背景
最近项目中需要对一条数据,在半小时候更改其状态,类似于提交商城订单半小时后未支付的订单需要更改为超时状态,当然这个解决方案有很多,最好的解决方案是用MQ的死信队列;但由于项目中没有引入MQ,故本文采用的是基于redis与定时器实现该需求。
不废话直接撸串!
代码示例
定义队列名称
public class QueueConstant {
public static final String DELAY_QUEUE = "delay-queue";
}
将数据放入redis的zset有序集合中
@Autowired
RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Value("${timeout:1800000}") //30*60*1000
private Integer timeout;
@Override
public R method(Long id) {
//业务代码
...
//将订单id(唯一识别号)放入redis中
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().add(QueueConstant.DELAY_QUEUE,id,System.currentTimeMillis()+timeout);
return R.success();
}
定时获取更新状态
@Slf4j
@Configuration
@EnableScheduling
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class ScheduleTask implements SchedulingConfigurer {
//查询定时表达式
@Autowired
CronMapper cronMapper;
@Autowired
RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
//处理业务更新订单状态
@Autowired
XXXMapper xxxMapper;
@Override
public void configureTasks(ScheduledTaskRegistrar taskRegistrar) {
taskRegistrar.addTriggerTask(() -> {
log.info("执行超时定时任务: " + LocalDateTime.now().toLocalTime());
Set<Long> idSet= redisTemplate.opsForZSet().rangeByScore(QueueConstant.DELAY_QUEUE, 0, System.currentTimeMillis());
if(!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(idSet)){
for (Long id : idSet) {
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().remove(QueueConstant.DELAY_QUEUE,id);
}
int num = xxxMapper.closeTimeoutOrder(idSet);
}
log.info("执行超时定时任务: 执行条数——>"+idSet.size());
}, triggerContext -> {
String cron = cronMapper.getTimeoutCron();
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(cron)) {
cron ="30 * * * * ?"; //每隔30秒执行
}
return new CronTrigger(cron).nextExecutionTime(triggerContext);
});
}
}
从上述中代码中可以看出 定时器我写的是每隔30秒执行一次,虽然频率高但是实时性好,只有当有数据需要处理时才会对数据库产生交互,平时我们项目中救援任务相对较少,所以对数据库基本造不成压力!缺点是没有ACK机制与重试机制。
总结
Redis中Zset 有序集合 实现延时队列,zset是一种特殊的集合,内部成员都是有序排列的,从上述demo中可以看出每个元素都关联一个分数值,跟进这个分数值对元素进行排序。我们把元素的过期时间作为分数值,从而可以实现延时队列。
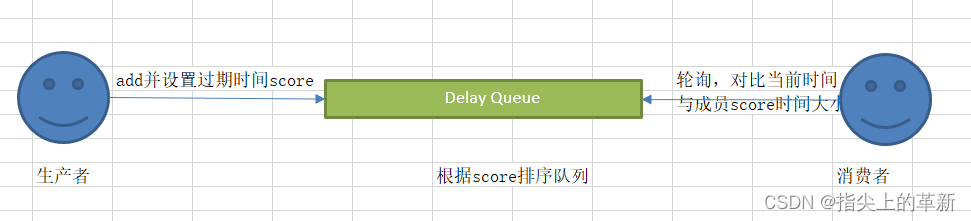
- 将任务最终到期时间作为分值,任务唯一标识作为消息体,添加到队列中
- 使用rangeByScore,根据当前时间戳获取分值小于当前时间的成员(需要处理的对象)
- 删除remove过期成员,防止重复消费
- 对获取到的成员(唯一标识)进行业务处理