文章目录
- 数据结构Mat
- 成员变量
- 成员方法
- 构造函数
- 1、普通构造函数
- 2、外部数据指针构造函数
- 3、拷贝构造函数和opertor =
- 深拷贝函数
- 类型转换
- 引用计数的实现
- 其他数据操作函数
数据结构Mat
个人认为一个框架中的比较核心的两个点,一个是数据结构,一个任务调度。两者之间其实是相互独立的,数据结构为调度过程中的数据流动提供了一个载体。在ncnn中的数据结构是Mat,类似于OpenCV中的Mat,但又增加了一些属于它本身的一些特性,在这个部分学习一下ncnn的Mat
成员变量
成员变量有7个
| 成员变量 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| int dims; | 表示当前数据是几维数据 |
| float* data; | Mat中数据的指针 |
| int* refcount; | 实现引用计数功能,实现类似智能指针的自动管理内存功能 |
| int w; | 第一个维度 |
| int h; | 第二个维度 |
| int c; | 第三个维度 |
| size_t cstep; | 表示在channel维的步长 |
| 这几个变量的,具体含义在成员函数中体会的会更加深刻。 |
成员方法
构造函数
构造函数主要完成对成员变量进行初始化
1、普通构造函数
- 空构造函数:所有的成员赋值0
- 一维数据构造:数据为1维,会分配相应的内存空间;
inline Mat::Mat(int _w)
: dims(0), data(0), refcount(0)
{
create(_w);
}
inline void Mat::create(int _w)
{
release();
dims = 1;
w = _w;
h = 1;
c = 1;
cstep = w;
if (cstep * c > 0)
{
size_t totalsize = cstep * c * sizeof(float);
data = (float*)fastMalloc(totalsize + (int)sizeof(*refcount));
refcount = (int*)(((unsigned char*)data) + totalsize);
*refcount = 1;
}
}
- 二维数据构造:数据为2维,会分配相应的内存空间;
inline Mat::Mat(int _w, int _h)
: dims(0), data(0), refcount(0)
{
create(_w, _h);
}
inline void Mat::create(int _w, int _h)
{
release();
dims = 2;
w = _w;
h = _h;
c = 1;
cstep = w * h;
if (cstep * c > 0)
{
size_t totalsize = cstep *c * sizeof(float);
data = (float*)fastMalloc(totalsize + (int)sizeof(*refcount));
refcount = (int*)(((unsigned char*)data) + totalsize);
*refcount = 1;
}
}
- 三维数据构造:数据为3维,会分配相应的内存空间;
inline Mat::Mat(int _w, int _h, int _c)
: dims(0), data(0), refcount(0)
{
create(_w, _h, _c);
}
inline void Mat::create(int _w, int _h, int _c)
{
release();
dims = 3;
w = _w;
h = _h;
c = _c;
cstep = alignSize(w * h * sizeof(float), 16) >> 2;
if (cstep * c > 0)
{
size_t totalsize = cstep * c * sizeof(float);
data = (float*)fastMalloc(totalsize + (int)sizeof(*refcount));
refcount = (int*)(((unsigned char*)data) + totalsize);
*refcount = 1;
}
}
上面的三个构造函数内部,都会调用到create函数,而在create内部又会调用release函数,这是因为create的调用者不局限在构造函数中,其它的调用在后面再细说。
上面构造中还调用了两个其他的函数:
static inline size_t alignSize(size_t sz, int n)
{
return (sz + n-1) & -n;
}
static inline void* fastMalloc(size_t size)
{
unsigned char* udata = (unsigned char*)malloc(size + sizeof(void*) + MALLOC_ALIGN);
if (!udata)
return 0;
unsigned char** adata = alignPtr((unsigned char**)udata + 1, MALLOC_ALIGN);
adata[-1] = udata;
return adata;
}
static inline void fastFree(void* ptr)
{
if (ptr)
{
unsigned char* udata = ((unsigned char**)ptr)[-1];
free(udata);
}
}
alignSize函数主要用来做对齐,,举例:
| 原始大小 | 8对齐 | 16对齐 |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 8 | 16 |
| 7 | 8 | 16 |
| 9 | 16 | 16 |
| 17 | 24 | 32 |
| 25 | 32 | 32 |
| 后面的fastMalloc和fastFree是对malloc和free的封装,其中也使用的内存对齐相关的内容 | ||
| 针对指针的对齐方法: |
template<typename _Tp> static inline _Tp* alignPtr(_Tp* ptr, int n=(int)sizeof(_Tp))
{
return (_Tp*)(((size_t)ptr + n-1) & -n);
}
fastMalloc方法中,针对要分配的空间会多分配,对齐大小+一个指针的大小
多分配的一个指针大小,将存储由malloc分配出来的原始指针用以内存的释放使用;
多分配的对齐大小将用来做内存对齐填充;
具体的操作在下面这两句代码:
unsigned char** adata = alignPtr((unsigned char**)udata + 1, MALLOC_ALIGN);
adata[-1] = udata;
udata为malloc得到的原始指针。先将原始指针偏移一个指针大小,然后再做内存对齐,偏移的一个指针大小用来存储原始指针。
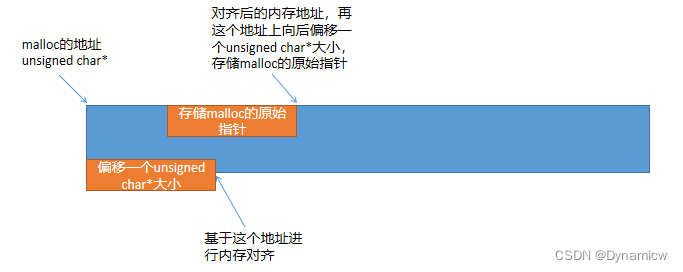
fastFree时,需要将使用的ptr指针,向后偏移一个指针大小,然后调用系统的free进行释放
2、外部数据指针构造函数
只能接受外部的float*类型的数据指针进行构造。同样的也是分为一维、二维和三维数据的构造
inline Mat::Mat(int _w, float* _data)
: dims(1), data(_data), refcount(0)
{
w = _w;
h = 1;
c = 1;
cstep = w;
}
inline Mat::Mat(int _w, int _h, float* _data)
: dims(2), data(_data), refcount(0)
{
w = _w;
h = _h;
c = 1;
cstep = w * h;
}
inline Mat::Mat(int _w, int _h, int _c, float* _data)
: dims(3), data(_data), refcount(0)
{
w = _w;
h = _h;
c = _c;
cstep = alignSize(w * h * sizeof(float), 16) >> 2;
}
3、拷贝构造函数和opertor =
- 拷贝构造函数,只是一个浅拷贝,两个Mat公用一块数据内存,引用计数加一
inline Mat::Mat(const Mat& m)
: dims(m.dims), data(m.data), refcount(m.refcount)
{
if (refcount)
NCNN_XADD(refcount, 1);
w = m.w;
h = m.h;
c = m.c;
cstep = m.cstep;
}
- operaotr=:也会导致引用计数加1,然后两个Mat也是共用一块数据内存,与构造不同的是,需要将左边Mat的进行release
inline Mat& Mat::operator=(const Mat& m)
{
if (this == &m)
return *this;
if (m.refcount)
NCNN_XADD(m.refcount, 1);
release();
dims = m.dims;
data = m.data;
refcount = m.refcount;
w = m.w;
h = m.h;
c = m.c;
cstep = m.cstep;
return *this;
}
深拷贝函数
inline Mat Mat::clone() const
{
if (empty())
return Mat();
Mat m;
if (dims == 1)
m.create(w);
else if (dims == 2)
m.create(w, h);
else if (dims == 3)
m.create(w, h, c);
if (total() > 0)
{
memcpy(m.data, data, total() * sizeof(float));
}
return m;
}
类型转换
inline Mat::operator float*()
{
return data;
}
inline Mat::operator const float*() const
{
return data;
}
引用计数的实现
实现:一段堆空间存储引用计数,当发生拷贝时,引用计数加1,销毁的时候,引用计数减1,如果引用计数为0,则释放资源。
在ncnn中的mat的实现方式:
- 在申请数据空间,多一段空间用来存储引用计数
data = (float*)fastMalloc(totalsize + (int)sizeof(*refcount));
refcount = (int*)(((unsigned char*)data) + totalsize);
当发生拷贝构造、赋值时,需要对引用计数加一
当析构的时候需要对引用计数减一,并判断引用计数,决定是否释放资源
inline void Mat::release()
{
if (refcount && NCNN_XADD(refcount, -1) == 1)
fastFree(data);
dims = 0;
data = 0;
w = 0;
h = 0;
c = 0;
cstep = 0;
refcount = 0;
}
其他数据操作函数
设计方法:在Mat.h中声明包含了上述的函数和一些数据操作函数,但具体的实现,可以在两个cpp中进行分类实现


![[SSM]MyBatis的缓存与逆向工程](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/23f28a3097a44badb6af0b1e47d4295c.png)