
if (OutputISspace(Node2->value.value) == "空格") {
cout << "第" << ++i << "次优先级队列 出队数据为:"<<OutputISspace(Node2->value.value) << " 权值:" << Node2->value.weight << endl << endl;
}
else {
cout << "第" << ++i << "次优先级队列 出队数据为:"<<(Node2->value.value) << " 权值:" << Node2->value.weight << endl << endl;
}
newNode->LeftChild = Node1;
Node1->Parent = newNode;
newNode->RightChild = Node2;
Node2->Parent = newNode;
newNode->value.value = Space;
newNode->value.weight = Node1->value.weight + Node2->value.weight;
cout << "合并新结点 优先级队列 入队数据为:" << OutputISspace(newNode->value.value) << " 权值:" << newNode->value.weight << endl << endl;
PushPriorityQueue(priorityQueue, newNode);
}
else {
tree.root = Node1;
break;
}
} while (true);
destroyPriorityQueue(priorityQueue);
}
合并成新的树节点
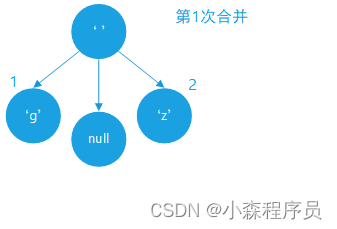
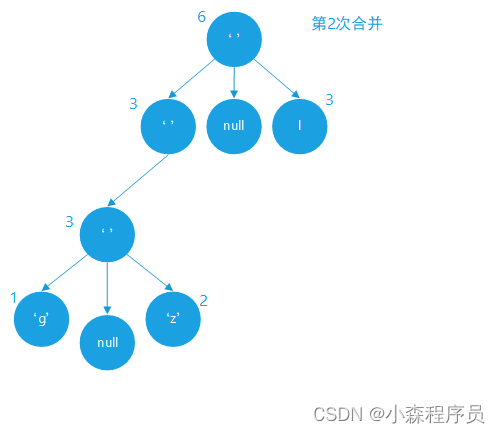
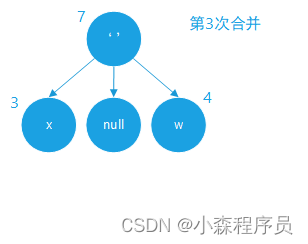
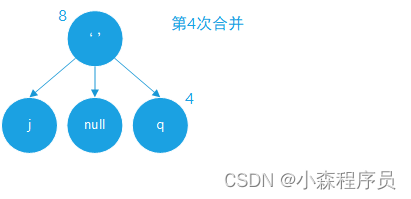
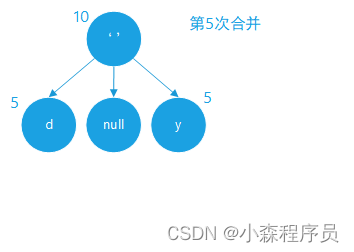
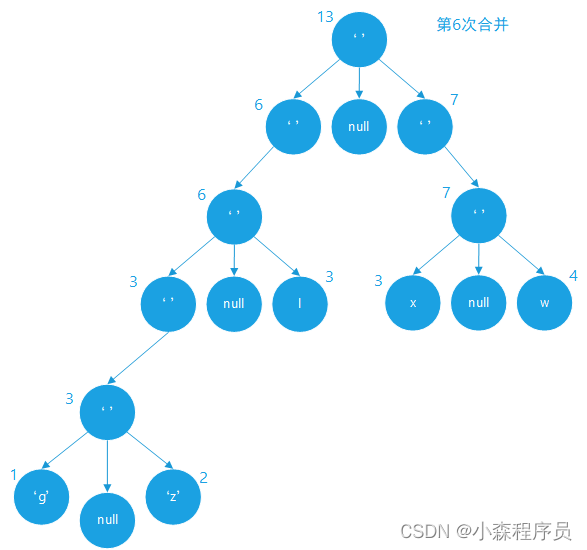
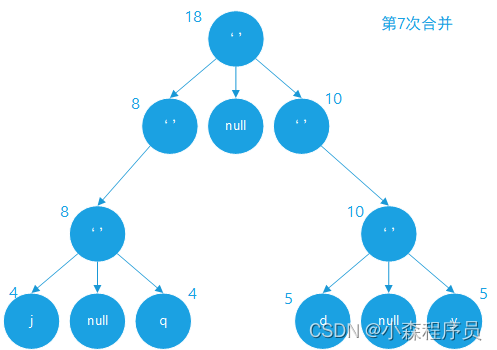
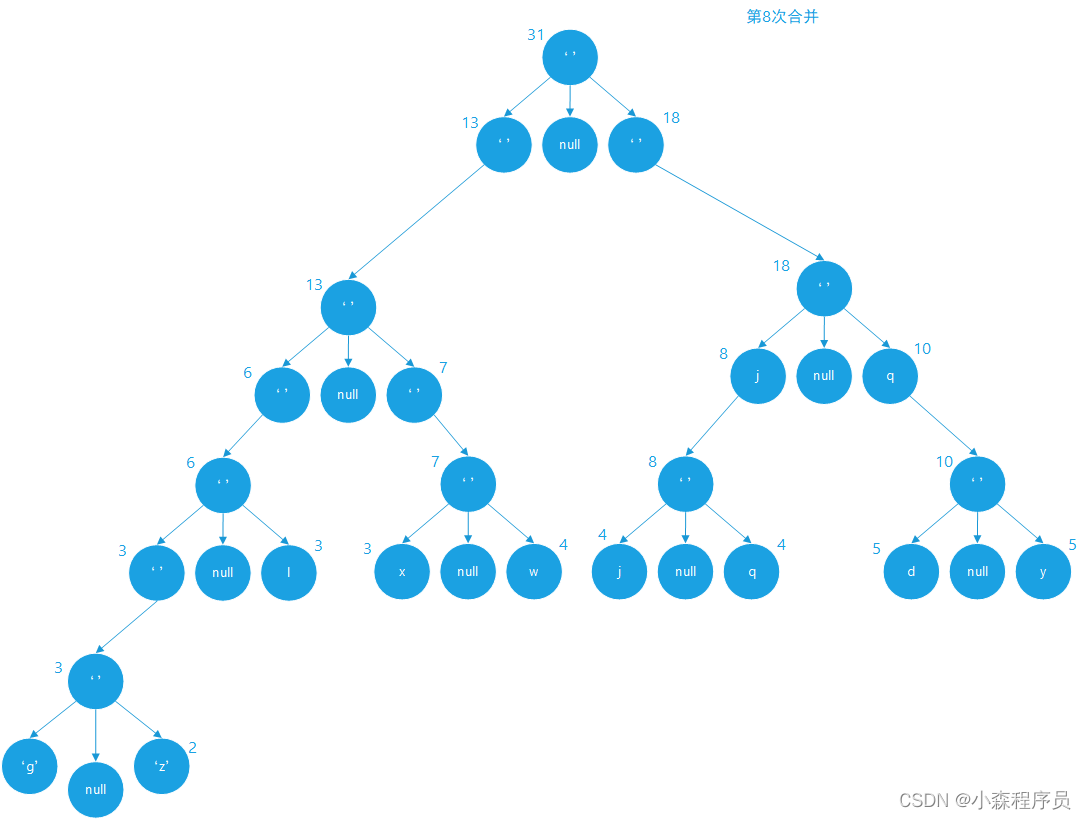
合并的结果
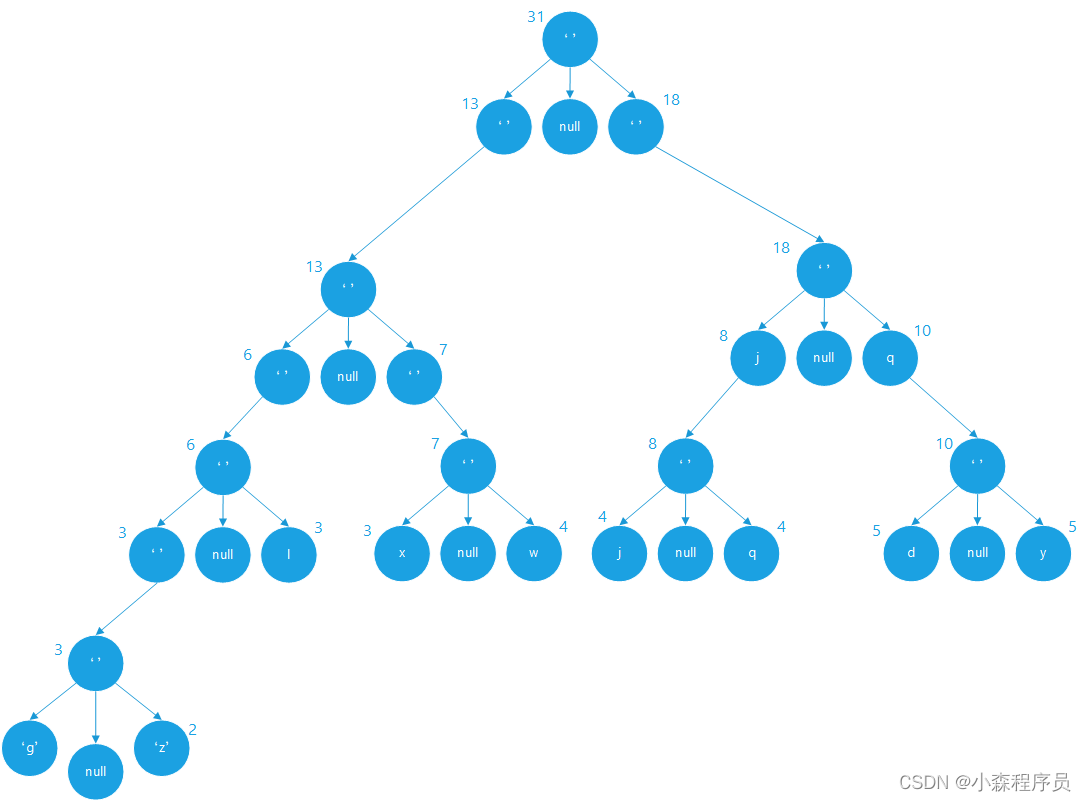
哈夫曼编码树算法实现
算法声明
bool priorityCompare(const int& Left, const int& Right);
//构建哈夫曼编码树
void build_HuffmanCodeTree(HuffmanCodeTree& tree, HuffmanCodeValue* value, size_t Size);
//前序遍历
void FirstOrderRecursiveTraversal(HuffmanCodeTreeNode*& Root);
//销毁哈夫曼编码树
void DestroyHuffmanCodeTree(HuffmanCodeTreeNode*& root);
算法实现
#include "HuffmanTree.h"
#include"PriorityQueue.h"
#include<iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
bool priorityCompare(const int& Left, const int& Right){
return Left < Right;
}
void build_HuffmanCodeTree(HuffmanCodeTree& tree, HuffmanCodeValue* value, size_t Size) {
PriorityQueue priorityQueue;
initPriorityQueue(priorityQueue, priorityCompare);
HuffmanCodeTreeNode* newNode = nullptr;
for (size_t i = 0; i < Size; i++) {
newNode = new HuffmanCodeTreeNode{};
newNode->value = value[i];
PushPriorityQueue(priorityQueue, newNode);
}
HuffmanCodeTreeNode* Node1 = nullptr;
HuffmanCodeTreeNode* Node2 = nullptr;
int i = 0;
do {
if (!emptyPriorityQueue(priorityQueue)) {
PopPriorityQueue(priorityQueue, Node1);
if (OutputISspace(Node1->value.value) == "空格") {
cout << "第"<<++i<<"次优先级队列 出队数据为:" << OutputISspace(Node1->value.value) << " 权值:" << Node1->value.weight << endl << endl;
}
else {
cout << "第" << ++i << "次优先级队列 出队数据为:" << (Node1->value.value) << " 权值:" << Node1->value.weight << endl << endl;
}
}
else {
break;
}
if (!emptyPriorityQueue(priorityQueue)) {
newNode = new HuffmanCodeTreeNode();
PopPriorityQueue(priorityQueue, Node2);
if (OutputISspace(Node2->value.value) == "空格") {
cout << "第" << ++i << "次优先级队列 出队数据为:"<<OutputISspace(Node2->value.value) << " 权值:" << Node2->value.weight << endl << endl;
}
else {
cout << "第" << ++i << "次优先级队列 出队数据为:"<<(Node2->value.value) << " 权值:" << Node2->value.weight << endl << endl;
}
newNode->LeftChild = Node1;
Node1->Parent = newNode;
newNode->RightChild = Node2;
Node2->Parent = newNode;
newNode->value.value = Space;
newNode->value.weight = Node1->value.weight + Node2->value.weight;
cout << "合并新结点 优先级队列 入队数据为:" << OutputISspace(newNode->value.value) << " 权值:" << newNode->value.weight << endl << endl;
PushPriorityQueue(priorityQueue, newNode);
}
else {
tree.root = Node1;
break;
}
} while (true);
destroyPriorityQueue(priorityQueue);
}
void FirstOrderRecursiveTraversal(HuffmanCodeTreeNode*& Root) {
if (Root) {
cout << "- :" << (Root->value.value) << " -" << endl;
//cout << "压缩数据为:" << (Root->value.value) << endl;
FirstOrderRecursiveTraversal(Root->LeftChild);
FirstOrderRecursiveTraversal(Root->RightChild);
}
}
void DestroyHuffmanCodeTree(HuffmanCodeTreeNode*& root) {
if (root) {
DestroyHuffmanCodeTree(root->LeftChild);
DestroyHuffmanCodeTree(root->RightChild);
delete root;
root = {};
}
}
main函数
#include<iostream>
#include"HuffmanTree.h"
#include"PriorityQueue.h"
using namespace std;
const char* FileName = "input.txt";
const char* OpenMode = "r";
//读取的格式: 数据 空格 权值 空格
const char* readFormat = "%c %d ";
//统计文件中的数据和频率的个数并且通过参数修改
bool getSize(int& size) {
FILE* ReadStream = nullptr;
const errno_t openState = fopen_s(&ReadStream, FileName, OpenMode);
bool ret = openState == 0;
if (ret) {
int i = 0;
char ch = getc(ReadStream);
ret = ch != EOF;
if (ret) {
ungetc(ch, ReadStream);
HuffmanCodeValue value{};
int ReadNum = 0;
char read[alignof(HuffmanCodeValue) +2];
//&value.value, sizeof(value.value), &space, sizeof(space), &value.weight, sizeof(value.weight)
while (!feof(ReadStream)) {
ReadNum = fscanf_s(ReadStream, readFormat, &value.value, sizeof(value.value), &value.weight, sizeof(value.weight));
++i;
}
size = i;
}
else {
cerr << "错误:" << FileName << "里文件为空" << endl;
}
fclose(ReadStream);
ReadStream = nullptr;
}
else {
char error[1024]{};
strerror_s(error, errno);
cerr << "错误:" << error << endl;
}
return ret;
}
//获取文件 哈夫曼编码 以及编码的权值
void loadValue(HuffmanCodeValue* value, const int &size) {
if (size!=0){
FILE* ReadStream = nullptr;
const errno_t openState = fopen_s(&ReadStream, FileName, OpenMode);
bool ret = openState == 0;
if (ret) {
auto First = 0;
int ReadNum = 0;
char read[alignof(HuffmanCodeValue)+ 1];
while (First != size && !feof(ReadStream)) {
ReadNum = fscanf_s(ReadStream, readFormat, &value[First].value, sizeof(value[First].value), &value[First].weight, sizeof(value[First].weight));
++First;
}
fclose(ReadStream);
//free(ReadStream);
ReadStream = nullptr;
}
}
}
int main(void) {
HuffmanCodeValue* value;
HuffmanCodeTree tree{};
int size;
if (getSize(size)){
value = new HuffmanCodeValue[size];
loadValue(value, size);
build_HuffmanCodeTree(tree, value, size);
FirstOrderRecursiveTraversal(tree.root);
delete [] value;
DestroyHuffmanCodeTree(tree.root);
}
return 0;
}
output:
第1次优先级队列 出队数据为:g 权值:1
第2次优先级队列 出队数据为:z 权值:2
合并新结点 优先级队列 入队数据为:空格 权值:3
第3次优先级队列 出队数据为:空格 权值:3
第4次优先级队列 出队数据为:1 权值:3
合并新结点 优先级队列 入队数据为:空格 权值:6
第5次优先级队列 出队数据为:x 权值:3
第6次优先级队列 出队数据为:w 权值:4
合并新结点 优先级队列 入队数据为:空格 权值:7
第7次优先级队列 出队数据为:j 权值:4
第8次优先级队列 出队数据为:q 权值:4
合并新结点 优先级队列 入队数据为:空格 权值:8
第9次优先级队列 出队数据为:d 权值:5
第10次优先级队列 出队数据为:y 权值:5
合并新结点 优先级队列 入队数据为:空格 权值:10
第11次优先级队列 出队数据为:空格 权值:6
第12次优先级队列 出队数据为:空格 权值:7
合并新结点 优先级队列 入队数据为:空格 权值:13
第13次优先级队列 出队数据为:空格 权值:8
第14次优先级队列 出队数据为:空格 权值:10
合并新结点 优先级队列 入队数据为:空格 权值:18
第15次优先级队列 出队数据为:空格 权值:13
第16次优先级队列 出队数据为:空格 权值:18
合并新结点 优先级队列 入队数据为:空格 权值:31
第17次优先级队列 出队数据为:空格 权值:31
- : -
- : -
- : -
- : -
- :g -
- :z -
- :1 -
- : -
- :x -
- :w -
- : -
- : -
- :j -
- :q -
- : -
- :d -
- :y -






![[效率工具] Git下对敏感文件/内容的处理](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/206bb4eefb7d45b7928e798660207cc9.png)