目录
forward_list
1. forward_list的成员函数
1.1 构造、析构和赋值运算符重载
1.1.1 构造函数
1.1.2 析构函数
1.1.3 赋值运算符重载
1.2 迭代器
1.3 容量
1.4 元素访问
1.4.1 遍历方法
1.5 修改器
1.6 操作
1.7 观察者
2. forward_list的非成员函数
forward_list
forward_list是序列容器,允许在序列的任何位置进行定时插入和删除操作。
forward_list是作为单链表实现的;单链表可以将其包含的每个元素存储在不同的、不相关的存储位置。单链表可以将其包含的每个元素存储在不同的相关存储位置中,通过将每个元素链接到序列中的下一个元素来保持排序。
forward_list容器和list容器在设计上的主要区别在于,前者只在内部保留一个指向下一个元素的链接,而后者则为每个元素保留两个链接:一个指向下一个元素,一个指向上一个元素,这样就可以在两个方向上高效地迭代,但每个元素会消耗额外的存储空间,而且插入和移除元素的时间开销会稍高一些。
与其他基本的标准序列容器(array、vector和deque)相比,forward_list在插入、提取和移动容器内任意位置的元素方面通常表现更好,因此在密集使用这些元素的算法(如排序算法)中也表现更好。
与这些其他序列容器相比,forward_list和list的主要缺点是它们不能通过元素的位置直接访问元素;例如,要访问forward_list中的第6个元素,就必须从开头迭代到该位置,这需要的时间与它们之间的距离成线性关系。它们还需要消耗一些额外的内存来保存与每个元素相关的链接信息(这对于由小尺寸元素组成的大列表来说可能是一个重要因素)。
forward_list类模板的设计考虑到了效率:事实上,它是唯一一个出于效率考虑而故意缺少size成员函数的标准容器:由于其作为链表的性质,如果size成员需要恒定的时间,那么它就需要为其大小保留一个内部计数器(就像list那样)。这将消耗一些额外的存储空间,并使插入和删除操作的效率略低。要获得一个forward_list对象的大小,可以使用距离算法来计算它的begin和end,这是一个需要线性时间的操作。
使用forward_list类型要包含forward_list头文件;forward_list定义在命名空间std中。
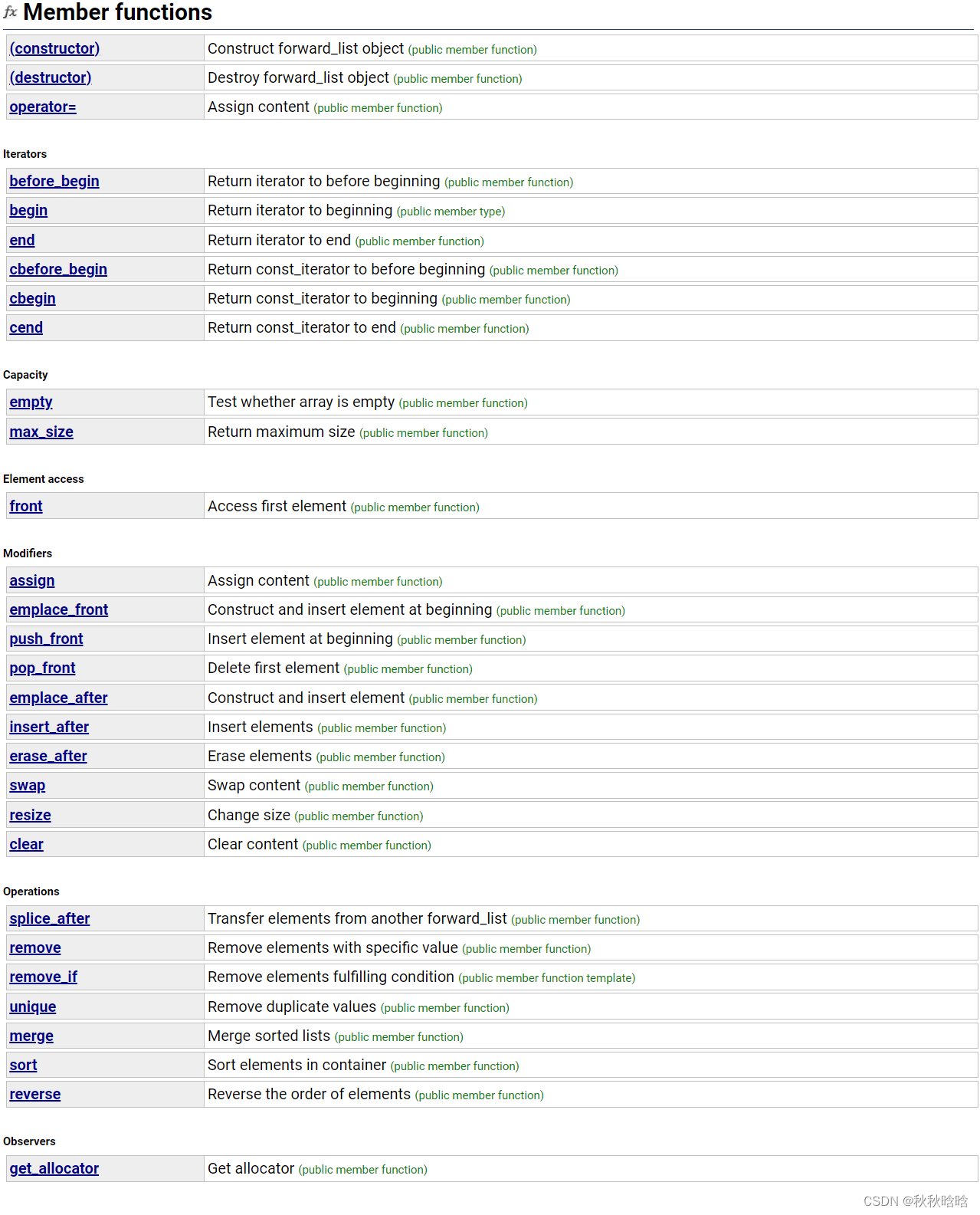
1. forward_list的成员函数
1.1 构造、析构和赋值运算符重载
1.1.1 构造函数
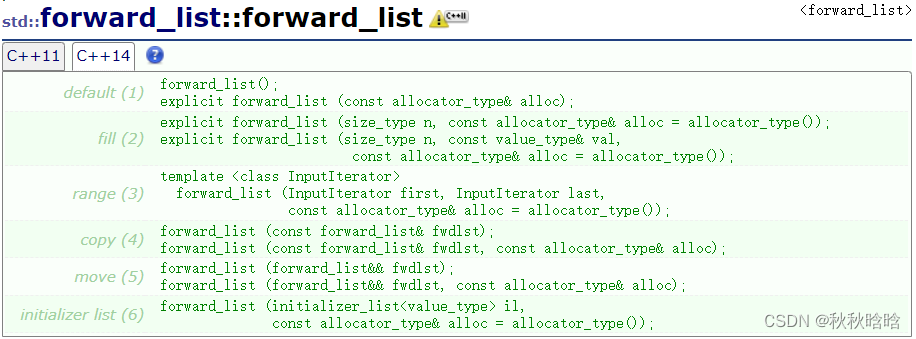
| 重载函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| default | 构造空的forward_list类对象 |
| fill | 用n个val来构造 |
| range | 用迭代器区间[first,last)中的元素顺序构造 |
| copy | 构造一个x的拷贝 |
| move | 移动构造函数 |
| initializer list | 用初始化列表来构造 |
#include <iostream>
#include <forward_list>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
forward_list<int> fl1;//default
for (auto e : fl1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//空
forward_list<int> fl2(10, 1);//fill
for (auto e : fl2)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
string s("hello world");
forward_list<char> fl3(s.begin() + 3, --s.end());//range
for (auto e : fl3)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//l o w o r l
forward_list<char> fl4(fl3);//copy
//等价于forward_list<char> fl4 = fl3;
for (auto e : fl4)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//l o w o r l
forward_list<int> fl5{ 2,4,6,8 };//initializer list
//等价于forward_list<int> fl5 = { 2,4,6,8 };
for (auto e : fl5)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//2 4 6 8
return 0;
}1.1.2 析构函数

1.1.3 赋值运算符重载

1.2 迭代器






| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| before_begin | before_begin返回一个迭代器,指向forward_list对象的第一个元素的前一个位置 |
| begin & end | begin返回一个迭代器,指向forward_list对象的第一个元素 end返回一个迭代器,指向forward_list对象的最后一个元素的下一个位置 |
| cbefore_begin | cbefore_begin返回一个const迭代器,指向forward_list对象的第一个元素的前一个位置 |
| cbegin & cend | cbegin返回一个const迭代器,指向forward_list对象的第一个元素 cend返回一个const迭代器,指向forward_list对象的最后一个元素的下一个位置 |
before_begin&begin&end返回的迭代器指向:
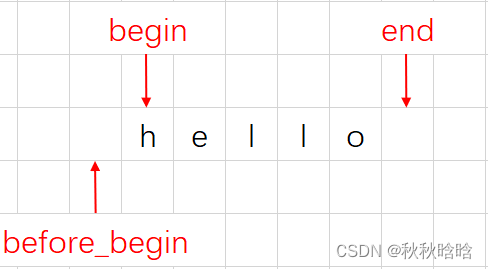
const_iterator是一个指向const内容的迭代器。迭代器本身可以修改,但是它不能被用来修改它所指向的内容。
before_begin&begin&end和cbefore_begin&cbegin&cend的不同:
- before_begin&begin&end的返回类型由对象是否是常量来决定。如果不是常量,返回iterator;如果是常量,返回const_iterator。
- cbefore_begin&cbegin&cend的返回类型是const_iterator,不管对象本身是否是常量。
#include <iostream>
#include <forward_list>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
forward_list<int> fl{ 4,5,6,7 };
fl.insert_after(fl.before_begin(), 3);
for (auto e : fl)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//3 4 5 6 7
forward_list<int>::iterator it = fl.begin();
while (it != fl.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
//3 4 5 6 7
return 0;
}1.3 容量


| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| empty | 检测forward_list是否为空,是返回true,否则返回false |
| max_size | 返回forward_list所能容纳的最大元素数 |
#include <iostream>
#include <forward_list>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
forward_list<int> fl{ 4,5,6,7 };
if (fl.empty())
cout << "forward_list为空" << endl;
else
cout << "forward_list不为空" << endl;
//forward_list不为空
cout << fl.max_size() << endl;//536870911
return 0;
}1.4 元素访问

| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| front | 返回forward_list中第一个元素的引用 |
#include <iostream>
#include <forward_list>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
forward_list<int> fl{ 4,5,6,7 };
cout << fl.front() << endl;//4
return 0;
}1.4.1 遍历方法
1.4.1.1 迭代器
#include <iostream>
#include <forward_list>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
forward_list<int> fl{ 4,5,6,7 };
forward_list<int>::iterator it = fl.begin();
while (it != fl.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
//4 5 6 7
return 0;
}1.4.1.2 范围for
#include <iostream>
#include <forward_list>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
forward_list<int> fl{ 4,5,6,7 };
for (auto e : fl)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//4 5 6 7
return 0;
}1.5 修改器









| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| assign | 给forward_list赋值,替换其当前内容 |
| emplace_front | 在开头构建和插入元素 |
| push_front | 头插 |
| pop_front | 头删 |
| emplace_after | 构建和插入元素 |
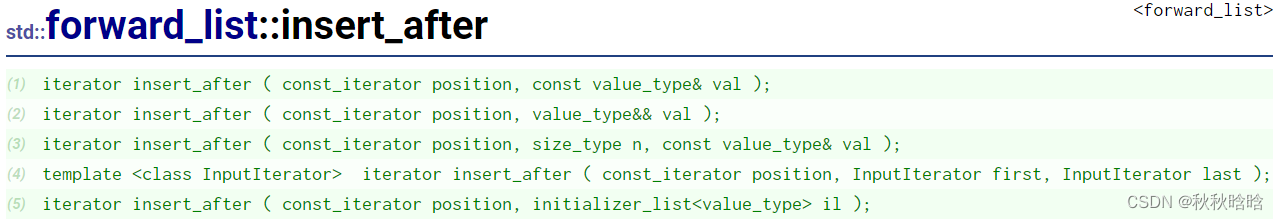
| insert_after | 在position位置之后插入 |
| erase_after | 删除position位置之后的元素或范围 |
| swap | 交换内容 |
| resize | 调整forward_list的大小为n(影响size) ●如果n<当前forward_list的大小,多余的元素会被截掉 ●如果n>当前forward_list的大小,则: 1)如果没有指定填充元素,则在最后插入尽可能多的元素以达到n的大小 2)如果指定了填充元素val,则多出的空间用val填充 ●如果n也>当前forward_list的容量,则会自动重新分配存储空间 |
| clear | 清空内容 |
#include <iostream>
#include <forward_list>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
forward_list<int> fl1{ 4,5,6,7 };
fl1.assign({ 1,2,3,4,5,6 });
for (auto e : fl1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//1 2 3 4 5 6
fl1.push_front(0);
for (auto e : fl1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//0 1 2 3 4 5 6
fl1.pop_front();
for (auto e : fl1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//1 2 3 4 5 6
fl1.insert_after(fl1.before_begin(), 0);
for (auto e : fl1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//0 1 2 3 4 5 6
fl1.erase_after(fl1.begin());
for (auto e : fl1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//0 2 3 4 5 6
forward_list<int> fl2{ 4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
fl1.swap(fl2);
for (auto e : fl1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//4 5 6 7 8 9 10
fl1.resize(12, 5);
for (auto e : fl1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//4 5 6 7 8 9 10 5 5 5 5 5
fl1.clear();
if (fl1.empty())
cout << "fl1被清空" << endl;
else
cout << "fl1没被清空" << endl;
//fl1被清空
return 0;
}1.6 操作




| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| splice_after | 将元素从x转移到容器中,在position位置之后插入 |
| remove | 移除具有特定值的元素 |
| remove_if | 删除满足条件的元素 |
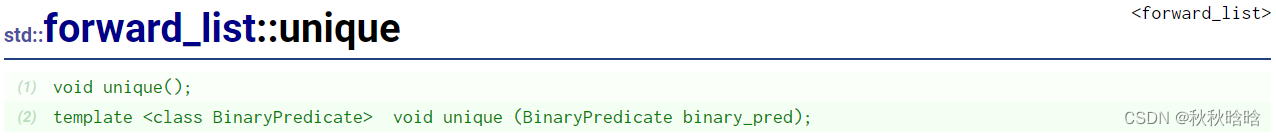
| unique | 去重 |
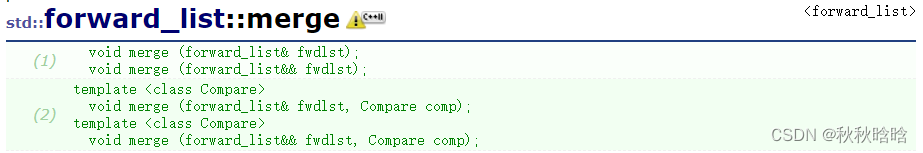
| merge | 合并有序列表 |
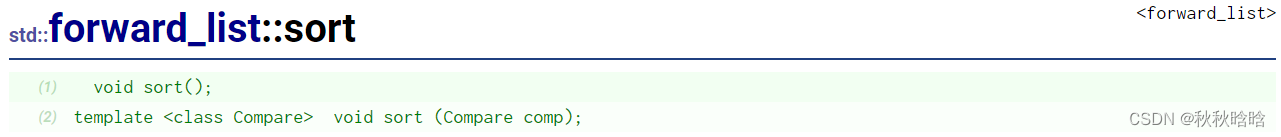
| sort | 排序 |
| reverse | 反转元素的顺序 |
1.7 观察者

| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| get_allocator | 获取空间配置器 |
2. forward_list的非成员函数


| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| relational operators | 关系运算符重载 |
| swap | 交换内容 |