ByteBuddy
1.ByteBuddy的用途
ByteBuddy通过修改字节码来新增、修改、删除Java类的现有功能,主要用于分离功能代码和非功能代码,比如
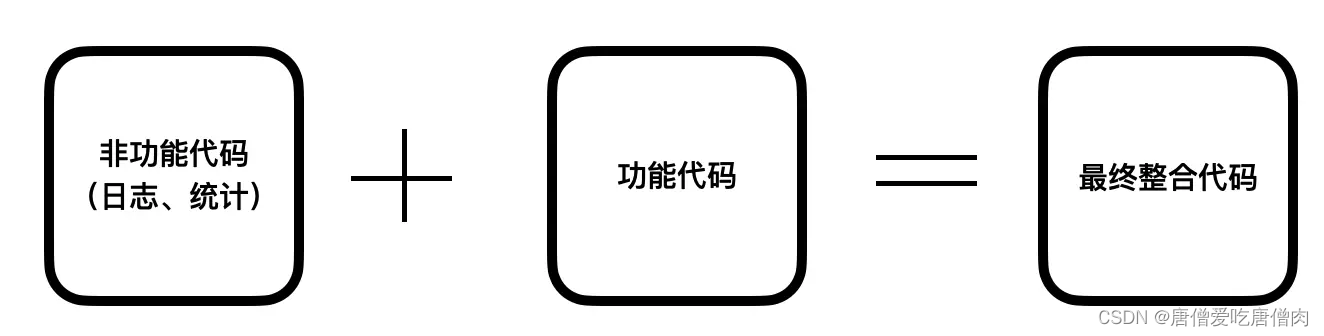
比如非功能代码如下:
public double calculatePrice(){
double discount = getDiscount();
double price = this.price + this.deliveryCharge - discount;
return price;
}
添加比如打印日志等非功能代码,形成如下的内容:
public double calculatePrice(){
long startTime = System.currentMilliseconds();
logger.info("CalculatePrice start");
double discount = getDiscount();
double price = this.price + this.deliveryCharge - discount;
logger.info("Method end");
logger.info("CalculatePrice execution time: " + (System.currentMillioseconds() - startTime));
return price;
}
2.ByteBuddy的初始化代码学习
首先在maven的dependencies标签之中配置上需要用到的库
<dependency>
<groupId>net.bytebuddy</groupId>
<artifactId>byte-buddy</artifactId>
<version>1.12.20</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.bytebuddy</groupId>
<artifactId>byte-buddy-agent</artifactId>
<version>1.12.20</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.bytebuddy</groupId>
<artifactId>byte-buddy-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.12.20</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter</artifactId>
<version>RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
然后学习示例的代码
public void test() throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
DynamicType.Unloaded unloadedType = new ByteBuddy()
//创建ByteBuddy类型的一个实例
.subclass(Object.class)
//动态创建的类是继承Object的
.method(ElementMatchers.isToString())
//method为筛选器,筛选Object中的toString方法
.intercept(FixedValue.value("Hello World ByteBuddy!"))
//提供了toString()的实现,返回固定值"Hello World ByteBuddy!"
//按照下面的最后定义函数优先,这里的类
.make();
//触发生成一个新的类
Class<?> dynamicType = unloadedType.load(getClass()
.getClassLoader())
.getLoaded();
//把unloadedType实例加载到JVM之中,此时dynamicType相当于一个类
Assertions.assertEquals(dynamicType.newInstance().toString(),"Hello World ByteBuddy!");
//调用dynamicType.toString()方法不会生效,因为此时调用的是ByteBuddy.class的toString()方法
}
3.ByteBuddy调用的优先级部分
public void test() throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
String r = new ByteBuddy()
.subclass(Foo.class)
.method(named("sayHelloFoo")
.and(isDeclaredBy(Foo.class))
.and(returns(String.class)))
//符合三个条件的方法
.intercept(MethodDelegation.to(Bar.class))
.make()
.load(getClass().getClassLoader())
.getLoaded()
.newInstance()
.sayHelloFoo();
assertEquals(r,Bar.sayHelloBar());
}
intercept提供了类的实现,因为这里的intercept初始化的是Bar.class,而Bar和Foo的类中都有sayHelloBar这个方法,因此这里最终实现的是Bar的sayHelloBar方法