文章目录
- 一、ElasticSearch 集群
- 二、Elasticsearch的核心概念
- 2.1、分片(Shards)
- 2.2、副本(Replicas)
- 2.3、路由计算
- 2.4、倒排索引
- 三、Kibana简介
- 四、Spring Data ElasticSearch
一、ElasticSearch 集群
Elasticsearch 集群有一个唯一的名字,默认就是”elasticsearch”。,一个节点只能通过指定某个集群的名字,来加入这个集群。

集群搭建如下:
- 复制ES的安装目录三份:esnode-1,esnode-2,esnode-3,分别编辑config/elasticsearch.yml 配置文件
node-1:
# ======================== Elasticsearch Configuration =========================
#
# NOTE: Elasticsearch comes with reasonable defaults for most settings.
# Before you set out to tweak and tune the configuration, make sure you
# understand what are you trying to accomplish and the consequences.
#
# The primary way of configuring a node is via this file. This template lists
# the most important settings you may want to configure for a production cluster.
#
# Please consult the documentation for further information on configuration options:
# https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/index.html
#
# ---------------------------------- Cluster -----------------------------------
#
# Use a descriptive name for your cluster:
#
cluster.name: my-elasticsearch
#
# ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------
#
# Use a descriptive name for the node:
#
node.name: node-1
node.master: true
node.data: true
#
# Add custom attributes to the node:
#
#node.attr.rack: r1
#
# ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------
#
# Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma):
#
#path.data: /path/to/data
#
# Path to log files:
#
#path.logs: /path/to/logs
#
# ----------------------------------- Memory -----------------------------------
#
# Lock the memory on startup:
#
#bootstrap.memory_lock: true
#
# Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available
# on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this
# limit.
#
# Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory.
#
# ---------------------------------- Network -----------------------------------
#
# Set the bind address to a specific IP (IPv4 or IPv6):
#
network.host: localhost
#
# Set a custom port for HTTP:
#
http.port: 1001
#tcp 监听端口
transport.tcp.port: 9301
#discovery.seed_hosts: ["localhost:9201", "localhost:9301", "localhost:9401"]
#discovery.zen.fd.ping_timeout: 1m
#discovery.zen.fd.ping_retries: 5
#
# Bootstrap the cluster using an initial set of master-eligible nodes:
#
#cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1", "node-2", "node-3"]
#
# For more information, consult the network module documentation.
#
# --------------------------------- Discovery ----------------------------------
#
# Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when this node is started:
# The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"]
#
#discovery.seed_hosts: ["localhost:9301", "localhost:9401"]
#discovery.zen.fd.ping_timeout: 1m
#discovery.zen.fd.ping_retries: 5
#
# Bootstrap the cluster using an initial set of master-eligible nodes:
#
#cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1", "node-2", "node-3"]
#
# For more information, consult the discovery and cluster formation module documentation.
#
# ---------------------------------- Gateway -----------------------------------
#
# Block initial recovery after a full cluster restart until N nodes are started:
#
#gateway.recover_after_nodes: 3
#
# For more information, consult the gateway module documentation.
#
# ---------------------------------- Various -----------------------------------
#
# Require explicit names when deleting indices:
#
#action.destructive_requires_name: true
#跨域配置
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
node-2:
# ======================== Elasticsearch Configuration =========================
#
# NOTE: Elasticsearch comes with reasonable defaults for most settings.
# Before you set out to tweak and tune the configuration, make sure you
# understand what are you trying to accomplish and the consequences.
#
# The primary way of configuring a node is via this file. This template lists
# the most important settings you may want to configure for a production cluster.
#
# Please consult the documentation for further information on configuration options:
# https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/index.html
#
# ---------------------------------- Cluster -----------------------------------
#
# Use a descriptive name for your cluster:
#
cluster.name: my-elasticsearch
#
# ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------
#
# Use a descriptive name for the node:
#
node.name: node-2
node.master: true
node.data: true
#
# Add custom attributes to the node:
#
#node.attr.rack: r1
#
# ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------
#
# Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma):
#
#path.data: /path/to/data
#
# Path to log files:
#
#path.logs: /path/to/logs
#
# ----------------------------------- Memory -----------------------------------
#
# Lock the memory on startup:
#
#bootstrap.memory_lock: true
#
# Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available
# on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this
# limit.
#
# Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory.
#
# ---------------------------------- Network -----------------------------------
#
# Set the bind address to a specific IP (IPv4 or IPv6):
#
network.host: localhost
#
# Set a custom port for HTTP:
#
http.port: 1002
transport.tcp.port: 9302
#
# For more information, consult the network module documentation.
#
# --------------------------------- Discovery ----------------------------------
#
# Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when this node is started:
# The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"]
#
discovery.seed_hosts: ["localhost:9301"]
discovery.zen.fd.ping_timeout: 1m
discovery.zen.fd.ping_retries: 5
#
# Bootstrap the cluster using an initial set of master-eligible nodes:
#
#cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1", "node-2", "node-3"]
#
# For more information, consult the discovery and cluster formation module documentation.
#
# ---------------------------------- Gateway -----------------------------------
#
# Block initial recovery after a full cluster restart until N nodes are started:
#
#gateway.recover_after_nodes: 3
#
# For more information, consult the gateway module documentation.
#
# ---------------------------------- Various -----------------------------------
#
# Require explicit names when deleting indices:
#
#跨域配置
#action.destructive_requires_name: true
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
node-3:
# ======================== Elasticsearch Configuration =========================
#
# NOTE: Elasticsearch comes with reasonable defaults for most settings.
# Before you set out to tweak and tune the configuration, make sure you
# understand what are you trying to accomplish and the consequences.
#
# The primary way of configuring a node is via this file. This template lists
# the most important settings you may want to configure for a production cluster.
#
# Please consult the documentation for further information on configuration options:
# https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/index.html
#
# ---------------------------------- Cluster -----------------------------------
#
# Use a descriptive name for your cluster:
#
cluster.name: my-elasticsearch
#
# ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------
#
# Use a descriptive name for the node:
#
node.name: node-3
node.master: true
node.data: true
#
# Add custom attributes to the node:
#
#node.attr.rack: r1
#
# ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------
#
# Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma):
#
#path.data: /path/to/data
#
# Path to log files:
#
#path.logs: /path/to/logs
#
# ----------------------------------- Memory -----------------------------------
#
# Lock the memory on startup:
#
#bootstrap.memory_lock: true
#
# Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available
# on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this
# limit.
#
# Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory.
#
# ---------------------------------- Network -----------------------------------
#
# Set the bind address to a specific IP (IPv4 or IPv6):
#
network.host: localhost
#
# Set a custom port for HTTP:
#
http.port: 1003
transport.tcp.port: 9303
#
# For more information, consult the network module documentation.
#
# --------------------------------- Discovery ----------------------------------
#
# Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when this node is started:
# The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"]
#
discovery.seed_hosts: ["localhost:9302", "localhost:9301"]
discovery.zen.fd.ping_timeout: 1m
discovery.zen.fd.ping_retries: 5
#
# Bootstrap the cluster using an initial set of master-eligible nodes:
#
#cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1", "node-2", "node-3"]
#
# For more information, consult the discovery and cluster formation module documentation.
#
# ---------------------------------- Gateway -----------------------------------
#
# Block initial recovery after a full cluster restart until N nodes are started:
#
#gateway.recover_after_nodes: 3
#
# For more information, consult the gateway module documentation.
#
# ---------------------------------- Various -----------------------------------
#
# Require explicit names when deleting indices:
#
#跨域配置
#action.destructive_requires_name: true
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
2、分别启动,浏览器访问http://localhost:1001/_cluster/health、http://localhost:1002/_cluster/health、http://localhost:1003/_cluster/health,集群启动成功。

搭建成功后,可以将请求发送到集群中的任何节点 ,包括主节点。 每个节点都知道文档所处的位置,并且能够将我们的请求直接转发到存储我们所需文档的节点。 无论我们将请求发送到哪个节点,它都能负责从各个包含我们所需文档的节点收集回数据,并将最终结果返回給客户端。 Elasticsearch 对这一切的管理都是透明的。
二、Elasticsearch的核心概念
2.1、分片(Shards)
一个索引可以存储超出单个节点硬件限制的大量数据。比如,一个具有 10 亿文档数据的索引占据 1TB 的磁盘空间,而任一节点都可能没有这样大的磁盘空间。或者单个节点处理搜索请求,响应太慢。为了解决这个问题,Elasticsearch 提供了将索引划分成多份的能力,每一份就称之为分片。当你创建一个索引的时候,你可以指定你想要的分片的数量。每个分片本身也是一个功能完善并且独立的“索引”,这个“索引”可以被放置到集群中的任何节点上。
分片很重要,主要有两方面的原因:
1)允许水平分割 / 扩展内容容量。
2)允许在分片之上进行分布式的、并行的操作,进而提高性能/吞吐量。
当 Elasticsearch 在索引中搜索的时候, 他发送查询到每一个属于索引的分片(Lucene 索引),然后合并每个分片的结果到一个全局的结果集。
2.2、副本(Replicas)
Elasticsearch 允许你创建分片的一份或多份拷贝,这些拷贝叫做复制分片(副本)。
复制分片之所以重要,有两个主要原因:
提供了高可用性。复制分片从不与原分片置于同一节点上是非常重要的。
扩展搜索量/吞吐量,因为搜索可以在所有的副本上并行运行。当拥有越多的副本分片时,也将拥有越高的吞吐量。
每个索引可以被分成多个分片。一经复制,每个索引就有了主分片(作为复制源的原来的分片)和复制分片(主分片的拷贝)之别。分片和复制的数量可以在索引创建的时候指定。在索引创建之后,你可以在任何时候动态地改变复制的数量,但是不能改变分片的数量。
默认情况下,Elasticsearch 中的每个索引被分片 1 个主分片和 1 个复制,根据索引需要确定分片个数。
2.3、路由计算
Elasticsearch 如何知道一个文档应该存放到哪个分片中呢?当我们创建文档时,它如何决定这个文档应当被存储在分片1 还是分片 2 中呢?
这个过程是根据下面这个公式决定的:
shard = hash(routing) % number of primary_shards
routing 是一个可变值,默认是文档的 _id ,也可以设置成一个自定义的值。 routing 通过hash 函数生成一个数字,然后这个数字再除以 number_of_primary_shards (主分片的数量)后得到的余数 就是文档所在分片的位置。
2.4、倒排索引
Elasticsearch 使用一种倒排索引的结构,适用于快速的全文搜索。
我们经常了解的是正向索引(forward index),所谓正向索引,就是搜索引擎会将待搜索的文件都对应一个文件 ID,搜索时将这个ID 和搜索关键字进行对应,形成 K-V 对,然后对关键字进行统计计数,常见Mysql中的表结构。
倒排索引,搜索引擎会将正向索引重新构建为倒排索引,即把文件ID对应到关键词的映射转换为关键词到文件ID的映射,每个关键词都对应着一系列的文件,这些文件中都出现这个关键词。
三、Kibana简介
Kibana 是一个免费且开放的用户界面,能够让你对 Elasticsearch 数据进行可视化,并让你在 Elastic Stack 中进行导航。你可以进行各种操作,从跟踪查询负载,到理解请求如何流经你的整个应用,都能轻松完成。
下载地址:点击下载windows版本
修改 config/kibana.yml 文件
server.port: 5601
server.host: "127.0.0.1"
elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://127.0.0.1:9200"]
kibana.index: ".kibana"
i18n.locale: "zh-CN"
运行行 bin/kibana.bat ,浏览器访问 http://localhost:5601
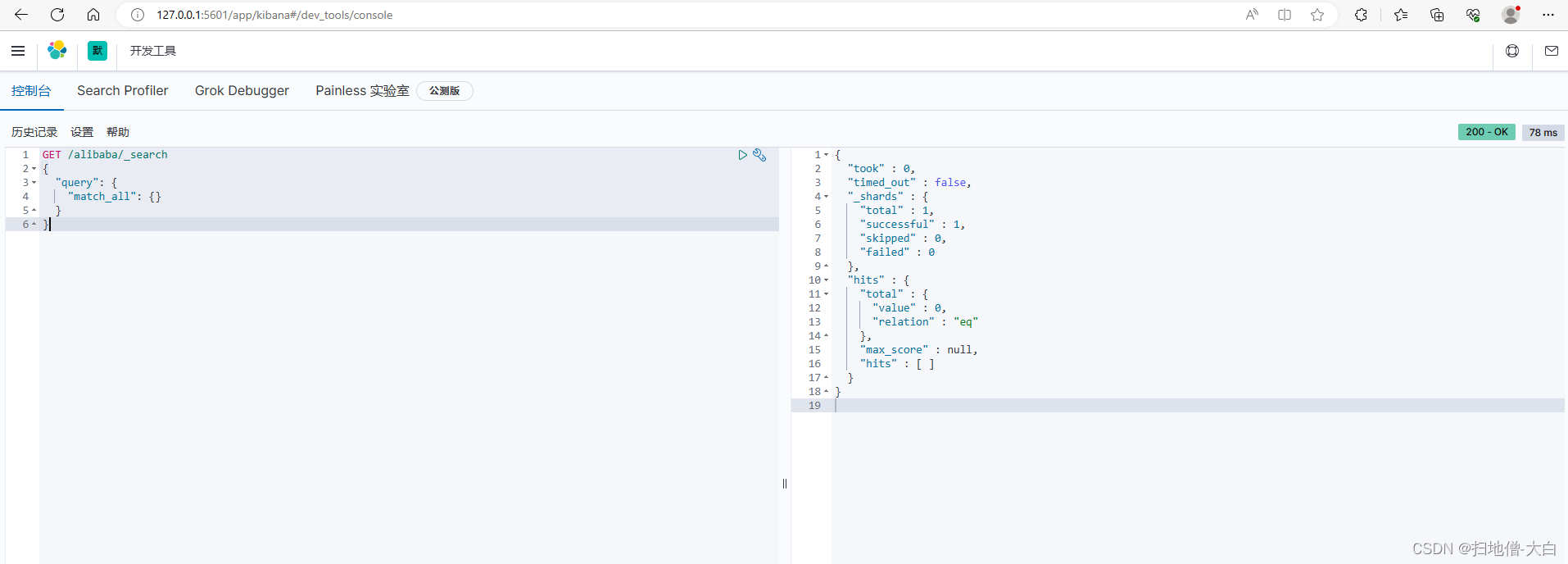
四、Spring Data ElasticSearch
Spring Data Elasticsearch 基于 spring data API 简化 Elasticsearch 操作,将原始操作Elasticsearch 的客户端 API 进行封装 。
Spring Data 为 Elasticsearch 项目提供集成搜索引擎。
官方网站: 点击进入
集成步骤:
1、新建Maven项目。POM文件添加依赖:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.2.13.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2、application.yml 配置:
# es 服务地址
elasticsearch:
host: localhost
port: 9200
3、Entity类:
package com.swc.es.entity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.ToString;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Document;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Field;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.FieldType;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
@Document(indexName = "user", shards = 3, replicas = 1)
public class User {
@Id
private Long id;
private String name;
@Field(index = false)
private String sex;
private int age;
private String address;
private Date birth;
}
4、增加配置类,读取配置信息
ElasticsearchRestTemplate 是基于 RestHighLevelClient 客户端的。只要自定义配置类,继承AbstractElasticsearchConfiguration,并实现 elasticsearchClient()抽象方法,创建 RestHighLevelClient 对
象。
public class ElasticSearchConfig extends AbstractElasticsearchConfiguration {
@Value("elasticsearch.host")
private String host ;
@Value("elasticsearch.port")
private Integer port ;
@Override
public RestHighLevelClient elasticsearchClient() {
RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(new HttpHost(host, port));
RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient = new
RestHighLevelClient(builder);
return restHighLevelClient;
}
}
5、DAO 数据访问对象
@Repository
public interface UserDao extends ElasticsearchRepository<User, Long> {
}
6、测试:
索引测试:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringDataESTest {
//注入 ElasticsearchRestTemplate
@Autowired
private ElasticsearchRestTemplate elasticsearchRestTemplate;
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@Test
public void createIndex(){
//
System.out.println("创建索引,系统初始化会自动创建索引");
}
@Test
public void deleteIndex(){
//创建索引,系统初始化会自动创建索引
boolean flg = elasticsearchRestTemplate.deleteIndex(User.class);
System.out.println("删除索引 = " + flg);
}
}
文档查询测试:
package com.swc.es.controller;
import com.swc.es.dao.UserDao;
import com.swc.es.entity.User;
import org.elasticsearch.index.query.QueryBuilders;
import org.elasticsearch.index.query.TermQueryBuilder;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.data.domain.PageRequest;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringDataESUserDaoTest {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
/**
* 新增
*/
@Test
public void save(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(1L);
user.setName("张三");
user.setAge(25);
user.setBirth(new Date());
user.setAddress("北京市丰台区");
userDao.save(user);
}
//修改
@Test
public void update(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(5L);
user.setName("张三大哥");
user.setSex("男");
user.setAge(25);
user.setBirth(new Date());
user.setAddress("北京市丰台区");
userDao.save(user);
}
//根据 id 查询
@Test
public void findById(){
User user = userDao.findById(5L).get();
System.out.println(user);
}
//查询所有
@Test
public void findAll(){
Iterable<User> Users = userDao.findAll();
for (User user : Users) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
//删除
@Test
public void delete(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(1L);
userDao.delete(user);
}
//批量新增
@Test
public void saveAll(){
List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 2; i < 10; i++) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(Long.valueOf(i));
user.setName("张三大哥");
user.setAge(25+i);
user.setBirth(new Date());
user.setAddress("北京市丰台区"+i+"号院");
userList.add(user);
}
userDao.saveAll(userList);
}
//分页查询
@Test
public void findByPageable(){
//设置排序(排序方式,正序还是倒序,排序的 id)
Sort sort = Sort.by(Sort.Direction.DESC,"id");
int currentPage=0;//当前页,第一页从 0 开始,1 表示第二页
int pageSize = 5;//每页显示多少条
//设置查询分页
PageRequest pageRequest = PageRequest.of(currentPage, pageSize,sort);
//分页查询
Page<User> UserPage = userDao.findAll(pageRequest);
for (User user : UserPage.getContent()) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
/**
* term 查询
* search(termQueryBuilder) 调用搜索方法,参数查询构建器对象
*/
@Test
public void termQuery(){
TermQueryBuilder termQueryBuilder = QueryBuilders.termQuery("name", "张三");
Iterable<User> users = userDao.search(termQueryBuilder);
for (User user : users) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
/**
* term 查询加分页
*/
@Test
public void termQueryByPage(){
int currentPage= 0 ;
int pageSize = 3;
//设置查询分页
PageRequest pageRequest = PageRequest.of(currentPage, pageSize);
TermQueryBuilder termQueryBuilder = QueryBuilders.termQuery("name", "张三");
Iterable<User> users = userDao.search(termQueryBuilder,pageRequest);
for (User user : users) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
}